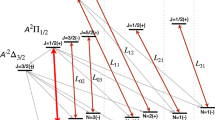
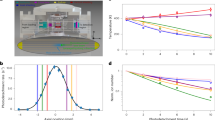
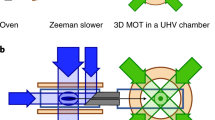
Abstract
Laser cooling of molecules is a powerful technique for producing cold, slow beams for precision measurements and quantum control, yet its implementation remains challenging due to molecular complexity. Here, we combine a cryogenic buffer gas beam, an electrostatic hexapole lens, and 2D transverse Doppler laser cooling to produce a bright beam of barium monofluoride (138Ba19F) molecules. We study both numerically and experimentally the laser cooling effect as a function of laser detuning, laser power, laser alignment, and interaction time. We find a scattering rate of 6.1(1.4) × 105 s−1 on the laser cooling transition (14% of the expected maximum) and identify suboptimal dark Zeeman state remixing, suboptimal laser sideband powers and detunings, and a lack of vibrational repump laser intensity as possible causes of such a low rate. Using 3 tuneable lasers with appropriate sidebands and detuning, each molecule scatters approximately 400 photons during 2D laser cooling, limited by the interaction time and scattering rate. Leaks to dark states are less than 10%. Finally, we use the experimental results to benchmark the trajectory simulations to predict the achievable flux 3.5 m downstream for a planned eEDM experiment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Code availability
The code we used for analyzing the experimental results and calculating the molecular trajectories is available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Ye, J. & Zoller, P. Essay: quantum sensing with atomic, molecular, and optical platforms for fundamental physics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 190001 (2024).
Langen, T., Valtolina, G., Wang, D. & Ye, J. Quantum state manipulation and cooling of ultracold molecules. Nat. Phys. 20, 702–712 (2024).
Cheuk, L. W. et al. Observation of collisions between two ultracold ground-state CaF molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 043401 (2020).
Blackmore, J. A. et al. Ultracold molecules for quantum simulation: rotational coherences in CaF and RbCs. Quantum Sci. Technol. 4, 014010 (2018).
White, A. D. et al. Slow molecular beams from a cryogenic buffer gas source. Phys. Rev. Res. 6, 043232 (2024).
DeMille, D., Hutzler, N. R., Rey, A. M. & Zelevinsky, T. Quantum sensing and metrology for fundamental physics with molecules. Nat. Phys. 20, 741–749 (2024).
Roussy, T. S. et al. An improved bound on the electron’s electric dipole moment. Science 381, 46–50 (2023).
Cesarotti, C., Lu, Q., Nakai, Y., Parikh, A. & Reece, M. Interpreting the electron EDM constraint. J. High. Energy Phys. 2019, 59 (2019).
Athanasakis-Kaklamanakis, M. et al. Community input to the European strategy on particle physics: Searches for permanent electric dipole moments. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2505.22281 (2025).
Hiramoto, A. et al. SiPM module for the ACME III electron EDM search. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A: Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 1045, 167513 (2023).
Vutha, A., Horbatsch, M. & Hessels, E. Oriented polar molecules in a solid inert-gas matrix: A proposed method for measuring the electric dipole moment of the electron. Atoms 6, 3 (2018).
Fitch, N. J., Lim, J., Hinds, E. A., Sauer, B. E. & Tarbutt, M. R. Methods for measuring the electron’s electric dipole moment using ultracold YbF molecules. Quantum Sci. Technol. 6, 014006 (2021).
Aggarwal, P. et al. Measuring the electric dipole moment of the electron in BaF. Eur. Phys. J. D. 72, 197 (2018).
Aggarwal, P. et al. Deceleration and trapping of SrF molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 173201 (2021).
Bause, R. et al. Prospects for measuring the electron’s electric dipole moment with polyatomic molecules in an optical lattice. Phys. Rev. A 111, 062815 (2025).
Arrowsmith-Kron, G. et al. Opportunities for fundamental physics research with radioactive molecules. Rep. Prog. Phys. 87, 084301 (2024).
Kozyryev, I. & Hutzler, N. R. Precision measurement of time-reversal symmetry violation with laser-cooled polyatomic molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 133002 (2017).
Zhou, Y. et al. Second-scale coherence measured at the quantum projection noise limit with hundreds of molecular ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 053201 (2020).
Andreev, V. et al. Improved limit on the electric dipole moment of the electron. Nature 562, 355–360 (2018).
Hutzler, N. R., Lu, H.-I. & Doyle, J. M. The buffer gas beam: an intense, cold, and slow source for atoms and molecules. Chem. Rev. 112, 4803–4827 (2012).
Truppe, S. et al. A buffer gas beam source for short, intense and slow molecular pulses. J. Mod. Opt. 65, 648–656 (2018).
Wu, X. et al. Electrostatic focusing of cold and heavy molecules for the ACME electron EDM search. N. J. Phys. 24, 073043 (2022).
Touwen, A. et al. Manipulating a beam of barium fluoride molecules using an electrostatic hexapole. N. J. Phys. 26, 073054 (2024).
Alauze, X. et al. An ultracold molecular beam for testing fundamental physics. Quantum Sci. Technol. 6, 044005 (2021).
Kozyryev, I. et al. Sisyphus laser cooling of a polyatomic molecule. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 173201 (2017).
Augenbraun, B. L. et al. Laser-cooled polyatomic molecules for improved electron electric dipole moment searches. N. J. Phys. 22, 022003 (2020).
Fitch, N. & Tarbutt, M. Laser-cooled molecules. Adv. At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 70, 157–262 (2021).
Hummon, M. T. et al. 2d magneto-optical trapping of diatomic molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 143001 (2013).
Zeng, Z., Deng, S., Yang, S. & Yan, B. Three-dimensional magneto-optical trapping of barium monofluoride. Phys. Rev. Lett. 133, 143404 (2024).
Langin, T. K. & DeMille, D. Toward improved loading, cooling, and trapping of molecules in magneto-optical traps. N. J. Phys. 25, 043005 (2023).
Shuman, E. S., Barry, J. F. & DeMille, D. Laser cooling of a diatomic molecule. Nature 467, 820–823 (2010).
Burau, J. J., Aggarwal, P., Mehling, K. & Ye, J. Blue-detuned magneto-optical trap of molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 130, 193401 (2023).
Jorapur, V., Langin, T. K., Wang, Q., Zheng, G. & DeMille, D. High density loading and collisional loss of laser-cooled molecules in an optical trap. Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 163403 (2024).
Vilas, N. B. et al. Magneto-optical trapping and sub-Doppler cooling of a polyatomic molecule. Nature 606, 70–74 (2022).
Lasner, Z. D. et al. Magneto-optical trapping of a heavy polyatomic molecule for precision measurement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 134, 083401 (2025).
Mitra, D. et al. Direct laser cooling of a symmetric top molecule. Science 369, 1366–1369 (2020).
Aggarwal, P. et al. Lifetime measurements of the a2Π1/2 and a2Π3/2 states in BaF. Phys. Rev. A 100, 052503 (2019).
Rockenhäuser, M., Kogel, F., Garg, T., Morales-Ramírez, S. A. & Langen, T. Laser cooling of barium monofluoride molecules using synthesized optical spectra. Phys. Rev. Res. 6, 043161 (2024).
Hao, Y. et al. High accuracy theoretical investigations of CaF, SrF, and BaF and implications for laser-cooling. J. Chem. Phys. 151, 034302 (2019).
Xia, M. et al. Destabilization of dark states in MgF molecules. Phys. Rev. A 103, 013321 (2021).
Kogel, F., Garg, T., Rockenhäuser, M., Morales-Ramírez, S. A. & Langen, T. Molecular laser cooling using serrodynes: implementation, characterization and prospects. N. J. Phys. 27, 055001 (2025).
Mooij, M. C. et al. Influence of source parameters on the longitudinal phase-space distribution of a pulsed cryogenic beam of barium fluoride molecules. N. J. Phys. 26, 053009 (2024).
Truppe, S. et al. Molecules cooled below the doppler limit. Nat. Phys. 13, 1173–1176 (2017).
Chen, T., Bu, W. & Yan, B. Radiative deflection of a BaF molecular beam via optical cycling. Phys. Rev. A 96, 053401 (2017).
Boeschoten, A. et al. Spin-precession method for sensitive electric dipole moment searches. Phys. Rev. A 110, L010801 (2024).
Aggarwal, P. et al. A supersonic laser ablation beam source with narrow velocity spreads. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 92, 033202 (2021).
Wright, S. C. et al. Cryogenic buffer gas beams of AlF, CaF, MgF, YbF, al, ca, yb and NO - a comparison. Mol. Phys. 121, e2146541 (2023).
Berkeland, D. J. & Boshier, M. G. Destabilization of dark states and optical spectroscopy in Zeeman-degenerate atomic systems. Phys. Rev. A 65, 033413 (2002).
Eckel, S., Barker, D. S., Norrgard, E. B. & Scherschligt, J. PyLCP: a Python package for computing laser cooling physics. Comput. Phys. Commun. 270, 108166 (2022).
Clausen, G. et al. Combining laser cooling and Zeeman deceleration for precision spectroscopy in supersonic beams. Phys. Rev. A 110, 042802 (2024).
Truppe, S. et al. An intense, cold, velocity-controlled molecular beam by frequency-chirped laser slowing. N. J. Phys. 19, 022001 (2017).
Rockenhäuser, M., Kogel, F., Pultinevicius, E. & Langen, T. Absorption spectroscopy for laser cooling and high-fidelity detection of barium monofluoride molecules. Phys. Rev. A 108, 062812 (2023).
Acknowledgements
The NL-eEDM collaboration receives funding (eEDM-166, XL21.074 and VI.C.212.016) from the Dutch Research Council (NWO). We acknowledge the technical support from L. Huisman and O. Böll.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
S.H., H.B., A.B., R.G.E.T., W.U., and L.W. conceived the experiment. J.H. developed the laser system, performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and drafted the first version of the manuscript. J.H., A.T., R.B., and T.F. developed the vacuum system. I.T. and J.H. performed the trajectory simulations using an adapted version of a code originally written by A.T. and H.B. A.T. helped with an early version of the experiment and data analysis. S.H. and H.B. supervised the project. J.H., I.T., A.T., N.B., R.B., H.B., A.B., T.F., S.H., S.J., J.L., M.M., H.M., B.N., E.P., B.S., L.S., R.T., W.U., J.V., and L.W. discussed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Communications Physics thanks Ben Sauer, Chi Zhang and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
van Hofslot, J.W.F., Thompson, I.E., Touwen, A. et al. 2D transverse laser cooling of a hexapole focused beam of cold BaF molecules. Commun Phys (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-025-02470-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-025-02470-x