Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the outcome of universal newborn eye screening with wide-field digital retinal imaging (WFDRI) system.
Methods
In this pilot study, we examined 1152 apparently healthy newborn infants in the obstetrics and gynecology ward of a civil hospital in Eastern India over 1.5 years. The examination included external eye examination, red reflex test and fundus imaging by WFDRI (RetCam II, Clarity medical system, Pleasanton, CA, USA) by a trained optometrist. The pathologies detected, net monetary gain and skilled manpower saved were documented. The results were compared with three similar studies thus far published in the literature.
Results
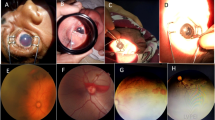
Ocular abnormality of any kind was seen in 172 (14.93%) babies. Retinal hemorrhage in 153 babies (88.9% of all abnormal findings) was the most common abnormality; it was bilateral in 118 (77.12%) babies and 4 babies had foveal hemorrhage. Other abnormalities included vitreous hemorrhage (n=1), congenital glaucoma (n=2), uveal coloboma (n=2), retinopathy mimicking retinopathy of prematurity (n=2), and cystic fovea (n=3). The retinal hemorrhages resolved spontaneously in all eyes. One baby with congenital glaucoma received surgery and the other was treated medically. The benefits included savings in skilled manpower, a net monetary gain of INR 4.195 million (US$ 62,612) and skilled manpower saving by 319.4 h.
Conclusions
The universal neonatal eye screening using WFDRI detected pathologies that needed immediate care or regular follow up; saved skilled manpower with a net monetary gain. But compared to a red reflex test the benefits were marginal in terms of detecting treatment warranting ocular pathologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Castillo-Riquelme MC, Lord J, Moseley MJ, Fielder AR, Haines L . Cost-effectiveness of digital photographic screening for retinopathy of prematurity in the United Kingdom. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 2004; 20 (2): 201–213.
Martínez Rubio M, Moya Moya M, Bellot Bernabé A, Belmonte Martínez J . Diabetic retinopathy screening and teleophthalmology. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol 2012; 87 (12): 392–395.
Jones S, Edwards RT . Diabetic retinopathy screening: A systematic review of the economic evidence. Diabet Med 2010; 27 (3): 249–256.
Census India. Govt of India Ministry of Home Affairs-Census report. Compendium of India’s Fertility and Mortality Indicators, based on SRS,1971-2013. Accessed at http://www.censusindia.gov.in/vital_statistics/Compendium/Srs_data.html.on 9 Dec 2016.
Li L-H, Li N, Zhao JY, Fei P, Zhang GM, Mao JB et al. Findings of perinatal ocular examination performed on 3573, healthy full-term newborns. Br J Ophthalmol 2013; 97 (5): 588–591.
Vinekar A, Govindaraj I, Jayadev C, Kumar AK, Sharma P, Mangalesh S et al. Universal ocular screening of 1021 term infants using wide-field digital imaging in a single public hospital in India - A pilot study. Acta Ophthalmol 2015; 93 (5): e372–e376.
Callaway NF, Ludwig CA, Blumenkranz MS, Jones JM, Fredrick DR, Moshfeghi DM . Retinal and optic nerve hemorrhages in the newborn infant: One-Year Results of the Newborn Eye Screen Test Study. Ophthalmology 2016; 123: 1043–1052.
Kaur B, Taylor D . Fundus hemorrhages in infancy. Surv Ophthalmol 1992; 37 (1): 1–17.
Zhao Q, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Li Z, Lin Y, Liu R et al. Birth-related retinal hemorrhages in healthy full-term newborns and their relationship to maternal, obstetric, and neonatal risk factors. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2015; 253 (7): 1021–1025.
Luo R, Liu J, Hu P, Cheng SS, Shi BZ, Zhu JH et al. Results of 779 cases of neonatal fundus screening and risk factors for neonatal fundus diseases. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2014; 16 (12): 1197–1201.
Padhi T, Rath S, Jalali S, Pradhan L, Kesarwani S, Nayak M et al. Larger and near-term baby retinopathy: a rare case series. Eye 2014; 29 (2): 286–289.
Cabrera MT, Maldonado RS, Toth CA, O'Connell RV, Chen BB, Chiu SJ et al. Subfoveal fluid in healthy full-term newborns observed by handheld spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 2012; 153 (1): 167–175.e3.
Lee AC, Maldonado RS, Sarin N, O'Connell RV, Wallace DK, Freedman SF et al. Macular features from spectral-domain optical coherence tomography as an adjunct to indirect ophthalmoscopy in retinopathy of prematurity. Retina 2011; 31 (8): 1470–1482.
Ganesh A, Khalighi M, Hammersmith K, Levin AV . Spontaneously resolving macular cyst in an infant. Oman J Ophthalmol 2013; 6 (3): 203–205.
Abramson DH, Du TT, Beaverson KL, Sciences C . (Neonatal) retinoblastoma in the first month of life. Arch Ophthalmol 2002; 120 (6): 738–742.
Acknowledgements
The LV Prasad eye institute receives funding for ROP related programs from Orbis international, Sight savers International, Queen Elizabeth Diamond Jubilee Trust, Miriam Hyman Children’s Eye Care Center and other philanthropists. These funding agencies are not involved directly in the present study and none of the authors get paid directly by them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Eye website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, P., Padhi, T., Das, T. et al. Outcome of universal newborn eye screening with wide-field digital retinal image acquisition system: a pilot study. Eye 32, 67–73 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2017.129
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2017.129
This article is cited by
-
Universal eye screening: perinatal risk factors and ocular abnormalities in 1795 newborns not meeting retinopathy of prematurity criteria
Eye (2024)
-
Incomplete retinal vascularization with retinopathy of prematurity-like ridges in healthy full-term newborns
International Ophthalmology (2023)
-
Design of English video course platform based on machine learning and Sobel algorithm
Soft Computing (2023)
-
Neonatal eye screening for 203 healthy term new-borns using a wide-field digital retinal imaging system
BMC Ophthalmology (2021)
-
Universal newborn eye screening: an effective strategy to improve ocular health?
Eye (2018)