Abstract
Introduction CariesCare International (CCI) is a practice-friendly, health outcomes-focused, patient-centred, risk-based approach to caries management designed for the practice. The unfeasibility of a randomised clinical trial and of aerosol generating procedures (AGPs) during the COVID-19 pandemic to test the caries control effectiveness of CCI shifted it to a non-AGP, reduced on-site consultation, single-interventional study.
Aim This 12-month, multicentre, single-group, interventional study aimed at primarily assessing the control of caries progression of a pandemic CCI-adapted protocol in children.
Methods In total, 17 centres (n≥ 20, 3-8-year-old children/centre) were included. Trained examiners assessed (baseline: T0; one-year follow-up: T1y): CCI caries risk; oral health-related behaviours; decayed, missing and filled teeth (primary, permanent) with the epidemiological merged International Caries Detection and Assessment System (severity, activity); dental sepsis; and toothache. Trained practitioners performed one-year CCI-adapted personalised care. Dental care process acceptance was assessed in parents and dentists.
Results A total of 16 centres finished the study (n = 337, 78.6%; mean age: 5.5 ± 1.6 years). There was a T0-T1y decrease in the mean number of combined primary and permanent tooth surfaces with caries lesions (8.4 ± 9.7 to 6.2 ± 7.6), with most children showing control of caries progression (75.1%), high caries risk (86.6%) and non-adequate oral-health behaviour (72.7%) (p <0.05). CCI acceptance was very high in parents and high/very high in dentists.
Discussion The limitations given by the pandemic challenges, the single-interventional study design, and the non-AGP and reduced in-office-consultation adaptations, might as well highlight the shown caries progression control, feasibility and acceptance of CCI.
Conclusion The one-year implementation of CCI showed control of caries progression and of risk and high acceptance among parents and dentists.
Key points
-
CariesCare International controlled caries progression in children.
-
CariesCare International reduced high caries risk in children.
-
CariesCare International could be successfully implemented during the COVID-19 pandemic.
-
Children's parents and dentists liked the principles of CariesCare International.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The 2020 World Health Organization's (WHO's) Oral global report shows an estimated global average prevalence of caries (cavitated) of primary teeth of 43% and permanent teeth, 29%.1 Even though caries management has recently been defined as ‘actions taken to interfere with mineral loss at all stages of the caries disease, including non-operative and operative interventions/treatments',2 the traditional course of action focuses on reparative approaches.3 Several approaches, including the caries management system, CariesCare International (CCI), have been developed to further help overcoming ongoing barriers, which have prevented the translation of caries management best practices into dental practice.4,5,6,7,8,9
CCI was derived in 2019 from International Caries Classification and Management System (ICCMS).8,10 It uses adapted evidence-based International Caries Detection and Assessment System (ICDAS) and ICCMS tools and resources,11 sharing the same principles and goals with ICCMS. CCI is a practice-friendly, health outcomes-focused, patient-centred, risk-based approach to caries management, designed for the practice in four steps, namely the CCI 4D cycle:
-
1D) Determine caries risk
-
2D) Detect caries lesions, stage their severity and assess their activity status
-
3D) Decide a personalised care plan, including risk-based intervals
-
4D) Do the preventive and tooth-preserving care, which includes risk-appropriate preventive care, control of initial non-cavitated lesions, and conservative restorative treatment of deep dentinal and cavitated caries lesions.8,9
Concepts of CCI, as well as of ICDAS and ICCMS, are being followed globally in many settings, with local adaptations, including a large number of dental schools and undergraduates' cariology-curriculum frameworks in Colombia, the USA and Caribbean countries,12,13,14 among others. ICCMS concepts have been encouraged by the FDI World Dental Federation to be followed,15 and ICCMS has shown to be used for caries management in the practice and dental schools.16
Cariologists, clinicians, educators and policymakers agree that the CCI consensus guide promotes best practice in the control of caries and in maintaining oral health in patients,8,9 also helping to raise awareness in public health, industry and the profession, and to promote a cavity-free future.5
To our knowledge, there are no studies to date which have reported on the caries progression control of CCI. In 2020, a collaborating group of 21 centres in 13 countries attempted to conduct a 12-month, multicentre, pragmatic randomised controlled trial (RCT) in schoolchildren to compare the CCI system versus standard care in the control of tooth-level and individual caries progression.17 Plans had to be revised due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the consequent restrictions imposed by universities' ethical boards in conducting RCTs. To make it feasible to offer caries care to children, we modified CCI protocols by avoiding aerosol generating procedures (AGPs) and reducing in-office appointment time (CCI-adapted) (Fig. 1).17 Furthermore, we modified the study design from a pragmatic RCT to a single-group interventional study.17 All of the original 21 centres were willing to attempt the revised study and were invited to participate having received the new CCI-adapted protocol. After internal discussions, 17 centres agreed to participate with ethics committee approval, while four centres abstained from participation: the two American centres were receiving periodical additional ethics committee amendments which could not be supplied; the university hospital in the United Kingdom was already conducting non-AGP on children, and the Netherlands centre lost interest.
Aim
This 12-month, multicentre, single-group, interventional study aimed at primarily assessing the control of caries progression of a pandemic CCI-adapted protocol in children.
Methods
This was a 12-month, multicentre, single-group, interventional study, with ethics committee approval from the lead centre's Research Ethics Institutional Committee of Universidad El Bosque (PCI2019-10718).
This report follows the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology guidelines (as they can take the form of a cohort study), and it has been registered in the Clinical Trials website (retrospectively-registered-ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04666597 07/12/2020; Protocol version 2: https://register.clinicaltrials.gov/prs/app/action/SelectProtocol?sid=S000AGM4&selectaction= Edit&uid=U00019IE&ts=2&cx=uwje3h).
The sample size (previously described in the study protocol)17 was determined from that calculated for the RCT, based on a caries care system similar to CCI, considering caries lesion care according to their severity and activity status, as well as individual caries risk.18 Their results showed differences in averages of tooth surfaces with caries progression. The Whitehead sample size calculation formula was used (type I error: 0.05; type II error: 10%; standard deviation: 2.5; expected average of the first and second groups: 1.3 and 2.1, respectively).18 Due to the pandemic health system and research restrictions, no control arm was sustainable in any centre and we achieved ethics committee approval to conduct a single-group interventional study. Thus, the original sample was halved. Despite this adjustment, a total of 258 participants was targeted, accounting for a 25% dropout rate, ensuring statistical robustness for detecting differences in caries progression.
Three- to eight-year-old children's parents of 17 centres (dental schools/private clinics) in ten countries (Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Dominican Republic, France, Mexico, Peru, Portugal, Russia and Uruguay) were invited to the study from routine dental visits to participate. The following exclusions applied: children with a major systemic disease, mental/physical disability, with orthodontic appliances, or whose family had plans to move city or dental practice during the study period. All invited children, regardless of their caries risk or caries status, were to be included in the study, with consent signed by parents/caregivers and written assent forms signed by children from all countries (as requested by regulatory guidelines), except the Dominican Republic. Subjects were coded to maintain confidentiality.
Training of dental examiners and dental practitioners
Centres either counted with a recent trained examiner in the ICDAS visual caries criteria or the local centres' leaders trained for the study by employing the ICDAS calibration e-learning in English or Spanish (accordingly),19,20 all showing inter-/intra-examiner Kappa-weighted values ≥0.7. The dental examiners and 1-2 dental practitioners per centre received online training, first by carrying out both CCI e-learnings (English/Spanish) on how to implement the CCI and CCI-adapted-with-no-AGPs caries management system.21,22 Online training and dental practitioners' standardisation was delivered by the steering committee through: four-hour English and Spanish workshops covering: the CCI 4D cycle steps;21 the non-AGP procedures (including defining NOC [non-operative care] and TPOC [tooth-preserving operative care] interventions at the tooth surface levels for primary and permanent teeth with an up-to-date range of dental materials and techniques)17,22,23 and online consultation;22 the short behaviour change tool (based on the behaviour change wheel);24,25 the completion of the designed oral health record (Microsoft Excel, 2010) (see online Supplementary Information); and discussing clinical cases to solve questions and achieve dental practitioners' standardisation (emphasising on individual and tooth-surface level care and the short behaviour-change tool, as well as in non-AGP).
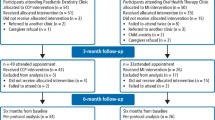
All centres received related e-learnings, forms, materials, full oral health records (English/Spanish), the CCI-adapted chart (Fig. 1) and didactic oral health practices and self-assessment aids (which were locally translated into country language, printed and provided to all children and parents).17 Uniformity in care was ensured through periodic case review between centre coordinator and dental practitioner. The oral health record included general information and three sections: baseline examinations (T0), intervention, and one-year follow-up examination (T1y) (same as in baseline), based on the CCI-adapted system (Fig. 1 and study protocol).17 These sections are displayed in the study flowchart (Fig. 2), the oral health record (see online Supplementary Information), and included at each centre.
Baseline examination (T0)
Caries risk (CCI-1D) was assessed with the adapted CCI caries risk tool, including three caries-protective factors, four social/medical/behavioural factors and four clinical/intra-oral caries risk factors (Fig. 1). The high/low caries risk classification was based on an algorithm constructed by the Study Steering Committee with caries protective and risk factors using multiple sources of information: the CCI Guide8 (derived from ICCMS),10,26 cariogram,27 American Dental Association (ADA),28 caries management by risk assessment (CAMBRA)29 and the Meyer-Lueckel et al.30 caries risk tools, after undergoing simulation tests with hypothetical cases and with patients, discussion and agreement.
Oral health behaviour was classified via a conjunctively defined (with the Steering Committee) algorithm into ‘very inadequate', ‘inadequate' or ‘adequate', based on four oral health behaviours/practices (caries protective/risk factors) related to toothbrushing, daily sugar consumption and poor oral hygiene practices, and on presence of active caries (Fig. 1 and online Supplementary Information). Additional eight agreed oral hygiene and diet oral health behaviours/practices were assessed to aid guiding the not validated short behaviour change tool based on the behaviour change wheel GPS (goal, planning, self-assessing) approach to enhance child/parents' volition leaning on the motivation component of the COM-B model (capability, opportunity, motivation, behaviour) (Fig. 1 and online Supplementary Information).25
The clinical examination (CCI-2D), conducted without air-drying, included Silness and Löe's modified biofilm index;31 plaque stagnation areas (i.e., erupting molars and dental malposition); missing/absent/close-to exfoliation teeth; and teeth presenting with toothache and with untreated cavitated caries consequences (pulpal involvement, roots, sepsis [PRS]).32 Assessments at the tooth surface level (conducted after assisted toothbrushing, with the aid of a WHO probe and drying tooth surfaces and/or removing dental biofilm only with cotton rolls/gauze, without using compressed air/water) included caries severity and activity assessment using the visual epidemiological merged ICDAS (ICDAS-merged-epi) criteria: initial or non-cavitated (I); moderate (Mo); extensive/cavitated (E); and active or inactive (Fig. 1).8,26 Fillings (f/F) and missing teeth (m/M) were also registered. Teeth in need of endodontics/extraction at T0 were referred and not considered for the analyses (due to need of AGP or radiographs, restricted during the pandemic).
Finally, care plans (CCI-3D) were co-created between examiner, practitioner and parent (with child). Each plan considered individual-level care according to risk and oral health behaviour classifications, and tooth surface-level care according to caries lesion activity and severity status, defining it into ‘no care' (0), ‘active monitoring' (AM), NOC or TPOC (Figure 1, Figure 2, online Supplementary Information).
Intervention
The intervention consisted of caries prevention and tooth preserving care (4D) (Fig. 1). Interventions were conducted by the trained dental practitioners. The basic individual and tooth surface levels-agreed care included only non-AGP approaches/interventions (remote when possible). Individual care involved homecare and clinical care, including the implementation of the short behaviour-change tool Goal, Planning, Self-monitoring (GPS), to improve oral hygiene and dietary habits, after discussing with the parent each inadequate behaviour and setting a goal (G) to be accomplished; then, planning together how best to achieve it (P) with the support of didactic aids and self-monitoring (S) (Fig. 1, see online Supplementary Information).17,25 While in low caries risk and adequate oral-health-behaviour patients, only homecare approaches were included (e.g., ≥1000 ppm fluoride toothpaste toothbrushing reinforced instructions with the dental team), in those with high caries risk and inadequate oral health behaviour, these would include additional clinical approaches (e.g., 5% sodium fluoride [NaF] varnish every three months) as well as homecare approaches using the short behaviour-change tool (Fig. 1, online Supplementary Information).17 At the tooth surface level, Figure 1 shows the possible non-AGP dental materials and techniques that each centre could use for TPOC and NOC for primary and permanent teeth, depending on their availability and accessibility during the pandemic (irrespective of manufacturers) (for more details see the study protocol, Table 1 and Table 2).17
In line with the adapted CCI 4D-cycle, if T0 patients were classified as low caries risk, they were recalled at one year (after T0), while those classified as high caries risk were recalled three months after the basic management (after around five months of T0). At the latter, shorter versions of risk determination and oral health behaviour were applied. One protective factor and six risk factors were re-assessed, as well as four coinciding oral health behaviour/risk items mentioned above, reclassifying the child accordingly (see online Supplementary Information). Individual- and tooth surface-level care followed as appropriate, including adjusting the risk-based recall interval.17
Throughout the study, caregivers/children phone call or message reminders were used regularly to plan online/on-site appointments and to enhance oral-health-related-behaviour adherence. Incentives included behaviour change online/printed didactic tools, online periodical assessment of oral health practices' progress, and messages on special dates like Christmas or birthdays.
One-year follow-up examination (T1y)
A follow-up reassessment was conducted after 12 months (T1y) by the examiner blind to the intervention. This included the same assessments as T0.
Parents' and dentists' acceptance of the dental care process was assessed at five months with an adapted version of the validated treatment evaluation inventory (TEI),33,34 which underwent at each site a local language understanding process. Instruments consisted of ten-item (parents/dentists) self-assessed online questionnaires. A five-point Likert answer scale was used, in which five corresponded to the highest grade for each domain: oral health knowledge/information (a lot more); care plan adherence (increased a lot); behaviour change (these contributed a lot); satisfaction with care (very satisfied); and care plan learnings' applicability (in a great measure), and one is the lowest grade.
The Study Steering Committee periodically audited online the general conduction of the study after receiving a periodic report from each coordinator centre. The latter also periodically audited their centre by assessing the databases of a number of subjects independently from the dental practitioners.17 Missing data were identified and collected through a meeting with respective centres' coordinators.
Child dropout criteria from the study included: patient's/parent's voluntary trial withdrawal; not attending appointments after three phone/message reminders; and moving from institution/school or city.
Outcomes
-
Primary health outcome - difference in T0-to-T1y mean number of tooth surfaces with caries and T1y percentage of tooth surfaces with control of caries progression
-
Secondary health outcomes - T1y proportion of children with caries-progression control, low caries risk, adequate oral health behaviour, no extractions, no toothache, and proportion of parents and dentists with reported high dental care process acceptance levels.
Statistical analysis
At T0 and T1y, the individual- and tooth surface-level data, as well as parents'/dentists' TEI data, were digitally registered per patient in each centre by a blinded research assistant and stored with limited access in a designed Microsoft Excel (2010) database. Each centre sent their data to the data-management team. Then, data were organised into a dataset with quality assurance and validation.
Demographic and clinical features of the participants (centre, sex, age, caries experience, caries risk, oral health behaviour, toothache) and dental care acceptance were described using mean and standard deviation (quantitative variables) and percentages (qualitative variables). The ICDAS-merged-epi caries experience (ICDAS-merged-epi; decayed, missing and filled teeth [dmfs/DMFS]) was calculated to characterise the population at T0 and T1y (for primary teeth: ICDAS-merged-epi dmfs; permanent teeth: ICDAS-merged-epi DMFS; and combining both: ICDAS-merged-epi dmfs/DMFS), and discriminating for the d/D component the caries severity (d/D-I, d/D-Mo, and d/D-E) and activity (active, inactive) stages. The T0 mean number of tooth surfaces with ICDAS-merged-epi dmfs/DMFS of patients who finished the study was compared with the one of the dropout patients (t test analysis).
The difference in T0-to-T1y mean number of tooth surfaces with caries lesions was calculated.
Caries progression was defined as a progression from the T0 tooth surface diagnosis (sound surface; sealing; initial/moderate/extensive active/inactive caries lesion; filling) and basic management care decision (no care; AM; NOC; TPOC) to the presence in T1y of new caries lesions; caries severity increase or an active caries lesion; or a new filling or a filling with caries (PRS, toothache or new extraction). The percentage of primary, permanent and combined tooth surfaces with T1y caries progression control was obtained by subtracting out of the total number of tooth surfaces at T0 after care decision (for each teeth type), the number of tooth surfaces in which there had been caries progression at T1y (e.g., if at T0 the care decision for a moderate inactive caries was NOC, and at T1y it was restored, this was considered as caries progression; on the contrary, if at T0 the care decision for a moderate inactive caries was TPOC, and at T1y it was assessed as filled, this was considered as no caries progression). Based on a previous study using ICCMS,35 a percentage of over 90% of tooth surfaces with control of caries progression was expected.
In addition, the proportion of children with T1y control of caries progression, extractions, toothache and failure of fillings was calculated.
The TEI responses were analysed using means and standard deviations, treating the Likert-scale data as continuous variables.
All statistical tests were two-tailed tests.17 Mainly parametric methods were used; non-parametric methods were used when data did not meet the former criteria. Statistical significance level for all two-sided tests were set at 0.05.
Results
Out of the 17 centres which participated, 16 finished the study with one-year follow-up at the set deadline (94.1%; 3 European, 13 Latin American [except Brazil]), with a total of 337 children (78.6%). Number of centres starting recruitment by year quarter corresponded to: n = 3 (2020 - 4th), n = 2 (2021 - 1st), n = 5 (2021 - 2nd), n = 2 (2021 - 3rd) and n = 5 (2021 - 4th). Table 1 shows demographic and clinical characteristics of the 17-centre sample who initiated the study (n = 429). Mean number of children participating per centre was of 25.2 ± 5.3 with a mean age of children of 5.5 ± 1.6 years. Most were classified as high caries risk (70.4%) and presented with ICDAS-merged-epi caries experience in primary and permanent teeth combined (ICDAS-merged-epi, dmfs/DMFS) (75.8%), with a mean number of tooth surfaces with ICDAS-merged-epi dmfs/DMFS of 8.7 ± 9.7. All countries, apart from Russia, counted with a community water or salt fluoridation programme.
In children who completed the study (n = 337), the T0 prevalence of ICDAS-merged-epi dmf/DMFS (primary and permanent teeth combined) was of 76.3%, with a mean number of tooth surfaces with ICDAS-merged-epi dmfs/DMFS of 8.4 ± 9.7. The T0 mean number of tooth surfaces with ICDAS-merged-epi dmfs/DMFS of children who finished the study was not significantly different from that of children the 92 (21.4%) who did not complete the study (8.4 ± 9.7 vs 9.3 ± 9.1, respectively) (p = 0.42).
Table 2 shows the mean number of tooth surfaces with ICDAS-merged-epi dmfs/DMFS for the primary teeth (n = 337), permanent teeth (n = 170), and combined primary and permanent teeth (n = 337), discriminating by each dmf/DMF component and considering besides the severity and the activity status of the caries lesions. There was a significant decrease from T0 to T1y in the mean number of tooth surfaces with ICDAS-merged-epi dmfs (T0: 7.2 ± 8.9; T1y: 5.2 ± 7.1) (p <0.05) and in the ICDAS-merged-epi dmfs/DMFS (T0: 8.4 ± 9.7; T1y: 6.2 ± 7.6) (p <0.05), while without statistical significance for ICDAS-merged-epi DMF (T0: 2.5 ± 3.2; T1y: 2.1 ± 2.8) (p >0.05). With respect to caries, with the exception of DS-E and of ds/DS I+Mo+E, there were overall significant decreases in the mean number of active caries lesions, together with a significant increase in the mean number of inactive caries lesions (p <0.05). Mean number of filled tooth surfaces increased significantly (p <0.05), except for the permanent teeth.
The online Supplementary Information shows the detailed one-year caries progression status (progression control/progression) and score (including sealing) for the primary and the permanent teeth, considering baseline score and care decision. There was a T1y tooth surface control of caries progression of 98.7% in the primary teeth (out of the 24,542 T0 tooth surfaces, after excluding for this analysis 31 primary teeth with extraction need). The corresponding figure for the permanent teeth was of 99.3% (out of 8,525 T0 tooth surfaces).
At the individual level, there was a T1y control of caries progression in 75.1% of children: extractions (98.2%), toothache (100%) and failure of fillings (97.3%).
After one year, high caries risk and very-inadequate/inadequate oral health behaviour were controlled in most children, with a significant increase of children with both low caries risk (T0: 32.9%; T1: 86.6%; p <0.05), and adequate oral-health behaviour (T0: 22.3%; T1: 72.7%; p <0.05) (Fig. 3).
Table 3 shows the results of the parents' and dentists' dental care process acceptance. All children's parents answered the TEI questionnaires (n = 337). There was a high/very high acceptance of CCI, with CCI principles (questions 1-7) showing a change to ‘more' and ‘a lot more' parents' knowledge/learning/information/understanding. They reported adhering to child's health recommendations ‘more' to ‘a lot more' by co-creating the child's care plan together with the dentists; likewise, with the change in behaviours regarding toothbrushing and sugar intake control, and in awareness to avoid cavity formation. They reported being ‘satisfied' to ‘very satisfied' with the use of the non-AGP procedures and that they could apply for themselves what they learnt from the child's dental care ‘a lot' to ‘very much'.
The dentists' TEI questionnaire was answered by the 2-3 dentists involved in each of the 16 centres (n = 40). Results were similar to those from parents, showing a high CCI use acceptance. The highest rated question corresponded to ‘more' to ‘a lot more' information in patients/parents about how to look after the child's teeth and mouth health. No significant differences were found between the 11-question answer scores in the parent/dentist questionnaire (p >0.05).
Discussion
This multicentre, single-group, interventional study found, after the 12-month implementation in children of CCI adapted for the pandemic, control of caries progression at the tooth-surface level, and control of caries progression and of caries risk, in most children. CCI was highly accepted by both parents and dentists.
Even though the original study design would have been a pragmatic RCT for which all 21 centres signed up in 2019, the pandemic still became an opportunity for implementing and testing the CCI system in another environment where there was a great need to adapt to new threats, hence the avoidance of aerosols (non-AGP) and reduction of in-person clinical time.17 No control group following standard practice including AGP procedures was ethically possible due to the public health emergency. This study type has been used elsewhere (e.g., oncology) as the only or one of the few options for evaluating therapies for which placebos are not ethical and control groups are limited.36 In addition to the ability to explore the caries progression control effectiveness of CCI in the dental practice setting, together with its feasibility in terms of acceptance,37 the CCI-adapted trial offered centres a pandemic-appropriate way to offer dental care to children.38 Such care was not possible for long periods of time during the pandemic in many countries.39,40,41,42 The study period of one year, linked to the ethical and technical viability, could also be a limitation of the study, altogether rendering the need to interpret findings carefully.
As for the one-year study duration, Zandona et al.43 shows that the use of the ICDAS criteria with severity and activity status assessment favours the assessment of progression of caries lesions and appearance of new lesions within that period of time.43 Also in the current study, with increasing severity, a higher percentage of lesions progressing to cavitation increased (28% of moderate caries lesions versus 1.5% of initial caries lesions) (see online Supplementary Information). The findings of this study could be partly explained by the comprehensiveness of the CCI caries management system through patient-centred, preventively-based care with an emphasis on caries prevention and control, and minimally invasive caries management where necessary.8,10 ICCMS demonstrated in a three-year multicentre RCT of children in Colombia to be more effective in controlling caries progression than the conventional national caries management system.35 While in that study the proportion of active caries lesions at the end of the study was over 49%, this correspondeds to 18% in this study. Current, more positive findings include a shorter follow-up time and the use of only low/high caries risk classification categories, instead of three (ICCMS),10 allowing for clearer management planning.8 Adapted CCI gave special emphasis to improve oral health practices through the use of a short COM-B behaviour change tool (Capability, Opportunity and Motivation capable of changing Behaviour),17 following psychological behaviour change science,24,25,44 proven to be effective in improving periodontal treatment outcomes.45 In addition, this tool focused on improving two critically relevant behaviours to prevent caries, namely, twice-a-day ≥1000 fluoride toothpaste toothbrushing,46 and reducing daily sugar intake.47 The remote consultation conducted with parents/children to assist the behaviour-change approaches would also possibly have had an impact in the study outcomes.48 Even though a Hawthorn effect could have been present,49 beside self-reporting practices, biological markers indicating pursuing practices (presence of dental biofilm and active caries lesions) were used. Success here could more possibly relate to the intervention behaviour change techniques, including education, training, modelling and incentivisation.24,25 The Hawthorn effect could also be the case for parents' acceptance of the system,49 but another explanation for this high acceptance could be related to the unique circumstances of pandemic period (e.g., more family time at home). The parents' and dentists' high acceptance of CCI, in particular on the knowledge of how to improve the children's oral health and the parents' participation in the treatment plan, show similarities with the TEI previously reported for the use of the Denplan/Previser patient assessment tool.34 As for the inability to compare the acceptance of parents (and dentists) with another intervention, the ICCMS caries-control effectiveness study using a similar caries management system, in comparison to standard care, showed a significantly higher compliance of parents towards ICCMS.35
Even though there is a potential examiner bias in the final assessment, the robustness of our results can be supported first by the fact that examiners were blind to the one-year interventions. Also, the T0-to-T1y decrease in the mean number of caries lesions could be explained in a large part by restorations and sealants used for moderate-extensive caries lesions, but also by sealants used for some initial ones, as well as by other strategies, such as fluoride topical application and increased frequency and quality of fluoridated toothpaste toothbrushing.23,38
The Brazilian centre did not finish by the study deadline due to ethical approval delays and a three-month clinic closure for structural issues after starting. Despite the loss of the latter and other children's dropouts, the sample size was achieved.
Besides ICCMS, other caries management systems that support NOC have also shown caries control effectiveness at longer period times in children50 and adults18 when compared to standard care, while Innes et al. did not find significant toothache/infection-episode differences of cavity sealing versus conventional operative care or only individual-level care in children.51 Risk-related personalised care has also been shown to offer caries-control effectiveness: in Russia with Nexö-method principles, which are similar to those of CCI,52 and in the USA with the CAMBRA system, which in contrast to CCI uses antibacterial therapy.29 The use of the Hall technique and atraumatic restorative treatment (ART) in the CCI-adapted protocols allowed for tooth-preserving operative care without AGPs. Both procedures, as well as other non-operative approaches, like silver diamine fluoride, fluoride varnish and sealants, have been recommended in recent caries-management guidelines,23 and could support the caries progression control found after one year. A cross-sectional survey assessing changes in dentists on minimum caries management interventions during COVID-19 disclosed increased use of ART and of NOC but with a small perceived effect.53 The use of non-AGP relates to non-restorative treatments for caries, supported by both systematic review and network meta-analysis,7 and derived ADA evidence-based clinical practice guidelines.23 NOC is not only considered for initial but also for moderate and extensive caries lesions. Coinciding with current study NOC options, most effective procedures for arresting non-cavitated carious lesions on primary/permanent teeth were sealants plus 5% sodium fluoride (NaF) varnish (occlusal/proximal); 5% NaF (buccal/lingual); and for arresting advanced cavitated carious lesions, 38% silver diamine fluoride solution applied biannually (any coronal surface).7,23 Nevertheless, the translation into practice of a less curative approach,7 with a patient-centred, preventively based and health-outcome focused caries care system (CCI) is still challenging. On the other hand, the increasing European, American and Latin American CCI website traffic and the CCI similarities to ICCMS (with friendly daily practice adaptations) encourages its adoption to move towards effective less invasive caries care.55
The implementation in practice of a caries management system such as CCI that focuses on health outcomes has widespread support from different areas (including the CCI webpage) but the process needs to speed up. The implementation of the cariology teaching consensus for undergraduates that started with the European core curriculum over ten years ago,56 and which was recommended and/or nationally adapted in many countries, seems to be slower than expected.57 From the policymaker perspective, the support that appeared over 20 years ago from the FDI for ‘minimal intervention in the management of caries' has also had a slow uptake in daily clinical practice, which further motivated the FDI in 2019 to promote the principles of ICCMS.15 This also led to the International Standards Organisation (ISO) using ICCMS terminology (equal to ICDAS-merged criteria) as the global standard for dental caries (https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:1942:ed-3:v1:en). The 2021 WHO resolution on oral health also supports the CCI approach,1,54 and furthermore, CCI addresses the dental coverage gap considering dental care as an essential health benefit for all age groups and working with the Global Collaboratory for Caries Management (with the Alliance for a Cavity-free Future) towards paying for comprehensive dental care.5,58 From the dental practitioner's perspective, there has been a worldwide spread of educational materials to translate the current care philosophy to clinical practice (besides the ones already mentioned above), including a short time to clinically assess caries with the ICDAS-merged criteria (around four minutes),59 the development of standardised software for the caries care oral health record,11 and assessment of the implementation of CCI in real clinical scenarios in eight Latin American dental schools within the Latin American Oral Health Organization call for action initiative (https://laoha.org/newsletters/en/ed10_eng_newsletter_laoha_2023.pdf).
Finally, given the current non-pandemic situation, confirmation of the findings of this study would benefit from an RCT testing the caries progression control effectiveness of the CCI caries management system in children.
Conclusion
CCI adapted for the COVID-19 pandemic showed, after one year of implementation, control of caries progression and caries risk in children, as well as a high acceptance by children's parents and dentists.
Data availability
Additional data supporting the findings of this study are not publicly available due to privacy and ethical restrictions but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
World Health Organization. Global oral health status report: towards universal health coverage for oral health by 2030. 2023. Available at https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240070868 (accessed 1 June 2024).
Machiulskiene V, Campus G, Carvalho J C et al. Terminology of dental caries and dental caries management: consensus report of a workshop organized by ORCA and Cariology Research Group of IADR. Caries Res 2020; 54: 7-14.
Selwitz R H, Ismail A I, Pitts N B. Dental caries. Lancet 2007; 369: 51-59.
Vernazza C R, Birch S, Pitts N B. Reorienting oral health services to prevention: economic perspectives. J Dent Res 2021; 100: 576-582.
Vernazza C R, Pitts N B, Mayne C, Mazevet M E. Dental policy lab 1 - towards a cavity-free future. Br Dent J 2021; 231: 754-758.
Pitts N B, Twetman S, Fisher J, Marsh P D. Understanding dental caries as a non-communicable disease. Br Dent J 2021; 231: 749-753.
Urquhart O, Tampi M P, Pilcher L et al. Nonrestorative treatments for caries: systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Dent Res 2019; 98: 14-26.
Martignon S, Pitts N B, Goffin G et al. CariesCare practice guide: consensus on evidence into practice. Br Dent J 2019; 227: 353-362.
Beltrán E O, Guiu L, Zarta O L, Pitts N B, Martignon S. Caries classification and management in the context of the CariesCare International (CCI™) consensus: a clinical case study. Br Dent J 2019; 227: 363-366.
Pitts N B, Ekstrand K R. International Caries Detection and Assessment System (ICDAS) and its International Caries Classification and Management System (ICCMS) - methods for staging of the caries process and enabling dentists to manage caries. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2013; DOI: 10.1111/cdoe.12025.
Pitts N B, Banerjee A, Mazevet M E, Goffin G, Martignon S. From ‘ICDAS' to ‘CariesCare International': the 20-year journey building international consensus to take caries evidence into clinical practice. Br Dent J 2021; 231: 769-774.
Martignon S, Marín L M, Pitts N, Jácome-Liévano S. Consensus on domains, formation objectives and contents in cariology for undergraduate dental students in Colombia. Eur J Dent Educ 2014; 18: 222-233.
Fontana M, Guzmán-Armstrong S, Schenkel A B et al. Development of a core curriculum framework in cariology for US dental schools. J Dent Educ 2016; 80: 705-720.
Abreu-Placeres N, Grau-Grullón P, Naidu R et al. Cariology consensus for undergraduates at dental schools in the Caribbean region. Eur J Dent Educ 2021; 25: 717-732.
Bondioni E. Carious lesions and first restorative treatment: adopted by the General Assembly: September 2019, San Francisco, United States of America. Int Dent J 2020; 70: 5-6.
Abreu-Placeres N, Newton J T, Avila V et al. How do dental practitioners, educators and students diagnose and manage caries risk and caries lesions? A COM-B analysis. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2023; 51: 265-273.
Martignon S, Cortes A, Douglas G V A et al. CariesCare International adapted for the pandemic in children: Caries OUT multicentre single-group interventional study protocol. BMC Oral Health 2021; 21: 329.
Curtis B, Evans R W, Sbaraini A, Schwarz E. The Monitor Practice Programme: is non-invasive management of dental caries in private practice effective? Aust Dent J 2008; 53: 306-313.
International Caries Classification and Management System. ICDAS Calibration for ICCMS™ - English. 2016. Available at https://www.iccms-web.com/course/1 (accessed 1 June 2024).
International Caries Classification and Management System. ICDAS Calibration for ICCMS™ - Spanish. 2016. Available at https://www.iccms-web.com/course/3 (accessed 1 June 2024).
Caries Care International. E-learning videos - English. 2020. Available at https://cariescareinternational.com/e-learning-english/ (accessed 1 June 2024).
Caries Care International. E-learning videos - Spanish. 2021. Available at https://cariescareinternational.com/e-learning-spanish/ (accessed 1 June 2024).
Slayton R L, Urquhart O, Araujo M W B et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guideline on nonrestorative treatments for carious lesions: a report from the American Dental Association. J Am Dent Assoc 2018; 149: 837-849.
Michie S, van Stralen M M, West R. The behaviour change wheel: a new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implement Sci 2011; 6: 42.
Newton J T, Asimakopoulou K. Minimally invasive dentistry: enhancing oral health related behaviour through behaviour change techniques. Br Dent J 2017; 223: 147-150.
International Caries Classification and Management System. ICCMSTM guide for practitioners and educators. 2014. Available at https://www.iccms-web.com/uploads/asset/592845add7ac8756944059.pdf (accessed 1 June 2024).
Bratthall D, Hänsel Petersson G. Cariogram - a multifactorial risk assessment model for a multifactorial disease. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2005; 33: 256-264.
American Dental Association. Caries risk assessment and management. 2023. Available at https://www.ada.org/resources/ada-library/oral-health-topics/caries-risk-assessment-and-management (accessed 1 February 2025).
Featherstone J D B, Alston P, Chaffee B W, Rechmann P. Caries management by risk assessment (CAMBRA): an update for use in clinical practice for patients aged 6 through adult. J Cali Dent Assoc 2019; 47: 25-34.
Meyer-Lueckel H, Paris S, Ekstrand K R. Caries risk assessment and prediction. In Meyer-Lueckel H, Paris S, Ekstrand K R (eds) Caries Management - Science and Clinical Practice. 1st ed. pp 402. Stuttgart: Georg Thieme Verlag RG, 2013.
Silness J, Löe H. Periodontal disease in pregnancy. II. Correlation between oral hygiene and periodontal condition. Acta Odontol Scand 1964; 22: 121-135.
Baginska J, Stowska W. Pulpal involvement-roots-sepsis index: a new method for describing the clinical consequences of untreated dental caries. Med Princ Pract 2013; 22: 555-560.
Newton J T, Asimakopoulou K. The perceived acceptability of the DEPPA patient assessment tool: a questionnaire survey of Denplan Excel patients. Br Dent J 2017; 222: 767-770.
Newton J T, Nabeyama R, Sturmey P. Internal consistency, factor structure, and concurrent validity of the treatment evaluation inventory. Psychol Rep 2007; 101: 731-738.
Martignon S, Cortes A, Gamboa L F et al. Effectiveness of the ICCMS caries management system for children: a 3-year multicentre randomised controlled trial. Acta Odontol Scand 2022; 80: 501-512.
Evans S R. Clinical trial structures. J Exp Stroke Transl Med 2010; 3: 8-18.
Bowen D J, Kreuter M, Spring B et al. How we design feasibility studies. Am J Prev Med 2009; 36: 452-457.
Eden E, Frencken J, Gao S, Horst J A, Innes N. Managing dental caries against the backdrop of COVID-19: approaches to reduce aerosol generation. Br Dent J 2020; 229: 411-416.
Okike I, Reid A, Woonsam K, Dickenson A. COVID-19 and the impact on child dental services in the UK. BMJ Paediatr Open 2021; DOI: 10.1136/bmjpo-2020-000853.
Lyu W, Wehby G L. Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on children's oral health and oral health care use. J Am Dent Assoc 2022; 153: 787-796.
Beltrán E O, Newton J T, Avila V et al. Dentists' perceptions of personal infection control measurements in response to COVID-19. JDR Clin Trans Res 2024; 9: 21-26.
Stennett M, Tsakos G. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on oral health inequalities and access to oral healthcare in England. Br Dent J 2022; 232: 109-114.
Ferreira-Zandoná A, Santiago E, Eckert G J et al. The natural history of dental caries lesions: a 4-year observational study. J Dent Res 2010; 91: 841-846.
Asimakopoulou K, Newton J T. The contributions of behaviour change science towards dental public health practice: a new paradigm. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2015; 43: 2-8.
Asimakopoulou K, Nolan M, McCarthy C, Newton J T. The effect of risk communication on periodontal treatment outcomes: a randomized controlled trial. J Periodontol 2019; 90: 948-956.
Walsh T, Worthington H V, Glenny A M, Marinho V C, Jeroncic A. Fluoride toothpastes of different concentrations for preventing dental caries. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2019; DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007868.pub3.
World Health Organization. Guideline: sugars intake for adults and children. 2015. Available at https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549028 (accessed 1 June 2024).
Alabdullah J H, Daniel S J. A systematic review on the validity of teledentistry. Telemed J E Health 2018; 24: 639-648.
Chiesa M, Hobbs S. Making sense of social research: how useful is the Hawthorne effect? Eur J Soc Psychol 2008; 38: 67-74.
Vermaire J H, Poorterman J H G, van Herwijnen L, van Loveren C. A three-year randomized controlled trial in 6-year-old children on caries-preventive strategies in a general dental practice in the Netherlands. Caries Res 2014; 48: 524-533.
Innes N P, Clarkson J E, Douglas G V A et al. Child caries management: a randomized controlled trial in dental practice. J Dent Res 2020; 99: 36-43.
Kuzmina I, Ekstrand K R. Outcomes 18 years after implementation of a nonoperative caries preventive program - the Nexö-method - on children in Moscow, Russia. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2015; 43: 308-316.
De Souza T F, Martins M L, Jural L A et al. Did the use of minimum interventions for caries management change during the COVID-19 pandemic? A cross-sectional study. Caries Res 2023; 57: 459-469.
World Health Organization. Seventy-fourth world health assembly: oral health. 2021. Available at https://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA74/A74_R5-en.pdf (accessed 1 June 2024).
Hancocks S. When least is most. Br Dent J 2019; 227: 325.
Schulte A G, Pitts N B, Huysmans M C, Splieth C, Buchalla W. European core curriculum in cariology for undergraduate dental students. Caries Res 2011; 45: 336-345.
Santamaría R, Fontana M, Chalas R et al. The core curriculum for cariology: fiction or reality? Challenges about implementation. Caries Res 2024; 58: 153-161.
Vujicic M. Our dental care system is stuck: and here is what to do about it. J Am Dent Assoc 2018; 149: 167-169.
Martignon S, Cortes A, Gómez S I et al. How long does it take to examine young children with the caries icdas system and how do they respond? Braz Dent J 2018; 29: 374-380.
Acknowledgements
Acknowledgements to: the International Association for Dental Research Regional Development Program Latin American Region (IADR RDP LAR); Universidad El Bosque PCI 2019-10718; CariesCare International (CCI) and the Global Collaboratory for Caries Management (GCCM) at King's College London; the children involved in the study and their parents/caregivers. The participating centres with their dental teams including: Alejandra Rodríguez (CIBO-UNIBE); Ana Karina Velasco, Olga Lucía Zarta, Viviana Avila, Margarita Úsuga-Vacca, Yaisa Vásquez (UNICA); Ana Norton (U. of Porto); Anabela Martín, Fernando Rafael Vásquez (U. Nacional de Córdoba); Emilia Ochoa (UCC); Jose María Maciel (CUCS); José Pertuz (Viva1A IPS); Juliana Díaz, Tatiana Moreno (UAM); Mariam Kuchuhidze (MSUMD); Patricia Castro (CURN); Sandra Caceres Matta (UCU); Shirley Díaz (U. de Cartagena); Maria Carolina Costas Prestes, Gabriela Manco Machado (USP).
Funding
International Association for Dental Research Regional Development Program Latin American Region (IADR RDP LAR), Universidad El Bosque PCI 2019-10718, the Colombian Chapter of the Alliance for a Cavity Free Future (CC-ACFF), and each participating centre. Universidad El Bosque Open Access funding provided by Colombia Consortium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SM, EOB, AC: substantially contributed to the conception and design of the study; contributed to data acquisition, analysis and interpretation; drafted the manuscript and critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content; gave final approval and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of work ensuring integrity and accuracy. GVAD, JTN, NBP, CD: contributed to the design of the study; contributed to interpretation; critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content; gave final approval and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of work ensuring integrity and accuracy. FPMCK, NF, MPC, NC, BE, IK, MMB, JRO, KR, JS, AS, RV, EA, SCM, LMC, AC, OLC, LH, JIL, JAO, AngieS, DS, AngelaS, MSM, AnaS, DZ, NAP, MMB, JSL, PM, CA, ART, PYF, ACFDL, EAMM, AFZ: contributed to data acquisition, critically revised the manuscript and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of work ensuring integrity and accuracy.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article. The authors declare a conflict of interest where the main author is one of the creators of the tool being investigated. Ethics Committee approval: Research Ethics Institutional Committee of Universidad El Bosque (PCI2019 10718). Consent was given by parents/caregivers and the children.
Supplementary Information
41415_2025_8640_MOESM3_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Information 3. Reproduced from Martignon et al., ‘CariesCare International adapted for the pandemic in children: Caries OUT multicentre single-group interventional study protocol’, BMC O (PDF 502KB)
Rights and permissions
Open Access. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0.© The Author(s) 2025.
About this article
Cite this article
Martignon, S., Beltrán, E., Douglas, G. et al. How did CariesCare International perform under pandemic conditions in children? A one-year, multicentre, single-group, interventional study. Br Dent J (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-025-8640-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-025-8640-4