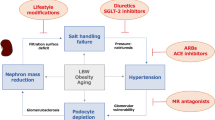
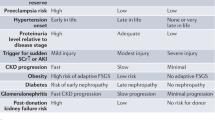
Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is defined by persistent abnormalities of kidney function or structure that have consequences for the health. A progressive decline of excretory kidney function has effects on body homeostasis. CKD is tightly associated with accelerated cardiovascular disease and severe infections, and with premature death. Kidney failure without access to kidney replacement therapy is fatal — a reality in many regions of the world. CKD can be the consequence of a single cause, but CKD in adults frequently relates rather to sequential injuries accumulating over the life course or to the presence of concomitant risk factors. The shared pathomechanism of CKD progression is the irreversible loss of kidney cells or nephrons together with haemodynamic and metabolic overload of the remaining nephrons, leading to further loss of kidney cells or nephrons. The management of patients with CKD focuses on early detection and on controlling all modifiable risk factors. This approach includes reducing the overload of the remaining nephrons with inhibitors of the renin–angiotensin system and the sodium-glucose transporter 2, as well as disease-specific drug interventions, if available. Hypertension, anaemia, metabolic acidosis and secondary hyperparathyroidism contribute to cardiovascular morbidity and reduced quality of life, and require diagnosis and treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 1 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $119.00 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 July 2025
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-025-00641-2
References
Curhan, G. C. Prediabetes, prehypertension … is it time for pre-CKD? Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 5, 557–559 (2010).
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group KDIGO 2024 Clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 105, S117–S314. Latest definition and classification of CKD, which sets the global standard on how to deal with CKD and all its consequences.
Luyckx, V. A. et al. Nephron overload as a therapeutic target to maximize kidney lifespan. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 18, 171–183 (2022).
Jager, K. J. et al. A single number for advocacy and communication-worldwide more than 850 million individuals have kidney diseases. Kidney Int. 96, 1048–1050 (2019).
Kovesdy, C. P. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: an update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. 12, 7–11 (2022).
Feng, X. et al. Secular trends of epidemiologic patterns of chronic kidney disease over three decades: an updated analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ Open 13, e064540 (2023).
Steiger, S. et al. Sex dimorphism in kidney health and disease: mechanistic insights and clinical implication. Kidney Int. 107, 51–67 (2025).
Dimitriadis, E. et al. Pre-eclampsia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 9, 8 (2023).
Zhang, J. J. et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes of pregnancy in CKD and CKD outcomes in pregnancy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10, 1964–1978 (2015).
Neugarten, J. & Golestaneh, L. Sex differences in acute kidney injury. Semin. Nephrol. 42, 208–218 (2022).
Ene-Iordache, B. et al. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk in six regions of the world (ISN-KDDC): a cross-sectional study. Lancet Glob. Health 4, e307–e319, (2016).
Harambat, J., van Stralen, K. J., Kim, J. J. & Tizard, E. J. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease in children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 27, 363–373 (2012).
Batte, A., Shahrin, L., Claure-Del Granado, R., Luyckx, V. A. & Conroy, A. L. Infections and acute kidney injury: a global perspective. Semin. Nephrol. 43, 151466 (2023).
Kamath, N., Iyengar, A., George, N. & Luyckx, V. A. Risk factors and rate of progression of CKD in children. Kidney Int. Rep. 4, 1472–1477 (2019).
Stern-Zimmer, M., Calderon-Margalit, R., Skorecki, K. & Vivante, A. Childhood risk factors for adulthood chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 36, 1387–1396 (2021).
Hill, N. R. et al. Global prevalence of chronic kidney disease — a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 11, e0158765 (2016).
Kim, G. H. Primary role of the kidney in pathogenesis of hypertension. Life 14, 119 (2024).
GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 395, 709–733 (2020).
Luyckx, V. A. & Brenner, B. M. Birth weight, malnutrition and kidney-associated outcomes—a global concern. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 11, 135–149 (2015).
Luyckx, V. A. et al. Reducing major risk factors for chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 7, 71–87 (2017).
Luks, A. M., Johnson, R. J. & Swenson, E. R. Chronic kidney disease at high altitude. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 19, 2262–2271 (2008).
Zeng, X. et al. Associations between socioeconomic status and chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 72, 270–279 (2018).
Inker, L. A. et al. New creatinine- and cystatin C–based equations to estimate GFR without race. N. Engl. J. Med. 385, 1737–1749 (2021).
Fabian, J. et al. Measurement of kidney function in Malawi, South Africa, and Uganda: a multicentre cohort study. Lancet Glob. Health 10, e1159–e1169 (2022).
Gansevoort, R. T. et al. What should European nephrology do with the new CKD-EPI equation? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 38, 1–6 (2023).
Knoers, N. et al. Genetic testing in the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease: recommendations for clinical practice. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 37, 239–254 (2022).
Becherucci, F. et al. A clinical workflow for cost-saving high-rate diagnosis of genetic kidney diseases. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 34, 706–720 (2023).
Boeckhaus, J. et al. Lifelong effect of therapy in young patients with the COL4A5 Alport missense variant p.(Gly624Asp): a prospective cohort study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 37, 2496–2504 (2022).
Egbuna, O. et al. Inaxaplin for proteinuric kidney disease in persons with two APOL1 variants. N. Engl. J. Med. 388, 969–979 (2023).
Genovese, G. et al. Association of trypanolytic ApoL1 variants with kidney disease in African Americans. Science 329, 841–845 (2010).
Khan, A. et al. Genome-wide polygenic score to predict chronic kidney disease across ancestries. Nat. Med. 28, 1412–1420 (2022).
Priyadarshani, W. V. D., de Namor, A. F. D. & Silva, S. R. P. Rising of a global silent killer: critical analysis of chronic kidney disease of uncertain aetiology (CKDu) worldwide and mitigation steps. Environ. Geochem. Health 45, 2647–2662 (2023).
Villalvazo, P., Carriazo, S., Martin-Cleary, C. & Ortiz, A. Aguascalientes: one of the hottest chronic kidney disease (CKD) hotspots in Mexico and a CKD of unknown aetiology mystery to be solved. Clin. Kidney J. 14, 2285–2294 (2021).
Chicas, R. et al. Chronic kidney disease among workers: a review of the Literature. Workplace Health Saf. 67, 481–490 (2019).
Luyckx, V. A. et al. Mind the gap in kidney care: translating what we know into what we do. Kidney Int. 105, 406–417 (2024).
Foreman, K. J. et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: reference and alternative scenarios for 2016–40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 392, 2052–2090 (2018).
GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators Global, regional, and national age–sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 385, 117–171 (2015).
Bello, A. K. et al. ISN–global kidney health atlas: a report by the International Society of Nephrology: an assessment of global kidney health care status focussing on capacity, availability, accessibility, affordability and outcomes of kidney disease. International Society of Nephrology https://www.theisn.org/wp-content/uploads/media/ISN%20Atlas_2023%20Digital_REV_2023_10_03.pdf (2023). Latest overview on kidney health care in all regions of the world displaying wide variation of access to nephrology specialists, quality of diagnostic workup and preferences for KRT.
Luyckx, V. A. et al. Equity and quality of global CKD care: what are we waiting for? Am. J. Nephrol. 55, 298–315 (2024).
Bello, A. K. et al. An update on the global disparities in kidney disease burden and care across world countries and regions. Lancet Glob. Health 12, e382–e395 (2024).
Huijben, J. A. et al. Increasing numbers and improved overall survival of patients on kidney replacement therapy over the last decade in Europe: an ERA Registry study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 38, 1027–1040 (2023).
Lentine, K. L. et al. OPTN/SRTR 2022 annual data report: kidney. Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients https://srtr.transplant.hrsa.gov/ADR/Chapter?name=Kidney&year=2022 (2022).
Miyazaki, M. et al. Comparison of survival rates between incident hemodialysis patients and peritoneal dialysis patients: a 5-year prospective cohort study with propensity score matching. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 27, 419–426 (2023).
Anders, H. J., Huber, T. B., Isermann, B. & Schiffer, M. CKD in diabetes: diabetic kidney disease versus nondiabetic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 14, 361–377 (2018).
Bertram, J. F., Douglas-Denton, R. N., Diouf, B., Hughson, M. D. & Hoy, W. E. Human nephron number: implications for health and disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 26, 1529–1533 (2011).
Hingorani, S. et al. Prevalence and risk factors for kidney disease and elevated BP in 2-year-old children born extremely premature. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 17, 1129–1138 (2022).
Grams, M. E. et al. Kidney-failure risk projection for the living kidney-donor candidate. N. Engl. J. Med. 374, 411–421 (2016).
Mueller, T. F. & Luyckx, V. A. The natural history of residual renal function in transplant donors. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 23, 1462–1466 (2012).
Laouari, D. et al. TGF-α mediates genetic susceptibility to chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 22, 327–335 (2011).
Helal, I., Fick-Brosnahan, G. M., Reed-Gitomer, B. & Schrier, R. W. Glomerular hyperfiltration: definitions, mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 8, 293–300 (2012).
Cortinovis, M., Perico, N., Ruggenenti, P., Remuzzi, A. & Remuzzi, G. Glomerular hyperfiltration. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 18, 435–451 (2022). Important concept of increased kidney workload and its role in the progression of CKD.
D’Agati, V. D. et al. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: clinical and pathologic characteristics and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 12, 453–471 (2016).
Tonneijck, L. et al. Glomerular hyperfiltration in diabetes: mechanisms, clinical significance, and treatment. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 28, 1023–1039 (2017).
Kopp, J. B. et al. Podocytopathies. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 6, 68 (2020).
Denic, A. et al. The substantial loss of nephrons in healthy human kidneys with aging. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 28, 313–320 (2017). This paper explains how even healthy ageing involves loss of nephrons; thinking in terms of nephrons rather than eGFR or proteinuria provides a better framework to understand the pathophysiology of CKD and why it is more common in the second phase of life.
Hodgin, J. B. et al. Glomerular aging and focal global glomerulosclerosis: a podometric perspective. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 26, 3162–3178 (2015).
Kriz, W. & Lemley, K. V. The role of the podocyte in glomerulosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 8, 489–497 (1999).
Kriz, W. & Lemley, K. V. A potential role for mechanical forces in the detachment of podocytes and the progression of CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 26, 258–269 (2015).
Bedin, M. et al. Human C-terminal CUBN variants associate with chronic proteinuria and normal renal function. J. Clin. Invest. 130, 335–344 (2020).
Herold, J. M. et al. Population-based reference values for kidney function and kidney function decline in 25- to 95-year-old Germans without and with diabetes. Kidney Int. 106, 699–711 (2024).
Xie, X. et al. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors and kidney and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CKD: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 67, 728–741 (2016).
Barrera-Chimal, J., Jaisser, F. & Anders, H. J. The mineralocorticoid receptor in chronic kidney disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 179, 3152–3164 (2022).
Verma, S. et al. Aldosterone and aldosterone synthase inhibitors in cardiorenal disease. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 326, H670–H688 (2024).
Schiffrin, E. L. & Pollock, D. M. Endothelin system in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Hypertension 81, 691–701 (2024).
Nagasawa, H. et al. Sparsentan is superior to losartan in the gddY mouse model of IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 1494–1503 (2024).
Heerspink, H. J. L. et al. Sparsentan in patients with IgA nephropathy: a prespecified interim analysis from a randomised, double-blind, active-controlled clinical trial. Lancet 401, 1584–1594 (2023).
Vallon, V. How can inhibition of glucose and sodium transport in the early proximal tubule protect the cardiorenal system? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 1565–1573 (2024). The latest concepts about how SGLT2 inhibitors confer their beneficial effects on the kidney and the cardiovascular system.
Nuffield Department of Population Health Renal Studies Group & SGLT2 inhibitor Meta-Analysis Cardio-Renal Trialists’ Consortium. Impact of diabetes on the effects of sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors on kidney outcomes: collaborative meta-analysis of large placebo-controlled trials. Lancet 400, 1788–1801 (2022).
Billing, A. M. et al. Metabolic communication by SGLT2 inhibition. Circulation 149, 860–884 (2024).
Ge, M. et al. Empagliflozin reduces podocyte lipotoxicity in experimental Alport syndrome. eLife 12, e83353 (2023).
Ma, Q., Steiger, S. & Anders, H. J. Sodium glucose transporter-2 inhibition has no renoprotective effects on non-diabetic chronic kidney disease. Physiol. Rep. 5, e13228 (2017).
Zhu, Z. et al. Finerenone added to RAS/SGLT2 blockade for CKD in Alport syndrome. results of a randomized controlled trial with Col4a3−/− mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 34, 1513–1520 (2023).
Klinkhammer, B. M. et al. Current kidney function parameters overestimate kidney tissue repair in reversible experimental kidney disease. Kidney Int. 102, 307–320 (2022).
Friedrich, J., Bellmann, M., Klank, D., Porubsky, S. & Bergner, R. Clinical and histological comparison of IgA nephritis and renal IgA vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 40, 182–192 (2024).
Lazzeri, E. et al. Endocycle-related tubular cell hypertrophy and progenitor proliferation recover renal function after acute kidney injury. Nat. Commun. 9, 1344 (2018).
De Chiara, L., Lazzeri, E. & Romagnani, P. Polyploid tubular cells: a shortcut to stress adaptation. Kidney Int. 105, 709–716 (2024).
Li, L., Fu, H. & Liu, Y. The fibrogenic niche in kidney fibrosis: components and mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 18, 545–557 (2022).
Steiger, S. et al. Anti-transforming growth factor β IgG elicits a dual effect on calcium oxalate crystallization and progressive nephrocalcinosis-related chronic kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 9, 619 (2018).
Buchtler, S. et al. Cellular origin and functional relevance of collagen I production in the kidney. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 29, 1859–1873 (2018).
Ninichuk, V. et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells reduce interstitial fibrosis but do not delay progression of chronic kidney disease in collagen4A3-deficient mice. Kidney Int. 70, 121–129 (2006).
Douglas, C. E. et al. Effect of age on hypertension recognition in children with chronic kidney disease: a report from the chronic kidney disease in children study. Hypertension 80, 1048–1056 (2023).
Novak, J. E. & Ellison, D. H. Diuretics in states of volume overload: core curriculum 2022. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 80, 264–276 (2022).
Vaz de Castro, P. A. S. et al. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: a comprehensive overview. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 35, 421–434 (2022).
Sarafidis, P. et al. A European Renal Association (ERA) synopsis for nephrology practice of the 2023 European Society of Hypertension (ESH) Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 929–943 (2024).
Palmer, B. F. & Clegg, D. J. Hyperkalemia treatment standard. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 1097–1104 (2024).
Raphael, K. L. Metabolic acidosis and subclinical metabolic acidosis in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 29, 376–382 (2018).
Fan, Z. et al. Correlation between soluble klotho and chronic kidney disease–mineral and bone disorder in chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 14, 4477 (2024).
Barrera-Baena, P. et al. Serum phosphate is associated with increased risk of bone fragility fractures in hemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 618–626 (2023).
Bacchetta, J. et al. Diagnosis and management of mineral and bone disorders in infants with CKD: clinical practice points from the ESPN CKD-MBD and Dialysis working groups and the Pediatric Renal Nutrition Taskforce. Pediatr. Nephrol. 38, 3163–3181 (2023).
Steiger, S., Ma, Q. & Anders, H. J. The case for evidence-based medicine for the association between hyperuricaemia and CKD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 16, 422 (2020).
Badve, S. V. et al. Effects of allopurinol on the progression of chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 2504–2513 (2020).
Ma, Q. et al. Soluble uric acid inhibits β2 integrin–mediated neutrophil recruitment in innate immunity. Blood 139, 3402–3417 (2022).
Ma, Q. et al. Soluble uric acid is an intrinsic negative regulator of monocyte activation in monosodium urate crystal-induced tissue inflammation. J. Immunol. 205, 789–800 (2020).
Steiger, S., Rossaint, J., Zarbock, A. & Anders, H. J. Secondary immunodeficiency related to kidney disease (SIDKD)-definition, unmet need, and mechanisms. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 33, 259–278 (2022). This paper introduces a definition and mechanisms for secondary immunodeficiency due to CKD, which may help to understand why infections are the second cause of death in patients with CKD.
Rossaint, J. et al. FGF23 signaling impairs neutrophil recruitment and host defense during CKD. J. Clin. Invest. 126, 962–974 (2016).
Meijers, B., Evenepoel, P. & Anders, H. J. Intestinal microbiome and fitness in kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 15, 531–545 (2019).
Holle, J. et al. Inflammation in children with CKD linked to gut dysbiosis and metabolite imbalance. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 33, 2259–2275 (2022).
Jin, Q. et al. Circulating metabolomic markers linking diabetic kidney disease and incident cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: analyses from the Hong Kong Diabetes Biobank. Diabetologia 67, 837–849 (2024).
Lee, A. M. et al. Circulating metabolomic associations with neurocognitive outcomes in pediatric CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 19, 13–25 (2024).
Le Gall, L. et al. Haemoglobin trajectories in chronic kidney disease and risk of major adverse cardiovascular events. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 669–682 (2023).
Barbieri, M. et al. Efficacy of erythropoietin as a neuroprotective agent in CKD-associated cognitive dysfunction: a literature systematic review. Pharmacol. Res. 203, 107146 (2024).
Babitt, J. L. & Lin, H. Y. Mechanisms of anemia in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 23, 1631–1634 (2012).
Go, A. S., Chertow, G. M., Fan, D., McCulloch, C. E. & Hsu, C. Y. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 351, 1296–1305 (2004).
Speer, T., Dimmeler, S., Schunk, S. J., Fliser, D. & Ridker, P. M. Targeting innate immunity-driven inflammation in CKD and cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 18, 762–778 (2022).
Grabner, A. et al. Activation of cardiac fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 causes left ventricular hypertrophy. Cell Metab. 22, 1020–1032 (2015).
Anker, S. D. et al. Empagliflozin in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 385, 1451–1461 (2021).
McMurray, J. J. V. et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 381, 1995–2008 (2019).
Agarwal, R. et al. Cardiovascular and kidney outcomes with finerenone in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: the FIDELITY pooled analysis. Eur. Heart J. 43, 474–484 (2022).
Buchanan, C. et al. Intradialytic cardiac magnetic resonance imaging to assess cardiovascular responses in a short-term trial of hemodiafiltration and hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 28, 1269–1277 (2017).
Fernandez-Fernandez, B. et al. Albumin downregulates Klotho in tubular cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 33, 1712–1722 (2018).
Chou, J., Kiebalo, T., Jagiello, P. & Pawlaczyk, K. Multifaceted sexual dysfunction in dialyzing men and women: pathophysiology, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Life 11, 311 (2021).
van der Heijden, B. J., van Dijk, P. C., Verrier-Jones, K., Jager, K. J. & Briggs, J. D. Renal replacement therapy in children: data from 12 registries in Europe. Pediatr. Nephrol. 19, 213–221 (2004).
Tonshoff, B., Kiepe, D. & Ciarmatori, S. Growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor system in children with chronic renal failure. Pediatr. Nephrol. 20, 279–289 (2005).
Rhee, C. M. & Kovesdy, C. P. Epidemiology: spotlight on CKD deaths—increasing mortality worldwide. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 11, 199–200 (2015).
Faye, M. et al. Five-year symptom trajectories in nondialysis-dependent CKD patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 17, 1588–1597 (2022).
Fitzpatrick, J. et al. Frailty, body composition and the risk of mortality in incident hemodialysis patients: the Predictors of Arrhythmic and Cardiovascular Risk in End Stage Renal Disease study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 34, 346–354 (2019).
Viggiano, D. et al. Mechanisms of cognitive dysfunction in CKD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 16, 452–469 (2020).
Lu, J. L. et al. Association of age and BMI with kidney function and mortality: a cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 3, 704–714 (2015).
Kim, H. W. et al. Insomnia in patients on incident maintenance dialysis and the risk of major acute cardio-cerebrovascular events and all-cause mortality. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 830–837 (2023).
Zhou, X. H. et al. Global prevalence of restless legs syndrome among hemodialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. 14, e3378 (2024).
Grams, M. E. et al. Estimated glomerular filtration rate, albuminuria, and adverse outcomes: an individual-participant data meta-analysis. JAMA 330, 1266–1277 (2023).
Delanaye, P. et al. CKD: a call for an age-adapted definition. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 30, 1785–1805 (2019).
Ku, E., Lee, B. J., Wei, J. & Weir, M. R. Hypertension in CKD: core curriculum 2019. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 74, 120–131 (2019).
Chu, K. H. et al. Long-term outcomes of living kidney donors: a single centre experience of 29 years. Nephrology 17, 85–88 (2012).
Groen In ‘t Woud, S. et al. Clinical management of children with a congenital solitary functioning kidney: overview and recommendations. Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 25, 11–20 (2021).
Sanderson, K. R. et al. Albuminuria, hypertension, and reduced kidney volumes in adolescents born extremely premature. Front. Pediatr. 8, 230 (2020).
Georgianos, P. I. & Agarwal, R. Hypertension in chronic kidney disease—treatment standard 2023. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 38, 2694–2703 (2023).
Keefe, P. & Bokhari, S. R. A. Fanconi syndrome in StatPearls (StatPearls, 2024).
Leung, N., Bridoux, F. & Nasr, S. H. Monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 1931–1941 (2021).
Kalantar-Zadeh, K. et al. Patient-centred approaches for the management of unpleasant symptoms in kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 18, 185–198 (2022). Good review summarizing the current standards of quality of life-focused treatment approaches in patients with advanced CKD.
Akalay, S. et al. Impact of preterm birth on kidney health and development. Front. Med. 11, 1363097 (2024).
Friedman, D. J. & Pollak, M. R. APOL1 nephropathy: from genetics to clinical applications. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 16, 294–303 (2021).
Ataga, K. I., Saraf, S. L. & Derebail, V. K. The nephropathy of sickle cell trait and sickle cell disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 18, 361–377 (2022).
Correa-Rotter, R. & García-Trabanino, R. Mesoamerican nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 39, 263–271 (2019).
Wang, H. et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of high-altitude polycythemia-related kidney disease in Tibetan inhabitants. Kidney Int. 102, 196–206 (2022).
Koirala, A. et al. Etiology and management of edema: a review. Adv. Kidney Dis. Health 30, 110–123 (2023).
Kashtan, C. E. Alport syndrome: achieving early diagnosis and treatment. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 77, 272–279 (2021).
Zand, L., Fervenza, F. C. & Coppo, R. Microscopic hematuria as a risk factor for IgAN progression: considering this biomarker in selecting and monitoring patients. Clin. Kidney J. 16, ii19–ii27 (2023).
Anders, H. J., Kitching, A. R., Leung, N. & Romagnani, P. Glomerulonephritis: immunopathogenesis and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 23, 453–471 (2023).
Obrycki, Ł. et al. Kidney length normative values in children aged 0–19 years — a multicenter study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 37, 1075–1085 (2022).
Dahl, N. K. et al. The clinical utility of genetic testing in the diagnosis and management of adults with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 34, 2039–2050 (2023).
Tuttle, K. R. CKD screening for better kidney health: why? Who? How? When? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 1537–1539 (2024).
Luyckx, V. A. et al. A developmental approach to the prevention of hypertension and kidney disease: a report from the Low Birth Weight and Nephron Number Working Group. Lancet 309, 424–428 (2017).
Benghanem Gharbi, M. et al. Chronic kidney disease, hypertension, diabetes, and obesity in the adult population of Morocco: how to avoid “over”- and “under”-diagnosis of CKD. Kidney Int. 89, 1363–1371 (2016).
Clark, W. F. et al. Dipstick proteinuria as a screening strategy to identify rapid renal decline. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 22, 1729–1736 (2011).
Fink, H. A. et al. Screening for, monitoring, and treatment of chronic kidney disease stages 1 to 3: a systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force and for an American College of Physicians Clinical Practice Guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 156, 570–581 (2012).
Imai, E. et al. Kidney disease screening program in Japan: history, outcome, and perspectives. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2, 1360–1366 (2007).
Moyer, V. A. & US Preventive Services Task Force Screening for chronic kidney disease: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 157, 567–570 (2012).
Ozyilmaz, A. et al. Screening for albuminuria with subsequent screening for hypertension and hypercholesterolaemia identifies subjects in whom treatment is warranted to prevent cardiovascular events. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 28, 2805–2815 (2013).
Pouwels, X. G. L. V. et al. Cost-effectiveness of home-based screening of the general population for albuminuria to prevent progression of cardiovascular and kidney disease. eClinicalMedicine 68, 102414 (2024).
Okpechi, I. G. et al. Early identification of CKD—a scoping review of the global populations. Kidney Int. Rep. 7, 1341–1353 (2022).
Cordero, L. & Ortiz, A. Decreased life expectancy: a health outcome not corrected by kidney replacement therapy that emphasizes the need for primary prevention of CKD. Clin. Kidney J. 17, sfae053 (2024).
Jiang, W. et al. Establishment and validation of a risk prediction model for early diabetic kidney disease based on a systematic review and meta-analysis of 20 cohorts. Diabetes Care 43, 925–933 (2020).
Hoerger, T. J. et al. A health policy model of CKD: 2. The cost-effectiveness of microalbuminuria screening. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 55, 463–473 (2010).
Levin, A. et al. Global kidney health 2017 and beyond: a roadmap for closing gaps in care, research, and policy. Lancet 390, 1888–1917 (2017). This article provides a roadmap on how to close gaps in global kidney health.
Maddux, F. W. The authority of courage and compassion: healthcare policy leadership in addressing the kidney disease public health epidemic. Semin. Dial. 33, 35–42 (2020).
Donohue, J. F. et al. Bridging the “Know-Do” gaps in five non-communicable diseases using a common framework driven by implementation science. J. Healthc. Leadersh. 15, 103–119 (2023).
Ndumele, C. E. et al. Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic health: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 148, 1606–1635 (2023). Inspired by the latest therapeutic advances, cardiovascular disease, CKD and metabolic disease are interconnected and, therefore, form a clinical syndrome that responds in all aspects to interventions against shared pathomechanisms.
Lim, L. L. et al. Gender-associated cardiometabolic risk profiles and health behaviors in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional analysis of the Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation (JADE) program. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 32, 100663 (2023).
Neale, E. P. et al. Lifestyle interventions, kidney disease progression, and quality of life: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Med. 5, 100643 (2023).
Kellum, J. A. et al. Acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 7, 52 (2021).
Morris, Z. S., Wooding, S. & Grant, J. The answer is 17 years, what is the question: understanding time lags in translational research. J. R. Soc. Med. 104, 510–520 (2011).
Lim, L. L. et al. Aspects of multicomponent integrated care promote sustained improvement in surrogate clinical outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 41, 1312–1320 (2018).
Chan, J. C. et al. Effects of structured versus usual care on renal endpoint in type 2 diabetes: the SURE study: a randomized multicenter translational study. Diabetes Care 32, 977–982 (2009).
Chan, J. C. N. et al. Effect of a web-based management guide on risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease: a JADE randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 5, e223862 (2022).
Ueki, K. et al. Effect of an intensified multifactorial intervention on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes (J-DOIT3): an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 5, 951–964 (2017).
Stanifer, J. W., Von Isenburg, M., Chertow, G. M. & Anand, S. Chronic kidney disease care models in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. BMJ Glob. Health 3, e000728 (2018).
Hawthorne, G., Lightfoot, C. J., Smith, A. C., Khunti, K. & Wilkinson, T. J. Multimorbidity prevalence and patterns in chronic kidney disease: findings from an observational multicentre UK cohort study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 55, 2047–2057 (2023).
Ettehad, D. et al. Blood pressure lowering for prevention of cardiovascular disease and death: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 387, 957–967 (2016).
Emdin, C. A. et al. Blood pressure lowering in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 313, 603–615 (2015).
SHARP Collaborative Group Study of Heart and Renal Protection (SHARP): randomized trial to assess the effects of lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol among 9,438 patients with chronic kidney disease. Am. Heart J. 160, 785–794.e10 (2010).
Agarwal, R. Statin induced proteinuria: renal injury or renoprotection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 15, 2502–2503 (2004).
de Zeeuw, D. et al. Renal effects of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin in patients with diabetes who have progressive renal disease (PLANET I): a randomised clinical trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 3, 181–190 (2015).
Shin, J. I. et al. Association of rosuvastatin use with risk of hematuria and proteinuria. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 33, 1767–1777 (2022).
Wijesurendra, R. S. et al. Mechanisms of rosuvastatin-related acute kidney injury following cardiac surgery: the STICS trial. Eur. Heart J. 45, 629–631 (2024).
Birmingham, B. K. et al. Impact of ABCG2 and SLCO1B1 polymorphisms on pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin, atorvastatin and simvastatin acid in Caucasian and Asian subjects: a class effect. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 71, 341–355 (2015).
Lewis, E. J., Hunsicker, L. G., Bain, R. P. & Rohde, R. D. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 329, 1456–1462 (1993).
Brenner, B. M. et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 345, 861–869 (2001).
Parving, H. H. et al. The effect of irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 345, 870–878 (2001).
Mishima, E., Haruna, Y. & Arima, H. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in hypertensive adults with non-diabetic CKD with or without proteinuria: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Hypertens. Res. 42, 469–482 (2019).
Fried, L. F. et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 369, 1892–1903 (2013).
Georgianos, P. I. & Agarwal, R. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 6, 2281–2291 (2021).
Agarwal, R. et al. Effect of finerenone on ambulatory blood pressure in chronic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. J. Hypertens. 41, 295–302 (2023).
Rossing, P. et al. Finerenone in predominantly advanced CKD and type 2 diabetes with or without sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor therapy. Kidney Int. Rep. 7, 36–45 (2022).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05047263 (2024).
Fried, L. et al. High unmet treatment needs in patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes: real-world evidence from a US claims database. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 38, 630–643 (2023).
Agarwal, R., Bills, J. E., Hecht, T. J. & Light, R. P. Role of home blood pressure monitoring in overcoming therapeutic inertia and improving hypertension control: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertension 57, 29–38 (2011).
Ling, J., Ng, J. K. C., Chan, J. C. N. & Chow, E. Use of continuous glucose monitoring in the assessment and management of patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Front. Endocrinol. 13, 869899 (2022).
Gregg, E. W. et al. Association of the magnitude of weight loss and changes in physical fitness with long-term cardiovascular disease outcomes in overweight or obese people with type 2 diabetes: a post-hoc analysis of the Look AHEAD randomised clinical trial. lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 4, 913–921 (2016).
Lachin, J. M., Genuth, S., Cleary, P., Davis, M. D. & Nathan, D. M. Retinopathy and nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes four years after a trial of intensive therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 342, 381–389 (2000).
Holman, R. R., Paul, S. K., Bethel, M. A., Matthews, D. R. & Neil, H. A. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 359, 1577–1589 (2008).
Laiteerapong, N. et al. The legacy effect in type 2 diabetes: impact of early glycemic control on future complications (The Diabetes & Aging Study). Diabetes Care 42, 416–426 (2019).
Zoungas, S. et al. Effects of intensive glucose control on microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 5, 431–437 (2017).
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Diabetes Work Group. KDIGO 2022 Clinical practice guideline for diabetes management in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 102, S1–S127 (2022). The latest international treatment standards for patients with CKD and diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for fast progression of kidney function loss.
Imai, E. et al. Effects of blood pressure on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes and overt nephropathy: a post hoc analysis (ORIENT-blood pressure). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 31, 447–454 (2016).
Hammoud, R. & Drucker, D. J. Beyond the pancreas: contrasting cardiometabolic actions of GIP and GLP1. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 19, 201–216 (2023).
Marso, S. P. et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 375, 1834–1844 (2016).
Gerstein, H. C. et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 394, 121–130 (2019).
Rossing, P. et al. The rationale, design and baseline data of FLOW, a kidney outcomes trial with once-weekly semaglutide in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 38, 2041–2051 (2023).
Perkovic, V. et al. Effects of semaglutide on chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 391, 109–121 (2024).
Chow, E., Yang, A., Chung, C. H. L. & Chan, J. C. N. A clinical perspective of the multifaceted mechanism of metformin in diabetes, infections, cognitive dysfunction, and cancer. Pharmaceuticals 15, 442 (2022).
Yang, A. et al. Clinical outcomes following discontinuation of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes and advanced chronic kidney disease in Hong Kong: a territory-wide, retrospective cohort and target trial emulation study. eClinicalMedicine 71, 102568 (2024).
Yang, A. et al. Clinical outcomes following discontinuation of renin-angiotensin-system inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes and advanced chronic kidney disease: a prospective cohort study. eClinicalMedicine 55, 101751 (2023).
Bhandari, S. et al. Renin–angiotensin system inhibition in advanced chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 387, 2021–2032 (2022). A clinical trial to investigate whether renin–angiotensin system inhibitors should or should not be stopped as patients approach ultimate kidney failure.
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Anemia Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2, 279–335 (2012).
Del Vecchio, L. et al. Iron biology. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 1404–1415 (2024).
Elliott, J., Mishler, D. & Agarwal, R. Hyporesponsiveness to erythropoietin: causes and management. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 16, 94–100 (2009).
Agarwal, R., Kusek, J. W. & Pappas, M. K. A randomized trial of intravenous and oral iron in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 88, 905–914 (2015).
Macdougall, I. C. Anaemia in CKD—treatment standard. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 770–777 (2024).
Wang, C. et al. Comparative risk of anaphylactic reactions associated with intravenous iron products. JAMA 314, 2062–2068 (2015).
Singh, A. K. et al. Daprodustat for the treatment of anemia in patients undergoing dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 385, 2325–2335 (2021).
Stoumpos, S. et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for anaemia in chronic kidney disease: a clinical practice document by the European Renal Best Practice board of the European Renal Association. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 1710–1730 (2024).
Evenepoel, P. et al. Recommended calcium intake in adults and children with chronic kidney disease—a European consensus statement. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 341–366 (2024).
Rodríguez-Ortiz, M. E. & Rodríguez, M. Recent advances in understanding and managing secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic kidney disease. F1000Research https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.22636.1 (2020).
Markham, A. Tenapanor: first approval. Drugs 79, 1897–1903 (2019).
FDA. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2024/213931Orig1s000TOC.cfm (2024).
Ardelyx. https://ir.ardelyx.com/news-releases/news-release-details/ardelyx-announces-acceptance-new-drug-application-tenapanor (2023).
PMDA. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000271700.pdf (2023).
King, A. J. et al. Inhibition of sodium/hydrogen exchanger 3 in the gastrointestinal tract by tenapanor reduces paracellular phosphate permeability. Sci. Transl. Med. 10, eaam6474 (2018).
Chertow, G. M. et al. Effect of cinacalcet on cardiovascular disease in patients undergoing dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 367, 2482–2494 (2012).
Amaya-Garrido, A. et al. Calprotectin is a contributor to and potential therapeutic target for vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 15, eabn5939 (2023).
Engler, F., Kerschbaum, J., Keller, F. & Mayer, G. Prevalence, patient burden and physicians’ perception of pruritus in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 277–285 (2024).
Agarwal, R. et al. Alleviating symptoms in patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis: a focus on chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus. Clin. Kidney J. 16, 30–40 (2023).
Fishbane, S., Jamal, A., Munera, C., Wen, W. & Menzaghi, F. A phase 3 trial of difelikefalin in hemodialysis patients with pruritus. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 222–232 (2020). A phase 3 trial that led to the approval for a drug to alleviate uraemic pruritus, a very annoying symptom with negative impact on quality of life for patients with kidney failure.
Porter, A. C. et al. Predictors and outcomes of health-related quality of life in adults with CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 11, 1154–1162 (2016).
Jesky, M. D. et al. Health-related quality of life impacts mortality but not progression to end-stage renal disease in pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease: a prospective observational study. PLoS ONE 11, e0165675 (2016).
Morton, R. L., Tong, A., Howard, K., Snelling, P. & Webster, A. C. The views of patients and carers in treatment decision making for chronic kidney disease: systematic review and thematic synthesis of qualitative studies. BMJ 340, c112 (2010).
Hussien, H., Apetrii, M. & Covic, A. Health-related quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 21, 43–54 (2021).
Brown, E. A. et al. Burden of kidney disease, health-related quality of life, and employment among patients receiving peritoneal dialysis and in-center hemodialysis: findings from the DOPPS program. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 78, 489–500.e1 (2021).
Fletcher, B. R. et al. Symptom burden and health-related quality of life in chronic kidney disease: a global systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 19, e1003954 (2022).
Murtagh, F. E. et al. Symptoms in advanced renal disease: a cross-sectional survey of symptom prevalence in stage 5 chronic kidney disease managed without dialysis. J. Palliat. Med. 10, 1266–1276 (2007).
Eckardt, K. U. et al. Trends and perspectives for improving quality of chronic kidney disease care: conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 104, 888–903 (2023).
Al Sayah, F., Lahtinen, M., Bonsel, G. J., Ohinmaa, A. & Johnson, J. A. A multi-level approach for the use of routinely collected patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) data in healthcare systems. J. Patient Rep. Outcomes 5, 98 (2021).
Da Silva-Gane, M. et al. Quality of life and survival in patients with advanced kidney failure managed conservatively or by dialysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 7, 2002–2009 (2012).
Vilar, E. et al. A multicenter feasibility randomized controlled trial to assess the impact of incremental versus conventional initiation of hemodialysis on residual kidney function. Kidney Int. 101, 615–625 (2022).
McIntyre, C., McQuillan, R., Bell, C. & Battistella, M. Targeted deprescribing in an outpatient hemodialysis unit: a quality improvement study to decrease polypharmacy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 70, 611–618 (2017).
Moryousef, J. et al. Deprescribing opportunities for hospitalized patients with end-stage kidney disease on hemodialysis: a secondary analysis of the MedSafer cluster randomized controlled trial. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 9, 20543581221098778 (2022).
Valenzuela, P. L., Castillo-García, A., Saco-Ledo, G., Santos-Lozano, A. & Lucia, A. Physical exercise: a polypill against chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 1384–1391 (2024).
Time to sound the alarm about the hidden epidemic of kidney disease. Nature 628, 7–8 (2024).
Francis, A. et al. Chronic kidney disease and the global public health agenda: an international consensus. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 20, 473–485 (2024).
Denic, A. et al. Single-nephron glomerular filtration rate in healthy adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 376, 2349–2357 (2017).
Rothberg, A. E. & Herman, W. H. How to assess kidney outcomes in obese people with substantial weight loss: the case of GLP1- and dual-receptor agonists. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 1060–1062 (2024).
Kotwal, S., Perkovic, E. & Perkovic, V. Combination therapy with kidney protective therapies: optimizing the benefits. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 33, 136–143 (2024).
Gross, O., Haffner, D., Schaefer, F. & Weber, L. T. SGLT2 inhibitors: approved for adults and cats but not for children with CKD. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 39, 907–909 (2024).
Afsar, B. et al. Sodium–glucose cotransporter inhibition in polycystic kidney disease: fact or fiction. Clin. Kidney J. 15, 1275–1283 (2022).
Heerspink, H. J. L. et al. Development and validation of a new hierarchical composite end point for clinical trials of kidney disease progression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 34, 2025–2038 (2023).
Levey, A. S. et al. Change in albuminuria and GFR as end points for clinical trials in early stages of CKD: a scientific workshop sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation in collaboration with the US Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 75, 84–104 (2020).
Thompson, A. et al. Proteinuria reduction as a surrogate end point in trials of IgA nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 14, 469–481 (2019).
Zoccali, C. et al. Funding kidney research as a public health priority: challenges and opportunities. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 37, 21–28 (2021).
Kidney disease: a global health priority. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 20, 421–423 (2024).
Carriazo, S., Vanessa Perez-Gomez, M. & Ortiz, A. Hypertensive nephropathy: a major roadblock hindering the advance of precision nephrology. Clin. Kidney J. 13, 504–509 (2020).
Freedman, B. I. & Cohen, A. H. Hypertension-attributed nephropathy: what’s in a name? Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 12, 27–36 (2016).
Snoek, R. et al. Genetics-first approach improves diagnostics of ESKD patients <50 years old. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 37, 349–357 (2022).
Heerspink, H. J. L. et al. Atrasentan and renal events in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (SONAR): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 393, 1937–1947 (2019).
Freeman, M. W. et al. Phase 2 trial of baxdrostat for treatment-resistant hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 388, 395–405 (2023).
Narva, A. Population health for CKD and diabetes: lessons from the Indian Health Service. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 71, 407–411 (2018).
Beaulieu, M. & Levin, A. Analysis of multidisciplinary care models and interface with primary care in management of chronic kidney disease. Semin. Nephrol. 29, 467–474 (2009).
What are the sustainable development goals? United Nations Development Programme https://www.undp.org/sustainable-development-goals (2024).
Karam, S., Wong, M. M. Y. & Jha, V. Sustainable development goals: challenges and the role of the international society of nephrology in improving global kidney health. Kidney360 4, 1494–1502 (2023).
Ke, C., Liang, J., Liu, M., Liu, S. & Wang, C. Burden of chronic kidney disease and its risk-attributable burden in 137 low-and middle-income countries, 1990–2019: results from the global burden of disease study 2019. BMC Nephrol. 23, 17 (2022).
Nguyen, L. T., Pollock, C. A. & Saad, S. Nutrition and developmental origins of kidney disease. Nutrients 15, 4207 (2023).
Dupuis, L., Varshney, A., Patel, J. & Joshi, S. Climate crisis and nephrology: a review of climate change’s impact on nephrology and how to combat it. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 33, 110–114 (2024).
Sasai, F. et al. Climate change and nephrology. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 38, 41–48 (2023).
Kaze, A. D., Ilori, T., Jaar, B. G. & Echouffo-Tcheugui, J. B. Burden of chronic kidney disease on the African continent: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 19, 125 (2018).
Georgianos, P. I. & Agarwal, R. Ambulatory blood pressure reduction with SGLT-2 inhibitors: dose-response meta-analysis and comparative evaluation with low-dose hydrochlorothiazide. Diabetes Care 42, 693–700 (2019).
Carrero, J. J. et al. Plant-based diets to manage the risks and complications of chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 16, 525–542 (2020).
Palmer, B. F., Kelepouris, E. & Clegg, D. J. Renal tubular acidosis and management strategies: a narrative review. Adv. Ther. 38, 949–968 (2021).
Matsushita, K. et al. Epidemiology and risk of cardiovascular disease in populations with chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 18, 696–707 (2022).
Kalim, S. et al. Protein carbamylation and the risk of ESKD in patients with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 34, 876–885 (2023).
Xu, J. et al. Renalase is a novel, soluble monoamine oxidase that regulates cardiac function and blood pressure. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 1275–1280 (2005).
Whitlock, R. et al. The association between dual RAAS inhibition and risk of acute kidney injury and hyperkalemia in patients with diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 38, 2503–2516 (2023).
Anders, H. J., Peired, A. J. & Romagnani, P. SGLT2 inhibition requires reconsideration of fundamental paradigms in chronic kidney disease, ‘diabetic nephropathy’, IgA nephropathy and podocytopathies with FSGS lesions. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 37, 1609–1615 (2022).
Ortiz, A., Wanner, C. & Gansevoort, R. Chronic kidney disease as cardiovascular risk factor in routine clinical practice: a position statement by the Council of the European Renal Association. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 38, 527–531 (2023).
de Zeeuw, D. et al. Bardoxolone methyl in type 2 diabetes and stage 4 chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 369, 2492–2503 (2013).
Lewis, E. J. et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 345, 851–860 (2001).
Mann, J. F. et al. Avosentan for overt diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 21, 527–535 (2010).
Parving, H. H. et al. Cardiorenal end points in a trial of aliskiren for type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 367, 2204–2213 (2012).
Perkovic, V. et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 380, 2295–2306 (2019).
Pfeffer, M. A. et al. A trial of darbepoetin alfa in type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 361, 2019–2032 (2009).
Pitt, B. et al. Cardiovascular events with finerenone in kidney disease and type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 385, 2252–2263 (2021).
Sharma, K. et al. Pirfenidone for diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 22, 1144–1151 (2011).
Tuttle, K. R., McGill, J. B., Haney, D. J., Lin, T. E. & Anderson, P. W. Kidney outcomes in long-term studies of ruboxistaurin for diabetic eye disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2, 631–636 (2007).
Wanner, C. et al. Atorvastatin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing hemodialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 353, 238–248 (2005).
Bakris, G. L. et al. Effect of finerenone on chronic kidney disease outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 2219–2229 (2020).
Herrington, W. G. et al. Empagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 388, 117–127 (2023).
Packham, D. K. et al. Sulodexide fails to demonstrate renoprotection in overt type 2 diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 23, 123–130 (2012).
Singh, A. K. & Singh, R. Renin-angiotensin system blockers-SGLT2 inhibitors-mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in diabetic kidney disease: a tale of the past two decades. World J. Diabetes 13, 471–481 (2022).
Lichtnekert, J. & Anders, H. J. Lupus nephritis-related chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 20, 699–711 (2024).
Yau, K., Kuah, R., Cherney, D. Z. I. & Lam, T. K. T. Obesity and the kidney: mechanistic links and therapeutic advances. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 20, 321–335 (2024).
Anders, H. J., Davis, J. M. & Thurau, K. Nephron protection in diabetic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 375, 2096–2098 (2016).
Vallon, V. The mechanisms and therapeutic potential of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetes mellitus. Annu. Rev. Med. 66, 255–270 (2015).
Beers, K. & Patel, N. Kidney physiology in pregnancy. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 27, 449–454 (2020).
Perazella, M. A. Pharmacology behind common drug nephrotoxicities. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13, 1897–1908 (2018).
Hall, R. K. et al. Drug stewardship in chronic kidney disease to achieve effective and safe medication use. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 20, 386–401 (2024).
Brenner, B. M., Garcia, D. L. & Anderson, S. Glomeruli and blood pressure. Less of one, more the other? Am. J. Hypertens. 1, 335–347 (1988).
Cirillo, L. et al. Chronic kidney disease in children: an update. Clin. Kidney J. 16, 1600–1611 (2023).
The Low Birth Weight and Nephron Number Working Group The impact of kidney development on the life course: a consensus document for action. Nephron 136, 3–49 (2017).
Trautmann, A. et al. Spectrum of steroid-resistant and congenital nephrotic syndrome in children: the PodoNet registry cohort. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10, 592–600 (2015).
Vivante, A. & Hildebrandt, F. Exploring the genetic basis of early-onset chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 12, 133–146 (2016).
Oliveira, B., Kleta, R., Bockenhauer, D. & Walsh, S. B. Genetic, pathophysiological, and clinical aspects of nephrocalcinosis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 311, F1243–F1252 (2016).
Eckardt, K. U. et al. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease: diagnosis, classification, and management—a KDIGO consensus report. Kidney Int. 88, 676–683 (2015).
Cain, J. E., Di Giovanni, V., Smeeton, J. & Rosenblum, N. D. Genetics of renal hypoplasia: insights into the mechanisms controlling nephron endowment. Pediatr. Res. 68, 91–98 (2010).
Uy, N. & Reidy, K. Developmental genetics and congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract. J. Pediatr. Genet. 5, 51–60 (2016).
Yuan, X. et al. Genetic variants of the COL4A3, COL4A4, and COL4A5 genes contribute to thinned glomerular basement membrane lesions in sporadic IgA nephropathy patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 34, 132–144 (2023).
Dummer, P. D. et al. APOL1 kidney disease risk variants: an evolving landscape. Semin. Nephrol. 35, 222–236 (2015).
Kruzel-Davila, E. et al. APOL1-mediated cell injury involves disruption of conserved trafficking processes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 28, 1117–1130 (2017).
Köttgen, A. et al. Multiple loci associated with indices of renal function and chronic kidney disease. Nat. Genet. 41, 712–717 (2009).
De Chiara, L. et al. Tubular cell polyploidy protects from lethal acute kidney injury but promotes consequent chronic kidney disease. Nat. Commun. 13, 5805 (2022).
Acknowledgements
P.R. is funded by the European Research Council under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (grant agreement no. 101019891). H.-J.A. has received support by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (AN372/29-1). R.K. is supported by the Rainer Arnhold Grant by Mulago Foundation. The authors thank B. Wang for their contribution in Box 4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to all sections of the Primer, with H.-J.A. coordinating the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Related to the content of this paper, H.-J.A. received funding from Boehringer Ingelheim and consultancy fees from Novartis, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Vifor, Otsuka, Roche and Eli Lilly. H.-J.A. received payments from the European Renal Association for his role as Editor-in-Chief of Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. H.-J.A. is a member of the Western-European Regional board of the International Society of Nephrology (ISN). Related to the content of this paper, M.N. received research funding from Kyowa-Kirin, Daiichi-Sankyo, Astellas, Ono, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Japan Tobacco, Chugai, Bayer, Torii and Takeda. M.N. received honoraria and advisory fees from Kyowa-Kirin, Astellas, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Daiichi-Sankyo, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Chugai, Torii, Japan Tobacco, Novo Nordisk and Boehringer Ingelheim. M.N. is President of the ISN, President of the Japanese Society of Nephrology, Immediate President of the Asian Pacific Society of Nephrology, President of the Japanese Society of Internal Medicine and Vice President of the Japanese Medical Science Federation. A.L. has no conflicts of interest regarding her contribution to this article, although she was the co-chair of the KDIGO Update on Chronic Kidney Disease Evaluation and Management 2024. B.R.-I. and P.R. declare no competing interests. R.A. reports personal fees from Akebia Therapeutics, Inc., Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals Inc., Boehringer Ingelheim, Chinook, Vertex, Alynlam, Intercept, Eloxx and Novartis. R.A. is an associate editor at Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation and American Journal of Nephrology, and acting Editor in Chief of American Journal of Nephrology. He is a section editor of nephrology at UpToDate. J.C.N.C. reports receiving grants (through institutions) and/or honoraria for consultancy or giving lectures from Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Hua Medicine, Powder Pharmaceuticals, Roche, Merck, MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi, Servier, Viatris and Zuellig Therapeutics. She is a co-inventor of patents assigned to the Chinese University of Hong Kong with claims of using genetic and multiomic markers to identify patients at high risk for diabetes and its complications for personalized treatment. She is the co-founder of GemVCare, a technology company, with partial support from the Hong Kong Government, which uses biogenetic markers and information technology to implement precision diabetes care and prevention through partnerships. J.C.N.C. is the Chief Executive Officer (pro bono) of the Asia Diabetes Foundation that developed the web-based JADE platform for implementation of data-driven diabetes care. She is a member of the Global Council of the European Association for Study of Diabetes and a member of the International Diabetes Federation Global Guidelines for type 2 diabetes and member of working groups of KDIGO. R.K. is a member of the African board of the ISN. S.K. is a member of the North American board of the ISN, an adviser to the Middle-East board of the ISN, a member of the education workgroup and the social media team of the ISN, a member of the core program committee of the ISN, and the chair of the young nephrologists committee of the ISN. S.K. is also a member of the clinical nephrology commission of the Société Francophone de Néphrologie Dialyse et Transplantation (SFNDT) and of the webinars committee of the SFNDT. She is also the co-chair of the education committee of the American Society of Onco-nephrology.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Disease Primers thanks S. H. Han, K. Kalantar-Zadeh, I. Ulasi and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Informed consent
The authors affirm that patient participants provided informed consent for publication of their experiences.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Romagnani, P., Agarwal, R., Chan, J.C.N. et al. Chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 11, 8 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-024-00589-9
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-024-00589-9
This article is cited by
-
Association of the C-reactive protein–to–albumin ratio (CAR) with clinical outcomes in chronic kidney disease patients undergoing surgery: a retrospective cohort analysis of the INSPIRE database
BMC Nephrology (2026)
-
Multifactorial chronic kidney disease and the kidney capacity–workload balance
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2026)
-
Progranulin impairs efferocytosis of macrophages in renal fibrosis by negatively regulating PPAR-δ-mediated inhibition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2026)
-
The Assessment of Disease Activity and Renal Prognosis in AAV – The Contribution of Urinary Biomarkers and Renal Biopsy
Current Rheumatology Reports (2026)
-
Nocturnal hypoxemic burden is associated with worsening prognosis of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Cardiovascular Diabetology (2025)