Abstract
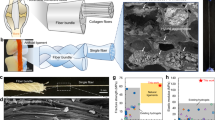
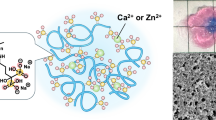
Polyoxometalate hydrogels, normally fabricated by linking polyanionic polyoxometalate particles with cationic ligands or multivalent ions, have found widespread potential applications in materials science and technology. Nevertheless, the binding with ligands/ions may adversely affect the intrinsic properties of polyoxometalates. And the prospects of polyoxometalate hydrogels in 4D printing and tribological fields have hardly been explored. Here we show that polyoxometalate hydrogels with favorable viscoelasticity, shear thinning, thixotropy, and thermal responsiveness, thus being capable of constructing various complex 4D printing geometries with shape reconfigurability and lubricating different types of solid tribopairs, can be created solely from high-speed centrifugation of aqueous dispersions of hybrid polyoxometalate nanosheets. By effectively preserving the inherent tribochemical activity and physical lubrication of the polyoxometalate nanosheet gelator using this approach, the hydrogels can provide potent lubrication for contacting surfaces for at least 200000 consecutive reciprocating friction cycles, featuring a high suitability for practical tribological applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data supporting the findings in this work are available from the corresponding authors (Y. Y. and L. X.) on reasonable request.
References
Miras, H. N., Yan, J., Long, D.-L. & Cronin, L. Engineering polyoxometalates with emergent properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 7403–7430 (2012).
Du, D.-Y., Qin, J.-S., Li, S.-L., Su, Z.-M. & Lan, Y.-Q. Recent advances in porous polyoxometalate-based metal–organic framework materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 4615–4632 (2014).
Ly, H. G. T., Absillis, G., Janssens, R., Proost, P. & Parac-Vogt, T. N. Highly amino acid selective hydrolysis of myoglobin at aspartate residues as promoted by zirconium (IV)-substituted polyoxometalates. Angew. Chem. 127, 7499–7502 (2015).
Yin, P. et al. Exploring the programmable assembly of a polyoxometalate–organic hybrid via metal ion coordination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 13425–13432 (2013).
Banerjee, A., Bassil, B. S., Röschenthaler, G.-V. & Kortz, U. Diphosphates and diphosphonates in polyoxometalate chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 7590–7604 (2012).
Huang, S.-C., Xia, X.-X., Fan, R.-X. & Qian, Z.-G. Programmable electrostatic interactions expand the landscape of dynamic functional hydrogels. Chem. Mater. 32, 1937–1945 (2020).
Xu, J. et al. Wet and functional adhesives from one-step aqueous self-assembly of natural amino acids and polyoxometalates. Angew. Chem. 129, 8857–8861 (2017).
Huang, S.-C., Zhu, Y.-J., Huang, X.-Y., Xia, X.-X. & Qian, Z.-G. Programmable adhesion and morphing of protein hydrogels for underwater robots. Nat. Commun. 15, 195 (2024).
Hua, Y. et al. Lanthanide–polyoxometalate-based self-erasing luminescent hydrogels with time-dependent and resilient properties for advanced information encryption. Mater. Horiz. 12, 2369–2379 (2025).
Wu, A., Gao, X., Sun, P., Lu, F. & Zheng, L. Co-assembly of polyoxometalates and zwitterionic amphiphiles into supramolecular hydrogels: from crystalline fibrillar to amorphous micellar networks. Angew. Chem. 130, 4089–4093 (2018).
Xu, X. et al. Critical conditions regulating the gelation in macroionic cluster solutions. Adv. Sci. 11, 2308902 (2024).
Ishiba, K. et al. Photoresponsive nanosheets of polyoxometalates formed by controlled self-assembly pathways. Angew. Chem. 129, 3020–3024 (2017).
Li, B., Li, W., Li, H. & Wu, L. Ionic complexes of metal oxide clusters for versatile self-assemblies. Acc. Chem. Res. 50, 1391–1399 (2017).
Wu, A., Sun, P., Sun, N., Yu, Y. & Zheng, L. Coassembly of a polyoxometalate and a zwitterionic amphiphile into a luminescent hydrogel with excellent stimuli responsiveness. Chem. Eur. J. 24, 16857–16864 (2018).
Zhang, S., Shi, W. & Wang, X. Locking volatile organic molecules by subnanometer inorganic nanowire-based organogels. Science 377, 100–104 (2022).
Zhang, F., Li, Z. & Wang, X. Mechanically tunable organogels from highly charged polyoxometalate clusters loaded with fluorescent dyes. Nat. Commun. 14, 8327 (2023).
Guedes, G. et al. Dual-crosslinked dynamic hydrogel incorporating {Mo154} with pH and NIR responsiveness for chemo-photothermal therapy. Adv. Mater. 33, 2007761 (2021).
Cao, F. et al. Polyoxometalate-containing nanocomposite hydrogels for cascade-catalytic and photothermal dually enhanced chemodynamic therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 17, 33633–33647 (2025).
Zhang, S., Shi, W., Yu, B. & Wang, X. Versatile inorganic subnanometer nanowire adhesive. J Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 16389–16394 (2022).
Ma, M. et al. Three birds, one stone: a multifunctional POM-based ionic hydrogel integrating strain sensing, fluorescent and antibacterial properties. Chem. Eng. J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.163257 (2025).
Chakraborty, A. et al. Polyoxometalate-guanosine monophosphate hydrogels with haloperoxidase-like activity for antibacterial performance. Biomacromolecules 25, 104–118 (2023).
Musumeci, C. et al. Smart high-κ nanodielectrics using solid supported polyoxometalate-rich nanostructures. ACS Nano 5, 9992–9999 (2011).
Hiyoshi, N. Keggin-type polyoxometalate nanosheets: synthesis and characterization via scanning transmission electron microscopy. Chem. Commun. 54, 5217–5220 (2018).
Liu, J., Shi, W. & Wang, X. Cluster–nuclei coassembled into two-dimensional hybrid CuO-PMA Sub-1 nm nanosheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 18754–18758 (2019).
Sun, R. Z. et al. Self-assembled polyoxometalate supramolecular nanosheets for efficient and durable water oxidation. Angew. Chem. 137, e202513915 (2025).
Li, H., Zheng, L., Lu, Q., Li, Z. & Wang, X. A monolayer crystalline covalent network of polyoxometalate clusters. Sci. Adv. 9, eadi6595 (2023).
Ahn, S. et al. Pushing the limits on metal–organic frameworks as a catalyst support: NU-1000 supported tungsten catalysts for o-xylene isomerization and disproportionation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 8535–8543 (2018).
Wang, L. et al. Macroscale superlubrication achieved with shear-thinning semisolid lubricants. Adv. Mater. 36, 2412257 (2024).
Wang, Y. et al. Biocompatible and biodegradable emulsion gel lubricants. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 12, 17982–17991 (2024).
Yan, F. et al. Highly interfacial active gemini surfactants as simple and versatile emulsifiers for stabilizing, lubricating and structuring liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 63, e202318926 (2024).
Yu, W. et al. Versatile MXene gels assisted by brief and low-strength centrifugation. Nano-Micro Lett 16, 94 (2024).
Yu, W. et al. Versatile pickering emulsion gel lubricants stabilized by cooperative interfacial graphene oxide-polymer assemblies. Mater. Horiz. 11, 3298–3306 (2024).
Kuang, X. et al. Advances in 4D printing: materials and applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1805290 (2019).
Ding, Z. et al. Direct 4D printing via active composite materials. Sci. Adv. 3, e1602890 (2017).
Lee, S. C., Gillispie, G., Prim, P. & Lee, S. J. Physical and chemical factors influencing the printability of hydrogel-based extrusion bioinks. Chemical reviews 120, 10834–10886 (2020).
Jeon, O. et al. Stem cell-laden hydrogel bioink for generation of high resolution and fidelity engineered tissues with complex geometries. Bioact. Mater. 15, 185–193 (2022).
Farsheed, A. C., Thomas, A. J., Pogostin, B. H. & Hartgerink, J. D. 3D printing of self-assembling nanofibrous multidomain peptide hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 35, 2210378 (2023).
Ribeiro, A. et al. Assessing bioink shape fidelity to aid material development in 3D bioprinting. Biofabrication 10, 014102 (2017).
Hu, L., Yang, Y., Hao, J. & Xu, L. Dual-driven mechanically and tribologically adaptive hydrogels solely constituted of graphene oxide and water. Nano Lett 22, 6004–6009 (2022).
Phillips, B. T. et al. Additive manufacturing aboard a moving vessel at sea using passively stabilized stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing. Addit. Manuf. 31, 100969 (2020).
Griffiths, R. J., Gotawala, N., Hahn, G. D., Garcia, D. & Yu, H. Z. Towards underwater additive manufacturing via additive friction stir deposition. Mater. Design 223, 111148 (2022).
Jiang, P. et al. Growing hydrogel organ mannequins with interconnected cavity structures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2108845 (2022).
Liu, D. et al. Tough, transparent, and slippery PVA hydrogel led by syneresis. Small 19, 2206819 (2023).
Hu, L. et al. Highly lubricative, self-healing, chemically degradable, anti-flaming and anti-irradiating magnetic gels simply prepared from binary mixtures of Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles and water. J. Mater. Chem. A 12, 7549–7563 (2024).
Liang, H., Bu, Y., Zhang, J., Cao, Z. & Liang, A. Graphene oxide film as solid lubricant. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 6369–6375 (2013).
Yang, Y. et al. Hydrogels totally from inorganic nanosheets and water with mechanical robustness, self-healing, controlled lubrication and anti-corrosion. Nano Res. 16, 1533–1544 (2023).
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22202220&22202221), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2022QB190), the Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (E3290201) and the Program of Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (E0SX0282).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L. X. and J. H. supervised the research. B. X., Y. Y., and W. Y. conducted the sample preparation and characterization. B. X. and Y. Z. performed the tribological measurements. L.X. drafted the paper. L. X. and Y. Y. commented and revised the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Communications Materials thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, B., Yang, Y., Yang, Y. et al. 4D Printing of polyoxometalate hydrogels from centrifuged inks for semi-solid lubricants. Commun Mater (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43246-026-01075-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43246-026-01075-3