Abstract
Study design:
A cross-sectional experimental study.
Objective:
The purpose of this study is to examine the benefit of elastic abdominal binders on voluntary cough in persons with spinal cord injury.
Setting:
Spinal rehabilitation unit in a teaching hospital.
Methods:
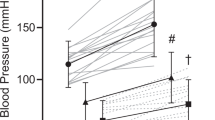
We measured voluntary cough peak expiratory flow rate (in 21 subjects with spinal cord injury, (18 tetraplegia, 3 paraplegia) under three conditions: without abdominal binder as the baseline, with single-strap abdominal binder and triple-strap abdominal binder.
Results:
The results showed that the mean cough peak expiratory flow rate in all subjects without abdominal binder was 277.1 l per min. There was a significant increase in flow rate with the use of abdominal binders: 325.7 l per min with single-strap abdominal binder and 345.2 l per min with triple-strap abdominal binder (P<0.05, paired t-test). The mean cough peak expiratory flow rate in tetraplegic subjects using triple-strap abdominal binders was significantly higher compared with those using single-strap abdominal binders (322.1 l per min and 299.4 l per min, respectively).
Conclusion:
Abdominal binders can be used as an effective method to improve cough ability in spinal cord injured patients, with triple-strap abdominal binder achieving greater cough peak expiratory flows.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Winslow C, Rozovsky J . Effect of spinal cord injury on the respiratory system. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2003; 82: 803–814.
DeVivo MJ, Black KJ, Stover SL . Causes of death the first 12 years after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1993; 74: 248–254.
De Vivo MJ, Krause JS, Lammertse DP . Recent trends in mortality and causes of death among persons with spinal cord injury. Arch Phy Med Rehabil 1999; 80: 1411–1419.
Estenne M, De Troyer A . Cough in tetraplegic subjects: an active process. Ann Intern Med 1990; 112: 22–28.
De Troyer A, Estenne M, Heilporn A . Mechanism of active expiration in tetraplegic subjects. N Engl J Med 1986; 314: 700–744.
Fujiwara T, Hara Y, Chino N . Expiratory function in complete tetraplegics: study of spirometry, maximal expiratory pressure, and muscle activity of pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi muscles. Am J Phy Med Rehabil 1999; 78: 464–469.
Jaeger RJ, Turba RM, Yarkony GM, Roth EJ . Cough in spinal cord injured patients: comparison of three methods to produce cough. Arch Phy Med Rehabil 1993; 74: 1358–1361.
Kirby NA, Banerias MJ, Siebens AA . An evaluation of assisted cough in quadriparetic patients. Arch Phy Med Rehabil 1966; 47: 705–710.
Estenne M, Van Muylem A, gorini M, Kinnear W, Heilporn A, De troyer A . Effects of abdominal strapping on forced expiration in tetraplegic patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998; 157: 95–98.
Goldman JM, Rose LS, Williams SJ, Silver JR, Denison DM . Effects of abdominal binders on breathing in tetraplegic patients. Thorax 1986; 41: 940–945.
Boaventura CM, Gastaldi AC, Silveira JM, Santos PR, Guimaraes RC, De Lima LC . Effect of an abdominal binder on the efficacy of respiratory muscles in seated and supine tetraplegic patients. Physiotherapy 2003; 89: 290–295.
Maloney FP . Pulmonary function in quadriplegia: effects of a corset. Arch Phy Med Rehabil 1979; 60: 261–265.
Bodin P, Olsen MF, Bake B, Kreuter M . Effects of abdominal binding on breathing patterns during breathing exercises in persons with tetraplegia. Spinal Cord 2005; 43: 117–122.
Lin K-H, Lai Y-L, Wu H-D, Wang T-Q, Wang Y-H . Effects of an abdominal binder and electrical stimulation on cough in patients with spinal cord injury. J Formos Med Assoc 1998; 97: 292–295.
Linder SH . Functional electrical stimulation to enhance cough in quadriplegia. Chest 1993; 103: 166–169.
Lin VWH, Hsieh C, Hsiao IN, Canfield J . Functional magnetic stimulation of expiratory muscles: a non-invasive and new method for restoring cough. J Appl Phy 1998; 84: 1144–1150.
Lin VWH, Singh H, Chitkara RK, Perkash I . Functional magnetic stimulation for restoring cough in patients with tetraplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1998; 79: 517–522.
Shapiro SM, Handler JM, Ogirala RG, Aldrich TK, Shapiro MB . An evaluation of the accuracy of Assess and MiniWright Peak Flowmeters. Chest 1991; 99: 358–362.
Leiner GC, Abramovitz S, Small MJ, Stenby VB . Cough peak flow rate. Am J Med Sci 1966; 251: 211–214.
Braun SR, Giovannoni R, O’Connor M . Improving the cough in patients with spinal cord injury. Am J Phys Med 1984; 63: 1–10.
Lin KH, Chuang CC, Wu HD, Chang CW, Kou YR . Abdominal weights and inspiratory resistance: their immediate effects on inspiratory muscle functions during maximal voluntary breathing in chronic tetraplegic patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1999; 80: 741–745.
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the short-term project grant from University Malaya, Malaysia; IPPP/UPDiT/Geran(PJP)/F0169/2005A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Julia, P., Sa'ari, M. & Hasnan, N. Benefit of triple-strap abdominal binder on voluntary cough in patients with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 49, 1138–1142 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2011.53
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2011.53
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Acute Cervical Spinal Cord Injury: A Literature Review
Dysphagia (2022)
-
Question of Stamina for the Diaphragm
Spinal Cord (2012)