Abstract
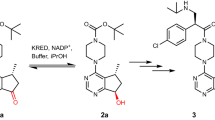
This protocol describes the step-by-step procedures for the efficient assembly of bidentate inhibitor libraries of a target enzyme, using the so-called 'click chemistry' between an alkyne-bearing core group and an azide-modified peripheral group, followed by direct biological screening for the identification of potential 'hits'. The reaction is highlighted by its modularity, high efficiency (∼100% yield in most cases) and tolerance toward many functional groups present in the fragments, as well as biocompatibility (typically carried out in aqueous conditions with small amounts of biocompatible catalysts). The approach consists of three steps: (i) chemical synthesis of alkyne-bearing protein tyrosine phosphatase or matrix metalloprotease core groups and diverse azide-modified peripheral groups; (ii) click chemistry to assemble the bidentate inhibitor libraries; and (iii) direct screening of the libraries with target enzymes using 384-well microplate assays. Following the chemical synthesis of the core and peripheral groups and optimization of the click chemistry conditions (∼1 week), steps (ii) and (iii) take 3 d to complete (∼1–2 d for library assembly and 1 d for inhibitor screening).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, H., Chattopadhaya, S., Wang, J. & Yao, S.Q. Recent development in microarray-based enzyme assays: from functional annotation to substrate/inhibitor fingerprinting. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 386, 416–426 (2006).
Christensen, C. & Meldal, M. Peptidotriazoles on solid phase: [1,2,3]-triazoles by regiospecific copper(I)-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions of terminal alkynes to azides. J. Org. Chem. 67, 3057–3062 (2002).
Rostovtsev, V.V., Green, L.G., Fokin, V.V. & Sharpless, K.B. A stepwise huisgen cycloaddition process: copper(I)-catalyzed regioselective 'Ligation' of azides and terminal alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 41, 2596–2599 (2002).
Kolb, H.C., Finn, M.G. & Sharpless, K.B. Click chemistry: diverse chemical function from a few good reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 40, 2004–2021 (2001).
Kolb, H.C. & Sharpless, K.B. The growing impact of click chemistry on drug discovery. Drug Disc. Today 8, 1128–1137 (2003).
Szczepankiewicz, B.G. et al. Discovery of a potent, selective protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitor using a linked-fragment strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 4087–4096 (2003).
Erlanson, D.A. et al. Site-directed ligand discovery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 9367–9372 (2000).
Hunter, T. Signaling—2000 and beyond. Cell 100, 113–127 (2000).
Johnson, T.O., Ermolieff, J. & Jirousek, M.R. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors for diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Disc. 1, 696–709 (2002).
Zhang, Z.-Y. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: prospects for therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 5, 416–423 (2001).
Fazio, F., Bryan, M.C., Blixt, O., Paulson, J.C. & Wong, C.-H. Synthesis of sugar arrays in microtiter plate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 14397–14402 (2002).
Wu, C.Y., Chang, C.-F., Chen, J.S.-Y., Wong, C.-H. & Lin, C.-H. Rapid diversity-oriented synthesis in microtiter plates for in situ screening: discovery of potent and selective α-fucosidase inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 42, 4661–4664 (2003).
Brik, A., Wu, C.Y. & Wong, C.-H. Microtiter plate based chemistry and in situ screening: a useful approach for rapid inhibitor discovery. Org. Biomol. Chem. 4, 1446–1457 (2006).
Srinivasan, R., Uttamchandani, M. & Yao, S.Q. Rapid assembly and in situ screening of bidentate inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs). Org. Lett. 8, 713–716 (2006).
Liu, G. et al. Fragment screening and assembly: a highly efficient approach to a selective and cell active protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 46, 4232–4235 (2003).
Whittaker, M., Floyd, C.D., Brown, P. & Gearing, A.J.H. Design and therapeutic application of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Chem. Rev. 99, 2735–2776 (1999).
Overall, C.M. & Kleifeld, O. Validating matrix metalloproteinases as drug targets and anti-targets for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 227–239 (2006).
Wang, J., Uttamchandani, M., Li, J., Hu, M. & Yao, S.Q. Rapid assembly of matrix metalloprotease (MMP) inhibitors using click chemistry. Org. Lett. 8, 3821–3824 (2006).
Still, W.C., Kahn, M. & Mitra, A. Rapid chromatographic techniques for preparative separation with moderate resolution. J. Org. Chem. 43, 2923–2925 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasan, R., Li, J., Ng, S. et al. Methods of using click chemistry in the discovery of enzyme inhibitors. Nat Protoc 2, 2655–2664 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.323
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.323