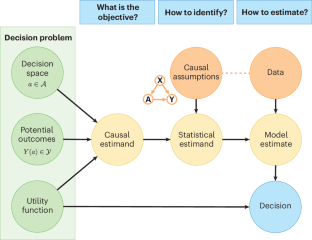
Decision-making inherently involves cause–effect relationships that introduce causal challenges. We argue that reliable algorithms for decision-making need to build upon causal reasoning. Addressing these causal challenges requires explicit assumptions about the underlying causal structure to ensure identifiability and estimatability, which means that the computational methods must successfully align with decision-making objectives in real-world tasks.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
References
Corbett-Davies, S., Pierson, E., Feller, A., Goel, S. & Huq, A. Algorithmic decision making and the cost of fairness. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 797–806 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2017).
Dulac-Arnold, G. et al. Mach. Learn. 110, 2419–2468 (2021).
Obermeyer, Z., Powers, B., Vogeli, C. & Mullainathan, S. Science 366, 447–453 (2019).
Pearl, J. Causality: Models, Reasoning, and Inference (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2009).
Feuerriegel, S. et al. Nat. Med. 30, 958–968 (2024).
Manski, C. F. Identification for Prediction and Decision (Harvard Univ. Press, 2009).
Dawid, P. J. Causal Inference 9, 39–77 (2021).
Coston, C., Mishler, A., Kennedy, E. H. & Chouldechova, A. Counterfactual risk assessments, evaluation, and fairness. In Proceedings of the Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (FAT*), 582–593 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2020).
Kleinberg, J., Ludwig, J., Mullainathan, S. & Obermeyer, Z. Am. Econ. Rev. 105, 491–495 (2015).
Heaven, W. D. The complex math of counterfactuals could help Spotify pick your next favorite song. MIT Technology Review (4 April 2023).
Bareinboim, E. & Pearl, J. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artificial Intelligence 26, 698–704 (2021).
Kallus, N. & Zhou, A. Confounding-robust policy improvement. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 31 (NeurIPS) (eds Bengio, S. et al.) (Curran Associates, Inc., 2018).
Richens, J. & Everitt, T. Robust agents learn causal world models. In The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2024).
Perdomo, J., Zrnic, T., Mendler-Dünner, C. & Hardt, M. Performative prediction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (eds Daumé, H. III & Singh, A.) 7599–7609 (PMLR, 2020).
Gamella, J. L., Peters, J. & Bühlmann, P. Nat. Mach. Intell. 7, 107–118 (2025).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the DAAD program Konrad Zuse Schools of Excellence in Artificial Intelligence, sponsored by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and writing (original draft): C.K., U.F.-A., S.F.; writing (original draft): J.S., D.F.; supervision and writing (reviewing and editing): R.G., M.v.d.S., F.K.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Computational Science thanks Stefan Lessmann and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kern, C., Fischer-Abaigar, U., Schweisthal, J. et al. Algorithms for reliable decision-making need causal reasoning. Nat Comput Sci 5, 356–360 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43588-025-00814-9
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43588-025-00814-9
