Abstract
Infantile spasms (ISS) are an epilepsy disorder frequently associated with severe developmental outcome and have diverse genetic etiologies. We ascertained 11 subjects with ISS and novel copy number variants (CNVs) and combined these with a new cohort with deletion 1p36 and ISS, and additional published patients with ISS and other chromosomal abnormalities. Using bioinformatics tools, we analyzed the gene content of these CNVs for enrichment in pathways of pathogenesis. Several important findings emerged. First, the gene content was enriched for the gene regulatory network involved in ventral forebrain development. Second, genes in pathways of synaptic function were overrepresented, significantly those involved in synaptic vesicle transport. Evidence also suggested roles for GABAergic synapses and the postsynaptic density. Third, we confirm the association of ISS with duplication of 14q12 and maternally inherited duplication of 15q11q13, and report the association with duplication of 21q21. We also present a patient with ISS and deletion 7q11.3 not involving MAGI2. Finally, we provide evidence that ISS in deletion 1p36 may be associated with deletion of KLHL17 and expand the epilepsy phenotype in that syndrome to include early infantile epileptic encephalopathy. Several of the identified pathways share functional links, and abnormalities of forebrain synaptic growth and function may form a common biologic mechanism underlying both ISS and autism. This study demonstrates a novel approach to the study of gene content in subjects with ISS and copy number variation, and contributes further evidence to support specific pathways of pathogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lux AL, Osborne JP : A proposal for case definitions and outcome measures in studies of infantile spasms and West syndrome: consensus statement of the West Delphi group. Epilepsia 2004; 45: 1416–1428.
Saemundsen E, Ludvigsson P, Rafnsson V : Risk of autism spectrum disorders after infantile spasms: a population-based study nested in a cohort with seizures in the first year of life. Epilepsia 2008; 49: 1865–1870.
Saitsu H, Kato K, Mizuguchi T et al: De novo mutations in the gene encoding STXBP1 (MUNC18-1) cause early infantile epileptic encephalopathy. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 782–788.
Strømme P, Mangelsdorf ME, Scheffer IE, Gécz J : Infantile spasms, dystonia, and other X-linked phenotypes caused by mutations in Aristaless related homeobox gene, ARX. Brain Dev 2002; 24: 266–268.
Kato M, Das S, Petras K, Sawaishi Y, Dobyns WB : Polyalanine expansion of ARX associated with cryptogenic West syndrome. Neurology 2003; 61: 267–276.
Weaving LS, Christodoulou J, Williamson SL et al: Mutations of CDKL5 cause a severe neurodevelopmental disorder with infantile spasms and mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 1079–1093.
Marshall CR, Young EJ, Pani AM et al: Infantile spasms is associated with deletion of the MAGI2 gene on chromosome 7q11.23-q21.11. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 83: 106–111.
Yeung A, Bruno D, Scheffer IE et al: 4.45 Mb microduplication in chromosome band 14q12 including FOXG1 in a girl with refractory epilepsy and intellectual impairment. Eur J Med Genet 2009; 52: 440–442.
Le Meur N, Holder-Espinasse M, Jaillard S et al: MEF2C haploinsufficiency caused by either microdeletion of the 5q14.3 region or mutation is responsible for severe mental retardation with stereotypic movements, epilepsy and/or cerebral malformations. J Med Genet 2010; 47: 22–29.
Saitsu H, Tohyama J, Kumada T et al: Dominant-negative mutations in alpha-II spectrin cause West syndrome with severe cerebral hypomyelination, spastic quadriplegia, and developmental delay. Am J Hum Genet 2010; 86: 881–891.
Brunetti-Pierri N, Paciorkowski AR, Ciccone R et al: Duplications of FOXG1 in 14q12 are associated with developmental epilepsy, mental retardation, and severe speech impairment. Eur J Hum Genet 2011; 19: 102–107.
Ding Y, Zhang Y, He B, Yue W, Zhang D, Zou L : A possible association of responsiveness to adrenocorticotropic hormone with specific GRIN1 haplotypes in infantile spasms. Dev Med Child Neurol 2010; 52: 1028–1032.
Endele S, Rosenberger G, Geider K et al: Mutations in GRIN2A and GRIN2B encoding regulatory subunits of NMDA receptors cause variable neurodevelopmental phenotypes. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 1021–1026.
Molinari F, Kaminska A, Fiermonte G et al: Mutations in the mitochondrial glutamate carrier SLC25A22 in neonatal epileptic encephalopathy with suppression bursts. Clin Genet 2009; 76: 188–194.
Hébert JM, Fishell G : The genetics of early telencephalon patterning: some assembly required. Nat Rev Neurosci 2008; 9: 678–685.
Colasante G, Sessa A, Crispi S et al: Arx acts as a regional key selector gene in the ventral telencephalon mainly through its transcriptional repression activity. Dev Biol 2009; 334: 59–71.
Fulp CT, Cho G, Marsh ED, Nasrallah IM, Labosky PA, Golden JA : Identification of Arx transcriptional targets in the developing basal forebrain. Hum Mol Genet 2008; 17: 3740–3760.
Ciufo LF, Barclay JW, Burgoyne RD, Morgan A : Munc18-1 regulates early and late stages of exocytosis via syntaxin-independent protein interactions. Mol Biol Cell 2005; 16: 470–482.
Deng F, Price MG, Davis CF, Mori M, Burgess DL : Stargazin and other transmembrane AMPA receptor regulating proteins interact with synaptic scaffolding protein MAGI-2 in brain. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 7875–7884.
Voas MG, Lyons DA, Naylor SG, Arana N, Rasband MN, Talbot WS : AlphaII-spectrin is essential for assembly of the nodes of Ranvier in myelinated axons. Curr Biol 2007; 17: 562–568.
Fan J, Vasuta OC, Zhang LY, Wang L, George A, Raymond LA : N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit- and neuronal-type dependence of excitotoxic signaling through post-synaptic density 95. J Neurochem 2010; 115: 1045–1056.
Craig AM, Kang Y : Neurexin-neuroligin signaling in synapse development. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2007; 17: 43–52.
Durand CM, Betancur C, Boeckers TM et al: Mutations in the gene encoding the synaptic scaffolding protein SHANK3 are associated with autism spectrum disorders. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 25–27.
Arking DE, Cutler DJ, Brune CW et al: A common genetic variant in the neurexin superfamily member CNTNAP2 increases familial risk of autism. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 82: 160–164.
Huang ZJ, Scheiffele P : GABA and neuroligin signaling: linking synaptic activity and adhesion in inhibitory synapse development. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2008; 18: 77–83.
Zhang C, Milunsky JM, Newton S et al: A neuroligin-4 missense mutation associated with autism impairs neuroligin-4 folding and endoplasmic reticulum export. J Neurosci 2009; 29: 10843–10854.
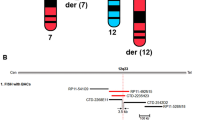
Gajecka M, Glotzbach CD, Jarmuz M, Ballif BC, Shaffer LG : Identification of cryptic imbalance in phenotypically normal and abnormal translocation carriers. Eur J Hum Genet 2006; 14: 1255–1262.
Jensen LJ, Kuhn M, Stark M et al: STRING 8—a global view on proteins and their functional interactions in 630 organisms. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37: D412–D416.
Brohée S, van Helden J : Evaluation of clustering algorithms for protein-protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics 2006; 7: 488.
Heilstedt HA, Burgess DL, Anderson AE et al: Loss of the potassium channel beta-subunit gene, KCNAB2, is associated with epilepsy in patients with 1p36 deletion syndrome. Epilepsia 2001; 42: 1103–1111.
Rosenfeld JA, Crolla JA, Tomkins S et al: Refinement of causative genes in monosomy 1p36 through clinical and molecular cytogenetic characterization of small interstitial deletions. Am J Med Genet A 2010; 152A: 1951–1959.
Thienpont B, Mertens L, Buyse G, Vermeesch JR, Devriendt K : Left-ventricular non-compaction in a patient with monosomy 1p36. Eur J Med Genet 2007; 50: 233–236.
Oishi K, Watatani K, Itoh Y et al: Selective induction of neocortical GABAergic neurons by the PDK1-Akt pathway through activation of Mash1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 13064–13069.
Salinas GD, Blair LA, Needleman LA et al: Actinfilin is a Cul3 substrate adaptor, linking GluR6 kainate receptor subunits to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 40164–40173.
Berg JS, Potocki L, Bacino CA : Common recurrent microduplication syndromes: diagnosis and management in clinical practice. Am J Med Genet A 2010; 152A: 1066–1078.
Huang N, Lee I, Marcotte EM, Hurles ME : Characterising and predicting haploinsufficiency in the human genome. PLoS Genet 2010; 6: e1001154.
Djukic A, Lado FA, Shinnar S, Moshé SL : Are early myoclonic encephalopathy (EME) and the Ohtahara syndrome (EIEE) independent of each other? Epilepsy Res 2006; 70 (Suppl 1): S68–S76.
Philippi H, Wohlrab G, Bettendorf U et al: Electroencephalographic evolution of hypsarrhythmia: toward an early treatment option. Epilepsia 2008; 49: 1859–1864.
Depienne C, Moreno-De-Luca D, Heron D et al: Screening for genomic rearrangements and methylation abnormalities of the 15q11-q13 region in autism spectrum disorders. Biol Psychiatry 2009; 66: 349–359.
Marsh E, Fulp C, Gomez E et al: Targeted loss of Arx results in a developmental epilepsy mouse model and recapitulates the human phenotype in heterozygous females. Brain 2009; 132: 1563–1576.
Price MG, Yoo JW, Burgess DL et al: A triplet repeat expansion genetic mouse model of infantile spasms syndrome, Arx(GCG)10+7, with interneuronopathy, spasms in infancy, persistent seizures, and adult cognitive and behavioral impairment. J Neurosci 2009; 29: 8752–8763.
Cobos I, Calcagnotto ME, Vilaythong AJ et al: Mice lacking Dlx1 show subtype-specific loss of interneurons, reduced inhibition and epilepsy. Nat Neurosci 2005; 8: 1059–1068.
Lee S, Walker CL, Wevrick R : Prader-Willi syndrome transcripts are expressed in phenotypically significant regions of the developing mouse brain. Gene Expr Patterns 2003; 3: 599–609.
Frost JD, Hrachovy RA : Pathogenesis of infantile spasms: a model based on developmental desynchronization. J Clin Neurophysiol 2005; 22: 25–36.
Boczan J, Leenders AGM, Sheng Z : Phosphorylation of syntaphilin by cAMP-dependent protein kinase modulates its interaction with syntaxin-1 and annuls its inhibitory effect on vesicle exocytosis. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 18911–18919.
Kang J, Tian JH, Pan PY et al: Docking of axonal mitochondria by syntaphilin controls their mobility and affects short-term facilitation. Cell 2008; 132: 137–148.
Andreyeva A, Leshchyns’ka I, Knepper M et al: CHL1 is a selective organizer of the presynaptic machinery chaperoning the SNARE complex. PLoS One 2010; 5: e12018.
Passafaro M, Sala C, Niethammer M, Sheng M : Microtubule binding by CRIPT and its potential role in the synaptic clustering of PSD-95. Nat Neurosci 1999; 2: 1063–1069.
Valtschanoff JG, Weinberg RJ : Laminar organization of the NMDA receptor complex within the postsynaptic density. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 1211–1217.
Röthlisberger B, Hoigné I, Huber AR, Brunschwiler W, Capone Mori A : Deletion of 7q11.21-q11.23 and infantile spasms without deletion of MAGI2. Am J Med Genet A 2010; 152A: 434–437.
Komoike Y, Fujii K, Nishimura A et al: Zebrafish gene knockdowns imply roles for human YWHAG in infantile spasms and cardiomegaly. Genesis 2010; 48: 233–243.
Neddens J, Buonanno A : Selective populations of hippocampal interneurons express ErbB4 and their number and distribution is altered in ErbB4 knockout mice. Hippocampus 2010; 20: 724–744.
Zhao Y, Flandin P, Long JE, Cuesta MD, Westphal H, Rubenstein JL : Distinct molecular pathways for development of telencephalic interneuron subtypes revealed through analysis of Lhx6 mutants. J Comp Neurol 2008; 510: 79–99.
Glykys J, Mann EO, Mody I : Which GABA(A) receptor subunits are necessary for tonic inhibition in the hippocampus? J Neurosci 2008; 28: 1421–1426.
Costa V, Conte I, Ziviello C et al: Identification and expression analysis of novel Jakmip1 transcripts. Gene 2007; 402: 1–8.
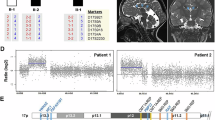
Bahi-Buisson N, Guttierrez-Delicado E, Soufflet C et al: Spectrum of epilepsy in terminal 1p36 deletion syndrome. Epilepsia 2008; 49: 509–515.
Chen Y, Derin R, Petralia RS, Li M : Actinfilin, a brain-specific actin-binding protein in postsynaptic density. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 30495–30501.
Dobyns WB, Mirzaa G, Christian SL et al: Consistent chromosome abnormalities identify novel polymicrogyria loci in 1p36.3, 2p16.1-p23.1, 4q21.21-q22.1, 6q26-q27, and 21q2. Am J Med Genet A 2008; 146A: 1637–1654.
Saito Y, Kubota M, Kurosawa K et al: Polymicrogyria and infantile spasms in a patient with 1p36 deletion syndrome. Brain Dev 2011; 33: 437–441.
Gajecka M, Glotzbach CD, Shaffer LG : Characterization of a complex rearrangement with interstitial deletions and inversion on human chromosome 1. Chromosome Res 2006; 14: 277–282.
Kubo T, Kakinuma H, Nakamura T, Kitatani M, Ozaki M, Takahashi H : Infantile spasms in a patient with partial duplication of chromosome 2p. Clin Genet 1999; 56: 93–94.
Gérard-Blanluet M, Romana S, Munier C et al: Classical West ‘syndrome’ phenotype with a subtelomeric 4p trisomy. Am J Med Genet A 2004; 130A: 299–302.
Schneider A, Benzacken B, Guichet A et al: Molecular cytogenetic characterization of terminal 14q32 deletions in two children with an abnormal phenotype and corpus callosum hypoplasia. Eur J Hum Genet 2008; 16: 680–687.
Auvin S, Holder-Espinasse M, Lamblin M, Andrieux J : Array-CGH detection of a de novo 0.7-Mb deletion in 19p13.13 including CACNA1A associated with mental retardation and epilepsy with infantile spasms. Epilepsia 2009; 50: 2501–2503.
Backx L, Ceulemans B, Vermeesch JR, Devriendt K, Van Esch H : Early myoclonic encephalopathy caused by a disruption of the neuregulin-1 receptor ErbB4. Eur J Hum Genet 2009; 17: 378–382.
Bursztejn AC, Bronner M, Peudenier S, Gregoire MJ, Jonveaux P, Nemos C : Molecular characterization of a monosomy 1p36 presenting as an Aicardi syndrome phenocopy. Am J Med Genet A 2009; 149A: 2493–2500.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the families of the subjects who enrolled in this study. The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health including NINDS Neurologic Sciences Academic Development Award K12 NS001690-12 to ARP and R01-NS046616 to WBD; Washington University Children's Discovery Institute, Grant MD-F-2010-62 to ARP; and the Ministry of Education and Science, Poland, Grant NN 301238836 to MG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paciorkowski, A., Thio, L., Rosenfeld, J. et al. Copy number variants and infantile spasms: evidence for abnormalities in ventral forebrain development and pathways of synaptic function. Eur J Hum Genet 19, 1238–1245 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.121
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.121
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
KLHL17/Actinfilin, a brain-specific gene associated with infantile spasms and autism, regulates dendritic spine enlargement
Journal of Biomedical Science (2020)
-
6q22.1 microdeletion and susceptibility to pediatric epilepsy
European Journal of Human Genetics (2015)
-
Genomic analysis identifies candidate pathogenic variants in 9 of 18 patients with unexplained West syndrome
Human Genetics (2015)
-
A genomic copy number variant analysis implicates the MBD5 and HNRNPUgenes in Chinese children with infantile spasms and expands the clinical spectrum of 2q23.1 deletion
BMC Medical Genetics (2014)
-
Genotype–phenotype correlation in interstitial 6q deletions: a report of 12 new cases
neurogenetics (2012)