Abstract
Study design:
Case series from a prospectively acquired database and phone survey.
Objectives:
To assess the efficacy of upper limb reanimation (ULR) protocols on acquisition of intermittent self-catheterization (ISC) in C5–C7 ASIA tetraplegic patients.
Setting:
University Hospital, Paris, France.
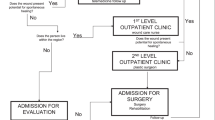
Methods:
A prospectively acquired database of 152 tetraplegic patients followed in ULR consultation between 1997 and 2008 in a rehabilitation unit was studied. A total of 20 patients met the inclusion criteria, which mainly were traumatic C5–C7 tetraplegic adult patients who were unable to perform ISC, and who benefited from ULR with the objectives of improving hand abilities and of ISC acquisition, through urethral orifice for males or via a continent urinary stoma for females. The main outcome measure was ISC acquisition (ISC+) proportion. Population characteristics and secondary outcome measures: ISC+/ISC− patients were compared regarding epidemiological and surgical data, key-grip strength, patient global improvement score, activities of daily living and quality of life (PGI-I, Wuolle questionnaire, verbal rating scale).
Results:
ISC+ was 75%. It depended on key-grip strength (P<0.05) and led to a statistically significant improvement of urinary status compared with ISC− patients (P<0.01). ULR improved patients’ abilities and QoL in both ISC+ and ISC− patients.
Conclusion:
ULR protocols allow ISC in most C5–C7 tetraplegic patients. Multidisciplinary care with surgeons and PRM physicians improves patients’ vital and functional prognosis by changing their urological-management method.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Cardenas DD, Hoffman JM, Kirshblum S, McKinley W . Etiology and incidence of rehospitalization after traumatic spinal cord injury: a multicenter analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2004; 85: 1757–1763.
Snoek GJ, Ijzerman MJ, Hermens HJ, Maxwell D, Biering-Sorensen F . Survey of the needs of patients with spinal cord injury: impact and priority for improvement in hand function in tetraplegics. Spinal Cord 2004; 42: 526–532.
Lapides J, Diokno AC, Silber SJ, Lowe BS . Clean, intermittent self-catheterization in the treatment of urinary tract disease. J Urol 1972; 107: 458–461.
Weld KJ, Dmochowski RR . Effect of bladder management on urological complications in spinal cord injured patients. J Urol 2000; 163: 768–772.
Killorin W, Gray M, Bennett JK, Green BG . The value of urodynamics and bladder management in predicting upper urinary tract complications in male spinal cord injury patients. Paraplegia 1992; 30: 437–441.
Zommick JN, Simoneau AR, Skinner DG, Ginsberg DA . Continent lower urinary tract reconstruction in the cervical spinal cord injured population. J Urol 2003; 169: 2184–2187.
Karsenty G, Chartier-Kastler E, Mozer P, Even-Schneider A, Denys P, Richard F . A novel technique to achieve cutaneous continent urinary diversion in spinal cord-injured patients unable to catheterize through native urethra. Spinal Cord 2008; 46: 305–310.
Asayama K, Kihara K, Shidoh T, Shigaki M, Ikeda T . The functional limitations of tetraplegic hands for intermittent clean self-catheterisation. Paraplegia 1995; 33: 30–33.
Kiyono Y, Hashizume C, Ohtsuka K, Igawa Y . Improvement of urological-management abilities in individuals with tetraplegia by reconstructive hand surgery. Spinal Cord 2000; 38: 541–545.
Moberg E . Surgical treatment for absent single-hand grip and elbow extension in quadriplegia. Principles and preliminary experience. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1975; 57: 196–206.
Revol M, Cormerais A, Laffont I, Pedelucq JP, Dizien O, Servant JM . Tendon transfers as applied to tetraplegia. Hand Clin 2002; 18: 423–439.
Vaynman S, Gomez-Pinilla F . License to run: exercise impacts functional plasticity in the intact and injured central nervous system by using neurotrophins. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 2005; 19: 283–295.
Mohammed KD, Rothwell AG, Sinclair SW, Willems SM, Bean AR . Upper-limb surgery for tetraplegia. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1992; 74: 873–879.
Wuolle KS, Bryden AM, Peckham PH, Murray PK, Keith M . Satisfaction with upper-extremity surgery in individuals with tetraplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2003; 84: 1145–1149.
Hashizume C, Fukui J . Improvement of upper limb function with respect to urination techniques in quadriplegia. Paraplegia 1994; 32: 354–357.
Maynard Jr FM, Bracken MB, Creasey G, Ditunno Jr JF, Donovan WH, Ducker TB et al. International Standards for Neurological and Functional Classification of Spinal Cord Injury. American Spinal Injury Association. Spinal Cord 1997; 35: 266–274.
McDowell CL, Moberg EA, Smith AG . International conference on surgical rehabilitation of the upper limb in tetraplegia. J Hand Surg Am 1979; 4: 387–390.
Boirel E, Vaultier S . Experience of an evaluation tool in occupational therapy for the choice of an urinary diversion. Ergotherapies 2008; 29: 57–64.
Yalcin I, Bump RC . Validation of two global impression questionnaires for incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003; 189: 98–101.
Studenski S, Hayes RP, Leibowitz RQ, Bode R, Lavery L, Walston J et al. Clinical Global Impression of Change in Physical Frailty: development of a measure based on clinical judgment. J Am Geriatr Soc 2004; 52: 1560–1566.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernuz, B., Guinet, A., Rech, C. et al. Self-catheterization acquisition after hand reanimation protocols in C5–C7 tetraplegic patients. Spinal Cord 49, 313–317 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2010.120
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2010.120
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
How many spinal cord injury patients can catheterize their own bladder? The epidemiology of upper extremity function as it affects bladder management
Spinal Cord (2016)
-
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in the Elderly
Current Bladder Dysfunction Reports (2015)
-
Intermittent self-catheterization in tetraplegic patients: a 6-year experience gained in the spinal cord unit in Prague
Spinal Cord (2014)