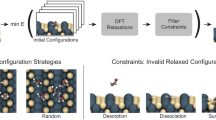
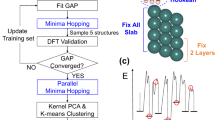
Abstract
Adsorbates often cover the surfaces of catalysts densely as they carry out reactions, dynamically altering their structure and reactivity. Understanding adsorbate-induced phenomena and harnessing them in our broader quest for improved catalysts is a substantial challenge that is only beginning to be addressed. Here we chart a path toward a deeper understanding of such phenomena by focusing on emerging in silico modeling methodologies, which will increasingly incorporate machine learning techniques. We first examine how adsorption on catalyst surfaces can lead to local and even global structural changes spanning entire nanoparticles, and how this affects their reactivity. We then evaluate current efforts and the remaining challenges in developing robust and predictive simulations for modeling such behavior. Last, we provide our perspectives in four critical areas—integration of artificial intelligence, building robust catalysis informatics infrastructure, synergism with experimental characterization, and adaptive modeling frameworks—that we believe can help surmount the remaining challenges in rationally designing catalysts in light of these complex phenomena.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao, F. & Goodman, D. W. Model catalysts: simulating the complexities of heterogeneous catalysts. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 63, 265–286 (2012).
Li, Z. et al. Well-defined materials for heterogeneous catalysis: from nanoparticles to isolated single-atom sites. Chem. Rev. 120, 623–682 (2020).
Groppo, E., Rojas-Buzo, S. & Bordiga, S. The role of in situ/operando IR spectroscopy in unraveling adsorbate-induced structural changes in heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 123, 12135–12169 (2023).
Liu, L. & Corma, A. Structural transformations of solid electrocatalysts and photocatalysts. Nat. Rev. Chem. 5, 256–276 (2021).
Kalz, K. F. et al. Future challenges in heterogeneous catalysis: understanding catalysts under dynamic reaction conditions. ChemCatChem 9, 17–29 (2017).
Zugic, B. et al. Dynamic restructuring drives catalytic activity on nanoporous gold–silver alloy catalysts. Nat. Mater. 16, 558–564 (2017).
Zhang, X. et al. Reversible loss of core–shell structure for Ni–Au bimetallic nanoparticles during CO2 hydrogenation. Nat. Catal. 3, 411–417 (2020).
Piccolo, L. Restructuring effects of the chemical environment in metal nanocatalysis and single-atom catalysis. Catal. Today 373, 80–97 (2021).
Liu, J., Hibbitts, D. & Iglesia, E. Dense CO adlayers as enablers of CO hydrogenation turnovers on Ru surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 11789–11802 (2017).
Ojeda, M. et al. CO activation pathways and the mechanism of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. J. Catal. 272, 287–297 (2010).
van Deelen, T. W., Hernández Mejía, C. & de Jong, K. P. Control of metal–support interactions in heterogeneous catalysts to enhance activity and selectivity. Nat. Catal. 2, 955–970 (2019).
Imbihl, R. & Ertl, G. Oscillatory kinetics in heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 95, 697–733 (1995).
Timoshenko, J. & Roldan Cuenya, B. In situ/operando electrocatalyst characterization by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Chem. Rev. 121, 882–961 (2021).
Zhu, Y., Wang, J., Chu, H., Chu, Y.-C. & Chen, H. M. In situ/operando studies for designing next-generation electrocatalysts. ACS Energy Lett. 5, 1281–1291 (2020).
Nørskov, J. K., Bligaard, T., Rossmeisl, J. & Christensen, C. H. Towards the computational design of solid catalysts. Nat. Chem. 1, 37–46 (2009).
Grajciar, L. et al. Towards operando computational modeling in heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47, 8307–8348 (2018).
Yang, Y. et al. Operando studies reveal active Cu nanograins for CO2 electroreduction. Nature 614, 262–269 (2023).
Zhang, J. et al. Sinter-resistant metal nanoparticle catalysts achieved by immobilization within zeolite crystals via seed-directed growth. Nat. Catal. 1, 540–546 (2018).
Liu, Y., Wang, S., Li, Z., Chu, H. & Zhou, W. Insight into the surface-reconstruction of metal-organic framework-based nanomaterials for the electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction. Coord. Chem. Rev. 484, 215117 (2023).
Horch, S. et al. Enhancement of surface self-diffusion of platinum atoms by adsorbed hydrogen. Nature 398, 134–136 (1999).
Parkinson, G. S. et al. Carbon monoxide-induced adatom sintering in a Pd-Fe3O4 model catalyst. Nat. Mater. 12, 724–728 (2013).
Wang, Y.-G., Mei, D., Glezakou, V.-A., Li, J. & Rousseau, R. Dynamic formation of single-atom catalytic active sites on ceria-supported gold nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 6, 6511 (2015).
Xu, L. et al. Formation of active sites on transition metals through reaction-driven migration of surface atoms. Science 380, 70–76 (2023).
Auer, A. et al. Self-activation of copper electrodes during CO electro-oxidation in alkaline electrolyte. Nat. Catal. 3, 797–803 (2020).
Tao, F. F. et al. Formation of second-generation nanoclusters on metal nanoparticles driven by reactant gases. Nano Lett. 16, 5001–5009 (2016).
Eren, B. et al. Activation of Cu(111) surface by decomposition into nanoclusters driven by CO adsorption. Science 351, 475–478 (2016).
Liu, L. et al. Generation of subnanometric platinum with high stability during transformation of a 2D zeolite into 3D. Nat. Mater. 16, 132–138 (2017).
Kumari, G., Kamarudheen, R., Zoethout, E. & Baldi, A. Photocatalytic surface restructuring in individual silver nanoparticles. ACS Catal. 11, 3478–3486 (2021).
Luo, Z., Zhao, G., Pan, H. & Sun, W. Strong metal–support interaction in heterogeneous catalysts. Adv. Energy Mater. 12, 2201395 (2022).
Beck, A. et al. The dynamics of overlayer formation on catalyst nanoparticles and strong metal-support interaction. Nat. Commun. 11, 3220 (2020).
Saavedra, J., Doan, H. A., Pursell, C. J., Grabow, L. C. & Chandler, B. D. The critical role of water at the gold–titania interface in catalytic CO oxidation. Science 345, 1599–1602 (2014).
Matsubu, J. C. et al. Adsorbate-mediated strong metal–support interactions in oxide-supported Rh catalysts. Nat. Chem. 9, 120–127 (2017).
He, Y., Zhang, J., Polo-Garzon, F. & Wu, Z. Adsorbate-induced strong metal-support interactions: implications for catalyst design. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14, 524–534 (2023).
Li, D. et al. Induced activation of the commercial Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst for the steam reforming of methanol. Nat. Catal. 5, 99–108 (2022).
Chen, P. C. et al. Chemical and structural evolution of AgCu catalysts in electrochemical CO2 reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 10116–10125 (2023).
Cui, C., Gan, L., Heggen, M., Rudi, S. & Strasser, P. Compositional segregation in shaped Pt alloy nanoparticles and their structural behaviour during electrocatalysis. Nat. Mater. 12, 765–771 (2013).
Andersson, K. J., Calle-Vallejo, F., Rossmeisl, J. & Chorkendorff, I. Adsorption-driven surface segregation of the less reactive alloy component. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 2404–2407 (2009).
Price, C. C., Singh, A., Frey, N. C. & Shenoy, V. B. Efficient catalyst screening using graph neural networks to predict strain effects on adsorption energy. Sci. Adv. 8, eabq5944 (2022).
Somorjai, G. A. Surface reconstruction and catalysis. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 45, 721–751 (1994).
Trunschke, A. et al. Towards experimental handbooks in catalysis. Top. Catal. 63, 1683–1699 (2020).
Gruznev, D. V., Zotov, A. V. & Saranin, A. A. Tailoring of spin-split metallic surface-state bands on silicon. J. Electron Spectros. Relat. Phenomena 201, 81–87 (2015).
Bondarenko, L. V. et al. Large spin splitting of metallic surface-state bands at adsorbate-modified gold/silicon surfaces. Sci. Rep. 3, 1826 (2013).
Ghosh, T. et al. Periodic structural changes in Pd nanoparticles during oscillatory CO oxidation reaction. Nat. Commun. 13, 6176 (2022).
Huang, J. et al. Potential-induced nanoclustering of metallic catalysts during electrochemical CO2 reduction. Nat. Commun. 9, 3117 (2018).
Gao, F. et al. Solvent‐mediated shell dimension reconstruction of core@shell PdAu@Pd nanocrystals for robust C1 and C2 alcohol electrocatalysis. Small 17, 2101428 (2021).
Chung, D. Y. et al. Dynamic stability of active sites in hydr(oxy)oxides for the oxygen evolution reaction. Nat. Energy 5, 222–230 (2020).
Zeng, R. et al. Origins of enhanced oxygen reduction activity of transition metal nitrides. Nat. Mater. 23, 1695–1703 (2024).
Yang, Y. et al. Dynamic evolution of copper nanowires during CO2 reduction probed by operando electrochemical 4D-STEM and X-ray spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 23398–23405 (2024).
Kuai, C. et al. Phase segregation reversibility in mixed-metal hydroxide water oxidation catalysts. Nat. Catal. 3, 743–753 (2020).
Liu, Q. Y., Shang, C. & Liu, Z. P. In situ active site for CO activation in Fe-catalyzed Fischer-Tropsch synthesis from machine learning. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 11109–11120 (2021).
Marimuthu, A., Zhang, J. & Linic, S. Tuning selectivity in propylene epoxidation by plasmon mediated photo-switching of Cu oxidation state. Science 340, 1590–1593 (2013).
Luo, S. et al. Light-induced dynamic restructuring of Cu active sites on TiO2 for low-temperature H2 production from methanol and water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 20530–20538 (2023).
Jiang, H. First-principles approaches for strongly correlated materials: a theoretical chemistry perspective. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 115, 722–730 (2015).
Liao, X. et al. Density functional theory for electrocatalysis. Energy Environ. Mater. 5, 157–185 (2022).
Samanta, B. et al. Challenges of modeling nanostructured materials for photocatalytic water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 51, 3794–3818 (2022).
Sauer, J. The future of computational catalysis. J. Catal. 433, 115482 (2024).
Chen, B. W. J., Xu, L. & Mavrikakis, M. Computational methods in heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 121, 1007–1048 (2021).
Rogal, J., Reuter, K. & Scheffler, M. First-principles statistical mechanics study of the stability of a subnanometer thin surface oxide in reactive environments: CO oxidation at Pd(100). Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 046101 (2007).
Gossenberger, F., Roman, T. & Groß, A. Hydrogen and halide co-adsorption on Pt(111) in an electrochemical environment: a computational perspective. Electrochim. Acta 216, 152–159 (2016).
Nørskov, J. K. et al. Origin of the overpotential for oxygen reduction at a fuel-cell cathode. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 17886–17892 (2004).
Li, W.-X., Stampfl, C. & Scheffler, M. Why is a noble metal catalytically active? The role of the O-Ag interaction in the function of silver as an oxidation catalyst. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 256102 (2003).
Wang, S. & Hensley, A. J. R. Probing the nanoscale driving forces for adsorbate-induced Rh50Pd50 nanoparticle reconstruction via mean-field models of multi-faceted nanoparticles. Catal. Sci. Technol. 14, 1122–1137 (2023).
Bajpai, A., Mehta, P., Frey, K., Lehmer, A. M. & Schneider, W. F. Benchmark first-principles calculations of adsorbate free energies. ACS Catal. 8, 1945–1954 (2018).
Sprowl, L. H., Campbell, C. T. & Árnadóttir, L. Hindered translator and hindered rotor models for adsorbates: partition functions and entropies. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 9719–9731 (2016).
Wulf, G. Zur Frage der Geschwindigkeit des Wachstums und der Auflösung von Krystallflächen. Z. Krist. 34, 449–530 (1901).
Jiang, Z., Qin, P. & Fang, T. Decomposition mechanism of formic acid on Cu(111) surface: a theoretical study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 396, 857–864 (2017).
Du, J., Meng, J., Li, X.-Y., Zhu, B. & Gao, Y. Multiscale atomistic simulation of metal nanoparticles under working conditions. Nanoscale Adv. 1, 2478–2484 (2019).
Chee, S. W., Arce-Ramos, J. M., Li, W., Genest, A. & Mirsaidov, U. Structural changes in noble metal nanoparticles during CO oxidation and their impact on catalyst activity. Nat. Commun. 11, 2133 (2020).
Cheula, R., Soon, A. & Maestri, M. Prediction of morphological changes of catalyst materials under reaction conditions by combined: ab initio thermodynamics and microkinetic modelling. Catal. Sci. Technol. 8, 3493–3503 (2018).
Cheula, R., Maestri, M. & Mpourmpakis, G. Modeling morphology and catalytic activity of nanoparticle ensembles under reaction conditions. ACS Catal. 10, 6149–6158 (2020).
Bussi, G. & Laio, A. Using metadynamics to explore complex free-energy landscapes. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2, 200–212 (2020).
Zhang, X.-J., Shang, C. & Liu, Z.-P. Stochastic surface walking reaction sampling for resolving heterogeneous catalytic reaction network: a revisit to the mechanism of water-gas shift reaction on Cu. J. Chem. Phys. 147, 152706 (2017).
Wales, D. J. & Doye, J. P. K. Global optimization by basin-hopping and the lowest energy structures of Lennard-Jones clusters containing up to 110 atoms. J. Phys. Chem. A 101, 5111–5116 (1997).
Wang, Y., Lv, J., Zhu, L. & Ma, Y. Crystal structure prediction via particle-swarm optimization. Phys. Rev. B 82, 094116 (2010).
Wexler, R. B., Qiu, T. & Rappe, A. M. Automatic prediction of surface phase diagrams using ab initio grand canonical Monte Carlo. J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 2321–2328 (2019).
Zhou, Y., Zhu, C., Scheffler, M. & Ghiringhelli, L. M. Ab initio approach for thermodynamic surface phases with full consideration of anharmonic effects: the example of hydrogen at Si(100). Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 246101 (2022).
Du, X. et al. Machine-learning-accelerated simulations to enable automatic surface reconstruction. Nat. Comput. Sci. 3, 1034–1044 (2023).
Ronne, N., Aspuru-Guzik, A. & Hammer, B. Generative diffusion model for surface structure discovery. Phys. Rev. B 110, 235427 (2024).
Groß, A. Challenges for ab initio molecular dynamics simulations of electrochemical interfaces. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 40, 101345 (2023).
Papanikolaou, K. G., Darby, M. T. & Stamatakis, M. Engineering the surface architecture of highly dilute alloys: an ab initio Monte Carlo approach. ACS Catal. 10, 1224–1236 (2020).
Foppa, L., Iannuzzi, M., Copéret, C. & Comas-Vives, A. Adlayer dynamics drives CO activation in Ru-catalyzed Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. ACS Catal. 8, 6983–6992 (2018).
Sun, J.-J. & Cheng, J. Solid-to-liquid phase transitions of sub-nanometer clusters enhance chemical transformation. Nat. Commun. 10, 5400 (2019).
Zhang, Z., Zandkarimi, B. & Alexandrova, A. N. Ensembles of metastable states govern heterogeneous catalysis on dynamic interfaces. Acc. Chem. Res. 53, 447–458 (2020).
Almithn, A. S. & Hibbitts, D. D. Supra-monolayer coverages on small metal clusters and their effects on H2 chemisorption particle size estimates. AIChE J. 64, 3109–3120 (2018).
Yang, Y., Shen, X. & Han, Y. F. Diffusion mechanisms of metal atoms in Pd-Au bimetallic catalyst under CO atmosphere based on ab initio molecular dynamics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 483, 991–1005 (2019).
Mager-Maury, C., Bonnard, G., Chizallet, C., Sautet, P. & Raybaud, P. H2-induced reconstruction of supported Pt clusters: metal–support interaction versus surface hydride. ChemCatChem 3, 200–207 (2011).
Chen, B. W. J., Zhang, X. & Zhang, J. Accelerating explicit solvent models of heterogeneous catalysts with machine learning interatomic potentials. Chem. Sci. 14, 8338–8354 (2023).
Yan, X. et al. A collaborative diffusion mechanism of multiple atoms during Cu-Ag bimetal surface reconstruction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 25, 10405–10416 (2023).
Owen, C. J. et al. Unraveling the catalytic effect of hydrogen adsorption on Pt nanoparticle shape-change. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.00901 (2023).
Lim, J. S., Molinari, N., Duanmu, K., Sautet, P. & Kozinsky, B. Automated detection and characterization of surface restructuring events in bimetallic catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 16332–16344 (2019).
Tappan, B. A., Barim, G., Kwok, J. C. & Brutchey, R. L. Utilizing diselenide precursors toward rationally controlled synthesis of metastable CuInSe2 nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 30, 5704–5713 (2018).
Mou, T., Han, X., Zhu, H. & Xin, H. Machine learning of lateral adsorbate interactions in surface reaction kinetics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 36, 100825 (2022).
Ghanekar, P. G., Deshpande, S. & Greeley, J. Adsorbate chemical environment-based machine learning framework for heterogeneous catalysis. Nat. Commun. 13, 5788 (2022).
Mou, T. et al. Bridging the complexity gap in computational heterogeneous catalysis with machine learning. Nat. Catal. 6, 122–136 (2023).
Wang, Y., Su, Y. Q., Hensen, E. J. M. & Vlachos, D. G. Insights into supported subnanometer catalysts exposed to CO via machine-learning-enabled multiscale modeling. Chem. Mater. 34, 1611–1619 (2022).
Piccinin, S. & Stamatakis, M. CO oxidation on Pd(111): a first-principles-based kinetic Monte Carlo study. ACS Catal. 4, 2143–2152 (2014).
Sumaria, V., Nguyen, L., Tao, F. F. & Sautet, P. Atomic-scale mechanism of platinum catalyst restructuring under a pressure of reactant gas. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 392–401 (2023).
Sun, G. & Sautet, P. Metastable structures in cluster catalysis from first-principles: structural ensemble in reaction conditions and metastability triggered reactivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 2812–2820 (2018).
Owen, C. J., Xie, Y., Johansson, A., Sun, L. & Kozinsky, B. Low-index mesoscopic surface reconstructions of Au surfaces using Bayesian force fields. Nat. Commun. 15, 3790 (2024).
Unke, O. T. et al. Learning force fields with electronic degrees of freedom and nonlocal effects. Nat. Commun. 12, 7273 (2021).
Noé, F., Olsson, S., Köhler, J. & Wu, H. Boltzmann generators: sampling equilibrium states of many-body systems with deep learning. Science 365, 6457 (2019).
Jain, M. et al. GFlowNets for AI-driven scientific discovery. Digit. Discov. 2, 557–577 (2023).
Kim, S., Noh, J., Gu, G. H., Aspuru-Guzik, A. & Jung, Y. Generative adversarial networks for crystal structure prediction. ACS Cent. Sci. 6, 1412–1420 (2020).
Zeni, C. et al. A generative model for inorganic materials design. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-08628-5 (2025).
Cherevko, S. et al. Oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions on Ru, RuO2, Ir and IrO2 thin film electrodes in acidic and alkaline electrolytes: a comparative study on activity and stability. Catal. Today 262, 170–180 (2016).
Otor, H. O., Steiner, J. B., García-Sancho, C. & Alba-Rubio, A. C. Encapsulation methods for control of catalyst deactivation: a review. ACS Catal. 10, 7630–7656 (2020).
Li, C. W., Ciston, J. & Kanan, M. W. Electroreduction of carbon monoxide to liquid fuel on oxide-derived nanocrystalline copper. Nature 508, 504–507 (2014).
Mariano, R. G., McKelvey, K., White, H. S. & Kanan, M. W. Selective increase in CO2 electroreduction activity at grain-boundary surface terminations. Science 358, 1187–1192 (2017).
Stamenkovic, V. R., Mun, B. S., Mayrhofer, K. J. J., Ross, P. N. & Markovic, N. M. Effect of surface composition on electronic structure, stability and electrocatalytic properties of Pt-transition metal alloys: Pt-skin versus Pt-skeleton surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 8813–8819 (2006).
Tuinier, R. et al. Tuning the activity of Pt alloy electrocatalysts by means of the lanthanide contraction. Science 352, 73–76 (2016).
Mufan Li et al. Ultrafine jagged platinum nanowires enable ultrahigh mass activity for the oxygen reduction reaction. Science 354, 1410–1414 (2016).
Zhao, S. et al. Structural transformation of highly active metal–organic framework electrocatalysts during the oxygen evolution reaction. Nat. Energy 5, 881–890 (2020).
Ding, H., Liu, H., Chu, W., Wu, C. & Xie, Y. Structural transformation of heterogeneous materials for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction. Chem. Rev. 121, 13174–13212 (2021).
Li, T. et al. Atomic-scale insights into surface species of electrocatalysts in three dimensions. Nat. Catal. 1, 300–305 (2018).
Sun, H. et al. Hierarchical structure of CuO nanowires decorated with Ni(OH)2 supported on Cu foam for hydrogen production via urea electrocatalysis. Small Methods 6, 1–11 (2022).
Wu, T. et al. Iron-facilitated dynamic active-site generation on spinel CoAl2O4 with self-termination of surface reconstruction for water oxidation. Nat. Catal. 2, 763–772 (2019).
Zandkarimi, B. & Alexandrova, A. N. Dynamics of subnanometer Pt clusters can break the scaling relationships in catalysis. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10, 460–467 (2019).
Löffler, T., Ludwig, A., Rossmeisl, J. & Schuhmann, W. What makes high-entropy alloys exceptional electrocatalysts? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 26894–26903 (2021).
Cepitis, R., Ivaništšev, V., Rossmeisl, J. & Kongi, N. Bypassing the scaling relations in oxygen electrocatalysis with geometry-adaptive catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 14, 2105–2113 (2024).
Li, J. et al. Self-adaptive dual-metal-site pairs in metal–organic frameworks for selective CO2 photoreduction to CH4. Nat. Catal. 4, 719–729 (2021).
Szilvási, T., Chen, B. W. J. & Mavrikakis, M. Identification of stable adsorption sites and diffusion paths on nanocluster surfaces: an automated scanning algorithm. npj Comput. Mater. 5, 101 (2019).
Boes, J. R., Mamun, O., Winther, K. & Bligaard, T. Graph theory approach to high-throughput surface adsorption structure generation. J. Phys. Chem. A 123, 2281–2285 (2019).
Kolluru, A. & Kitchin, J. R. AdsorbDiff: adsorbate placement via conditional denoising diffusion. Proc. Mach. Learn. Res. 235, 25042–25057 (2024).
Lan, J. et al. AdsorbML: a leap in efficiency for adsorption energy calculations using generalizable machine learning potentials. npj Comput. Mater. 9, 172 (2023).
Margraf, J. T., Jung, H., Scheurer, C. & Reuter, K. Exploring catalytic reaction networks with machine learning. Nat. Catal. 6, 112–121 (2023).
Choksi, T. S., Roling, L. T., Streibel, V. & Abild-Pedersen, F. Predicting adsorption properties of catalytic descriptors on bimetallic nanoalloys with site-specific precision. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10, 1852–1859 (2019).
Greeley, J. Theoretical heterogeneous catalysis: scaling relationships and computational catalyst design. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 7, 605–635 (2016).
Calle-Vallejo, F., Loffreda, D., Koper, M. T. M. & Sautet, P. Introducing structural sensitivity into adsorption-energy scaling relations by means of coordination numbers. Nat. Chem. 7, 403–410 (2015).
Ma, X. & Xin, H. Orbitalwise coordination number for predicting adsorption properties of metal nanocatalysts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 036101 (2017).
Hammer, B. & Nørskov, J. K. Electronic factors determining the reactivity of metal surfaces. Surf. Sci. 343, 211–220 (1995).
Schumann, J., Stamatakis, M., Michaelides, A. & Réocreux, R. Ten-electron count rule for the binding of adsorbates on single-atom alloy catalysts. Nat. Chem. 16, 749–754 (2024).
Chen, B. W. J. & Mavrikakis, M. Formic acid: a hydrogen-bonding cocatalyst for formate decomposition. ACS Catal. 10, 10812–10825 (2020).
Martínez-Suarez, L., Siemer, N., Frenzel, J. & Marx, D. Reaction network of methanol synthesis over Cu/ZnO nanocatalysts. ACS Catal. 5, 4201–4218 (2015).
Yang, X., Bhowmik, A., Vegge, T. & Hansen, H. A. Neural network potentials for accelerated metadynamics of oxygen reduction kinetics at Au-water interfaces. Chem. Sci. 14, 3913–3922 (2023).
Kim, S., Woo, J. & Kim, W. Y. Diffusion-based generative AI for exploring transition states from 2D molecular graphs. Nat. Commun. 15, 341 (2024).
Foscato, M. & Jensen, V. R. Automated in silico design of homogeneous catalysts. ACS Catal. 10, 2354–2377 (2020).
Xu, L. & Henkelman, G. Adaptive kinetic Monte Carlo for first-principles accelerated dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 129, 114104 (2008).
Zhang, X. J., Shang, C. & Liu, Z. P. Double-ended surface walking method for pathway building and transition state location of complex reactions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 9, 5745–5753 (2013).
Kang, P. L., Shang, C. & Liu, Z. P. Glucose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural: origin of site-selectivity resolved by machine learning based reaction sampling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 20525–20536 (2019).
Kang, P. L., Shi, Y. F., Shang, C. & Liu, Z. P. Artificial intelligence pathway search to resolve catalytic glycerol hydrogenolysis selectivity. Chem. Sci. 13, 8148–8160 (2022).
Shayesteh Zadeh, A., Khan, S. A., Vandervelden, C. & Peters, B. Site-averaged ab initio kinetics: importance learning for multistep reactions on amorphous supports. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 19, 2873–2886 (2023).
Sun, G., Fuller, J. T., Alexandrova, A. N. & Sautet, P. Global activity search uncovers reaction induced concomitant catalyst restructuring for alkane dissociation on model Pt catalysts. ACS Catal. 11, 1877–1885 (2021).
Chen, D., Shang, C. & Liu, Z.-P. Machine-learning atomic simulation for heterogeneous catalysis. npj Comput. Mater. 9, 2 (2023).
Schilter, O., Vaucher, A., Schwaller, P. & Laino, T. Designing catalysts with deep generative models and computational data. A case study for Suzuki cross coupling reactions. Digit. Discov. 2, 728–735 (2023).
Peng, J. et al. Human- and machine-centred designs of molecules and materials for sustainability and decarbonization. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7, 991–1009 (2022).
Bort, W. et al. Discovery of novel chemical reactions by deep generative recurrent neural network. Sci. Rep. 11, 3178 (2021).
Esterhuizen, J. A., Goldsmith, B. R. & Linic, S. Interpretable machine learning for knowledge generation in heterogeneous catalysis. Nat. Catal. 5, 175–184 (2022).
Weng, B. et al. Simple descriptor derived from symbolic regression accelerating the discovery of new perovskite catalysts. Nat. Commun. 11, 3513 (2020).
Miyazaki, R., Belthle, K. S., Tüysüz, H., Foppa, L. & Scheffler, M. Materials genes of CO2 hydrogenation on supported cobalt catalysts: an artificial intelligence approach integrating theoretical and experimental data. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 5433–5444 (2024).
Behler, J. & Parrinello, M. Generalized neural-network representation of high-dimensional potential-energy surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 146401 (2007).
Bartók, A. P., Payne, M. C., Kondor, R. & Csányi, G. Gaussian approximation potentials: the accuracy of quantum mechanics, without the electrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 136403 (2010).
Batatia, I., Kovács, D. P., Simm, G. N. C., Ortner, C. & Csányi, G. MACE: higher order equivariant message passing neural networks for fast and accurate force fields. In Proc. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems Vol. 35 (eds Koyejo, S. et al.) 11423–11436 (Curran Associates, 2022).
Batzner, S. et al. E(3)-equivariant graph neural networks for data-efficient and accurate interatomic potentials. Nat. Commun. 13, 2453 (2022).
Ko, T. W., Finkler, J. A., Goedecker, S. & Behler, J. General-purpose machine learning potentials capturing nonlocal charge transfer. Acc. Chem. Res. 54, 808–817 (2021).
Ko, T. W., Finkler, J. A., Goedecker, S. & Behler, J. A fourth-generation high-dimensional neural network potential with accurate electrostatics including non-local charge transfer. Nat. Commun. 12, 398 (2021).
Gubler, M., Finkler, J. A., Schäfer, M. R., Behler, J. & Goedecker, S. Accelerating fourth-generation machine learning potentials using quasi-linear scaling particle mesh charge equilibration. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 20, 7264–7271 (2015).
Frank, J. T., Unke, O. T. & Müller, K. R. So3krates: equivariant attention for interactions on arbitrary length-scales in molecular systems. In Proc. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems Vol. 35 (eds Koyejo, S. et al.) 29400–29413 (Curran Associates, 2022).
Jumper, J. et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 596, 583–589 (2021).
Schimka, L. et al. Accurate surface and adsorption energies from many-body perturbation theory. Nat. Mater. 9, 741–744 (2010).
Ramakrishnan, R., Dral, P. O., Rupp, M. & von Lilienfeld, O. A. Big data meets quantum chemistry approximations: the Δ-machine learning approach. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 11, 2087–2096 (2015).
Zaverkin, V., Holzmüller, D., Bonfirraro, L. & Kästner, J. Transfer learning for chemically accurate interatomic neural network potentials. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 25, 5383–5396 (2023).
Kim, J. et al. Data-efficient multi-fidelity training for high-fidelity machine learning interatomic potentials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 147, 1042–1054 (2025).
Zhao, Z. J. et al. Importance of metal–oxide interfaces in heterogeneous catalysis: a combined DFT, microkinetic and experimental study of water-gas shift on Au/MgO. J. Catal. 345, 157–169 (2017).
Bergmann, A. & Roldan Cuenya, B. Operando insights into nanoparticle transformations during catalysis. ACS Catal. 9, 10020–10043 (2019).
Santos, K. et al. Breaking the molecular dynamics timescale barrier using a wafer-scale system. In Proc. SC24: International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis 8 (IEEE, 2024).
Noh, J. et al. Inverse design of solid-state materials via a continuous representation. Matter 1, 1370–1384 (2019).
Xie, T., Fu, X., Ganea, O.-E., Barzilay, R. & Jaakkola, T. Crystal diffusion variational autoencoder for periodic material generation. In Proc. ICLR 2022—10th International Conference on Learning Representations (OpenReview.net, 2021).
Zhao, Y. et al. Physics guided deep learning for generative design of crystal materials with symmetry constraints. npj Comput. Mater. 9, 38 (2023).
Su, Y. et al. Automation and machine learning augmented by large language models in a catalysis study. Chem. Sci. 15, 12200–12233 (2024).
Ock, J., Guntuboina, C. & Barati Farimani, A. Catalyst energy prediction with CatBERTa: unveiling feature exploration strategies through large language models. ACS Catal. 13, 16032–16044 (2023).
Qi, J., Ko, T. W., Wood, B. C., Pham, T. A. & Ong, S. P. Robust training of machine learning interatomic potentials with dimensionality reduction and stratified sampling. npj Comput. Mater. 10, 43 (2024).
Montes de Oca Zapiain, D. et al. Training data selection for accuracy and transferability of interatomic potentials. npj Comput. Mater. 8, 189 (2022).
Bernstein, N., Csányi, G. & Deringer, V. L. De novo exploration and self-guided learning of potential-energy surfaces. npj Comput. Mater. 5, 99 (2019).
van der Oord, C., Sachs, M., Kovács, D. P., Ortner, C. & Csányi, G. Hyperactive learning for data-driven interatomic potentials. npj Comput. Mater. 9, 168 (2023).
Schwalbe-Koda, D., Tan, A. R. & Gómez-Bombarelli, R. Differentiable sampling of molecular geometries with uncertainty-based adversarial attacks. Nat. Commun. 12, 5104 (2021).
Hirschfeld, L., Swanson, K., Yang, K., Barzilay, R. & Coley, C. W. Uncertainty quantification using neural networks for molecular property prediction. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 60, 3770–3780 (2020).
Tan, A. R., Urata, S., Goldman, S., Dietschreit, J. C. B. & Gómez-Bombarelli, R. Single-model uncertainty quantification in neural network potentials does not consistently outperform model ensembles. npj Comput. Mater. 9, 225 (2023).
Xu, L. & Mavrikakis, M. Structure sensitivity in adsorbate-induced adatom formation on FCC transition-metal surfaces. J. Catal. 431, 115373 (2024).
Evans, M. L. et al. Developments and applications of the OPTIMADE API for materials discovery, design and data exchange. Digit. Discov. 3, 1509–1533 (2024).
Chanussot, L. et al. Open Catalyst 2020 (OC20) dataset and community challenges. ACS Catal. 2021, 6059–6072 (2020).
Draxl, C. & Scheffler, M. The NOMAD Laboratory: from data sharing to artificial intelligence. J. Phys. Mater. 2, 036001 (2019).
Winther, K. T. et al. Catalysis-Hub.Org, an open electronic structure database for surface reactions. Sci. Data 6, 75 (2019).
Wellendorff, J. et al. A benchmark database for adsorption bond energies to transition metal surfaces and comparison to selected DFT functionals. Surf. Sci. 64, 36–44 (2019).
Burte, A. et al. CatTestHub: a benchmarking database of experimental heterogeneous catalysis for evaluating advanced materials. J. Catal. 442, 115902 (2025).
Salmeron, M. & Eren, B. High-pressure scanning tunneling microscopy. Chem. Rev. 121, 962–1006 (2021).
Yao, L., Ou, Z., Luo, B., Xu, C. & Chen, Q. Machine learning to reveal nanoparticle dynamics from liquid-phase TEM videos. ACS Cent. Sci. 6, 1421–1430 (2020).
Chen, M. et al. In-situ/operando Raman techniques for in-depth understanding on electrocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 461, 141939 (2023).
Frenkel, A. I. et al. Critical review: effects of complex interactions on structure and dynamics of supported metal catalysts. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 32, 020801 (2014).
Lim, J. S. et al. Evolution of metastable structures at bimetallic surfaces from microscopy and machine-learning molecular dynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 15907–15916 (2020).
Meldgaard, S. A., Mortensen, H. L., Jørgensen, M. S. & Hammer, B. Structure prediction of surface reconstructions by deep reinforcement learning. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 32, 404005 (2020).
Kwon, H. et al. Spectroscopy-guided discovery of three-dimensional structures of disordered materials with diffusion models. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol 5, 045037 (2024).
Bhandari, S., Rangarajan, S. & Mavrikakis, M. Combining computational modeling with reaction kinetics experiments for elucidating the in situ nature of the active site in catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 53, 1893–1904 (2020).
Sabadell-Rendón, A. et al. Automated multiscale simulation environment. Digit. Discov. 2, 1721–1732 (2023).
Bruix, A., Margraf, J. T., Andersen, M. & Reuter, K. First-principles-based multiscale modelling of heterogeneous catalysis. Nat. Catal. 2, 659–670 (2019).
Matera, S. et al. Evidence for the active phase of heterogeneous catalysts through in situ reaction product imaging and multiscale modeling. ACS Catal. 5, 4514–4518 (2015).
Matera, S., Maestri, M., Cuoci, A. & Reuter, K. Predictive-quality surface reaction chemistry in real reactor models: integrating first-principles kinetic Monte Carlo simulations into computational fluid dynamics. ACS Catal. 4, 4081–4092 (2014).
Wehinger, G. D. et al. Quo vadis multiscale modeling in reaction engineering? A perspective. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 184, 39–58 (2022).
Acknowledgements
B.W.J.C. is grateful for support by the A*STAR SERC Central Research Fund award. Work at UW-Madison was supported by the US Department of Energy, Basic Energy Sciences (DOE-BES), Division of Chemical Sciences, Catalysis Science Program, grant number DE-FG02-05ER15731. We used resources at the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center, a DOE Office of Science User Facility supported by the Office of Science of the US Department of Energy under contract no. DE-AC02-05CH11231 using NERSC award number BES-ERCAP0032205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.W.J.C. and M.M. contributed to the conceptualization and writing of the original draft, and review and editing of the final paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Chemical Engineering thanks Hongliang Xin and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, B.W.J., Mavrikakis, M. Modeling the impact of structure and coverage on the reactivity of realistic heterogeneous catalysts. Nat Chem Eng 2, 181–197 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44286-025-00179-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44286-025-00179-w