Abstract
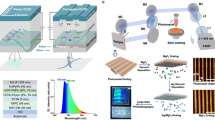
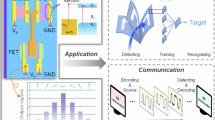
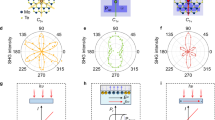
Polarized emissive media are crucial for various applications in display, lighting and optical communication. An attractive research direction is to develop intrinsically white organic polarized emissive semiconductors as ideal candidates for miniaturized polarized light-emitting devices; however, it has been a considerable challenge to achieve polarized white-light emission due to the lack of suitable materials and effective preparation methods. Here we overcome this bottleneck by realizing white organic polarized emissive semiconductor single crystals (WOPESSCs). We employ a bimolecular doping method based on using highly polarized, blue-emitting 2,6-diphenylanthracene as the host single crystal, and controlling energy and polarization transfer with green- and red-emitting guests. The fabricated WOPESSCs achieve a photoluminescence quantum yield of 38.3% and a mobility of 4.9 cm2 V–1 s–1. The emitted light exhibits a degree of polarization as high as 0.96 with Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage coordinates of (0.3258, 0.3396). We also demonstrate the tunable emission properties of WOPESSCs from blue–white to yellow–white light by adjusting polarization angles, and three-primary-colour optical imaging with a wide colour gamut that covers 112% of the National Television System Committee standard. Furthermore, we fabricate highly polarized microscale WOPESSCs light-emitting diodes and light-emitting transistors, achieving high-quality white-light emission and wide-range colour tunability enabled by gate voltage-driven energy transfer processes. We believe these findings pave the way for manufacturing white and multicolour polarized emissive semiconductors and microscale light-emitting devices, promising diverse applications across various fields.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data needed to evaluate the conclusions of this study are present in the paper and the Supplementary Information. Additional data are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
References
Rein, M. et al. Diode fibres for fabric-based optical communications. Nature 560, 214–218 (2018).
Dorrah, A. H., Rubin, N. A., Zaidi, A., Tamagnone, M. & Capasso, F. Metasurface optics for on-demand polarization transformations along the optical path. Nat. Photon. 15, 287–296 (2021).
Zeng, D., Dai, J., Yao, W., Xiao, D. & Cui, X. Valley polarization in MoS2 monolayers by optical pumping. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 490–493 (2012).
Li, Y. et al. Longitudinally variable 3D optical polarization structures. Sci. Adv. 9, eadj6675 (2023).
Zhang, Y. J., Oka, T., Suzuki, R., Ye, J. T. & Iwasa, Y. Electrically switchable chiral light-emitting transistor. Science 344, 725–728 (2014).
Stanciu, C. D. et al. All-optical magnetic recording with circularly polarized light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 047601 (2007).
Zhang, G. X. et al. High-brightness polarized green InGaN/GaN light-emitting diode structure with Al-coated p-GaN grating. ACS Photon. 3, 1912–1918 (2016).
Ding, R., Ye, G.-D. & Feng, J. Recent advances in linearly polarized emission from organic light-emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 123, 010501 (2023).
Zhang, D. W., Li, M. & Chen, C. F. Recent advances in circularly polarized electroluminescence based on organic light-emitting diodes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 1331–1343 (2020).
Chen, X. et al. Solution-processed inorganic perovskite crystals as achromatic quarter-wave plates. Nat. Photon. 15, 813–816 (2021).
Jia, R. et al. Highly efficient inherent linearly polarized electroluminescence from small-molecule organic single crystals. Adv. Mater. 35, 2208789 (2023).
Sun, P., Liu, D., Zhu, F. & Yan, D. An efficient solid-solution crystalline organic light-emitting diode with deep-blue emission. Nat. Photon. 17, 264–272 (2023).
Diao, Y. et al. Solution coating of large-area organic semiconductor thin films with aligned single-crystalline domains. Nat. Mater. 12, 665–671 (2013).
Pan, X., Lan, L., Di, Q., Yang, X. & Zhang, H. Acidichromic organic crystals with manifold mechanical deformations for reconfigurable flexible optical tuner. Wearable Electron. 1, 111–118 (2024).
Wang, C., Dong, H., Jiang, L. & Hu, W. Organic semiconductor crystals. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47, 422–500 (2018).
Kasha, M. Characterization of electronic transitions in complex molecules. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 9, 14–19 (1950).
Turro, N. J., Ramamurthy, V. & Scaiano, J. C. Modern Molecular Photochemistry of Organic Molecules (University Science Books, 2010).
Chen, M. et al. A unique blend of 2-fluorenyl-2-anthracene and 2-anthryl-2 anthracence showing white emission and high charge mobility. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 722–727 (2017).
Jin, J. et al. Modulating tri-mode emission for single-component white organic afterglow. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 24984–24990 (2021).
Wang, Y. et al. Host-guest materials with room temperature phosphorescence: tunable emission color and thermal printing patterns. SmartMat 1, e1006 (2020).
Yamashita, Y. et al. Efficient molecular doping of polymeric semiconductors driven by anion exchange. Nature 572, 634–638 (2019).
Qin, Z. et al. Organic polarized light-emitting transistors. Adv. Mater. 35, 2301955 (2023).
Lu, T. & Chen, F. Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 33, 580–592 (2012).
Lu, T. & Chen, F. Quantitative analysis of molecular surface based on improved marching tetrahedra algorithm. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 38, 314–323 (2012).
Frisch, M. J. et al. Gaussian 16, Revision B.01 (Gaussian, 2016).
Lu, T. & Chen, Q. Revealing molecular electronic structure via analysis of valence electron density. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 34, 503–513 (2018).
Liu, J. et al. High mobility emissive organic semiconductor. Nat. Commun. 6, 10032 (2015).
Liu, J. et al. Thin film field-effect transistors of 2,6-diphenyl anthracene (DPA). Chem. Commun. 51, 11777–11779 (2015).
Qin, Z. et al. High-efficiency single-component organic light-emitting transistors. Adv. Mater. 31, 1903175 (2019).
Ding, R. et al. High-color-rendering and high-efficiency white organic light-emitting devices based on double-doped organic single crystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1807606 (2019).
Wang, T. et al. Intrinsic linear dichroism of organic single crystals toward high-performance polarization-sensitive photodetectors. Adv. Mater. 34, 2105665 (2022).
Zhang, J. et al. Strong linearly polarized photoluminescence and electroluminescence from halide perovskite/azobenzene dye composite film for display applications. Adv. Opt. Mater. 8, 1901824 (2020).
Wang, J. et al. Polarized light-emitting diodes based on anisotropic excitons in few-layer ReS2. Adv. Mater. 32, 2001890 (2020).
Fung, M. K., Li, Y. Q. & Liao, L. S. Tandem organic light-emitting diodes. Adv. Mater. 28, 10381–10408 (2016).
Li, Y. et al. Tailor-made nanostructures bridging chaos and order for highly efficient white organic light-emitting diodes. Nat. Commun. 10, 2972 (2019).
Chen, J. et al. Efficient and bright white light-emitting diodes based on single-layer heterophase halide perovskites. Nat. Photon. 15, 238–244 (2020).
Ding, R. et al. Clarification of the molecular doping mechanism in organic single-crystalline semiconductors and their application in color-tunable light-emitting devices. Adv. Mater. 30, 1801078 (2018).
Wang, H. et al. Preparation, optical property and field-effect mobility investigation of stable white-emissive doped organic crystal. CrystEngComm 17, 2168–2175 (2015).
He, Z. et al. white-light emission from a single organic molecule with dual phosphorescence at room temperature. Nat. Commun. 8, 416 (2017).
Manna, B., Nandi, A. & Ghosh, R. Energy transfer-mediated white-light emission from Nile red-doped 9,10-diphenylanthracene nanoaggregates upon excitation with near UV light. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 18, 2748–2758 (2019).
Sun, Y., Lei, Y., Liao, L. & Hu, W. Competition between arene-perfluoroarene and charge-transfer interactions in organic light-harvesting systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 10352–10356 (2017).
Chen, S. et al. Organic white-light sources: multiscale construction of organic luminescent materials from molecular to macroscopic level. Sci. China Chem. 65, 740–745 (2022).
Lei, Y., Liao, Q., Fu, H. & Yao, J. Orange-blue-orange triblock one-dimensional heterostructures of organic microrods for white-light emission. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 1742–1743 (2010).
Zhuo, M. P. et al. Hierarchical self-assembly of organic core/multi-shell microwires for trichromatic white-light sources. Adv. Mater. 33, 2102719 (2021).
Li, Z. Z. et al. White-emissive self-assembled organic microcrystals. Small 13, 1604110 (2017).
Gwinner, M. C. et al. Highly efficient single-layer polymer ambipolar light-emitting field-effect transistors. Adv. Mater. 24, 2728–2734 (2012).
Tu, L., Xie, Y., Li, Z. & Tang, B. Aggregation-induced emission: red and near-infrared organic light-emitting diodes. SmartMat 2, 326–346 (2021).
Fan, X. C. et al. Thermally activated delayed fluorescence materials for nondoped organic light-emitting diodes with nearly 100% exciton harvest. SmartMat 4, e1122 (2022).
Wang, C., Liu, Y. & Guo, Y. Intrinsically flexible organic phototransistors for bioinspired neuromorphic sensory system. Wearable Electron. 1, 41–52 (2024).
Lin, C.-C. et al. A solution processable dithioalkyl dithienothiophene (DSDTT) based small molecule and its blends for high performance organic field effect transistors. ACS Nano 15, 727–738 (2021).
Wang, C., Dong, H., Hu, W., Liu, Y. & Zhu, D. Semiconducting π-conjugated systems in field-effect transistors: a material odyssey of organic electronics. Chem. Rev. 112, 2208–2267 (2012).
Wang, S. et al. Skin electronics from scalable fabrication of an intrinsically stretchable transistor array. Nature 555, 83–88 (2018).
Hepp, A. et al. Light-emitting field-effect transistor based on a tetracene thin film. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 157406 (2003).
Hou, L. et al. Optically switchable organic light-emitting transistors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 14, 347–353 (2019).
Wu, Z. et al. Efficient and low-voltage vertical organic permeable base light-emitting transistors. Nat. Mater. 20, 1007–1014 (2021).
Qin, Z., Gao, H., Dong, H. & Hu, W. Organic light-emitting transistors entering a new development stage. Adv. Mater. 33, 2007149 (2021).
Chen, Y. et al. Nanofloating gate modulated synaptic organic light-emitting transistors for reconfigurable displays. Sci. Adv. 8, eabq4824 (2022).
Capelli, R. et al. Organic light-emitting transistors with an efficiency that outperforms the equivalent light-emitting diodes. Nat. Mater. 9, 496–503 (2010).
Chen, L. et al. High-performance ambipolar and n-type emissive semiconductors based on perfluorophenyl-substituted perylene and anthracene. Adv. Sci. 10, 2300530 (2023).
Chen, H., Huang, W., Marks, T. J., Facchetti, A. & Meng, H. Recent advances in multi-layer light-emitting heterostructure transistors. Small 17, 2007661 (2021).
Khasminskaya, S. et al. Fully integrated quantum photonic circuit with an electrically driven light source. Nat. Photon. 10, 727–732 (2016).
Fan, F., Turkdogan, S., Liu, Z., Shelhammer, D. & Ning, C. Z. A monolithic white laser. Nat. Nanotechnol. 10, 796–803 (2015).
So, J.-P. et al. Electrically driven strain-induced deterministic single-photon emitters in a van der Waals heterostructure. Sci. Adv. 7, eabj3176 (2021).
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 52233010 to H.D. and C.G., 52103245 to C.G., 52403342 to Z.Q., 52121002 to W.H., U21A6002 to W.H., T2441002 to W.H. and H.D., and 22021002 to H.D.), the CAS Project for Young Scientists in Basic Research (grant no. YSBR-053 to H.D.), the Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (grant no. BNLMS-CXXM-202012 to H.D., C.G., T.W., H.G. and Z.Q.), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant no. 2023M743552 to Z.Q.), the China National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents (grant no. BX20230372 to Z.Q.), and Haihe Laboratory of Sustainable Chemical Transformations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.D. and W.H. conceived the project and designed the experiments. Z.Q. prepared the molecular doped organic semiconductor single crystals, fabricated devices, and measured their optical and electrical properties. Y.Z. prepared and characterized organic field-effect transistor devices. Y.Z. participated in the fabrication of OPLEDs. T.W., H.G. and C.G. assisted with the experiment characterizations and data analysis. Z.Q. performed the theoretical calculations. Z.Q., H.D. and W.H. wrote the paper. X.Z kindly provided help for atomic force microscopy morphology characterization. All authors discussed the results and commented on the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Photonics thanks Qingdong Ou, Qichun Zhang and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–33, Notes 1–4 and Tables 1–3.
Supplementary Video 1
A video of the OPLEDs device in operation.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, T. et al. Intrinsically white organic polarized emissive semiconductors. Nat. Photon. 19, 378–386 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-024-01609-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-024-01609-6
This article is cited by
-
Polarized white-light emission from organic semiconductors
Nature Photonics (2025)
-
High performance white emission polarized single crystal and device
Science China Materials (2025)