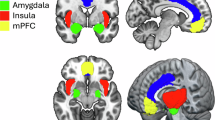
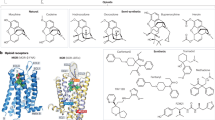
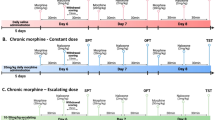
Abstract
Despite the unprecedented toll of the opioid epidemic in the United States, the neurobehavioural features of opioid use disorder remain substantially understudied. Impulsivity has a central role in substance use disorders, but might not be as prominent in opioid addiction. Impulsivity has multiple dimensions, related to stability and change (trait versus state) and emotion (emotion elicited versus emotion neutral). In this Review, we suggest that trait and state impulsivity in opioid use disorder is primarily emotion elicited and mediated by negative reinforcement mechanisms that aim to relieve opioid users from acute or protracted opioid withdrawal or chronic negative affective states (for example, physical or emotional pain). Indeed, negative reinforcement mechanisms are involved in all stages of the opioid addiction cycle and are more heavily implicated in opioid use than in other substance use. Moreover, we identify that impulsive behaviour in opioid use disorder frequently occurs in the context of negative affectivity manifested as a personality trait (such as negative urgency) or a personality disorder (such as psychopathy), which are less common in other substance use disorders. Further examination of these mechanisms will deepen current knowledge of the neurobehavioural underpinnings of opioid addiction and improve clinical treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$59.00 per year
only $4.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moeller, F. G., Barratt, E. S., Dougherty, D. M., Schmitz, J. M. & Swann, A. C. Psychiatric aspects of impulsivity. Am. J. Psychiatry 158, 1783–1793 (2001).
Conrod, P. J. & Nikolaou, K. Annual research review: on the developmental neuropsychology of substance use disorders. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 57, 371–394 (2016).
de Wit, H. Impulsivity as a determinant and consequence of drug use: a review of underlying processes. Addict. Biol. 14, 22–31 (2009). This seminal paper discusses the bidirectional role of impulsivity in substance use disorders.
Kreek, M. J., Nielsen, D. A., Butelman, E. R. & LaForge, K. S. Genetic influences on impulsivity, risk taking, stress responsivity and vulnerability to drug abuse and addiction. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1450–1457 (2005).
Verdejo-Garcia, A. & Albein-Urios, N. Impulsivity traits and neurocognitive mechanisms conferring vulnerability to substance use disorders. Neuropharmacology 183, 108402 (2021). This review identifies distinct personality and neurocognitive dimensions of impulsivity as robust and common predictors of addiction vulnerability.
Bickel, W. K. Discounting of delayed rewards as an endophenotype. Biol. Psychiatry 77, 846–847 (2015).
MacKillop, J. Integrating behavioral economics and behavioral genetics: delayed reward discounting as an endophenotype for addictive disorders. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 99, 14–31 (2013).
Vassileva, J. & Conrod, P. J. Impulsivities and addictions: a multidimensional integrative framework informing assessment and interventions for substance use disorders. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 374, 20180137 (2019). This review outlines a hierarchical framework as a key target for prevention and treatment strategies.
Bari, A. & Robbins, T. W. Inhibition and impulsivity: behavioral and neural basis of response control. Prog. Neurobiol. 108, 44–79 (2013).
Dalley, J. W., Everitt, B. J. & Robbins, T. W. Impulsivity, compulsivity, and top-down cognitive control. Neuron 69, 680–694 (2011).
Evenden, J. L. Varieties of impulsivity. Psychopharmacology 146, 348–361 (1999).
Hamilton, K. R. et al. Rapid-response impulsivity: definitions, measurement issues, and clinical implications. Personal. Disord. 6, 168–181 (2015).
Hamilton, K. R. et al. Choice impulsivity: definitions, measurement issues, and clinical implications. Personal. Disord. 6, 182–198 (2015).
Tolomeo, S., Davey, F., Steele, J. D. & Baldacchino, A. Compulsivity and impulsivity in opioid dependence. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 229, 109018 (2021). This study describes compulsivity and impulsivity as fundamental neurocognitive components of opioid dependence that vary across treatment stages.
Koob, G. F. & Le Moal, M. Drug abuse: hedonic homeostatic dysregulation. Science 278, 52–58 (1997). This seminal paper introduces the three-stage model of addiction, including the changes in neurotransmitter systems and stress-response neuroadaptations caused by chronic drug use that lead to reward dysregulation.
Koob, G. F. & Volkow, N. D. Neurobiology of addiction: a neurocircuitry analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 3, 760–773 (2016).
Kwako, L. E., Momenan, R., Litten, R. Z., Koob, G. F. & Goldman, D. Addictions neuroclinical assessment: a neuroscience-based framework for addictive disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 80, 179–189 (2016). This seminal paper introduces the Addictions Neuroclinical Assessment framework that supports studying incentive salience, negative emotionality and executive function to enhance understanding of addictions.
Insel, T. et al. Research domain criteria (RDoC): toward a new classification framework for research on mental disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 167, 748–751 (2010).
Kwako, L. E. et al. Neurofunctional domains derived from deep behavioral phenotyping in alcohol use disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 176, 744–753 (2019).
Nieto, S. J. & Ray, L. A. Applying the Addictions Neuroclinical Assessment to derive neurofunctional domains in individuals who use methamphetamine. Behav. Brain Res. 427, 113876 (2022).
Koob, G. F. Neurobiology of opioid addiction: opponent process, hyperkatifeia, and negative reinforcement. Biol. Psychiatry 87, 44–53 (2020). This paper describes how opioids disrupt reward pathways and activate stress systems, with hyperkatifeia driving compulsion and relapse through negative reinforcement.
Wise, R. A. & Koob, G. F. The development and maintenance of drug addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 39, 254–262 (2014).
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results from the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. HHS Publication No. PEP23-07-01-006, NSDUH Series H-58 (US Department of Health and Human Services, 2023).
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. The NSDUH Report. (US Department of Health and Human Services, 2022).
Badiani, A., Belin, D., Epstein, D., Calu, D. & Shaham, Y. Opiate versus psychostimulant addiction: the differences do matter. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 12, 685–700 (2011). This landmark paper challenges the unitary concept of addiction by differentiating the behavioural and neurobiological factors of opioid and stimulant addictions.
Mahu, I. T., Barrett, S. P., Conrod, P. J., Bartel, S. J. & Stewart, S. H. Different drugs come with different motives: examining motives for substance use among people who engage in polysubstance use undergoing methadone maintenance therapy (MMT). Drug Alcohol Depend. 229, 109133 (2021).
Tsai, B. NCHS: a blog of the National Center for Health Statistics. Center for Disease Control and Prevention https://blogs.cdc.gov/nchs/2024/05/15/7623/ (2024).
Koob, G. F. The dark side of emotion: the addiction perspective. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 753, 73–87 (2015).
Koob, G. F. The dark side of addiction: the Horsley Gantt to Joseph Brady connection. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 205, 270–272 (2017). This seminal paper introduces the ‘dark side of addiction model’ in which negative reinforcement mechanisms reflect progressive reward dysregulation and overactivation of brain stress systems.
MacKillop, J. et al. The latent structure of impulsivity: impulsive choice, impulsive action, and impulsive personality traits. Psychopharmacology 233, 3361–3370 (2016). This paper defines impulsivity through three distinct latent dimensions: impulsive choice, impulsive action and impulsive personality traits.
Sharma, L., Markon, K. E. & Clark, L. A. Toward a theory of distinct types of ‘impulsive’ behaviors: a meta-analysis of self-report and behavioral measures. Psychol. Bull. 140, 374–408 (2014).
Gullo, M. J., Loxton, N. J. & Dawe, S. Impulsivity: four ways five factors are not basic to addiction. Addict. Behav. 39, 1547–1556 (2014).
Leshem, R. Using dual process models to examine impulsivity throughout neural maturation. Dev. Neuropsychol. 41, 125–143 (2016).
Wilson, M. J. & Vassileva, J. Neurocognitive and psychiatric dimensions of hot, but not cool, impulsivity predict HIV sexual risk behaviors among drug users in protracted abstinence. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 42, 231–241 (2016).
Salehinejad, M. A., Ghanavati, E., Rashid, M. H. A. & Nitsche, M. A. Hot and cold executive functions in the brain: a prefrontal-cingular network. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 5, 23982128211007769 (2021).
Mischel, W. The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-Control (Little, Brown Spark, 2014).
Friedman, N. P. & Robbins, T. W. The role of prefrontal cortex in cognitive control and executive function. Neuropsychopharmacology 47, 72–89 (2022).
Leshem, R. & King, R. Trait impulsivity and callous-unemotional traits as predictors of inhibitory control and risky choices among high-risk adolescents. Int. J. Psychol. 56, 314–321 (2021).
Lynam, D. R., Smith, G. T., Whiteside, S. P. & Cyders, M. A. The UPPS-P: assessing five personality pathways to impulsive behavior. Purdue University (2006).
Patton, J. H., Stanford, M. S. & Barratt, E. S. Factor structure of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale. J. Clin. Psychol. 51, 768–774 (1995).
Leshem, R. & Yefet, M. Does impulsivity converge distinctively with inhibitory control? Disentangling the cold and hot aspects of inhibitory control. Pers. Individ. Differ. 145, 44–51 (2019).
Hung, Y., Gaillard, S. L., Yarmak, P. & Arsalidou, M. Dissociations of cognitive inhibition, response inhibition, and emotional interference: voxelwise ALE meta-analyses of fMRI studies. Hum. Brain Mapp. 39, 4065–4082 (2018).
Song, S. et al. The influence of emotional interference on cognitive control: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies using the emotional Stroop task. Sci. Rep. 7, 2088 (2017).
Spielberger, C. D., Gorsuch, R. L., Lushene, R., Vagg, P. R. & Jacobs, G. A. Manual for the State–Trait Anxiety Inventory (Consulting Psychologists, 1983).
Spielberger, C. D. State–Trait Anger Expression Inventory: Professional Manual (Psychological Assessment Resources, 1988).
McCrae, R. R. & Costa, P. T. Trait explanations in personality psychology. Eur. J. Personality 9, 231–252 (1995).
Odum, A. L. & Baumann, A. A. L. in Impulsivity: The Behavioral and Neurological Science of Discounting (eds Madden, G. J. & Bickel, W. K.) 39–65 (American Psychological Association, 2010).
Cloninger, C. R. A systematic method for clinical description and classification of personality variants. A proposal. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 44, 573–588 (1987).
Eysenck, S. B. G. & Eysenck, H. J. Impulsiveness and venturesomeness: their position in a dimensional system of personality description. Psychol. Rep. 43, 1247–1255 (1978).
Gray, J. A. The Neuropsychology of Anxiety: An Enquiry into the Functions of the Septo-Hippocampal System. (Clarendon Press/Oxford Univ. Press, 1982).
McCrae, R. R. & Costa Jr, P. T. in Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research 2nd edn. 139–153 (Guilford Press, 1999).
Zuckerman, M. The psychobiological model for impulsive unsocialized sensation seeking: a comparative approach. Neuropsychobiology 34, 125–129 (1996).
Hyatt, C. S. et al. Personality traits share overlapping neuroanatomical correlates with internalizing and externalizing psychopathology. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 128, 1–11 (2019).
Bickel, W. K. et al. Excessive discounting of delayed reinforcers as a trans-disease process: update on the state of the science. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 30, 59–64 (2019). This review supports delay discounting as a fundamental trans-disease process and endophenotype, and discusses interventions targeting delay discounting.
McTeague, L. M., Goodkind, M. S. & Etkin, A. Transdiagnostic impairment of cognitive control in mental illness. J. Psychiatr. Res. 83, 37–46 (2016).
Verdejo-Garcia, A., Lawrence, A. J. & Clark, L. Impulsivity as a vulnerability marker for substance-use disorders: review of findings from high-risk research, problem gamblers and genetic association studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 32, 777–810 (2008).
Um, M., Hershberger, A. R., Whitt, Z. T. & Cyders, M. A. Recommendations for applying a multi-dimensional model of impulsive personality to diagnosis and treatment. Borderline Personal. Disord. Emot. Dysregul. 5, 6 (2018).
Barratt, E. S. in The Impulsive Client: Theory, Research, and Treatment. (eds Johnson, J. L., McCown, W. G. & Shure, M. B.) 39–56 (American Psychological Association, 1993).
Qin, S., Hermans, E. J., van Marle, H. J., Luo, J. & Fernández, G. Acute psychological stress reduces working memory-related activity in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Biol. Psychiatry 66, 25–32 (2009).
Zhou, L., Yang, Y. & Li, S. Music-induced emotions influence intertemporal decision making. Cogn. Emot. 36, 211–229 (2022).
Voon, V. & Dalley, J. W. Translatable and back-translatable measurement of impulsivity and compulsivity: convergent and divergent processes. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 28, 53–91 (2016).
Dalley, J. W. & Robbins, T. W. Fractionating impulsivity: neuropsychiatric implications. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 18, 158–171 (2017).
Bartra, O., McGuire, J. T. & Kable, J. W. The valuation system: a coordinate-based meta-analysis of BOLD fMRI experiments examining neural correlates of subjective value. Neuroimage 76, 412–427 (2013).
Gola, M. et al. Can pornography be addictive? An fMRI study of men seeking treatment for problematic pornography use. Neuropsychopharmacology 42, 2021–2031 (2017).
Zheng, L., Miao, M. & Gan, Y. A systematic and meta-analytic review on the neural correlates of viewing high- and low-calorie foods among normal-weight adults. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 138, 104721 (2022).
Aron, A. R., Robbins, T. W. & Poldrack, R. A. Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex: one decade on. Trends Cogn. Sci. 18, 177–185 (2014).
Ridderinkhof, K. R., Ullsperger, M., Crone, E. A. & Nieuwenhuis, S. The role of the medial frontal cortex in cognitive control. Science 306, 443–447 (2004).
Peters, S. K., Dunlop, K. & Downar, J. Cortico–striatal–thalamic loop circuits of the salience network: a central pathway in psychiatric disease and treatment. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 10, 104 (2016).
Kable, J. W. & Glimcher, P. W. The neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 1625–1633 (2007).
McClure, S. M., Laibson, D. I., Loewenstein, G. & Cohen, J. D. Separate neural systems value immediate and delayed monetary rewards. Science 306, 503–507 (2004).
Halvorson, M. A. et al. Impulsive states and impulsive traits: a study of the multilevel structure and validity of a multifaceted measure of impulsive states. Assessment 28, 796–812 (2021).
Tomko, R. L. et al. Measuring impulsivity in daily life: the momentary impulsivity scale. Psychol. Assess. 26, 339–349 (2014).
Nguyen, R., Brooks, M., Bruno, R. & Peacock, A. Behavioral measures of state impulsivity and their psychometric properties: a systematic review. Pers. Individ. Differ. 135, 67–79 (2018).
Yip, S. W. et al. From computation to clinic. Biol. Psychiatry Glob. Open Sci. 3, 319–328 (2023).
Vassileva, J., Lee, J.-H., Psederska, E. & Ahn, W.-Y. in Computational Neuroscience (eds Stoyanov, D., Draganski, B., Brambilla, P. & Lamm, C.) 211–231 (Springer, 2023).
Ahn, W. Y. et al. Decision-making in stimulant and opiate addicts in protracted abstinence: evidence from computational modeling with pure users. Front. Psychol. 5, 849 (2014).
Konova, A. B. et al. Computational markers of risky decision-making for identification of temporal windows of vulnerability to opioid use in a real-world clinical setting. JAMA Psychiatry 77, 368–377 (2020). This article supports computational approaches to uncover cognitive factors that predict vulnerability to opioid reuse and offers insights for clinical applications.
Kvam, P. D., Romeu, R. J., Turner, B. M., Vassileva, J. & Busemeyer, J. R. Testing the factor structure underlying behavior using joint cognitive models: impulsivity in delay discounting and Cambridge gambling tasks. Psychol. Methods 26, 18–37 (2021).
Alvarez, E. E., Hafezi, S., Bonagura, D., Kleiman, E. M. & Konova, A. B. A proof-of-concept ecological momentary assessment study of day-level dynamics in value-based decision-making in opioid addiction. Front. Psychiatry 13, 817979 (2022).
Enkavi, A. Z. & Poldrack, R. A. Implications of the lacking relationship between cognitive task and self-report measures for psychiatry. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 6, 670–672 (2021).
Hedge, C., Powell, G. & Sumner, P. The reliability paradox: why robust cognitive tasks do not produce reliable individual differences. Behav. Res. Methods 50, 1166–1186 (2018).
Kim, T., Kim, S., Kang, J., Kwon, M. & Lee, S. H. The common effects of sleep deprivation on human long-term memory and cognitive control processes. Front. Neurosci. 16, 883848 (2022).
Parmentier, F. B. The cognitive determinants of behavioral distraction by deviant auditory stimuli: a review. Psychol. Res. 78, 321–338 (2014).
Moriarty, O., McGuire, B. E. & Finn, D. P. The effect of pain on cognitive function: a review of clinical and preclinical research. Prog. Neurobiol. 93, 385–404 (2011).
Odum, A. L. et al. Delay discounting of different outcomes: review and theory. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 113, 657–679 (2020).
Mischel, W. & Shoda, Y. A cognitive-affective system theory of personality: reconceptualizing situations, dispositions, dynamics, and invariance in personality structure. Psychol. Rev. 102, 246–268 (1995).
Mischel, W., Shoda, Y. & Mendoza-Denton, R. Situation–behavior profiles as a locus of consistency in personality. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 11, 50–54 (2002).
Whiteside, S. P. & Lynam, D. R. The Five Factor Model and impulsivity: using a structural model of personality to understand impulsivity. Pers. Individ. Differ. 30, 669–689 (2001).
Joseph, J. E., Liu, X., Jiang, Y., Lynam, D. & Kelly, T. H. Neural correlates of emotional reactivity in sensation seeking. Psychol. Sci. 20, 215–223 (2009).
Cyders, M. A. & Coskunpinar, A. Measurement of constructs using self-report and behavioral lab tasks: is there overlap in nomothetic span and construct representation for impulsivity? Clin. Psychol. Rev. 31, 965–982 (2011). This work underscores that self-report and behavioural measures of impulsivity capture distinct underlying constructs.
Friedman, N. P. & Gustavson, D. E. Do rating and task measures of control abilities assess the same thing? Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 31, 262–271 (2022).
Clark, S. L., Gillespie, N. A., Adkins, D. E., Kendler, K. S. & Neale, M. C. Psychometric modeling of abuse and dependence symptoms across six illicit substances indicates novel dimensions of misuse. Addict. Behav. 53, 132–140 (2016).
Kendler, K. S., Jacobson, K. C., Prescott, C. A. & Neale, M. C. Specificity of genetic and environmental risk factors for use and abuse/dependence of cannabis, cocaine, hallucinogens, sedatives, stimulants, and opiates in male twins. Am. J. Psychiatry 160, 687–695 (2003).
Tsuang, M. T. et al. Co-occurrence of abuse of different drugs in men: the role of drug-specific and shared vulnerabilities. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 55, 967–972 (1998).
Ahn, W. Y. & Vassileva, J. Machine-learning identifies substance-specific behavioral markers for opiate and stimulant dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 161, 247–257 (2016).
Bjork, J. M. et al. Social information processing in substance use disorders: insights from an emotional go–nogo task. Front. Psychiatry 12, 672488 (2021).
Bjork, J. M. et al. Attentional function and inhibitory control in different substance use disorders. Psychiatry Res. 313, 114591 (2022).
Fernandez-Serrano, M. J., Perez-Garcia, M. & Verdejo-Garcia, A. What are the specific vs. generalized effects of drugs of abuse on neuropsychological performance? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 35, 377–406 (2011).
Vassileva, J. et al. Heroin and amphetamine users display opposite relationships between trait and neurobehavioral dimensions of impulsivity. Addict. Behav. 39, 652–659 (2014).
Verdejo-Garcia, A. & Perez-Garcia, M. Profile of executive deficits in cocaine and heroin polysubstance users: common and differential effects on separate executive components. Psychopharmacology 190, 517–530 (2007).
Verdejo-Garcia, A. J., Perales, J. C. & Perez-Garcia, M. Cognitive impulsivity in cocaine and heroin polysubstance abusers. Addict. Behav. 32, 950–966 (2007).
Garami, J. et al. Intolerance of uncertainty in opioid dependency—relationship with trait anxiety and impulsivity. PLoS ONE 12, e0181955 (2017).
Ghosh, A. et al. Risk, reversibility and resilience of brain circuitries linked to opioid dependence: a diffusion tensor imaging study of actively opioid-using subjects and three comparison groups. Asian J. Psychiatry 40, 107–115 (2019).
Yang, W. et al. Novel circuit biomarker of impulsivity and craving in male heroin-dependent individuals. Drug Alcohol Depend. 219, 108485 (2021).
Nielsen, D. A. et al. Former heroin addicts with or without a history of cocaine dependence are more impulsive than controls. Drug Alcohol Depend. 124, 113–120 (2012).
Clark, L., Robbins, T. W., Ersche, K. D. & Sahakian, B. J. Reflection impulsivity in current and former substance users. Biol. Psychiatry 60, 515–522 (2006).
Ersche, K. D. et al. Abnormal frontal activations related to decision-making in current and former amphetamine and opiate dependent individuals. Psychopharmacology 180, 612–623 (2005).
Rodriguez-Cintas, L. et al. Impulsivity and addiction severity in cocaine and opioid dependent patients. Addict. Behav. 58, 104–109 (2016).
Lejuez, C. W., Bornovalova, M. A., Daughters, S. B. & Curtin, J. J. Differences in impulsivity and sexual risk behavior among inner-city crack/cocaine users and heroin users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 77, 169–175 (2005).
Mohammadzadeh, A., Khosravani, V. & Feizi, R. The comparison of impulsivity and craving in stimulant-dependent, opiate-dependent and normal individuals. J. Substance Use 23, 312–317 (2018).
Peters, L. & Soyka, M. Interrelationship of opioid dependence, impaired impulse control, and depressive symptoms: an open-label cross-sectional study of patients in maintenance therapy. Neuropsychobiology 77, 73–82 (2019).
Bozkurt, M., Evren, C., Yilmaz, A., Can, Y. & Cetingok, S. Aggression and impulsivity in different groups of alcohol and heroin dependent inpatient men. Bull. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 23, 335–344 (2013).
Hettie, G. et al. Lack of premeditation predicts aberrant behaviors related to prescription opioids in patients with chronic pain: a cross-sectional study. Subst. Use Misuse 56, 1904–1909 (2021).
Loree, A. M., Lundahl, L. H. & Ledgerwood, D. M. Impulsivity as a predictor of treatment outcome in substance use disorders: review and synthesis. Drug Alcohol Rev. 34, 119–134 (2015).
Grall-Bronnec, M. et al. Prevalence of coaddictions and rate of successful treatment among a french sample of opioid-dependent patients with long-term opioid substitution therapy: the OPAL study. Front. Psychiatry 10, 726 (2019).
Moshier, S. J., Ewen, M. & Otto, M. W. Impulsivity as a moderator of the intention–behavior relationship for illicit drug use in patients undergoing treatment. Addict. Behav. 38, 1651–1655 (2013).
Woicik, P. A., Stewart, S. H., Pihl, R. O. & Conrod, P. J. The substance use risk profile scale: a scale measuring traits linked to reinforcement-specific substance use profiles. Addict. Behav. 34, 1042–1055 (2009).
Ferguson, E. et al. CANUE: a theoretical model of pain as an antecedent for substance use. Ann. Behav. Med. 55, 489–502 (2021). This article discusses the ‘catastrophizing, anxiety, negative urgency and expectancy’ model that links pain-related risk factors to substance use.
Goncalves, S. F. et al. Negative urgency linked to craving and substance use among adults on buprenorphine or methadone. J. Behav. Health Serv. Res. 51, 114–122 (2024).
Li, J. et al. Impulsivity and craving in subjects with opioid use disorder on methadone maintenance treatment. Drug Alcohol Depend. 219, 108483 (2021).
Fishbein, D. H. et al. Neurocognitive characterizations of Russian heroin addicts without a significant history of other drug use. Drug Alcohol Depend. 90, 25–38 (2007).
Lee, R. S. C., Hoppenbrouwers, S. & Franken, I. A systematic meta-review of impulsivity and compulsivity in addictive behaviors. Neuropsychol. Rev. 29, 14–26 (2019). This is the first systematic review of neurocognitive literature examining specific impairments in impulsive–compulsive domains across the addiction spectrum.
Baldacchino, A., Balfour, D. J., Passetti, F., Humphris, G. & Matthews, K. Neuropsychological consequences of chronic opioid use: a quantitative review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 36, 2056–2068 (2012). This meta-analytic study discusses the most robust neurocognitive deficits observed in opioid users.
Biernacki, K., McLennan, S. N., Terrett, G., Labuschagne, I. & Rendell, P. G. Decision-making ability in current and past users of opiates: a meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 71, 342–351 (2016).
Mintzer, M. Z. & Stitzer, M. L. Cognitive impairment in methadone maintenance patients. Drug Alcohol Depend. 67, 41–51 (2002).
Forman, S. D. et al. Opiate addicts lack error-dependent activation of rostral anterior cingulate. Biol. Psychiatry 55, 531–537 (2004).
Fu, L. P. et al. Impaired response inhibition function in abstinent heroin dependents: an fMRI study. Neurosci. Lett. 438, 322–326 (2008).
Psederska, E. & Vassileva, J. Neurocognitive impulsivity in opiate users at different lengths of abstinence. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 20, 1236 (2023).
Lee, T. M. et al. Neural activity associated with cognitive regulation in heroin users: a fMRI study. Neurosci. Lett. 382, 211–216 (2005).
Morie, K. P. et al. Intact inhibitory control processes in abstinent drug abusers (II): a high-density electrical mapping study in former cocaine and heroin addicts. Neuropharmacology 82, 151–160 (2014).
Yang, B. et al. Event-related potentials in a Go/Nogo task of abnormal response inhibition in heroin addicts. Sci. China C 52, 780–788 (2009).
Yucel, M. et al. A combined spectroscopic and functional MRI investigation of the dorsal anterior cingulate region in opiate addiction. Mol. Psychiatry 12, 691–702 (2007).
Su, H. et al. Effect of automatic emotional processing on response inhibition among heroin abstainers. Psych. J. 11, 913–921 (2022).
Smith, J. L., Mattick, R. P., Jamadar, S. D. & Iredale, J. M. Deficits in behavioural inhibition in substance abuse and addiction: a meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend. 145, 1–33 (2014).
Verbruggen, F. & Logan, G. D. Automatic and controlled response inhibition: associative learning in the go/no-go and stop-signal paradigms. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 137, 649–672 (2008).
Littman, R. & Takacs, A. Do all inhibitions act alike? A study of go/no-go and stop-signal paradigms. PLoS ONE 12, e0186774 (2017).
Raud, L., Westerhausen, R., Dooley, N. & Huster, R. J. Differences in unity: the go/no-go and stop signal tasks rely on different mechanisms. Neuroimage 210, 116582 (2020).
Garland, E. L. & Howard, M. O. Prescription opioid misusers exhibit blunted parasympathetic regulation during inhibitory control challenge. Psychopharmacology 238, 765–774 (2021).
Li, X. et al. Decision-making deficits are still present in heroin abusers after short- to long-term abstinence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 130, 61–67 (2013).
Pirastu, R. et al. Impaired decision-making in opiate-dependent subjects: effect of pharmacological therapies. Drug Alcohol Depend. 83, 163–168 (2006).
Seeliger, C., Lippold, J. V. & Reuter, M. Variation on the CRH gene determines the different performance of opioid addicts and healthy controls in the Iowa gambling task. Neuropsychobiology 79, 150–160 (2020).
Sun, Y. et al. Disrupted white matter structural connectivity in heroin abusers. Addict. Biol. 22, 184–195 (2017).
Yan, W. S. et al. Working memory and affective decision-making in addiction: a neurocognitive comparison between heroin addicts, pathological gamblers and healthy controls. Drug Alcohol Depend. 134, 194–200 (2014).
Rogers, R. D. et al. Dissociable deficits in the decision-making cognition of chronic amphetamine abusers, opiate abusers, patients with focal damage to prefrontal cortex, and tryptophan-depleted normal volunteers: evidence for monoaminergic mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 20, 322–339 (1999).
Kriegler, J. et al. Decision making of individuals with heroin addiction receiving opioid maintenance treatment compared to early abstinent users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 205, 107593 (2019).
Tolomeo, S., Gray, S., Matthews, K., Steele, J. D. & Baldacchino, A. Multifaceted impairments in impulsivity and brain structural abnormalities in opioid dependence and abstinence. Psychol. Med. 46, 2841–2853 (2016).
Zhang, X. L. et al. Effects of stress on decision-making deficits in formerly heroin-dependent patients after different durations of abstinence. Am. J. Psychiatry 168, 610–616 (2011).
Baldacchino, A., Balfour, D. J. & Matthews, K. Impulsivity and opioid drugs: differential effects of heroin, methadone and prescribed analgesic medication. Psychol. Med. 45, 1167–1179 (2015).
Kirby, K. N., Petry, N. M. & Bickel, W. K. Heroin addicts have higher discount rates for delayed rewards than non-drug-using controls. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 128, 78–87 (1999).
Kirby, K. N. & Petry, N. M. Heroin and cocaine abusers have higher discount rates for delayed rewards than alcoholics or non-drug-using controls. Addiction 99, 461–471 (2004).
Karakula, S. L. et al. Delay discounting in opioid use disorder: differences between heroin and prescription opioid users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 169, 68–72 (2016).
Robles, E., Huang, B. E., Simpson, P. M. & McMillan, D. E. Delay discounting, impulsiveness, and addiction severity in opioid-dependent patients. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 41, 354–362 (2011).
Garami, J. & Moustafa, A. A. Probability discounting of monetary gains and losses in opioid-dependent adults. Behav. Brain Res. 364, 334–339 (2019).
Yang, L., Liu, W. & Wang, J. The hidden-zero effect in male individuals with opioid use disorder. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 49, 530–539 (2023).
Kluwe-Schiavon, B. et al. Substance related disorders are associated with impaired valuation of delayed gratification and feedback processing: a multilevel meta-analysis and meta-regression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 108, 295–307 (2020).
Bornovalova, M. A., Daughters, S. B., Hernandez, G. D., Richards, J. B. & Lejuez, C. W. Differences in impulsivity and risk-taking propensity between primary users of crack cocaine and primary users of heroin in a residential substance-use program. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 13, 311–318 (2005).
Barry, D. & Petry, N. M. Predictors of decision-making on the Iowa Gambling Task: independent effects of lifetime history of substance use disorders and performance on the Trail Making Test. Brain Cogn. 66, 243–252 (2008).
Krain, A. L., Wilson, A. M., Arbuckle, R., Castellanos, F. X. & Milham, M. P. Distinct neural mechanisms of risk and ambiguity: a meta-analysis of decision-making. Neuroimage 32, 477–484 (2006).
Moro, A. S. et al. Neural correlates of delay discounting in the light of brain imaging and non-invasive brain stimulation: what we know and what is missed. Brain Sci. 13, 403 (2023).
Biernacki, K. et al. A neuroeconomic signature of opioid craving: how fluctuations in craving bias drug-related and nondrug-related value. Neuropsychopharmacology 47, 1440–1448 (2022).
Passetti, F., Clark, L., Mehta, M. A., Joyce, E. & King, M. Neuropsychological predictors of clinical outcome in opiate addiction. Drug Alcohol Depend. 94, 82–91 (2008).
Passetti, F. et al. Risky decision-making predicts short-term outcome of community but not residential treatment for opiate addiction. Implications for case management. Drug Alcohol Depend. 118, 12–18 (2011).
Cyders, M. A. & Smith, G. T. Emotion-based dispositions to rash action: positive and negative urgency. Psychol. Bull. 134, 807–828 (2008).
Cyders, M. A. & Smith, G. T. Mood-based rash action and its components: positive and negative urgency. Pers. Individ. Differ. 43, 839–850 (2007).
Chester, D. S. et al. How do negative emotions impair self-control? A neural model of negative urgency. Neuroimage 132, 43–50 (2016).
Guller, L., Zapolski, T. C. & Smith, G. T. Personality measured in elementary school predicts middle school addictive behavior involvement. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 37, 523–532 (2015).
Kaiser, A. J., Milich, R., Lynam, D. R. & Charnigo, R. J. Negative urgency, distress tolerance, and substance abuse among college students. Addict. Behav. 37, 1075–1083 (2012).
Zorrilla, E. P. & Koob, G. F. Impulsivity derived from the dark side: neurocircuits that contribute to negative urgency. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 13, 136 (2019). This review elaborates on the mechanisms of the ‘dark side of addiction’ model that links negative urgency and stress-related neurocircuitry to compulsive drug-seeking behaviour.
Peck, K. R., Nighbor, T. D. & Price, M. Examining associations between impulsivity, opioid use disorder, and posttraumatic stress disorder: the additive relation between disorders. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 30, 486–493 (2022).
Vest, N., Reynolds, C. J. & Tragesser, S. L. Impulsivity and risk for prescription opioid misuse in a chronic pain patient sample. Addict. Behav. 60, 184–190 (2016).
Hains, A. B. & Arnsten, A. F. Molecular mechanisms of stress-induced prefrontal cortical impairment: implications for mental illness. Learn. Mem. 15, 551–564 (2008).
van Steenbergen, H., Band, G. P. & Hommel, B. Threat but not arousal narrows attention: evidence from pupil dilation and saccade control. Front. Psychol. 2, 281 (2011).
Otto, A. R., Raio, C. M., Chiang, A., Phelps, E. A. & Daw, N. D. Working-memory capacity protects model-based learning from stress. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 20941–20946 (2013).
Bechara, A. The role of emotion in decision-making: evidence from neurological patients with orbitofrontal damage. Brain Cogn. 55, 30–40 (2004).
Bechara, A. Risky business: emotion, decision-making, and addiction. J. Gambl. Stud. 19, 23–51 (2003). This paper underscores neurocognitive criteria to refine the diagnosis and treatment of addictions.
Verdejo-Garcia, A., Perez-Garcia, M. & Bechara, A. Emotion, decision-making and substance dependence: a somatic-marker model of addiction. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 4, 17–31 (2006).
Chick, C. F. Cooperative versus competitive influences of emotion and cognition on decision making: a primer for psychiatry research. Psychiatry Res. 273, 493–500 (2019).
Torres, A. et al. Emotional and non-emotional pathways to impulsive behavior and addiction. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 7, 43 (2013).
Allen, K. J. D. et al. Validation of an emotional stop-signal task to probe individual differences in emotional response inhibition: relationships with positive and negative urgency. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 5, 23982128211058269 (2021).
Cohen-Gilbert, J. E. et al. College binge drinking associated with decreased frontal activation to negative emotional distractors during inhibitory control. Front. Psychol. 8, 1650 (2017).
Roxburgh, A. D., White, D. J. & Cornwell, B. R. Negative urgency is related to impaired response inhibition during threatening conditions. Acta Psychol. 228, 103648 (2022).
Wilbertz, T. et al. Response inhibition and its relation to multidimensional impulsivity. Neuroimage 103, 241–248 (2014).
De Brito, S. A. et al. Psychopathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 7, 49 (2021).
Hare, R. D. & Neumann, C. S. Psychopathy as a clinical and empirical construct. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 4, 217–246 (2008).
Edens, J. F., Marcus, D. K., Lilienfeld, S. O. & Poythress, N. G. Jr. Psychopathic, not psychopath: taxometric evidence for the dimensional structure of psychopathy. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 115, 131–144 (2006).
Guay, J. P., Ruscio, J., Knight, R. A. & Hare, R. D. A taxometric analysis of the latent structure of psychopathy: evidence for dimensionality. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 116, 701–716 (2007).
Pemment, J. Psychopathy versus sociopathy: why the distinction has become crucial. Aggress. Violent Behav. 18, 458–461 (2013).
Walsh, A. & Wu, H. H. Differentiating antisocial personality disorder, psychopathy, and sociopathy: evolutionary, genetic, neurological, and sociological considerations. Crim. Justice Stud. 21, 135–152 (2008).
Neumann, C. S., Hare, R. D. & Newman, J. P. The super-ordinate nature of the psychopathy checklist–revised. J. Pers. Disord. 21, 102–117 (2007).
Gray, N. S. & Snowden, R. J. Psychopathy in women: prediction of criminality and violence in UK and USA psychiatric patients resident in the community. Psychiatry Res. 237, 339–343 (2016).
Bergstrøm, H. & Farrington, D. P. Psychopathic personality and criminal violence across the life-course in a prospective longitudinal study: does psychopathic personality predict violence when controlling for other risk factors? J. Crim. Justice 80, 101817 (2022).
Thomson, N. D. et al. Which features of psychopathy and impulsivity matter most for prison violence? New evidence among female prisoners. Int. J. Law Psychiatry 64, 26–33 (2019).
Thomson, N. D., Bozgunov, K., Psederska, E. & Vassileva, J. Sex differences on the four-facet model of psychopathy predict physical, verbal, and indirect aggression. Aggress. Behav. 45, 265–274 (2019).
Berger, K., Rotermund, P., Vieth, E. R. & Hohnhorst, A. The prognostic value of the PCL-R in relation to the SUD treatment ending. Int. J. Law Psychiatry 35, 198–201 (2012).
Salekin, R. T., Worley, C. & Grimes, R. D. Treatment of psychopathy: a review and brief introduction to the mental model approach for psychopathy. Behav. Sci. Law 28, 235–266 (2010).
Sewall, L. A. & Olver, M. E. Psychopathy and treatment outcome: results from a sexual violence reduction program. Personal. Disord. 10, 59–69 (2019).
Psederska, E. et al. Effects of psychopathy on neurocognitive domains of impulsivity in abstinent opiate and stimulant users. Front. Psychiatry 12, 660810 (2021).
Hicks, B. M. & Patrick, C. J. Psychopathy and negative emotionality: analyses of suppressor effects reveal distinct relations with emotional distress, fearfulness, and anger-hostility. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 115, 276–287 (2006).
Hyde, L. W., Byrd, A. L., Votruba-Drzal, E., Hariri, A. R. & Manuck, S. B. Amygdala reactivity and negative emotionality: divergent correlates of antisocial personality and psychopathy traits in a community sample. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 123, 214–224 (2014).
Cleckley, H. M. The Mask of Sanity: An Attempt to Reinterpret the So-Called Psychopathic Personality (St. Louis, The C. V. Mosby Company, 1941).
Cima, M. & Raine, A. Distinct characteristics of psychopathy relate to different subtypes of aggression. Pers. Individ. Differ. 47, 835–840 (2009).
Garofalo, C., Neumann, C. S. & Velotti, P. Difficulties in emotion regulation and psychopathic traits in violent offenders. J. Crim. Justice 57, 116–125 (2018).
Garofalo, C., Neumann, C. S. & Velotti, P. Psychopathy and aggression: the role of emotion dysregulation. J. Interpers. Violence 36, NP12640–NP12664 (2021).
Garofalo, C., Neumann, C. S., Kosson, D. S. & Velotti, P. Psychopathy and emotion dysregulation: more than meets the eye. Psychiatry Res. 290, 113160 (2020). This article shows that all dimensions of psychopathy are closely related to compromised emotion regulation.
Burghart, M. & Mier, D. No feelings for me, no feelings for you: a meta-analysis on alexithymia and empathy in psychopathy. Pers. Individ. Differ. 194, 111658 (2022).
Hofmann, M. J., Schneider, S. & Mokros, A. Fearless but anxious? A systematic review on the utility of fear and anxiety levels to classify subtypes of psychopathy. Behav. Sci. Law 39, 512–540 (2021).
Falkenbach, D. M., Stern, S. B. & Creevy, C. Psychopathy variants: empirical evidence supporting a subtyping model in a community sample. Personal. Disord. 5, 10–19 (2014).
Vassileva, J., Kosson, D. S., Abramowitz, C. & Conrod, P. Psychopathy versus psychopathies in classifying criminal offenders. Leg. Criminol. Psychol. 10, 27–43 (2005).
Lander, G. C., Lutz-Zois, C. J., Rye, M. S. & Goodnight, J. A. The differential association between alexithymia and primary versus secondary psychopathy. Pers. Individ. Differ. 52, 45–50 (2012).
Psederska, E., Savov, S., Atanassov, N. & Vassileva, J. Relationships between alexithymia and psychopathy in heroin dependent individuals. Front. Psychol. 10, 2269 (2019).
Anestis, M. D., Anestis, J. C. & Joiner, T. E. Affective considerations in antisocial behavior: an examination of negative urgency in primary and secondary psychopathy. Pers. Individ. Differ. 47, 668–670 (2009).
Gray, N. S., Weidacker, K. & Snowden, R. J. Psychopathy and impulsivity: the relationship of psychopathy to different aspects of UPPS-P impulsivity. Psychiatry Res. 272, 474–482 (2019).
West, S. J. et al. Comparing psychopathy across measurement modalities. Personal. Disord. 14, 274–286 (2023).
Vassileva, J., Shahidi, R., Taylor, B., Moeller, F. G. & Ahn, W. Y. Machine learning identifies common and specific markers of addiction to five different classes of drugs. Biol. Psychiatry 85, S378 (2019).
Khantzian, E. J. The self-medication hypothesis of addictive disorders: focus on heroin and cocaine dependence. Am. J. Psychiatry 142, 1259–1264 (1985).
Thomson, N. D. et al. Substance dependence and aggression: the mediating role of psychopathy. Biol. Psychiatry 87, S444 (2020).
Alterman, A. I., Rutherford, M. J., Cacciola, J. S., McKay, J. R. & Boardman, C. R. Prediction of 7 months methadone maintenance treatment response by four measures of antisociality. Drug Alcohol Depend. 49, 217–223 (1998).
Potik, D., Abramsohn, Y., Schreiber, S., Adelson, M. & Peles, E. Drug abuse and behavioral transgressions during methadone maintenance treatment (MMT) are related to high psychopathy levels. Subst. Use Misuse 55, 460–468 (2020).
Vassileva, J., Georgiev, S., Martin, E., Gonzalez, R. & Segala, L. Psychopathic heroin addicts are not uniformly impaired across neurocognitive domains of impulsivity. Drug Alcohol Depend. 114, 194–200 (2011).
Gudonis, L. C., Derefinko, K. & Giancola, P. R. The treatment of substance misuse in psychopathic individuals: why heterogeneity matters. Subst. Use Misuse 44, 1415–1433 (2009).
Patrick, C. J., Hicks, B. M., Krueger, R. F. & Lang, A. R. Relations between psychopathy facets and externalizing in a criminal offender sample. J. Pers. Disord. 19, 339–356 (2005).
Smith, S. S. & Newman, J. P. Alcohol and drug abuse–dependence disorders in psychopathic and nonpsychopathic criminal offenders. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 99, 430–439 (1990).
Hemphill, J. F. & Hart, S. D. Psychopathy and substance use. J. Pers. Disord. 8, 169–180 (1994).
Long, K., Felton, J. W., Lilienfeld, S. O. & Lejuez, C. W. The role of emotion regulation in the relations between psychopathy factors and impulsive and premeditated aggression. Personal. Disord. 5, 390–396 (2014).
Koob, G. F. Drug addiction: hyperkatifeia/negative reinforcement as a framework for medications development. Pharmacol. Rev. 73, 163–201 (2021).
Koob, G. F. & Le Moal, M. Addiction and the brain antireward system. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 59, 29–53 (2008).
Pantazis, C. B. et al. Cues conditioned to withdrawal and negative reinforcement: neglected but key motivational elements driving opioid addiction. Sci. Adv. 7, eabf0364 (2021). This paper shows that external and internal cues conditioned by withdrawal have a critical motivational role in fuelling opioid addiction.
Patterson, J. T., Koob, G. F. & Anderson, R. I. Understanding hyperkatifeia to inform treatment for alcohol use disorder: an assessment of the national institute on alcohol abuse and alcoholism research portfolio. Biol. Psychiatry 91, e53–e59 (2022).
Koob, G. F. et al. Addiction as a stress surfeit disorder. Neuropharmacology 76, 370–382 (2014).
Shurman, J., Koob, G. F. & Gutstein, H. B. Opioids, pain, the brain, and hyperkatifeia: a framework for the rational use of opioids for pain. Pain Med. 11, 1092–1098 (2010).
Neugebauer, V., Li, W., Bird, G. C. & Han, J. S. The amygdala and persistent pain. Neuroscientist 10, 221–234 (2004).
Koob, G. F., Powell, P. & White, A. Addiction as a coping response: hyperkatifeia, deaths of despair, and COVID-19. Am. J. Psychiatry 177, 1031–1037 (2020).
Minozzi, S., Amato, L. & Davoli, M. Development of dependence following treatment with opioid analgesics for pain relief: a systematic review. Addiction 108, 688–698 (2013).
Seabury, B. A. Problem Behavior and Psychological Development: A Longitudinal Study of Youth (eds Jessor, R. & Jessor, S. L.) 281 (Academic, 1977).
Vanyukov, M. M. et al. Common liability to addiction and ‘gateway hypothesis’: theoretical, empirical and evolutionary perspective. Drug Alcohol Depend. 123, S3–S17 (2012).
Kaye, A. D. et al. Prescription opioid abuse in chronic pain: an updated review of opioid abuse predictors and strategies to curb opioid abuse (Part 2). Pain Physician 20, S111–S133 (2017).
Kendler, K. S., Lönn, S. L., Ektor-Andersen, J., Sundquist, J. & Sundquist, K. Risk factors for the development of opioid use disorder after first opioid prescription: a Swedish national study. Psychol. Med. 53, 6223–6231 (2023).
Dol, M. & Oremus, M. Iatrogenic addiction or dependence as a result of prescription oxycodone use in persons with chronic noncancer pain: a systematic review. J. Opioid Manag. 17, 79–96 (2021).
Higgins, C., Smith, B. H. & Matthews, K. Incidence of iatrogenic opioid dependence or abuse in patients with pain who were exposed to opioid analgesic therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 120, 1335–1344 (2018).
Moe, S., Kirkwood, J. & Allan, G. M. Incidence of iatrogenic opioid use disorder. Can. Fam. Physician 65, 724 (2019).
Thomas, K. H. et al. Prevalence of problematic pharmaceutical opioid use in patients with chronic non-cancer pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Addiction https://doi.org/10.1111/add.16616 (2024).
Pecina, M. et al. Endogenous opioid system dysregulation in depression: implications for new therapeutic approaches. Mol. Psychiatry 24, 576–587 (2019).
Sansone, R. A., Watts, D. A. & Wiederman, M. W. The misuse of prescription pain medication and borderline personality symptomatology. J. Opioid Manag. 9, 275–279 (2013).
Kaye, A. D. et al. Prescription opioid abuse in chronic pain: an updated review of opioid abuse predictors and strategies to curb opioid abuse: part 1. Pain Physician 20, S93–s109 (2017).
Stalter, N., Ma, S., Simon, G. & Pruinelli, L. Psychosocial problems and high amount of opioid administration are associated with opioid dependence and abuse after first exposure for chronic pain patients. Addict. Behav. 141, 107657 (2023).
Hooten, W. M. Chronic pain and mental health disorders: shared neural mechanisms, epidemiology, and treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 91, 955–970 (2016).
Meda, R. T. et al. Chronic pain-induced depression: a review of prevalence and management. Cureus 14, e28416 (2022).
Gohari, J. et al. Clinical factors and pre-surgical depression scores predict pain intensity in cardiac surgery patients. BMC Anesthesiol. 22, 204 (2022).
Kim, Y. S. et al. Patient reporting pain intensity immediately after surgery can be associated with underlying depression in women with breast cancer. Psychooncology 25, 308–315 (2016).
O’Connell, C. et al. Preoperative depression, lumbar fusion, and opioid use: an assessment of postoperative prescription, quality, and economic outcomes. Neurosurg. Focus 44, E5 (2018).
Stone, A. V. et al. Mood disorders are associated with increased perioperative opioid usage and health care costs in patients undergoing knee cartilage restoration procedure. Cartilage 13, 19476035221087703 (2022).
Cooper, M. L., Kuntsche, E., Levitt, A., Barber, L. L. & Wolf, S. in The Oxford Handbook of Substance Use and Substance Use Disorders (ed. Sher, K. J.) 1 (Oxford Univ. Press, 2016).
Hogarth, L. Addiction is driven by excessive goal-directed drug choice under negative affect: translational critique of habit and compulsion theory. Neuropsychopharmacology 45, 720–735 (2020). This article suggests that addiction is primarily motivated by negative emotional states rather than by habituality or compulsion.
Evans, C. J. & Cahill, C. M. Neurobiology of opioid dependence in creating addiction vulnerability. F1000Res https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.8369.1 (2016).
Polak, K. B., Reisweber, T., Bjork, J. & Four-Session Transcending Self, J. Therapy for substance use, depression, and treatment retention among veterans with substance use disorders: a pilot study. J. Addiction Res. Ther. 10, 378 (2019).
Polak, K., Meyer, B. L., Neale, Z. E. & Reisweber, J. Program evaluation of group transcending self therapy: an integrative modular cognitive-behavioral therapy for substance use disorders. Subst. Abuse 14, 1178221820947653 (2020).
Conrod, P. J. Personality-targeted interventions for substance use and misuse. Curr. Addict. Rep. 3, 426–436 (2016).
Edalati, H. & Conrod, P. J. A review of personality-targeted interventions for prevention of substance misuse and related harm in community samples of adolescents. Front. Psychiatry 9, 770 (2018).
Ekhtiari, H., Rezapour, T., Aupperle, R. L. & Paulus, M. P. in Progress in Brain Research (eds Calvey, T. & Daniels, W. M. U.) 239–264 (Elsevier, 2017).
Rezapour, T. et al. Neuroscience-informed classification of prevention interventions in substance use disorders: an RDoC-based approach. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 159, 105578 (2024).
Santo, T. Jr et al. Prevalence of comorbid substance use disorders among people with opioid use disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Drug Policy 128, 104434 (2024).
Amer, T., Ngo, K. W. & Hasher, L. Cultural differences in visual attention: implications for distraction processing. Br. J. Psychol. 108, 244–258 (2017).
Hedden, T., Ketay, S., Aron, A., Markus, H. R. & Gabrieli, J. D. Cultural influences on neural substrates of attentional control. Psychol. Sci. 19, 12–17 (2008).
Nisbett, R. E. & Miyamoto, Y. The influence of culture: holistic versus analytic perception. Trends Cognit. Sci. 9, 467–473 (2005).
Ishii, K., Eisen, C. & Hitokoto, H. The effects of social status and culture on delay discounting. Jpn Psychol. Res. 59, 230–237 (2017).
Kim, B., Sung, Y. S. & McClure, S. M. The neural basis of cultural differences in delay discounting. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 367, 650–656 (2012).
Raineri, A., Kausel, E., Jin, Z. & Chamorro, N. Cultural differences in intertemporal decision making: a comparison between Chile and China. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 122, 103–116 (2023).
Chen, X. J., Ba, L. & Kwak, Y. Neurocognitive underpinnings of cross-cultural differences in risky decision making. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 15, 671–680 (2020).
Seo, M., Na, J. & Kim, Y. H. Moral in whose eyes? Cross-cultural differences in moral decision making and behaviour. Int. J. Psychol. 56, 175–182 (2021).
Legare, C. H., Dale, M. T., Kim, S. Y. & Deák, G. O. Cultural variation in cognitive flexibility reveals diversity in the development of executive functions. Sci. Rep. 8, 16326 (2018).
Tran, C. D., Arredondo, M. M. & Yoshida, H. Early executive function: the influence of culture and bilingualism. Biling. Lang. Cogn. 22, 714–732 (2019).
Jachimowicz, J. M., Chafik, S., Munrat, S., Prabhu, J. C. & Weber, E. U. Community trust reduces myopic decisions of low-income individuals. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 5401–5406 (2017).
Shah, A. K., Mullainathan, S. & Shafir, E. Some consequences of having too little. Science 338, 682–685 (2012).
Tunney, R. J. & James, R. J. E. Individual differences in decision-making: evidence for the scarcity hypothesis from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. R. Soc. Open Sci. 9, 220102 (2022).
Wang, M., Rieger, M. O. & Hens, T. The impact of culture on loss aversion. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 30, 270–281 (2017).
Haines, N., Vassileva, J. & Ahn, W. Y. The outcome-representation learning model: a novel reinforcement learning model of the Iowa Gambling Task. Cogn. Sci. 42, 2534–2561 (2018).
Henrich, J., Heine, S. J. & Norenzayan, A. Most people are not WEIRD. Nature 466, 29–29 (2010).
Bender, A. & Beller, S. Cognition is fundamentally cultural. Behav. Sci. 3, 42–54 (2013).
Eysenck, S. B. G., Pearson, P. R., Easting, G. & Allsopp, J. F. Age norms for impulsiveness, venturesomeness and empathy in adults. Pers. Individ. Differ. 6, 613–619 (1985).
Mayhew, M. J. & Powell, J. H. The development of a brief self-report questionnaire to measure ‘recent’ rash impulsivity: a preliminary investigation of its validity and association with recent alcohol consumption. Addict. Behav. 39, 1597–1605 (2014).
Cyders, M. A. et al. Integration of impulsivity and positive mood to predict risky behavior: development and validation of a measure of positive urgency. Psychol. Assess. 19, 107–118 (2007).
Carver, C. S. & White, T. L. Behavioral inhibition, behavioral activation, and affective responses to impending reward and punishment: the BIS/BAS Scales. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 67, 319–333 (1994).
Zuckerman, M. Behavioral Expressions and Biosocial Bases of Sensation Seeking (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1994).
Zuckerman, M. P-Impulsive sensation seeking and its behavioral, psychophysiological and biochemical correlates. Neuropsychobiology 28, 30–36 (2008).
Torrubia, R., Ávila, C., Moltó, J. & Caseras, X. The sensitivity to punishment and sensitivity to reward questionnaire (SPSRQ) as a measure of Gray’s anxiety and impulsivity dimensions. Pers. Individ. Differ. 31, 837–862 (2001).
Dougherty, D. M., Marsh, D. M. & Mathias, C. W. Immediate and delayed memory tasks: a computerized behavioral measure of memory, attention, and impulsivity. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 34, 391–398 (2002).
Eriksen, B. A. & Eriksen, C. W. Effects of noise letters upon the identification of a target letter in a nonsearch task. Percept. Psychophys. 16, 143–149 (1974).
Beck, L. H., Bransome, E. D. Jr, Mirsky, A. F., Rosvold, H. E. & Sarason, I. A continuous performance test of brain damage. J. Consult. Psychol. 20, 343–350 (1956).
Kaufman, J. N., Ross, T. J., Stein, E. A. & Garavan, H. Cingulate hypoactivity in cocaine users during a Go–Nogo task as revealed by event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging. J. Neurosci. 23, 7839–7843 (2003).
Stroop, J. R. Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J. Exp. Psychol. 18, 643 (1935).
Logan, G. D., Schachar, R. J. & Tannock, R. Impulsivity and inhibitory control. Psychol. Sci. 8, 60–64 (1997).
Massaly, N. et al. Pain, negative affective states and opioid-based analgesics: safer pain therapies to dampen addiction. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 157, 31–68 (2021).
Richards, J. B., Zhang, L., Mitchell, S. H. & de Wit, H. Delay or probability discounting in a model of impulsive behavior: effect of alcohol. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 71, 121–143 (1999).
Bechara, A. et al. Decision-making deficits, linked to a dysfunctional ventromedial prefrontal cortex, revealed in alcohol and stimulant abusers. Neuropsychologia 39, 376–389 (2001).
Chiu, Y. C. et al. Immediate gain is long-term loss: are there foresighted decision makers in the Iowa Gambling Task? Behav. Brain Funct. 4, 13 (2008).
Levy, I., Snell, J., Nelson, A. J., Rustichini, A. & Glimcher, P. W. Neural representation of subjective value under risk and ambiguity. J. Neurophysiol. 103, 1036–1047 (2010).
Lejuez, C. W. et al. Evaluation of a behavioral measure of risk taking: the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART). J. Exp. Psychol. Appl. 8, 75–84 (2002).
Figner, B., Mackinlay, R. J., Wilkening, F. & Weber, E. U. Affective and deliberative processes in risky choice: age differences in risk taking in the Columbia Card Task. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 35, 709–730 (2009).
Brand, M. et al. Decision-making deficits of Korsakoff patients in a new gambling task with explicit rules: associations with executive functions. Neuropsychology 19, 267–277 (2005).
Daw, N. D., Gershman, S. J., Seymour, B., Dayan, P. & Dolan, R. J. Model-based influences on humans’ choices and striatal prediction errors. Neuron 69, 1204–1215 (2011).
Newman, J. P. & Kosson, D. S. Passive avoidance learning in psychopathic and nonpsychopathic offenders. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 95, 252–225 (1986).
Koob, G. & Le Moal, M. Drug addiction, dysregulation of reward, and allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology 24, 97–129 (2001).
Bloom, E. L., Matsko, S. V. & Cimino, C. R. The relationship between cigarette smoking and impulsivity: a review of personality, behavioral, and neurobiological assessment. Addict. Res. Theory 22, 386–397 (2014).
Kale, D., Stautz, K. & Cooper, A. Impulsivity related personality traits and cigarette smoking in adults: a meta-analysis using the UPPS-P model of impulsivity and reward sensitivity. Drug Alcohol Depend. 185, 149–167 (2018).
Bos, J., Hayden, M. J., Lum, J. A. G. & Staiger, P. K. UPPS-P impulsive personality traits and adolescent cigarette smoking: a meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend. 197, 335–343 (2019).
Wellman, R. J. et al. Predictors of the onset of cigarette smoking: a systematic review of longitudinal population-based studies in youth. Am. J. Prev. Med. 51, 767–778 (2016).
Doran, N. et al. A prospective study of the Acquired Preparedness Model: the effects of impulsivity and expectancies on smoking initiation in college students. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 27, 714–722 (2013).
Conti, A. A., McLean, L., Tolomeo, S., Steele, J. D. & Baldacchino, A. Chronic tobacco smoking and neuropsychological impairments: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 96, 143–154 (2019).
Coskunpinar, A., Dir, A. L. & Cyders, M. A. Multidimensionality in impulsivity and alcohol use: a meta-analysis using the UPPS model of impulsivity. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 37, 1441–1450 (2013).
Stautz, K. & Cooper, A. Impulsivity-related personality traits and adolescent alcohol use: a meta-analytic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 33, 574–592 (2013).
Stavro, K., Pelletier, J. & Potvin, S. Widespread and sustained cognitive deficits in alcoholism: a meta-analysis. Addict. Biol. 18, 203–213 (2013).
Courtney, K. E. et al. The relationship between measures of impulsivity and alcohol misuse: an integrative structural equation modeling approach. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 36, 923–931 (2012).
Petry, N. M. Delay discounting of money and alcohol in actively using alcoholics, currently abstinent alcoholics, and controls. Psychopharmacology 154, 243–250 (2001).
Takahashi, T., Ohmura, Y., Oono, H. & Radford, M. Alcohol use and discounting of delayed and probabilistic gain and loss. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 30, 749–752 (2009).
Brevers, D. et al. Impaired decision-making under risk in individuals with alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 38, 1924–1931 (2014).
Galandra, C., Basso, G., Cappa, S. & Canessa, N. The alcoholic brain: neural bases of impaired reward-based decision-making in alcohol use disorders. Neurol. Sci. 39, 423–435 (2018).
Tomassini, A. et al. Decision making, impulsivity, and personality traits in alcohol-dependent subjects. Am. J. Addict. 21, 263–267 (2012).
Zorlu, N. et al. Abnormal white matter integrity and decision-making deficits in alcohol dependence. Psychiatry Res. 214, 382–388 (2013).
Fein, G., Klein, L. & Finn, P. Impairment on a simulated gambling task in long-term abstinent alcoholics. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 28, 1487–1491 (2004).
VanderVeen, J. D., Hershberger, A. R. & Cyders, M. A. UPPS-P model impulsivity and marijuana use behaviors in adolescents: a meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend. 168, 181–190 (2016).
Figueiredo, P. R., Tolomeo, S., Steele, J. D. & Baldacchino, A. Neurocognitive consequences of chronic cannabis use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 108, 358–369 (2020).
Lovell, M. E., Akhurst, J., Padgett, C., Garry, M. I. & Matthews, A. Cognitive outcomes associated with long-term, regular, recreational cannabis use in adults: a meta-analysis. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 28, 471–494 (2020).
Strickland, J. C., Lee, D. C., Vandrey, R. & Johnson, M. W. A systematic review and meta-analysis of delay discounting and cannabis use. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 29, 696–710 (2021).
Gonzalez, R. et al. Performance of young adult cannabis users on neurocognitive measures of impulsive behavior and their relationship to symptoms of cannabis use disorders. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 34, 962–976 (2012).
Albein-Urios, N., Martinez-González, J. M., Lozano, O., Clark, L. & Verdejo-García, A. Comparison of impulsivity and working memory in cocaine addiction and pathological gambling: implications for cocaine-induced neurotoxicity. Drug Alcohol Depend. 126, 1–6 (2012).
Fernández-Serrano, M. J., Perales, J. C., Moreno-López, L., Pérez-García, M. & Verdejo-García, A. Neuropsychological profiling of impulsivity and compulsivity in cocaine dependent individuals. Psychopharmacology 219, 673–683 (2012).
Ersche, K. D. et al. Distinctive personality traits and neural correlates associated with stimulant drug use versus familial risk of stimulant dependence. Biol. Psychiatry 74, 137–144 (2013).
Ersche, K. D., Turton, A. J., Pradhan, S., Bullmore, E. T. & Robbins, T. W. Drug addiction endophenotypes: impulsive versus sensation-seeking personality traits. Biol. Psychiatry 68, 770–773 (2010).
Ramey, T. & Regier, P. S. Cognitive impairment in substance use disorders. CNS Spectr. 24, 102–113 (2019).
Spronk, D. B., van Wel, J. H., Ramaekers, J. G. & Verkes, R. J. Characterizing the cognitive effects of cocaine: a comprehensive review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 37, 1838–1859 (2013).
Verdejo-Garcia, A. & Rubenis, A. J. in Cognition and Addiction (ed. Verdejo-Garcia, A.) 155–163 (Academic, 2020).
MacKillop, J. et al. Delayed reward discounting and addictive behavior: a meta-analysis. Psychopharmacology 216, 305–321 (2011).
Casey, B. J. & Jones, R. M. Neurobiology of the adolescent brain and behavior: implications for substance use disorders. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 49, 1189–1201 (2010). quiz 1285.
Kahneman, D. A. Thinking, Fast and Slow 1st edn (Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 2011).
Barratt, E. S. Anxiety and impulsiveness related to psychomotor efficiency. Percept. Mot. Skills 9, 191–198 (1959).
Stanford, M. S. et al. Fifty years of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale: an update and review. Pers. Individ. Differ. 47, 385–395 (2009).
Ahn, W. Y., Dai, J., Vassileva, J., Busemeyer, J. R. & Stout, J. C. Computational modeling for addiction medicine: from cognitive models to clinical applications. Prog. Brain Res. 224, 53–65 (2016).
Zhou, R. & Pitt, M. A. Dual-process modeling of sequential decision making in the Balloon Analogue Risk Task. Cogn. Psychol. 149, 101629 (2024).
Odum, A. L. Delay discounting: trait variable? Behav. Process. 87, 1–9 (2011).
Enkavi, A. Z. et al. Large-scale analysis of test–retest reliabilities of self-regulation measures. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116, 5472–5477 (2019).
Heilig, M., Goldman, D., Berrettini, W. & O’Brien, C. P. Pharmacogenetic approaches to the treatment of alcohol addiction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 12, 670–684 (2011).
Babor, T. F. et al. Types of alcoholics, I. Evidence for an empirically derived typology based on indicators of vulnerability and severity. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 49, 599–608 (1992).
Cloninger, C. R. Neurogenetic adaptive mechanisms in alcoholism. Science 236, 410–416 (1987).
Kendler, K. S., Prescott, C. A., Myers, J. & Neale, M. C. The structure of genetic and environmental risk factors for common psychiatric and substance use disorders in men and women. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 60, 929–937 (2003).
Krueger, R. F. The structure of common mental disorders. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 56, 921–926 (1999).
Krueger, R. F. et al. Etiologic connections among substance dependence, antisocial behavior, and personality: modeling the externalizing spectrum. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 111, 411–424 (2002).
Krueger, R. F., Markon, K. E., Patrick, C. J., Benning, S. D. & Kramer, M. D. Linking antisocial behavior, substance use, and personality: an integrative quantitative model of the adult externalizing spectrum. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 116, 645–666 (2007).
Carragher, N. et al. The structure of adolescent psychopathology: a symptom-level analysis. Psychol. Med. 46, 981–994 (2016).
Savage, J. E., Dick, D. M. & Spit for Science Working Group Internalizing and externalizing subtypes of alcohol misuse and their relation to drinking motives. Addict. Behav. 136, 107461 (2023).
Conrod, P. J., Pihl, R. O., Stewart, S. H. & Dongier, M. Validation of a system of classifying female substance abusers on the basis of personality and motivational risk factors for substance abuse. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 14, 243–256 (2000).
Acknowledgements
J.V. discloses support for the research of this work from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the Fogarty International Center at the National Institutes of Health (grant number R01DA021421), and the National Institute on Drug Abuse (grant number R01DA058038). J.M.B. discloses support for the research of this work from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (grant number 1U01DA057846).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.V. and E.P researched data for the article. All authors wrote the article, contributed substantially to discussion of the content, and reviewed and/or edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Psychology thanks Dokyoung Sophia You and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vassileva, J., Psederska, E. & Bjork, J.M. Negative affectivity drivers of impulsivity in opioid use disorder. Nat Rev Psychol 4, 170–192 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44159-025-00404-6
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44159-025-00404-6