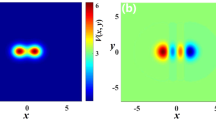
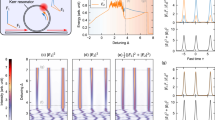
Abstract
Spontaneous symmetry breaking (SSB) plays a central role in many areas of physics, from particle interactions to optical systems. Exceptional points (EPs), where system properties become degenerate, are often believed to occur together with SSB. Here we investigate the intricate relationship between SSB and a specific class of EPs across three distinct, real-world scenarios in nonlinear optics. In these systems, the two phenomena do not coincide; they occur at dislocated points in parameter space, but are interdependent. This recurring behavior across disparate platforms implies that such decoupling is not unique to these optical systems, but likely reflects a more general principle. Our results highlight the need for careful analysis of assumed correlations between SSB and EPs in both theoretical and applied contexts. They deepen our understanding of nonlinear dynamics in optical systems and prompt a broader reconsideration of contexts where EPs and SSB are thought to be interdependent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Bergholtz, E. J., Budich, J. C. & Kunst, F. K. Exceptional topology of non-Hermitian systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 93, 015005 (2021).
Kato, T.Perturbation Theory for Linear Operators (Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1995).
Berry, M. Physics of Nonhermitian Degeneracies. Czechoslovak J. Phys. 54, 1039–1047 (2004).
Heiss, W. D. The physics of exceptional points. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 45, 444016 (2012).
Kaplan, A. E. & Meystre, P. Enhancement of the Sagnac effect due to nonlinearly induced nonreciprocity. Opt. Lett. 6, 590–592 (1981).
Kaplan, A. E. & Meystre, P. Directionally asymmetrical bistability in a symmetrically pumped nonlinear ring interferometer. Opt. Commun. 40, 229–232 (1982).
Wright, E. M., Meystre, P., Firth, W. J. & Kaplan, A. E. Theory of the nonlinear Sagnac effect in a fiber-optic gyroscope. Phys. Rev. A 32, 2857–2863 (1985).
Geddes, J. B., Moloney, J. V., Wright, E. M. & Firth, W. J. Polarisation patterns in a nonlinear cavity. Opt. Commun. 111, 623–631 (1994).
Xu, Y. & Coen, S. Experimental observation of the spontaneous breaking of the time-reversal symmetry in a synchronously pumped passive Kerr resonator. Opt. Lett. 39, 3492–3495 (2014).
Li, J., Zhan, X., Ding, C., Zhang, D. & Wu, Y. Enhanced nonlinear optics in coupled optical microcavities with an unbroken and broken parity-time symmetry. Phys. Rev. A 92, 043830 (2015).
Rossi, J., Carretero-González, R., Kevrekidis, P. G. & Haragus, M. On the spontaneous time-reversal symmetry breaking in synchronously-pumped passive Kerr resonators. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 49, 455201 (2016).
Del Bino, L., Silver, J. M., Stebbings, S. L. & Del’Haye, P. Symmetry Breaking of Counter-Propagating Light in a Nonlinear Resonator. Sci. Rep. 7, 43142 (2017).
Cao, Q.-T. et al. Experimental Demonstration of Spontaneous Chirality in a Nonlinear Microresonator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 033901 (2017).
Woodley, M. T. M. et al. Universal symmetry-breaking dynamics for the Kerr interaction of counterpropagating light in dielectric ring resonators. Phys. Rev. A 98, 053863 (2018).
Hendry, I. et al. Spontaneous symmetry breaking and trapping of temporal Kerr cavity solitons by pulsed or amplitude-modulated driving fields. Phys. Rev. A 97, 053834 (2018).
Bino, L. D. et al. Microresonator isolators and circulators based on the intrinsic nonreciprocity of the Kerr effect. Optica 5, 279–282 (2018).
Copie, F. et al. Interplay of Polarization and Time-Reversal Symmetry Breaking in Synchronously Pumped Ring Resonators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 013905 (2019).
Wu, C., Fan, J., Chen, G. & Jia, S. Symmetry-breaking-induced dynamics in a nonlinear microresonator. Opt. Express 27, 28133–28142 (2019).
Cuong, N. D. et al. Spontaneous symmetry breaking in coupled ring resonators with linear gain and nonlinear loss. Vinh Univ. J. Sci. 48, 39–48 (2019).
Hill, L., Oppo, G.-L., Woodley, M. T. M. & Del’Haye, P. Effects of self- and cross-phase modulation on the spontaneous symmetry breaking of light in ring resonators. Phys. Rev. A 101, 013823 (2020).
Garbin, B. et al. Asymmetric balance in symmetry breaking. Phys. Rev. Res. 2, 023244 (2020).
Dolinina, D. & Yulin, A. Spontaneous symmetry breaking of nonlinear states in optical cavities with radiative losses. Opt. Lett. 45, 3781–3784 (2020).
Moroney, N. et al. Logic Gates Based on Interaction of Counterpropagating Light in Microresonators. J. Lightwave Technol. 38, 1414–1419 (2020).
Ghalanos, G. N. et al. Kerr-Nonlinearity-Induced Mode-Splitting in Optical Microresonators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 223901 (2020).
Woodley, M. T. M., Hill, L., Del Bino, L., Oppo, G.-L. & Del’Haye, P. Self-Switching Kerr Oscillations of Counterpropagating Light in Microresonators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 043901 (2021).
Silver, J. M., Grattan, K. T. V. & Del’Haye, P. Critical dynamics of an asymmetrically bidirectionally pumped optical microresonator. Phys. Rev. A 104, 043511 (2021).
Xu, G. et al. Spontaneous symmetry breaking of dissipative optical solitons in a two-component Kerr resonator. Nat. Commun. 12, 4023 (2021).
Garbin, B. et al. Dissipative Polarization Domain Walls in a Passive Coherently Driven Kerr Resonator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 023904 (2021).
Fatome, J. et al. Self-symmetrization of symmetry-breaking dynamics in passive Kerr resonators. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.07642 (2021).
Li, Y.-Y., Cao, Q.-T., Chen, J. -h, Yu, X.-C. & Xiao, Y.-F. Microcavity Sensor Enhanced by Spontaneous Chiral Symmetry Breaking. Phys. Rev. Appl. 16, 044016 (2021).
Silver, J. M. et al. Nonlinear enhanced microresonator gyroscope. Optica 8, 1219–1226 (2021).
Xu, G. et al. Breathing dynamics of symmetry-broken temporal cavity solitons in Kerr ring resonators. Opt. Lett. 47, 1486–1489 (2022).
Sanvert, Y. et al. Symmetry Broken Localized Structures in a Coherently-Driven Fabry-Pérot Kerr Resonator. In 2025 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe & European Quantum Electronics Conference (CLEO/Europe-EQEC) (2025).
Ghosh, A. et al. Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking of Cavity Solitons in Coupled Resonators. In 2025 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe & European Quantum Electronics Conference (CLEO/Europe-EQEC) (2025).
Campbell, G. N., Zhang, S., Del Bino, L., Del’Haye, P. & Oppo, G.-L. Counterpropagating light in ring resonators: Switching fronts, plateaus, and oscillations. Phys. Rev. A 106, 043507 (2022).
Mai, J. & Cheah, K. W. Nonreciprocal transmission in a nonlinear coupled heterostructure. Opt. Express 30, 46357–46365 (2022).
Mai, J., Chen, Y., Li, G. & Cheah, K. W. Double exceptional points in grating coupled metal-insulator-metal heterostructure. Opt. Express 30, 40053–40062 (2022).
Moroney, N. et al. A Kerr polarization controller. Nat. Commun. 13, 398 (2022).
Hill, L., Oppo, G.-L. & Del’Haye, P. Multi-stage spontaneous symmetry breaking of light in Kerr ring resonators. Commun. Phys. 6, 1–9 (2023).
Ghosh, A., Hill, L., Oppo, G.-L. & Del’Haye, P. Four-field symmetry breakings in twin-resonator photonic isomers. Phys. Rev. Res. 5, L042012 (2023).
Bitha, R. D. D., Giraldo, A., Broderick, N. G. R. & Krauskopf, B. Bifurcation analysis of complex switching oscillations in a Kerr microring resonator. Phys. Rev. E 108, 064204 (2023).
Wang, W. et al. Spontaneous Synchronization and Exceptional Points in Breather Complexes. Phys. Rev. Appl. 20, 024060 (2023).
Quinn, L. et al. Random number generation using spontaneous symmetry breaking in a Kerr resonator. Opt. Lett. 48, 3741–3744 (2023).
Campbell, G. N., Hill, L., Del Haye, P. & Oppo, G. L. Vectorial light in fabry-perot resonators in the normal dispersion regime. arXiv preprint arXiv:2509.17663 (2025).
Mai, J., Huang, X., Guo, X., Fan, H. & Cheah, K. W. Spontaneous symmetry breaking of coupled Fabry–Pérot nanocavities. Commun. Phys. 7, 1–6 (2024).
Lucas, E. et al. Polarization Faticons: Chiral Localized Structures in Self-Defocusing Kerr Resonators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 135, 063803 (2025).
Hill, L. et al. Controlling Frequency Comb Line Spacing Via Symmetry Broken Faticons. In 2025 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe & European Quantum Electronics Conference (CLEO/Europe-EQEC) (2025).
Campbell, G. N., Hill, L., Del’Haye, P. & Oppo, G.-L. Frequency comb enhancement via the self-crystallization of vectorial cavity solitons. Opt. Express 32, 37691–37702 (2024).
Ghosh, A. et al. Controlled light distribution with coupled microresonator chains via Kerr symmetry breaking. Photonics Res. 12, 2376–2389 (2024).
Hill, L. et al. Symmetry broken vectorial Kerr frequency combs from Fabry-Pérot resonators. Commun. Phys. 7, 1–9 (2024).
Coen, S. et al. Nonlinear topological symmetry protection in a dissipative system. Nat. Commun. 15, 1398 (2024).
Pal, A. et al. Linear and nonlinear coupling of light in twin-resonators with Kerr nonlinearity. Photonics Res. 12, 2733–2740 (2024).
Rah, Y. & Yu, K. Demonstration of spontaneous symmetry breaking in self-modulated ring resonators. Phys. Rev. Res. 6, 013234 (2024).
Ghosh, A. et al. Phase Symmetry Breaking of Counterpropagating Light in Microresonators for Switches and Logic Gates. Laser Photonics Rev. e01500 (2025).
Zhang, Y. et al. Integrated optical switches based on Kerr symmetry breaking in microresonators. Photonics Res. 13, 360–366 (2025).
Jalas, D. et al. What is — and what is not — an optical isolator. Nat. Photonics 7, 579–582 (2013).
Chang, L. et al. Parity–time symmetry and variable optical isolation in active–passive-coupled microresonators. Nat. Photonics 8, 524–529 (2014).
Mai, J. & Cheah, K. W. Nonreciprocity through gain saturation in coupled nanocavities. Phys. Rev. B 109, 035101 (2024).
Shanavas, T., Krueper, G., Zhu, J., Park, W. & Gopinath, J. T. Nonlinear Symmetry Breaking to Enhance the Sagnac Effect in a Microresonator Gyroscope. arXiv preprint arXiv:2508.09132 (2025)
Wang, P., Li, C., Xiao, Z. & Xu, G. Observation of Polarization Symmetry-Broken Platicons in a Passive Kerr Resonator with Normal Dispersion. In 2025 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe & European Quantum Electronics Conference (CLEO/Europe-EQEC) (2025).
Pal, A. et al. Characterization of Light Scattering in Microresonator via Symmetry Breaking of Counterpropagating Light. In 2025 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe & European Quantum Electronics Conference (CLEO/Europe-EQEC) (2025).
Mazo-Vasquez, J. D., Gohsrich, J. T., Kunst, F. K. & Hill, L. An algebraic approach to bifurcations in kerr ring and fabry-perot resonators. arXiv preprint arXiv:2512.14168 (2025).
Campbell, G. N., Hill, L., Del’Haye, P. & Oppo, G.-L. Dark solitons in Fabry-Pérot resonators with Kerr media and normal dispersion. Phys. Rev. A 108, 033505 (2023).
Lugiato, L. A. & Lefever, R. Spatial Dissipative Structures in Passive Optical Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 2209–2211 (1987).
Lugiato, L. A., Prati, F., Gorodetsky, M. L. & Kippenberg, T. J. From the Lugiato–Lefever equation to microresonator-based soliton Kerr frequency combs. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A: Math., Phys. Eng. Sci. 376, 20180113 (2018).
Haelterman, M., Trillo, S. & Wabnitz, S. Dissipative modulation instability in a nonlinear dispersive ring cavity. Opt. Commun. 91, 401–407 (1992).
Cole, D. C., Gatti, A., Papp, S. B., Prati, F. & Lugiato, L. Theory of Kerr frequency combs in Fabry-Pérot resonators. Phys. Rev. A 98, 013831 (2018).
Skryabin, D. V. Hierarchy of coupled mode and envelope models for bi-directional microresonators with Kerr nonlinearity. OSA Contin. 3, 1364–1375 (2020).
Bernstein, J. Spontaneous symmetry breaking, gauge theories, the Higgs mechanism and all that. Rev. Mod. Phys. 46, 7–48 (1974).
Baskaran, G. & Anderson, P. W. Gauge theory of high-temperature superconductors and strongly correlated Fermi systems. Phys. Rev. B 37, 580–583 (1988).
Lin, Z. et al. Unidirectional Invisibility Induced by PT-Symmetric Periodic Structures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 213901 (2011).
Fleury, R., Sounas, D. L. & Alù, A. Negative Refraction and Planar Focusing Based on Parity-Time Symmetric Metasurfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 023903 (2014).
Goldzak, T., Mailybaev, A. A. & Moiseyev, N. Light Stops at Exceptional Points. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 013901 (2018).
Miri, M.-A. & Alù, A. Exceptional points in optics and photonics. Science 363, eaar7709 (2019).
Haus, H. & Huang, W. Coupled-mode theory. Proc. IEEE 79, 1505–1518 (1991).
Yariv, A. Coupled-mode theory for guided-wave optics. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 9, 919–933 (1973).
Gordon, J. P. & Kogelnik, H. PMD fundamentals: Polarization mode dispersion in optical fibers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 97, 4541–4550 (2000).
Kogelnik, H. Coupled wave theory for thick hologram gratings. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 48, 2909–2947 (1969).
Aspelmeyer, M., Kippenberg, T. J. & Marquardt, F. Cavity optomechanics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 86, 1391–1452 (2014).
Fox, M. Quantum Optics: An Introduction (Oxford University Press, 2006).
El-Ganainy, R. et al. Non-Hermitian physics and PT symmetry. Nat. Phys. 14, 11–19 (2018).
Özdemir, ŞK., Rotter, S., Nori, F. & Yang, L. Parity–time symmetry and exceptional points in photonics. Nat. Mater. 18, 783–798 (2019).
Bernard, D. & LeClair, A. A Classification of Non-Hermitian Random Matrices. In Cappelli, A. & Mussardo, G. (eds.) Statistical Field Theories, NATO Science Series, 207–214 (Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, 2002).
Kawabata, K., Shiozaki, K., Ueda, M. & Sato, M. Symmetry and Topology in Non-Hermitian Physics. Phys. Rev. X 9, 041015 (2019).
Delplace, P., Yoshida, T. & Hatsugai, Y. Symmetry-Protected Multifold Exceptional Points and Their Topological Characterization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 186602 (2021).
Sayyad, S. & Kunst, F. K. Realizing exceptional points of any order in the presence of symmetry. Phys. Rev. Res. 4, 023130 (2022).
Budich, J. C., Carlström, J., Kunst, F. K. & Bergholtz, E. J. Symmetry-protected nodal phases in non-Hermitian systems. Phys. Rev. B 99, 041406 (2019).
Yoshida, T., Peters, R., Kawakami, N. & Hatsugai, Y. Symmetry-protected exceptional rings in two-dimensional correlated systems with chiral symmetry. Phys. Rev. B 99, 121101 (2019).
Okugawa, R. & Yokoyama, T. Topological exceptional surfaces in non-Hermitian systems with parity-time and parity-particle-hole symmetries. Phys. Rev. B 99, 041202 (2019).
Bender, C. M. & Boettcher, S. Real Spectra in Non-Hermitian Hamiltonians Having PT Symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 5243–5246 (1998).
Bender, C. M. Making sense of non-Hermitian Hamiltonians. Rep. Prog. Phys. 70, 947 (2007).
Gräfe, M. et al. Correlations of indistinguishable particles in non-Hermitian lattices. N. J. Phys. 15, 033008 (2013).
Guo, A. et al. Observation of PT-Symmetry Breaking in Complex Optical Potentials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 093902 (2009).
Dal Cin, N., Marquardt, F. & Wanjura, C. C. Training nonlinear optical neural networks with Scattering Backpropagation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2508.11750 (2025).
Montag, A. & Kunst, F. K. Symmetry-induced higher-order exceptional points in two dimensions. Phys. Rev. Res. 6, 023205 (2024).
Kominis, Y., Kovanis, V. & Bountis, T. Spectral signatures of exceptional points and bifurcations in the fundamental active photonic dimer. Phys. Rev. A 96, 053837 (2017).
Felski, A. & Kunst, F. K. Exceptional points and stability in nonlinear models of population dynamics having PT symmetry. Phys. Rev. Res. 7, 013326 (2025).
Bai, K. et al. Nonlinear Exceptional Points with a Complete Basis in Dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 130, 266901 (2023).
Bai, K. et al. Observation of Nonlinear Exceptional Points with a Complete Basis in Dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 073802 (2024).
Yoshida, T., Isobe, T. & Hatsugai, Y. Exceptional points and non-Hermitian skin effects under nonlinearity of eigenvalues. Phys. Rev. B 111, 064310 (2025).
Fang, L. et al. Exceptional features in nonlinear Hermitian systems. Phys. Rev. B 111, L161102 (2025).
Leo, F. et al. Temporal cavity solitons in one-dimensional Kerr media as bits in an all-optical buffer. Nat. Photonics 4, 471–476 (2010).
Abramowitz, M. & Stegun, I. A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables (Dover Publications, 1964).
Acknowledgements
We thank Alexander Felski, George Ghalanos, Kyle Kawagoe, Jona Kayser, and Anton Montag for insightful discussions. We also acknowledge early, separate, and unpublished work by Michael T.M. Woodley exploring the connection between Jacobian EPs and SSB in counter-propagating light, which came to our attention late in the development of this project. L.H. acknowledges funding from the Max Planck Society (MPG) and the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS). J.T.G. and F.K.K. acknowledge support from the MPG Lise Meitner Excellence Program 2.0. L.H., J.T.G., and F.K.K. also acknowledge funding from the European Union’s ERC Starting Grant “NTopQuant” (101116680). L.H., A.G. and P.D’H. acknowledge support through the ERC Starting Grant “CounterLight” (756966). The views expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the EU or the ERC. Neither the EU nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.H. and J.T.G. carried out the majority of the calculations and theoretical work and should be considered co-first authors. They were supported by A.G. and J.F., who contributed to discussions and the analysis of results. F.K.K. and P.D’H. initiated the project and provided ongoing guidance, engaging in discussions with all authors. L.H. and J.T.G. prepared the manuscript with input from all co-authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Communications Physics thanks Kazuki Sone and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, L., Gohsrich, J.T., Ghosh, A. et al. Exceptional points preceding and enabling spontaneous symmetry breaking. Commun Phys (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-026-02491-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-026-02491-0