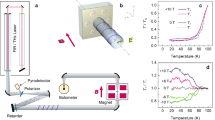
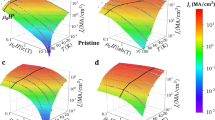
Abstract
The electromagnetic properties of type-II superconductors depend on vortices—magnetic flux lines whose motion introduces dissipation that can be mitigated by pinning from material defects. The material disorder landscape is tuned by the choice of materials growth technique and incorporation of impurities that serve as vortex pinning centers. For example, metal organic deposition (MOD) and pulsed laser deposition (PLD) produce high-quality superconducting films with uncorrelated versus correlated disorder, respectively. Here, we study vortex dynamics in PLD-grown EuBa2Cu3Oy films containing varying concentrations of BaHfO3 inclusions and compare our results with those of MOD-grown (Y,Gd)Ba2Cu3Oy films. Despite both systems exhibiting behavior consistent with strong pinning theory, which predicts the critical current density Jc based on vortex trapping by randomly distributed spherical inclusions, we find striking differences in the vortex dynamics owing to the correlated versus uncorrelated disorder. Specifically, we find that the EuBa2Cu3Oy films grown without inclusions exhibit surprisingly slow vortex creep, comparable to the slowest creep rates achieved in (Y,Gd)Ba2Cu3Oy films containing high concentrations of BaHfO3. Whereas adding inclusions to (Y,Gd)Ba2Cu3Oy is effective in slowing creep, BaHfO3 increases creep in EuBa2Cu3Oy even while concomitantly improving Jc. Lastly, we find evidence of variable range hopping and that Jc is maximized at the BaHfO3 concentration that hosts creep of large vortex bundles or a Bose glass state.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available on Mendeley Data (https://doi.org/10.17632/z7t5jtyvmw.2) as a zip file. This includes Origin files (.opju) that contain raw and processed data spreadsheets for all the samples and figures used in this paper, which can be opened using Origin Viewer, a free application that permits viewing and copying of data contained in Origin project files. README files are also included to guide the reader about the contents of each folder and provide captions and explanations for the corresponding data files.
Code availability
The custom Python codes used to process the raw data are available on Mendeley Data (https://doi.org/10.17632/z7t5jtyvmw.2) as a zip file. README files are included to guide the reader about the contents of each folder and provide captions and explanations for the corresponding data files. JupyterLab version 4.0.10 and Python version 3.11.5 are used.
References
Molodyk, A. & Larbalestier, D. C. The prospects of high-temperature superconductors. Science 380, 1220–1222 (2023).
MacManus-Driscoll, J. L. & Wimbush, S. C. Processing and application of high-temperature superconducting coated conductors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6, 587–604 (2021).
Hahn, S. et al. 45.5-tesla direct-current magnetic field generated with a high-temperature superconducting magnet. Nature 570, 496–499 (2019).
Foltyn, S. R. et al. Materials science challenges for high-temperature superconducting wire. Nat. Mater. 6, 631–642 (2007).
Feigel’man, M. V. & Vinokur, V. M. Thermal fluctuations of vortex lines, pinning, and creep in high-Tc superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 41, 8986–8990 (1990).
Kwok, W.-K. et al. Vortices in high-performance high-temperature superconductors. Rep. Prog. Phys, 79, 116501 (2016).
Puig, T., Gutierrez, J. & Obradors, X. Impact of high growth rates on the microstructure and vortex pinning of high-temperature superconducting coated conductors. Nat. Rev. Phys. 6, 132–148 (2024).
Eley, S., Miura, M., Maiorov, B. & Civale, L. Universal lower limit on vortex creep in superconductors. Nat. Mater. 16, 409–413 (2017).
Kang, S. et al. High-performance high-Tc superconducting wires. Science 311, 1911–1914 (2006).
Ruiz, H. et al. Critical current density in advanced superconductors. Prog. Mater. Sci. 155, 101492 (2026).
Blatter, G., Feigel’man, M. V., Geshkenbein, V. B., Larkin, A. I. & Vinokur, V. M. Vortices in high-temperature superconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 1125 (1994).
Bardeen, J. & Stephen, M. J. Theory of the motion of vortices in superconductors. Phys. Rev. 140, A1197–A1207 (1965).
Eley, S., Glatz, A. & Willa, R. Challenges and transformative opportunities in superconductor vortex physics. J. Appl. Phys. 130, 50901 (2021).
MacManus-Driscoll, J. L. et al. Strongly enhanced current densities in superconducting coated conductors of YBa2Cu3O7−x+BaZrO3. Nat. Mater. 3, 439–443 (2004).
Haugan, T., Barnes, P. N., Wheeler, R., Meisenkothen, F. & Sumption, M. Addition of nanoparticle dispersions to enhance flux pinning of the YBa2Cu3O7−x superconductor. Nature 430, 867–870 (2004).
Matsumoto, K. & Mele, P. Artificial pinning center technology to enhance vortex pinning in YBCO coated conductors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 23, 014001 (2009).
Teranishi, R. et al. Superconducting properties of ErBCO films with BaMO3 nanorods (M=Zr and Sn) by pulsed laser deposition. Phys. C 468, 1522–1526 (2008).
Jones, S. C. et al. Designing high-performance superconductors with nanoparticle inclusions: comparisons to strong pinning theory. APL Mater. 9, 091105 (2021).
Gutiérrez, J. et al. Strong isotropic flux pinning in solution-derived YBa2Cu3O7−x nanocomposite superconductor films. Nat. Mater. 6, 367–373 (2007).
Xu, A. et al. Strongly enhanced vortex pinning from 4 to 77 K in magnetic fields up to 31 T in 15 mol.% Zr-added (Gd, Y)-Ba-Cu-O superconducting tapes. APL Mater. 2, 46111 (2014).
Miura, M. et al. Tuning nanoparticle size for enhanced functionality in perovskite thin films deposited by metal organic deposition. NPG Asia Mater. 9, 1–10 (2017).
Tobita, H. et al. Fabrication of BaHfO3 doped Gd1Ba2Cu3O7−δ coated conductors with the high Ic of 85 A/cm-w under 3 T at liquid nitrogen temperature (77 K). Supercond. Sci. Technol. 25, 062002 (2012).
Miura, M. et al. Thermodynamic approach for enhancing superconducting critical current performance. NPG Asia Mater. 14, 85 (2022).
Gurevich, A. Pinning size effects in critical currents of superconducting films. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 20, S128 (2007).
Wimbush, S. C. Fundamentals: Flux Pinning Chap. 1, 1–104 (John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2015).
Matsushita, T. Flux Pinning in Superconductors (Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2007).
Ibi, A. et al. Development of multi-filamentated long EuBCO coated conductors with BHO doping by plane-plume PLD method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1293, 012034 (2019).
Fujita, S. et al. Flux-pinning properties of BaHfO3-doped EuBCO-coated conductors fabricated by hot-wall PLD. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 29, 1–5 (2019).
Ibi, A. et al. Improvement of in-field performance for EuBCO with heavily doped BHO coated conductors by PLD method with high temperature deposition and low temperature annealing. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 756, 12024 (2020).
Yokoe, D., Yoshida, R., Kato, T., Ibi, A. & Izumi, T. Nanostructural characterization of EuBa2Cu3Oy layers containing 3.5 mol%BaHfO3 nanorods grown by pulsed laser deposition growing in both vapor–solid and vapor–liquid–solid modes. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 33, 024002 (2020).
Wu, Y. et al. Ultra-fast dynamic deposition of EuBa2Cu3O7−δ-BaHfO3 nanocomposite films: self-assembly structure modulation and flux pinning behaviors. Mater. Des. 224, 111406 (2022).
Lojka, M. et al. Comparison of superconducting properties of YBCO and EuBCO single-domain bulks. AIP Conf. Proc. 2894, 020008 (2023).
Zhao, M. et al. Influence of thickness on the microstructure and performance of BaHfO3-doped EuBa2Cu3O7−δ layers grown by ultra-fast pld techniques. Appl. Surf. Sci. 694, 162791 (2025).
Suzuki, T. et al. Role of defects in increasing the critical current density of reel-to-reel PLD (Eu,Er)Ba2Cu3Oy+BaHfO3-coated conductors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 63, 060901 (2024).
Zhao, P. et al. Effect of local strain fields on the irradiation resistance of doped EuBa2Cu3O7−δ high-temperature superconducting tapes. ssrn.5182058 (2025).
Takahashi, K. et al. Investigation of thick PLD-GdBCO and ZrO2 doped GdBCO coated conductors with high critical current on PLD-CeO2 capped IBAD-GZO substrate tapes. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 19, 924 (2006).
Yoshida, T. et al. Fabrication of Eu1Ba2Cu3O7−δ+BaHfO3 coated conductors with 141 A/cm-w under 3 T at 77 K using the IBAD/PLD process. Phys. C 504, 42–46 (2014).
Yoshida, T. et al. Fabrication of 93.7 m long PLD-EuBCO+BaHfO3 coated conductors with 103 A/cm W at 77 K under 3 T. Phys. C 518, 54–57 (2015).
Tallon, J. L., Bernhard, C., Shaked, H., Hitterman, R. L. & Jorgensen, J. D. Generic superconducting phase behavior in high-Tc cuprates: Tc variation with hole concentration in YBa2Cu3O7-δ. Phys. Rev. B 51, 12911–12914 (1995).
Dam, B. et al. Origin of high critical currents in YBa2Cu3O7−δ superconducting thin films. Nature 399, 439–442 (1999).
Huijbregtse, J. M. et al. Natural strong pinning sites in laser-ablated YBa2Cu3O7−δ thin films. Phys. Rev. B 62, 1338–1349 (2000).
Miura, M. et al. Dislocation density and critical current density of Sm1+xBa2−xCu3Oy films prepared by various fabrication processes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45, L701 (2006).
Miura, M. et al. The effects of density and size of BaMO3 (M=Zr, Nb, Sn) nanoparticles on the vortex glassy and liquid phase in (Y, Gd)Ba2Cu3Oy coated conductors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 26, 035008 (2013).
Larkin, A. I. & Ovchinnikov, Y. N. Pinning in type-II superconductors. J. Low Temp. Phys. 34, 409 (1979).
Blatter, G., Geshkenbein, V. B. & Koopmann, J. A. G. Weak to strong pinning crossover. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 067009 (2004).
Ovchinnikov, Y. N. & Ivlev, B. I. Pinning in layered inhomogeneous superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 43, 8024–8029 (1991).
Willa, R., Koshelev, A. E., Sadovskyy, I. A. & Glatz, A. Strong-pinning regimes by spherical inclusions in anisotropic type-II superconductors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 31, 014001 (2017).
Willa, R., Koshelev, A. E., Sadovskyy, I. A. & Glatz, A. Peak effect due to competing vortex ground states in superconductors with large inclusions. Phys. Rev. B 98, 054517 (2018).
Buchacek, M., Willa, R., Geshkenbein, V. B. & Blatter, G. Persistence of pinning and creep beyond critical drive within the strong pinning paradigm. Phys. Rev. B 98, 094510 (2018).
van der Beek, C. J. et al. Strong pinning in high-temperature superconducting films. Phys. Rev. B 66, 024523 (2002).
Gyorgy, E. M., van Dover, R. B., Jackson, K. A., Schneemeyer, L. F. & Waszczak, J. V. Anisotropic critical currents in Ba2YCu3O7 analyzed using an extended Bean model. Appl. Phys. Lett. 55, 283–285 (1989).
Talantsev, E. F. & Tallon, J. L. Fundamental nature of the self-field critical current in superconductors. arXiv:2409.16758 (2024).
Polat, O. et al. Thickness dependence of magnetic relaxation and E-J characteristics in superconducting (Gd-Y)-Ba-Cu-O films with strong vortex pinning. Phys. Rev. B 84, 024519 (2011).
Tsuchiya, Y. et al. Flux pinning landscape up to 25 T in SmBa2Cu3Oy films with BaHfO3 nanorods fabricated by low-temperature growth technique. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 30, 104004 (2017).
Bartolomé, E. et al. Intrinsic anisotropy versus effective pinning anisotropy in YBa2Cu3O7 thin films and nanocomposites. Phys. Rev. B 100, 054502 (2019).
Maiorov, B. et al. Synergetic combination of different types of defect to optimize pinning landscape using BaZrO3-doped YBa2Cu3O7. Nat. Mater 8, 398–404 (2009).
Ijaduola, A. O. et al. Critical currents, magnetic relaxation and pinning in NdBa2Cu3O7−δ films with BaZrO3-generated columnar defects. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 25, 045013 (2012).
Díaz, A., Mechin, L., Berghuis, P. & Evetts, J. E. Evidence for vortex pinning by dislocations in YBa2Cu3O7−δ low-angle grain boundaries. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 3855–3858 (1998).
Gurevich, A. & Cooley, L. D. Anisotropic flux pinning in a network of planar defects. Phys. Rev. B 50, 13563–13576 (1994).
Abou El Hassan, A. et al. Magnetic penetration depth and coherence length in a single-crystal YBa2Cu3O7−δ. Phys. Status Solidi B 258, 2100292 (2021).
Yeshurun, Y., Malozemoff, A. P. & Shaulov, A. Magnetic relaxation in high-temperature superconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 68, 911–949 (1996).
Feigel’man, M. V., Geshkenbein, V. B., Larkin, A. I. & Vinokur, V. M. Theory of collective flux creep. Phys. Rev. Lett. 63, 2303 (1989).
Blatter, G. & Geshkenbein, V. B. Vortex Matter 725–936 (Springer, 2003).
Palau, A. et al. Disentangling vortex pinning landscape in chemical solution deposited superconducting YBa2 Cu3 O7−x films and nanocomposites. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 31, 034004 (2018).
Eley, S. et al. Decoupling and tuning competing effects of different types of defects on flux creep in irradiated YBa2Cu3O7−δ coated conductors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 30, 15010 (2016).
Miura, M. et al. Mixed pinning landscape in nanoparticle-introduced YGdBa2Cu3Oy films grown by metal organic deposition. Phys. Rev. B 83, 184519 (2011).
Mele, P. et al. Ultra-high flux pinning properties of BaMO3-doped YBa2Cu3O7−x thin films (M = Zr, Sn). Supercond. Sci. Technol. 21, 032002 (2008).
Eley, S. et al. Glassy Dynamics in a heavy ion irradiated NbSe2 crystal. Sci. Rep. 8, 13162 (2018).
Eley, S., Willa, R., Chan, M. K., Bauer, E. D. & Civale, L. Vortex phases and glassy dynamics in the highly anisotropic superconductor HgBa2CuO4+δ. Sci. Rep. 10, 10239 (2020).
Malozemoff, A. P. & Fisher, M. P. A. Universality in the current decay and flux creep of Y-Ba-Cu-O high-temperature superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 42, 6784–6786 (1990).
Nelson, D. R. & Vinokur, V. M. Boson localization and pinning by correlated disorder in high-temperature superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 2398–2401 (1992).
Nelson, D. R. & Vinokur, V. M. Boson localization and correlated pinning of superconducting vortex arrays. Phys. Rev. B 48, 13060–13097 (1993).
van Der Beek, C. J. & Kes, P. H. Handbook of Superconducting Materials, chap. Flux Pinning, 110–126 (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2021).
Civale, L. Vortex pinning and creep in high-temperature superconductors with columnar defects. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 10, A11 (1997).
Hwa, T., Le Doussal, P., Nelson, D. R. & Vinokur, V. M. Flux pinning and forced vortex entanglement by splayed columnar defects. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 3545–3548 (1993).
Wengel, C. & Täuber, U. C. Weakly pinned Bose glass vs Mott insulator phase in superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 4845–4848 (1997).
Wengel, C. & Täuber, U. C. Properties of the Bose glass phase in irradiated superconductors near the matching field. Phys. Rev. B 58, 6565–6579 (1998).
Gurevich, A. & Küpfer, H. Time scales of the flux creep in superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 48, 6477–6487 (1993).
Gurevich, A. & Brandt, E. H. Flux creep in superconducting films: an exact solution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 178–181 (1994).
Cornejo, H. S. et al. Vortex dynamics study on an uniaxially textured YBCO/MgO superconducting film from magnetic measurements. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 38, 35028 (2025).
Haberkorn, N. et al. High-temperature change of the creep rate in YBa2Cu3O7−δ films with different pinning landscapes. Phys. Rev. B 85, 174504 (2012).
Civale, L., Krusin-Elbaum, L., Thompson, J. R. & Holtzberg, F. Collective creep of vortex bundles in YBa2Cu3O7 crystals. Phys. Rev. B 50, 7188–7191 (1994).
Zhou, W., Xing, X., Wu, W., Zhao, H. & Shi, Z. Second magnetization peak effect, vortex dynamics, and flux pinning in 112-type superconductor Ca0.8La0.2Fe1−xCoxAs2. Sci. Rep. 6, 22278 (2016).
Sun, Y. et al. Enhancement of critical current density and mechanism of vortex pinning in H-irradiated FeSe single crystal. APEX 8, 113102 (2015).
Sun, Y. et al. Critical current density, vortex dynamics, and phase diagram of single-crystal FeSe. Phys. Rev. B 92, 144509 (2015).
Haberkorn, N. et al. Strong pinning and elastic to plastic vortex crossover in Na-doped CaFe2As2 single crystals. Phys. Rev. B 84, 094522 (2011).
Miu, L. et al. High Vortex Depinning Temperatures in YBCO Films with BZO Nanorods. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 26, 1167–1173 (2013).
Sundar, S. et al. Plastic pinning replaces collective pinning as the second magnetization peak disappears in the pnictide superconductor Ba0.75K0.25Fe2As2. Phys. Rev. B 95, 134509 (2017).
Joshi, K. et al. Measuring the lower critical field of superconductors using nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond optical magnetometry. Phys. Rev. Appl. 11, 014035 (2019).
Sonier, J. E. et al. New muon-spin-rotation measurement of the temperature dependence of the magnetic penetration depth in YBa2Cu3O6.95. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 744–747 (1994).
Tallon, J. L. et al. In-plane anisotropy of the penetration depth due to superconductivity on the Cu - O chains in YBa2Cu3O7−δ, Y2Ba4Cu7O15−δ, and YBa2Cu4O8. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 1008–1011 (1995).
Hardy, W. N., Bonn, D. A., Morgan, D. C., Liang, R. & Zhang, K. Precision measurements of the temperature dependence of λ in YBa2Cu3O6.95 : Strong evidence for nodes in the gap function. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 3999–4002 (1993).
Prozorov, R. & Giannetta, R. W. Magnetic penetration depth in unconventional superconductors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 19, R41–R67 (2006).
Thompson, J. R., Krusin-Elbaum, L., Civale, L., Blatter, G. & Feild, C. Superfast vortex creep in YBa2Cu3O7−δ crystals with columnar defects: Evidence for variable-range vortex hopping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 3181–3184 (1997).
Acknowledgements
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under grants DMR-1905909 and DMR-2330562 at the University of Washington (S.E.), as well as partial support through the University of Washington Materials Research Science and Engineering Center under grant DMR-2308979 (J.L.). We thank Sean Suh for performing some preliminary magnetization measurements. Work at Seikei University (M.M.) was supported by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) Fusion Oriented Research for disruptive Science and Technology (FOREST; grant No. JPMJFR202G, Japan). A part of this work at Seikei University was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI with No. 23K26147 and No.23H01453. The work at the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) was supported by NEDO. No competing interests are declared by all authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.E. and M.M. conceived and designed the experiment. M.M., A.I. and T.I. grew the (Y,Gd)BCO and EuBCO films. D.Y. and T.K. performed microstructural studies. J.L. performed magnetization studies and data analysis. S.E. determined data analysis procedures, S.E. and J.L. thoroughly reviewed the data analysis. S.E. and J.L. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Communications Materials thanks Alex Gurevich and Xavier Obradors for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Miura, M., Yokoe, D. et al. Higher critical currents yet faster vortex creep in EuBa2Cu3Oy films containing coherent artificial pinning centers. Commun Mater (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43246-025-01054-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43246-025-01054-0