Fig. 8: Summary of transcriptome and proteome changes in colon crypt homeostasis.
From: Transcriptomic and proteomic signatures of stemness and differentiation in the colon crypt
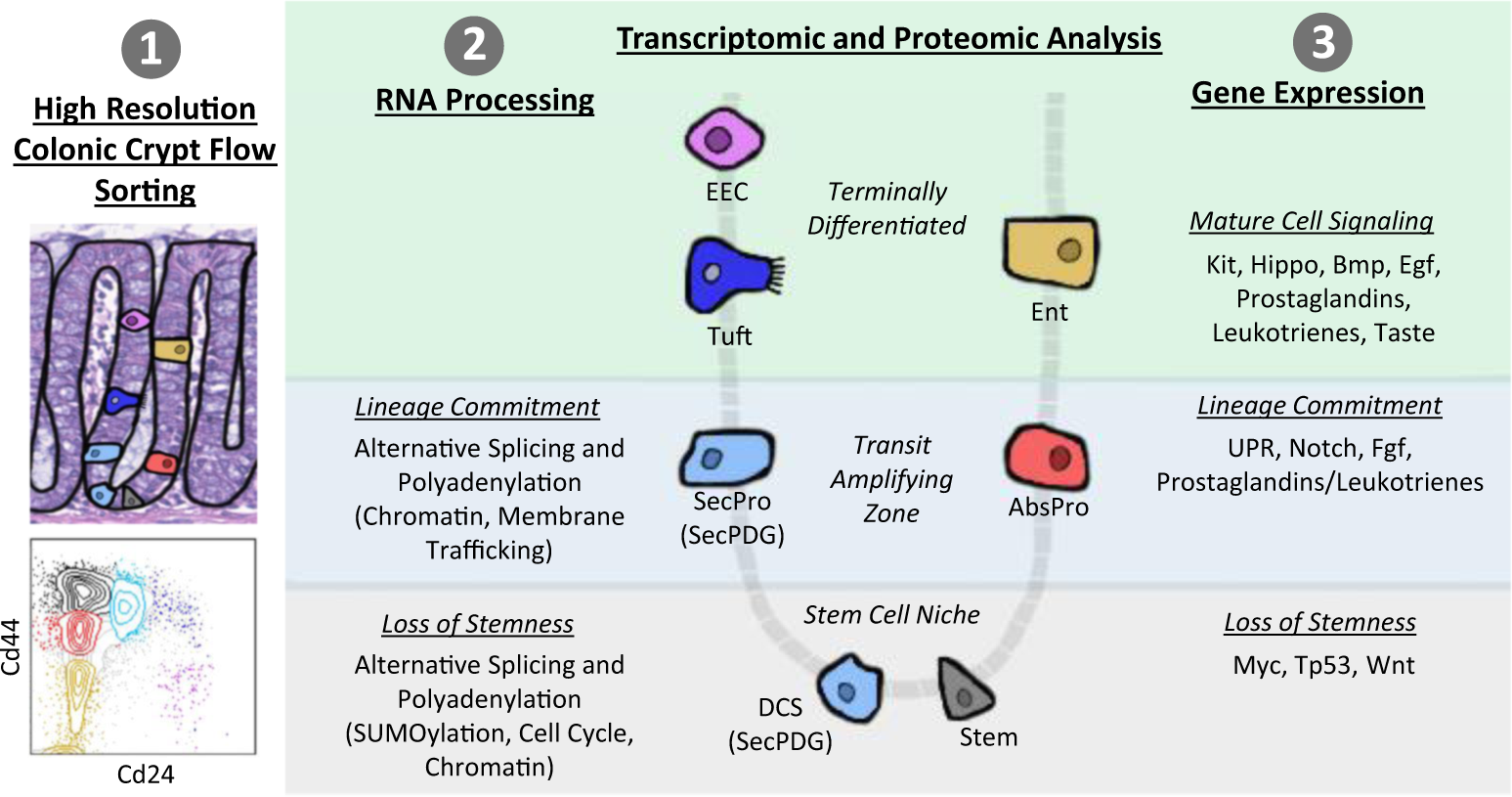
Our findings encompass three main themes: (1) methodology—high-resolution colonic crypt flow sorting to isolate stem cells, SecPDG (secretory progenitors/deep crypt secretory cells), AbsPro (absorptive progenitors), tuft cells, enterocytes (Ent), and enteroendocrine cells (EEC), (2) RNA processing (splicing and polyadenylation) influences the transcriptome most during loss of stemness and lineage commitment, and (3) gene expression changes influencing lineage commitment and mature cell signaling.
