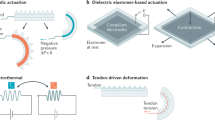
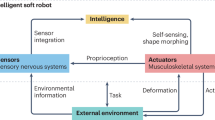
Abstract
Soft robotic systems prevail in wearable and haptic applications, offering adaptability, safety and comfort. In this Review, we explore the integration of soft robotics in wearable designs for applications in assistance, rehabilitation and haptic sensory stimulation. We outline various types of soft actuators, examining their properties with regard to adjustable stiffness, mechanical responsiveness and sensing capabilities and their integration into wearable devices for health-care applications. We also highlight challenges and opportunities in developing sustainable, self-healing, self-powering and self-actuating soft robots, particularly with regard to achieving efficient energy usage, long-term durability and personalized control. Finally, we examine how machine learning might be explored to optimize the performance and adaptability of soft robotic devices to transform real-time data into actionable insights for personalized experiences.
Key points
-
Soft actuators provide advantages for wearable technologies by supporting mobility and delivering nuanced, responsive haptic feedback.
-
Energy efficiency is essential to improving the portability, autonomy and user experience of wearable devices.
-
Durability and recyclability are crucial to maintaining long-term performance, and biodegradable materials offer promising solutions for short-term or disposable use.
-
Personalized, data-driven design enhances human–robot interaction, improving usability, comfort and user acceptance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cappello, L. et al. Assisting hand function after spinal cord injury with a fabric-based soft robotic glove. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 15, 59 (2018).
O’Neill, C. et al. Inflatable soft wearable robot for reducing therapist fatigue during upper extremity rehabilitation in severe stroke. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 5, 3899–3906 (2020).
Walker, S., Firouzeh, A., Robertson, M., Mengüç, Y. & Paik, J. 3D printed motor-sensory module prototype for facial rehabilitation. Soft Robot. 9, 354–363 (2022).
Agarwal, G., Robertson, M. A., Sonar, H. & Paik, J. Design and computational modeling of a modular, compliant robotic assembly for human lumbar unit and spinal cord assistance. Sci. Rep. 7, 14391 (2017).
Thalman, C. M., Hertzell, T. & Lee, H. Toward a soft robotic ankle-foot orthosis (SR-AFO) exosuit for human locomotion: preliminary results in late stance plantarflexion assistance. In 2020 3rd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft) 801–807 (IEEE, 2020).
Copaci, D., Cerro, D. S. D., Guadalupe, J. A., Lorente, L. M. & Rojas, D. B. sEMG-controlled soft exo-glove for assistive rehabilitation therapies. IEEE Access12, 43506–43518 (2024).
Feng, M., Yang, D. & Gu, G. High-force fabric-based pneumatic actuators with asymmetric chambers and interference-reinforced structure for soft wearable assistive gloves. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 6, 3105–3111 (2021).
Li, Y. & Hashimoto, M. PVC gel soft actuator-based wearable assist wear for hip joint support during walking. Smart Mater. Struct. 26, 125003 (2017).
Proietti, T. et al. Restoring arm function with a soft robotic wearable for individuals with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 15, eadd1504 (2023).
Lipomi, D. J., Dhong, C., Carpenter, C. W., Root, N. B. & Ramachandran, V. S. Organic haptics: intersection of materials chemistry and tactile perception. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1906850 (2020). This article discusses the engineering of molecularly controllable materials for emulating the haptic feel of everyday objects.
Lou, J. et al. A new strategy of discretionarily reconfigurable actuators based on self-healing elastomers for diverse soft robots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2008328 (2021).
Xu, J. et al. Self-healing high-performance dielectric elastomer actuator with novel liquid-solid interpenetrating structure. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 149, 106519 (2021).
Tang, W. et al. Customizing a self-healing soft pump for robot. Nat. Commun. 12, 2247 (2021).
Tan, Y. J., Susanto, G. J., Anwar Ali, H. P. & Tee, B. C. K. Progress and roadmap for intelligent self-healing materials in autonomous robotics. Adv. Mater. 33, 2002800 (2021).
Ali, A. et al. Recent progress in energy harvesting systems for wearable technology. Energy Strategy Rev. 49, 101124 (2023).
Zhou, X. et al. 3D printed auxetic structure-assisted piezoelectric energy harvesting and sensing. Adv. Energy Mater. 13, 2301159 (2023).
Ma, B., Xu, C., Cui, L., Zhao, C. & Liu, H. Magnetic printing of liquid metal for perceptive soft actuators with embodied intelligence. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 5574–5582 (2021).
Firouzeh, A., Salerno, M. & Paik, J. Soft pneumatic actuator with adjustable stiffness layers for multi-DoF actuation. In 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 1117–1124 (IEEE, 2015).
Giraud, F. H., Mete, M. & Paik, J. Flexure variable stiffness actuators. Adv. Intell. Syst. 4, 2100282 (2022).
Robertson, M. A., Murakami, M., Felt, W. & Paik, J. A compact modular soft surface with reconfigurable shape and stiffness. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 24, 16–24 (2019).
Yao, H. et al. Shape memory polymers enable versatile magneto-active structure with 4D printability, variable stiffness, shape-morphing and effective grasping. Smart Mater. Struct. 32, 095005 (2023).
Sonar, H. A., Gerratt, A. P., Lacour, S. P. & Paik, J. Closed-loop haptic feedback control using a self-sensing soft pneumatic actuator skin. Soft Robot. 7, 22–29 (2020).
Gariya, N., Kumar, P., Prasad, B. & Singh, T. Soft pneumatic actuator with an embedded flexible polymeric piezoelectric membrane for sensing bending deformation. Mater. Today Commun. 35, 105910 (2023).
Kellaris, N., Venkata, V. G., Smith, G. M., Mitchell, S. K. & Keplinger, C. Peano-HASEL actuators: muscle-mimetic, electrohydraulic transducers that linearly contract on activation. Sci. Robot. 3, eaar3276 (2018).
Janbaz, S. & Coulais, C. Diffusive kinks turn kirigami into machines. Nat. Commun. 15, 1255 (2024). This article reports how diffusive kinks in viscoelastic kirigami can be harnessed for machine-like functions, such as sensing, actuation and object manipulation.
Raeisinezhad, M., Pagliocca, N., Koohbor, B. & Trkov, M. Design Optimization of a pneumatic soft robotic actuator using model-based optimization and deep reinforcement learning. Front. Robot. AI 8, 639102 (2021).
Zolfagharian, A. et al. 4D printing soft robots guided by machine learning and finite element models. Sens. Actuators Phys. 328, 112774 (2021).
Lee, K.-H. et al. Nonparametric online learning control for soft continuum robot: an enabling technique for effective endoscopic navigation. Soft Robot. 4, 324–337 (2017).
Tang, Z. Q., Heung, H. L., Tong, K. Y. & Li, Z. Model-based online learning and adaptive control for a “human-wearable soft robot” integrated system. Int. J. Robot. Res. 40, 256–276 (2021).
Zahedi, F. & Lee, H. Biomechanics-based user-adaptive variable impedance control for enhanced physical human–robot interaction using Bayesian optimization. Adv. Intell. Syst. 7, 2400333 (2025).
Lee, J. et al. Intelligent upper-limb exoskeleton integrated with soft bioelectronics and deep learning for intention-driven augmentation. npj Flex. Electron. 8, 11 (2024).
Alam, U. K. & Haghshenas-Jaryani, M. Learning contact forces in human-wearable-robot interaction using morphological computation. In 2024 IEEE 7th International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft) 671–677 (IEEE, 2024).
Thalman, C. & Artemiadis, P. A review of soft wearable robots that provide active assistance: trends, common actuation methods, fabrication, and applications. Wearable Technol. 1, e3 (2020).
Tondu, B. & Lopez, P. Modeling and control of McKibben artificial muscle robot actuators. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 20, 15–38 (2000).
Robertson, M. A. & Paik, J. New soft robots really suck: vacuum-powered systems empower diverse capabilities. Sci. Robot. 2, eaan6357 (2017).
Joshi, S. & Paik, J. Pneumatic supply system parameter optimization for soft actuators. Soft Robot. 8, 152–163 (2021).
Sawicki, G. S. & Ferris, D. P. Mechanics and energetics of level walking with powered ankle exoskeletons. J. Exp. Biol. 211, 1402–1413 (2008).
Robertson, M. A. & Paik, J. Low-inertia vacuum-powered soft pneumatic actuator coil characterization and design methodology. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft) 431–436 (IEEE, 2018).
Rus, D. & Tolley, M. T. Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 521, 467–475 (2015).
Connolly, F., Walsh, C. J. & Bertoldi, K. Automatic design of fiber-reinforced soft actuators for trajectory matching. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 51–56 (2017).
Bishop-Moser, J. & Kota, S. Design and modeling of generalized fiber-reinforced pneumatic soft actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31, 536–545 (2015).
Sun, Y., Song, Y. S. & Paik, J. Characterization of silicone rubber based soft pneumatic actuators. In 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems 4446–4453 (IEEE, 2013).
Mosadegh, B. et al. Pneumatic networks for soft robotics that actuate rapidly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 2163–2170 (2014).
Agarwal, G., Besuchet, N., Audergon, B. & Paik, J. Stretchable materials for robust soft actuators towards assistive wearable devices. Sci. Rep. 6, 34224 (2016).
Paez, L., Agarwal, G. & Paik, J. Design and analysis of a soft pneumatic actuator with origami shell reinforcement. Soft Robot. 3, 109–119 (2016).
Buckner, T. L., Yuen, M. C., Kim, S. Y. & Kramer-Bottiglio, R. Enhanced variable stiffness and variable stretchability enabled by phase-changing particulate additives. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1903368 (2019).
Yang, B. et al. Reprogrammable soft actuation and shape-shifting via tensile jamming. Sci. Adv. 7, eabh2073 (2021).
Song, S., Joshi, S. & Paik, J. CMOS-inspired complementary fluidic circuits for soft robots. Adv. Sci. 8, 2100924 (2021).
Preston, D. J. et al. Digital logic for soft devices. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116, 7750–7759 (2019).
Wehner, M. et al. An integrated design and fabrication strategy for entirely soft, autonomous robots. Nature 536, 451–455 (2016).
Drotman, D., Jadhav, S., Sharp, D., Chan, C. & Tolley, M. T. Electronics-free pneumatic circuits for controlling soft-legged robots. Sci. Robot. 6, eaay2627 (2021).
Nemitz, M. P. et al. Soft non-volatile memory for non-electronic information storage in soft robots. In 2020 3rd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft) 7–12 (IEEE, 2020).
Kikkert, S., Sonar, H. A., Freund, P., Paik, J. & Wenderoth, N. Hand and face somatotopy shown using MRI-safe vibrotactile stimulation with a novel soft pneumatic actuator (SPA)-skin interface. NeuroImage 269, 119932 (2023).
Jung, Y., Kwon, K., Lee, J. & Ko, S. H. Untethered soft actuators for soft standalone robotics. Nat. Commun. 15, 3510 (2024).
Uramune, R. et al. HaPouch: a miniaturized, soft, and wearable haptic display device using a liquid-to-gas phase change actuator. IEEE Access 10, 16830–16842 (2022).
Sanchez, V. et al. Smart thermally actuating textiles. Adv. Mater. Technol. 5, 2000383 (2020). This article introduces thermally actuated textiles that rely on liquid–vapour phase change to enable tetherless wearable soft robots with integrated sensing and closed-loop control.
Lee, J. et al. Bioinspired soft robotic fish for wireless underwater control of gliding locomotion. Adv. Intell. Syst. 4, 2100271 (2022).
Mirvakili, S. M., Sim, D., Hunter, I. W. & Langer, R. Actuation of untethered pneumatic artificial muscles and soft robots using magnetically induced liquid-to-gas phase transitions. Sci. Robot. 5, eaaz4239 (2020).
Firouzeh, A., Mirrazavi Salehian, S. S., Billard, A. & Paik, J. An under actuated robotic arm with adjustable stiffness shape memory polymer joints. In 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2536–2543 (IEEE, 2015).
Shao, Y. et al. 4D printing light-driven soft actuators based on liquid-vapor phase transition composites with inherent sensing capability. Chem. Eng. J. 454, 140271 (2023).
Leroy, E., Hinchet, R. & Shea, H. Multimode hydraulically amplified electrostatic actuators for wearable haptics. Adv. Mater. 32, 2002564 (2020).
Acome, E. et al. Hydraulically amplified self-healing electrostatic actuators with muscle-like performance. Science 359, 61–65 (2018).
Kellaris, N., Venkata, V. G., Rothemund, P. & Keplinger, C. An analytical model for the design of Peano-HASEL actuators with drastically improved performance. Extreme Mech. Lett. 29, 100449 (2019). This article presents an analytical model for Peano-HASEL actuators, revealing how geometry and material choices enable tuneable performance.
Mitchell, S. K. et al. An easy-to-implement toolkit to create versatile and high-performance HASEL actuators for untethered soft robots. Adv. Sci. 6, 1900178 (2019).
Yoder, Z. et al. Design of a high-speed prosthetic finger driven by Peano-HASEL actuators. Front. Robot. AI 7, 586216 (2020).
Purnendu et al. Fingertip wearable high-resolution electrohydraulic interface for multimodal haptics. In 2023 IEEE World Haptics Conference (WHC) 299–305 (IEEE, 2023).
Rothemund, P., Kellaris, N., Mitchell, S. K., Acome, E. & Keplinger, C. HASEL artificial muscles for a new generation of lifelike robots — recent progress and future opportunities. Adv. Mater. 33, 2003375 (2021).
Xu, S., Nunez, C. M., Souri, M. & Wood, R. J. A compact DEA-based soft peristaltic pump for power and control of fluidic robots. Sci. Robot. 8, eadd4649 (2023).
Cacucciolo, V. et al. Stretchable pumps for soft machines. Nature 572, 516–519 (2019).
Gravert, S.-D. et al. Low-voltage electrohydraulic actuators for untethered robotics. Sci. Adv. 10, eadi9319 (2024).
Ji, X. et al. Untethered feel-through haptics using 18-µm thick dielectric elastomer actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2006639 (2021).
Park, W.-H., Shin, E.-J., Yoo, Y., Choi, S. & Kim, S.-Y. Soft haptic actuator based on knitted PVC gel fabric. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 67, 677–685 (2020).
Youn, J.-H., Mun, H. & Kyung, K.-U. A wearable soft tactile actuator with high output force for fingertip interaction. IEEE Access 9, 30206–30215 (2021).
Yu, A. et al. Core–shell-yarn-based triboelectric nanogenerator textiles as power cloths. ACS Nano 11, 12764–12771 (2017).
Lee, D.-Y. et al. A wearable textile-embedded dielectric elastomer actuator haptic display. Soft Robot. 9, 1186–1197 (2022).
Yoon, S. H. et al. HapSense: a soft haptic I/O device with uninterrupted dual functionalities of force sensing and vibrotactile actuation. In Proc. The 32nd Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology 949–961 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2019).
Kovacs, G., Düring, L., Michel, S. & Terrasi, G. Stacked dielectric elastomer actuator for tensile force transmission. Sens. Actuators Phys. 155, 299–307 (2009).
Fook, T. H. T., Jeon, J. H. & Lee, P. S. Transparent flexible polymer actuator with enhanced output force enabled by conductive nanowires interlayer. Adv. Mater. Technol. 5, 1900762 (2020).
Wang, F., Wang, L., Wang, Y. & Wang, D. Highly bendable ionic electroactive polymer actuator based on carboxylated bacterial cellulose by doping with MWCNT. Appl. Phys. A 128, 911 (2022).
Wang, F., Xie, C., Qian, L., He, B. & Li, J. Study on the preparation of ionic liquid doped chitosan/cellulose-based electroactive composites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 6198 (2019).
Nie, R.-P. et al. Surfactant-assisted fabrication of room-temperature self-healable dielectric elastomer toward actuation application. Compos. B Eng. 234, 109655 (2022).
Xu, J. et al. Fabrication and characterization of SMA film actuator array with bias spring for high-power MEMS tactile display. Microelectron. Eng. 227, 111307 (2020).
Loo, S. S. L. et al. Integrating photothermal-responsive shape memory and self-healing polymers in 4D-printed thermally comfortable smart wearables. ACS Appl. Eng. Mater. 2, 2569–2582 (2024).
Roach, D. J. et al. Long liquid crystal elastomer fibers with large reversible actuation strains for smart textiles and artificial muscles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 19514–19521 (2019).
Saharan, L., Andrade, M. J. de, Saleem, W., Baughman, R. H. & Tadesse, Y. iGrab: hand orthosis powered by twisted and coiled polymer muscles. Smart Mater. Struct. 26, 105048 (2017).
Zhang, W. et al. Magnetoactive microlattice metamaterials with highly tunable stiffness and fast response rate. NPG Asia Mater. 15, 45 (2023).
Zhakypov, Z., Huang, J.-L. & Paik, J. A novel torsional shape memory alloy actuator: modeling, characterization, and control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 23, 65–74 (2016).
Huang, X. et al. Highly dynamic shape memory alloy actuator for fast moving soft robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 4, 1800540 (2019).
Hamdan, N. A., Wagner, A., Voelker, S., Steimle, J. & Borchers, J. Springlets: expressive, flexible and silent on-skin tactile interfaces. In Proc. 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems 1–14 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2019).
Karaca, H. E. et al. Magnetic field-induced phase transformation in NiMnCoIn magnetic shape-memory alloys — a new actuation mechanism with large work output. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 983–998 (2009).
Neville, R. M. et al. A kirigami shape memory polymer honeycomb concept for deployment. Smart Mater. Struct. 26, 05LT03 (2017).
Xie, H., Yang, K.-K. & Wang, Y.-Z. Photo-cross-linking: a powerful and versatile strategy to develop shape-memory polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 95, 32–64 (2019).
Xue, J. et al. Photoprogrammable moisture-responsive actuation of a shape memory polymer film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 10836–10843 (2022).
Firouzeh, A., Salerno, M. & Paik, J. Stiffness control with shape memory polymer in underactuated robotic origamis. IEEE Trans. Robot. 33, 765–777 (2017).
Wang, Y., Sun, J., Liao, W. & Yang, Z. Liquid crystal elastomer twist fibers toward rotating microengines. Adv. Mater. 34, 2107840 (2022).
Kurylo, I., van der Tol, J., Colonnese, N., Broer, D. J. & Liu, D. Photo-responsive liquid crystal network-based material with adaptive modulus for haptic application. Sci. Rep. 12, 19512 (2022).
Fowler, H. E., Rothemund, P., Keplinger, C. & White, T. J. Liquid crystal elastomers with enhanced directional actuation to electric fields. Adv. Mater. 33, 2103806 (2021).
Ambulo, C. P. et al. Processing advances in liquid crystal elastomers provide a path to biomedical applications. J. Appl. Phys. 128, 140901 (2020).
Suzuki, M. & Kamamichi, N. Control of twisted and coiled polymer actuator with anti-windup compensator. Smart Mater. Struct. 27, 075014 (2018).
Forman, J. et al. ModiFiber: two-way morphing soft thread actuators for tangible interaction. In Proc. 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems 1–11 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2019).
Yang, X., Wang, W. & Miao, M. Moisture-responsive natural fiber coil-structured artificial muscles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 32256–32264 (2018).
Aziz, S., Martinez, J. G., Salahuddin, B., Persson, N.-K. & Jager, E. W. H. Fast and high-strain electrochemically driven yarn actuators in twisted and coiled configurations. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2008959 (2021).
Li, H., Go, G., Ko, S. Y., Park, J.-O. & Park, S. Magnetic actuated pH-responsive hydrogel-based soft micro-robot for targeted drug delivery. Smart Mater. Struct. 25, 027001 (2016).
Kim, Y., Yuk, H., Zhao, R., Chester, S. A. & Zhao, X. Printing ferromagnetic domains for untethered fast-transforming soft materials. Nature 558, 274–279 (2018).
Sratong-on, P., Chernenko, V. A., Feuchtwanger, J. & Hosoda, H. Magnetic field-induced rubber-like behavior in Ni-Mn-Ga particles/polymer composite. Sci. Rep. 9, 3443 (2019).
Zhang, J. et al. Liquid crystal elastomer-based magnetic composite films for reconfigurable shape-morphing soft miniature machines. Adv. Mater. 33, 2006191 (2021).
Kim, Y. & Zhao, X. Magnetic soft materials and robots. Chem. Rev. 122, 5317–5364 (2022).
Gong, X.-L. et al. pH- and thermal-responsive multishape memory hydrogel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 27432–27437 (2016).
Wang, Z., Guo, Y., Cai, S. & Yang, J. Three-dimensional printing of liquid crystal elastomers and their applications. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 4, 3153–3168 (2022).
Shaha, R. K. et al. Biocompatible liquid-crystal elastomers mimic the intervertebral disc. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 107, 103757 (2020).
Wu, J. et al. Liquid crystal elastomer metamaterials with giant biaxial thermal shrinkage for enhancing skin regeneration. Adv. Mater. 33, 2106175 (2021).
Kongahage, D., Spinks, G. M. & Foroughi, J. Twisted and coiled multi-ply yarns artificial muscles. Sens. Actuators Phys. 318, 112490 (2021).
Haines, C. S. et al. Artificial muscles from fishing line and sewing thread. Science 343, 868–872 (2014).
Lai, J. et al. Design and evaluation of a bidirectional soft glove for hand rehabilitation-assistance tasks. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 5, 730–740 (2023).
Wang, W., Rodrigue, H. & Ahn, S.-H. Smart soft composite actuator with shape retention capability using embedded fusible alloy structures. Compos. B Eng. 78, 507–514 (2015).
Akbari, S., Sakhaei, A. H., Panjwani, S., Kowsari, K. & Ge, Q. Shape memory alloy based 3D printed composite actuators with variable stiffness and large reversible deformation. Sens. Actuators Phys. 321, 112598 (2021).
Terentjev, E. M. Liquid crystal elastomers: 30 years after. Macromolecules 58, 2792–2806 (2025).
Liao, W. & Yang, Z. The integration of sensing and actuating based on a simple design fiber actuator towards intelligent soft robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 7, 2101260 (2022). This article reports liquid-crystal elastomer–liquid-metal coaxial fibres that integrate actuation and sensing via electrically triggered Joule heating and resistance feedback, while enhancing resilience.
Polygerinos, P., Wang, Z., Galloway, K. C., Wood, R. J. & Walsh, C. J. Soft robotic glove for combined assistance and at-home rehabilitation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 73, 135–143 (2015).
Shull, P. B. & Damian, D. D. Haptic wearables as sensory replacement, sensory augmentation and trainer — a review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 12, 59 (2015).
Zhu, M. et al. Soft, wearable robotics and haptics: technologies, trends, and emerging applications. Proc. IEEE 110, 246–272 (2022).
Park, S. J. & Park, C. H. Suit-type wearable robot powered by shape-memory-alloy-based fabric muscle. Sci. Rep. 9, 9157 (2019).
Das, S. & Kurita, Y. ForceArm: a wearable pneumatic gel muscle (PGM)-based assistive suit for the upper limb. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2, 269–281 (2020).
Sy, L. et al. M-SAM: miniature and soft artificial muscle-driven wearable robotic fabric exosuit for upper limb augmentation. In 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft) (IEEE, 2021).
Sharma, B. et al. A soft robotic textile-actuated anthropomorphic artificial shoulder mechanism. Adv. Intell. Syst. 7, 2400807 (2025).
Ohno, A., Nabae, H. & Suzumori, K. Static analysis of powered low-back orthosis driven by thin pneumatic artificial muscles considering body surface deformation. In 2015 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII) 39–44 (IEEE, 2015).
Kim, C. et al. Shape memory alloy actuator-embedded smart clothes for ankle assistance. Smart Mater. Struct. 29, 055003 (2020).
Liu, S. et al. A compact soft robotic wrist brace with origami actuators. Front. Robot. AI 8, 614623 (2021).
Tiziani, L. et al. Empirical characterization of modular variable stiffness inflatable structures for supernumerary grasp-assist devices. Int. J. Robot. Res. 36, 1391–1413 (2017).
Duanmu, D., Wang, X., Li, X., Wang, Z. & Hu, Y. Design of guided bending bellows actuators for soft hand function rehabilitation gloves. Actuators 11, 346 (2022).
Connolly, F., Wagner, D. A., Walsh, C. J. & Bertoldi, K. Sew-free anisotropic textile composites for rapid design and manufacturing of soft wearable robots. Extreme Mech. Lett. 27, 52–58 (2019).
Li, X. et al. Design, modeling and experiments of a variable stiffness soft robotic glove for stroke patients with clenched fist deformity. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 8, 4044–4051 (2023).
Robertson, M. A., Sadeghi, H., Florez, J. M. & Paik, J. Soft pneumatic actuator fascicles for high force and reliability. Soft Robot. 4, 23–32 (2017).
Liu, Y., Pharr, M. & Salvatore, G. A. Lab-on-skin: a review of flexible and stretchable electronics for wearable health monitoring. ACS Nano 11, 9614–9635 (2017).
Lee, S.-M., Jung, W.-K., Park, J. & Ahn, S.-H. Development of a 4D hand gripping aid using a knitted shape memory alloy and evaluation of finger-bending angles in elderly women. Fash. Text. 9, 11 (2022).
Kwon, J. et al. Selectively stiffening garments enabled by cellular composites. Adv. Mater. Technol. 7, 2101543 (2022).
Hauser, S., Robertson, M., Ijspeert, A. & Paik, J. JammJoint: a variable stiffness device based on granular jamming for wearable joint support. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2, 849–855 (2017).
Proietti, T. et al. Sensing and control of a multi-joint soft wearable robot for upper-limb assistance and rehabilitation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 6, 2381–2388 (2021).
O’Neill, C. T., Phipps, N. S., Cappello, L., Paganoni, S. & Walsh, C. J. A soft wearable robot for the shoulder: design, characterization, and preliminary testing. In 2017 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR) 1672–1678 (IEEE, 2017).
Maldonado-Mejía, J. C. et al. A fabric-based soft hand exoskeleton for assistance: the ExHand exoskeleton. Front. Neurorobot. 17, 1091827 (2023).
Campioni, L. et al. Preliminary evaluation of a soft wearable robot for shoulder movement assistance. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 7, 315–324 (2025).
Jeong, J. et al. Soft wearable robot with shape memory alloy (SMA)-based artificial muscle for assisting with elbow flexion and forearm supination/pronation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 7, 6028–6035 (2022).
Park, W.-H., Shin, E.-J., Yun, S. & Kim, S.-Y. An enhanced soft vibrotactile actuator based on ePVC gel with silicon dioxide nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Haptics 11, 22–29 (2018).
Mun, S. et al. Electro-active polymer based soft tactile interface for wearable devices. IEEE Trans. Haptics 11, 15–21 (2018).
Grasso, G., Rosset, S. & Shea, H. Fully 3D-printed, stretchable, and conformable haptic interfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2213821 (2023).
Firouzeh, A., Mizutani, A., Groten, J., Zirkl, M. & Shea, H. PopTouch: a submillimeter thick dynamically reconfigured haptic interface with pressable buttons. Adv. Mater. 36, 2307636 (2024).
Zhu, M. et al. PneuSleeve: in-fabric multimodal actuation and sensing in a soft, compact, and expressive haptic sleeve. In Proc. 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems 1–12 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2020).
Sonar, H. A., Huang, J.-L. & Paik, J. Soft touch using soft pneumatic actuator–skin as a wearable haptic feedback device. Adv. Intell. Syst. 3, 2000168 (2021).
Young, E. M., Memar, A. H., Agarwal, P. & Colonnese, N. Bellowband: a pneumatic wristband for delivering local pressure and vibration. In 2019 IEEE World Haptics Conference (WHC) 55–60 (IEEE, 2019).
Mete, M., Jeong, H., Wang, W. D. & Paik, J. SORI: a softness-rendering interface to unravel the nature of softness perception. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 121, e2314901121 (2024). This article reports a haptic device that decouples kinaesthetic forces and cutaneous feedback experienced through contact area of the fingertip for accurate softness perception.
Robertson, M. A., Kara, O. C. & Paik, J. Soft pneumatic actuator-driven origami-inspired modular robotic “pneumagami”. Int. J. Robot. Res. 40, 72–85 (2021).
Mete, M. & Paik, J. Closed-loop position control of a self-sensing 3-DoF origami module with pneumatic actuators. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 6, 8213–8220 (2021).
Lu, J., Liu, Z., Brooks, J. & Lopes, P. Chemical haptics: rendering haptic sensations via topical stimulants. In The 34th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology 239–257 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2021).
Smith, M., Cacucciolo, V. & Shea, H. Fiber pumps for wearable fluidic systems. Science 379, 1327–1332 (2023).
Liu, D., Liu, L., Onck, P. R. & Broer, D. J. Reverse switching of surface roughness in a self-organized polydomain liquid crystal coating. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 3880–3885 (2015).
Ohzono, T., Norikane, Y., Saed, M. O. & Terentjev, E. M. Light-driven dynamic adhesion on photosensitized nematic liquid crystalline elastomers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 31992–31997 (2020).
Chossat, J.-B., Chen, D. K. Y., Park, Y.-L. & Shull, P. B. Soft wearable skin-stretch device for haptic feedback using twisted and coiled polymer actuators. IEEE Trans. Haptics 12, 521–532 (2019).
Leroy, E. & Shea, H. Hydraulically amplified electrostatic taxels (HAXELs) for full body haptics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 8, 2300242 (2023).
Yu, M. et al. A self-sensing soft pneumatic actuator with closed-loop control for haptic feedback wearable devices. Mater. Des. 223, 111149 (2022).
Lee, J. et al. Stretchable skin-like cooling/heating device for reconstruction of artificial thermal sensation in virtual reality. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1909171 (2020).
Oh, J. et al. A liquid metal based multimodal sensor and haptic feedback device for thermal and tactile sensation generation in virtual reality. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2007772 (2021).
Kim, S., Kim, P., Park, C.-Y. & Choi, S.-B. A new tactile device using magneto-rheological sponge cells for medical applications: experimental investigation. Sens. Actuators Phys. 239, 61–69 (2016).
Mintchev, S., Salerno, M., Cherpillod, A., Scaduto, S. & Paik, J. A portable three-degrees-of-freedom force feedback origami robot for human–robot interactions. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1, 584–593 (2019).
Giraud, F. H., Joshi, S. & Paik, J. Haptigami: a fingertip haptic interface with vibrotactile and 3-DoF cutaneous force feedback. IEEE Trans. Haptics 15, 131–141 (2022).
Salerno, M., Firouzeh, A. & Paik, J. A low profile electromagnetic actuator design and model for an origami parallel platform. J. Mech. Robot. 9, 041005 (2017).
Carpenter, C. W. et al. Healable thermoplastic for kinesthetic feedback in wearable haptic devices. Sens. Actuators Phys. 288, 79–85 (2019).
Zuliani, F. & Paik, J. Electromagnetic actuator design for distributed stiffness. Smart Mater. Struct. 31, 115023 (2022).
Miruchna, V. et al. GelTouch: localized tactile feedback through thin, programmable gel. In Proc. The 28th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software & Technology 3–10 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2015).
Mazursky, A., Koo, J.-H. & Yang, T.-H. A compact and compliant electrorheological actuator for generating a wide range of haptic sensations. Smart Mater. Struct. 29, 055028 (2020).
Wang, Z. et al. A three-fingered force feedback glove using fiber-reinforced soft bending actuators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 67, 7681–7690 (2020).
Hinchet, R. & Shea, H. High force density textile electrostatic clutch. Adv. Mater. Technol. 5, 1900895 (2020).
Jiang, Y. et al. Compact pneumatic clutch with integrated stiffness variation and position feedback. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 6, 5697–5704 (2021).
Kishishita, Y. et al. Muscleblazer: force-feedback suit for immersive experience. In 2019 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR) 1813–1818 (IEEE, 2019).
Hartmann, F., Baumgartner, M. & Kaltenbrunner, M. Becoming sustainable, the new frontier in soft robotics. Adv. Mater. 33, 2004413 (2021). This article discusses sustainable solutions in soft robotics, showcasing how eco-friendly designs can reduce environmental impact.
Han, L. et al. A mussel-inspired conductive, self-adhesive, and self-healable tough hydrogel as cell stimulators and implantable bioelectronics. Small 13, 1601916 (2017).
Kang, J. et al. Tough and water-insensitive self-healing elastomer for robust electronic skin. Adv. Mater. 30, 1706846 (2018).
Zhang, C., Lu, X., Wang, Z. & Xia, H. Progress in utilizing dynamic bonds to fabricate structurally adaptive self-healing, shape memory, and liquid crystal polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 43, 2100768 (2022).
Terryn, S. et al. A review on self-healing polymers for soft robotics. Mater. Today 47, 187–205 (2021).
Koh, L.-D. et al. Structures, mechanical properties and applications of silk fibroin materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 46, 86–110 (2015).
Thomas, B. et al. Nanocellulose, a versatile green platform: from biosources to materials and their applications. Chem. Rev. 118, 11575–11625 (2018).
Kim, H. C. et al. Renewable smart materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 25, 073001 (2016).
Lv, P., Lu, X., Wang, L. & Feng, W. Nanocellulose-based functional materials: from chiral photonics to soft actuator and energy storage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2104991 (2021).
Baumgartner, M. et al. Resilient yet entirely degradable gelatin-based biogels for soft robots and electronics. Nat. Mater. 19, 1102–1109 (2020). This article introduces a fully biodegradable, gelatin-based biogel that is highly resilient while exhibiting elastic characteristics.
Rumley, E. H. et al. Biodegradable electrohydraulic actuators for sustainable soft robots. Sci. Adv. 9, eadf5551 (2023).
Belke, C. H. & Paik, J. Mori: a modular origami robot. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 22, 2153–2164 (2017).
Zhang, C., Zhu, P., Lin, Y., Jiao, Z. & Zou, J. Modular soft robotics: modular units, connection mechanisms, and applications. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2, 1900166 (2020).
Jiao, P., Mueller, J., Raney, J. R., Zheng, X. R. & Alavi, A. H. Mechanical metamaterials and beyond. Nat. Commun. 14, 6004 (2023).
Tao, R. et al. Multi-material fused filament fabrication of flexible 3D piezoelectric nanocomposite lattices for pressure sensing and energy harvesting applications. Appl. Mater. Today 29, 101596 (2022).
Mokhtari, F. et al. Wearable electronic textiles from nanostructured piezoelectric fibers. Adv. Mater. Technol. 5, 1900900 (2020).
Quinsaat, J. E. Q. et al. Stretchable piezoelectric elastic composites for sensors and energy generators. Compos. B Eng. 198, 108211 (2020).
Dong, K., Peng, X. & Wang, Z. L. Fiber/fabric-based piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators for flexible/stretchable and wearable electronics and artificial intelligence. Adv. Mater. 32, 1902549 (2020).
He, X. et al. Three-dimensional flexible thermoelectric fabrics for smart wearables. Nat. Commun. 16, 2523 (2025).
Bandodkar, A. J. et al. Soft, stretchable, high power density electronic skin-based biofuel cells for scavenging energy from human sweat. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 1581–1589 (2017).
Vallem, V., Sargolzaeiaval, Y., Ozturk, M., Lai, Y.-C. & Dickey, M. D. Energy harvesting and storage with soft and stretchable materials. Adv. Mater. 33, 2004832 (2021).
Onal, C. D., Chen, X., Whitesides, G. M. & Rus, D. Soft mobile robots with on-board chemical pressure generation. In Robotics Research: The 15th International Symposium ISRR (eds Christensen, H. I. & Khatib, O.) 525–540 (Springer, 2017).
Qu, Y. et al. Programmable chemical reactions enable ultrastrong soft pneumatic actuation. Adv. Mater. 36, 2403954 (2024). This article explores programmable chemical reactions for soft pneumatic actuation to generate high-pressure gas in a portable, controllable and silent manner.
Chun, S. & Park, Y.-J. Air-Able: fabrication and experiments of effervescent fabric chamber inflation with various shape of structures and wearables. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 26, 477–485 (2025).
Villeda-Hernandez, M., Baker, B. C., Romero, C., Rossiter, J. M. & Faul, C. F. Soft alchemy: a comprehensive guide to chemical reactions for pneumatic soft actuation. Soft Sci. https://doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.52 (2024).
Loepfe, M., Schumacher, C. M., Lustenberger, U. B. & Stark, W. J. An untethered, jumping roly-poly soft robot driven by combustion. Soft Robot. 2, 33–41 (2015).
Bartlett, N. W. et al. A 3D-printed, functionally graded soft robot powered by combustion. Science 349, 161–165 (2015).
Fusi, G., Del Giudice, D., Skarsetz, O., Di Stefano, S. & Walther, A. Autonomous soft robots empowered by chemical reaction networks. Adv. Mater. 35, 2209870 (2023).
Wang, T., Fan, X., Koh, J. J., He, C. & Yeow, C.-H. Self-healing approach toward catalytic soft robots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 40590–40598 (2022).
Yoon, J. E. et al. Evaluation of gait-assistive soft wearable robot designs for wear comfort, focusing on electroencephalogram and satisfaction. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 9, 8834–8841 (2024).
Saifi, S. et al. An ultraflexible energy harvesting-storage system for wearable applications. Nat. Commun. 15, 6546 (2024).
Rajappan, A. et al. Logic-enabled textiles. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119, e2202118119 (2022).
Picella, S., van Riet, C. M. & Overvelde, J. T. B. Pneumatic coding blocks enable programmability of electronics-free fluidic soft robots. Sci. Adv. 10, eadr2433 (2024). This article introduces analogue pneumatic coding blocks to mimic software control statements for electronics-free soft robots to make autonomous decisions based on environmental interactions.
Wu, Q., Chen, B. & Wu, H. Neural-network-enhanced torque estimation control of a soft wearable exoskeleton for elbow assistance. Mechatronics 63, 102279 (2019).
Torricelli, D. et al. Benchmarking wearable robots: challenges and recommendations from functional, user experience, and methodological perspectives. Front. Robot. AI 7, 561774 (2020).
Meattini, R. et al. Robotic muscular assistance-as-needed for physical and training/rehabilitation tasks: design and experimental validation of a closed-loop myoelectric control in grounded and wearable applications. In Human-Friendly Robotics 2020: 13th International Workshop 16–30 (Springer, 2021).
Reinkensmeyer, D. J. et al. Computational neurorehabilitation: modeling plasticity and learning to predict recovery. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 13, 42 (2016).
Jin, T. et al. Triboelectric nanogenerator sensors for soft robotics aiming at digital twin applications. Nat. Commun. 11, 5381 (2020).
Hwang, T., Frank, Z., Neubauer, J. & Kim, K. J. High-performance polyvinyl chloride gel artificial muscle actuator with graphene oxide and plasticizer. Sci. Rep. 9, 9658 (2019).
Yip, M. C. & Niemeyer, G. High-performance robotic muscles from conductive nylon sewing thread. In 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2313–2318 (IEEE, 2015).
Paternò, L. & Lorenzon, L. Soft robotics in wearable and implantable medical applications: translational challenges and future outlooks. Front. Robot. AI https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2023.1075634 (2023).
Kapeller, A., Felzmann, H., Fosch-Villaronga, E. & Hughes, A.-M. A taxonomy of ethical, legal and social implications of wearable robots: an expert perspective. Sci. Eng. Ethics 26, 3229–3247 (2020).
Won, P. et al. Transparent soft actuators/sensors and camouflage skins for imperceptible soft robotics. Adv. Mater. 33, 2002397 (2021).
Barclay, C. J. in Muscle and Exercise Physiology (ed. Zoladz, J. A.) Ch. 6, 111–127 (Academic, 2019).
Acknowledgements
This article has been supported in part by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions (grant number 899987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.P. and A.v.O. conceptualized the focus of the Review. A.v.O. and M.A.R. conducted the literature search and analysis. All authors contributed to the writing and critical revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Bioengineering thanks Seung Hwan Ko, Cristina Santos and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
van Oosterhout, A., Robertson, M.A. & Paik, J. Soft robotics for personalized and sustainable wearables. Nat Rev Bioeng 4, 30–46 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222-025-00359-6
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222-025-00359-6