Abstract
Trilocha varians is a member of the bombycid moths. Since T. varians has a considerably shorter generation period than the prevailing model species, Bombyx mori, this species would be a novel model insect in Lepidoptera. To facilitate further use of T. varians, we developed genome annotation information on the chromosome-scale assembly of T. varians previously published by our group. 9 RNA-seq datasets and 2 Iso-seq datasets were submitted for transcriptome-based gene prediction. As a result, 16,266 protein-coding genes were predicted on the latest genome assembly, and 98.6% of BUSCO sequences were present in our gene models. ATAC-seq was also conducted to determine chromatin accessibility across the genome. Finally, piRNA-targeted small RNA-seq revealed T. varians genome harbours 517 piRNA clusters (piCs). This information will encourage and facilitate potential users who plan to use this species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background & Summary
Trilocha varians (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae; Fig. 1a) is a member of bombycid moths. While in Japan this species was identified for the first time in Okinawa in 20011, T. varians is widely distributed in South and Southeast Asia2. Since T. varians lives in low latitude regions, it is a completely non-dormant insect that does not go dormant under any rearing conditions. T. varians mainly feed on banyan leaves, Ficus microcarpa while the domesticated silkworm, Bombyx mori, mainly feed on mulberry leaves. A notable characteristic of this insect is its short generation time. T. varians takes about 30 days at 25 °C and 22 days at 30 °C from hatching to eclosion3. In addition, under rearing at 25 °C, eggs hatch in 5 days. Compared to other lepidopteran model species such as Samia ricini4, approximately 30 days of generation time is remarkably short, which is a great advantage as a model species.
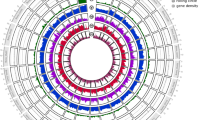
General genome annotation information. (a) Dorsal view of final instar larva of T. varians. (b) The 21-mer distribution for estimation of genome heterozygosity of T. varians. (c) Summary of T. varians genome characteristics. The outermost to the innermost circle show the following: I. chromosome ideograms; II. GC content; III. GC skew; IV. LTR element density; V. non-LTR retrotransposon density; VI. DNA transposon density; VII. rolling circle density; and VIII. gene model density.
We have recently published a chromosome-scale female genome assembly of T. varians (NCBI acc: GCA_030269945.2)5,6. Although T. varians genome retains micro and macro synteny to B. mori genome despite several chromosome fusion and fission events, the W chromosome of T. varians does not show any homology to the W chromosome of B. mori. The W chromosome of both species is derived from the Z chromosome5, but it is still uncertain whether the W chromosomes of both species are “orthologous” or not. As we have discussed, B. mori and T. varians have different physiological and genetic characteristics, even though they are members of the same family Bombycidae. Providing genome annotation information on T. varians will be useful in researching the evolution of the family Bombycidae.
T. varians is 2n = 52 species3, and females have 25 pairs of autosomes, Z chromosome, and W chromosome. T. varians used in this study is an inbred strain derived from descendants of females captured at Ishigaki island, Japan, in 2010. Therefore, the heterozygosity in the genome was 0.12% (Fig. 1b). In preparing the annotation information, we first attempted to locate the nucleolar organizer region (NOR) because NOR is a region of long repetitive sequences6, which often prevent chromosome-scale genome assembly. Transcriptome-based transcriptome-based gene prediction identified 16,226 protein-coding genes in T. varians genome. The following functional annotation was also performed using EnTAP7. Although application examples of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing in T. varians have not been reported, applying genome editing techniques should be a prerequisite for promoting further use of T. varians as a model species. Since Cas9 is known to be less efficient in heterochromatin regions8, we performed embryonic ATAC-seq to identify open chromatin regions.
It is known that piRNA is involved in the early development of lepidopteran insects. Although piRNA was originally discovered specifically in germline cells9,10,11,12, lepidopteran piRNAs are also present in the early embryos. A prominent example of the involvement of piRNAs in early development is Fem piRNA of B. mori13. Fem piRNA functions as master determinant of female. Although T. varians does not have Fem, it is known that in diamondback moths, Plutella xylostella, W-derived piRNAs are still responsible for female determination14. So far, there is no report that embryonic piRNAs are involved in developmental processes other than sex determination. However, the abundance of embryonic piRNAs does not rule out such possibility. To contribute to future piRNA research in T. varians, we performed small RNA-seq in early embryos, pupal testes, and pupal ovaries to identify piRNA clusters.
Methods
Insects
T. varians (NBRP strain, derived from individuals caught in Ishigaki Island, Japan)3 was provided from National BioResource Project-Wild moths (NBRP-Wild moths; http://shigen.nig.ac.jp/wildmoth/). T. varians larvae were fed on fresh leaves of F. microcarpa. T. varians was reared under a long-day condition (16 h light/8 h dark) at 25 °C.
Estimation of genome heterozygosity
Heterozygosity of female T. varians genome was estimated using a k-mer (k = 21) analysis. Down sampled (to one-tenth) genomic PE short read data derived from female T. varians (accession number: DRR452104)15 was subjected to Jellyfish (v2.3.0)16 to count k-mer. k-mer count was plotted by GenomeScope17 software. The k-mer distribution displays a single peak and the estimated heterozygosity in the genome was 0.119% (Fig. 1a).
Repetitive elements annotation in the genomes
Repetitive annotation of T. varians genome was previously defined by our group5. To improve readability, the process of repetitive annotation is briefly summarized here: repetitive elements in the genome assembly were identified using RepeatModeler (v 2.0.4)18 with “-LTRstruct” option for performing an LTR structural search. The annotated elements were masked using RepeatMasker v 4.1.2. (http://www.repeatmasker.org) with default settings. Among the repetitive elements, LTR, non-LTR (LINE or SINE), DNA transposons, and rolling circles were extracted and the density information of those repetitive groups were visualized by circlize (v 0.4.16)19 (Fig. 1c). GC content and GC skew did not differ significantly among chromosomes, with GC content averaging about 35.6% (Fig. 1c). However, the GC content was higher in the W chromosome, at about 39.0%. This may reflect the characteristics of W chromosomes to accumulate transposons5 (Fig. 1c).
Construction of a T. varians BAC library
Bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) construction was carried out as previously described5. Basically, the procedures were followed according to a method described in Okumura et al.20 with slight modifications20. We used male genomic DNAs extracted from T. varians pupae (600 mg), and the genomic DNAs were digested with HindIII (8–12 U/ml) at 37 °C for 25 min. The digested fragments were fractionated and collected using CHEF Mapper XA pulsed-field gel electrophoresis system (Bio-Rad). The extracted DNA fragments were ligated to the pBeloBAC11 vector, and the ligates were transformed by electroporation (GenePulser II, Bio-Rad) into DH5α Electro-Cells (TaKaRa). The electroporated cells were spread on L.B. plates containing 12.5 mg/l chloramphenicol (Cm), X-gal, and isopropyl β-D-thiogalactopyranoside. Grown white colonies were stocked in 384-well plates. Stocked plates were stored at −80 °C until further use.
Chromosome preparations
Chromosome specimens were prepared using a method described in Yoshido et al.21. Briefly, ovaries and testes of the last instar larvae of T. varians were dissected in a physiological solution, and testes and ovaries were treated with 75 mM and 100 mM KCl solution for 15 min, respectively. After the hypotonic treatment, the testes and ovaries were fixed in Carnoy’s fixative (ethanol: chloroform: acetic acid, 6:3:1) for 10 min. Spermatocytes and oocytes were transferred into a 60% acetic acid drop on a glass slide and spread at 55 °C using a heating plate. The preparations were passed through 70%, 80%, and 99% ethanol series, air dried, and stored at −20 °C until time to use.
BAC-FISH mapping
Using the STS primer pairs, we selected the BACs according to the methods written in Yoshido et al.21. The PCR-selected BACs were cultured in 1.5 ml of LB medium containing 20 mg/l chloramphenicol (Cm) for 16 h at 37 °C with a shaking incubator (Bio Shaker BR-23FH, Taitec). Then, plasmid DNA was extracted using a standard alkaline SDS method. BAC-DNA probe (18N21 on Chr11 and 15F13, 17O20 on Chr20, and Pieris brassicae 01A06 for NOR detection19) labeling and BAC-FISH were performed according to a method described in Yoshido et al.21. The FISH preparations were counterstained and mounted with Vectashield Antifade Mounting Medium with DAPI (Vector Laboratories). A Leica DM6000B fluorescence microscope (Leica Microsystems) and a DFC350FX black and white charge-coupled device camera (Leica Microsystems) were used for observation and image capturing. The images were processed with Adobe Photoshop 2022. As a result, we successfully located NOR of T. varians on chromosome 20 (Fig. 2), while in B. mori, the NOR is located on chromosome 11.
BAC-FISH mapping of NOR. BAC-FISH mapping was performed using BAC probes 17O20 (yellow), 01A06 (green), 18N21 (red), and 15F13 (magenta) on T. varians chromosomes to identify the chromosome location of the NOR. The images of chromosomes 11 and 20 on the right are the results of a previous BAC-FISH analysis using the same BAC (17O20, 18N21, 15F13) (see Lee et al.5, Fig. 3). The T. varians NOR is located in the middle of chromosome 20 while NOR of Bombyx mori is located on chromosome 11. Significant chromosome elongation can be observed in the region near the NOR. The picture of chromosome 20 in the top right is from the different sample. This picture shows that the two probes, 17O20 and 15F13, paint the same chromosome. For comparison, a picture of chromosome 11 from the same sample is also shown in the bottom right.
RNA sample preparation for sRNA-seq, RNA-seq, and Iso-seq
All RNA samples were prepared exactly as previously described5. Total RNA was extracted from multiple embryos, larval, pupal, and adult tissue using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Embryos were sampled 72 hours after oviposition. Testis and ovary-derived RNA samples were subjected to RNA-seq and sRNA-seq, respectively. Embryonic RNA samples were subjected to sRNA-seq, RNA-seq, and Iso-seq, respectively.
Library preparation for sRNA-seq, RNA-seq, and Iso-seq
The sRNA-seq library was prepared using TruSeq small RNA kit (Illumina) according to the manufacturer’s protocol with a slight modification. To target piRNA, a region of 147–158 nucleotides was extracted in the purification step of the cDNA construct using BluePippin (Sage Science, USA). The constructed library was sequenced on the Illumina HiSeq. 2500 platform (Illumina, USA). RNA-seq library was prepared using NEBNext Poly(A) mRNA Magnetic Isolation Module (New England BioLabs) and NEBNext® Ultra™ ll Directional RNA Library Prep Kit (New England BioLabs) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The constructed library was sequenced on the Illumina Novaseq. 6000 platform (Illumina, USA). For Iso-seq, the library was constructed using Sequel Iso-seq Express Template Prep (Pacific Bioscience, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The constructed library was sequenced on the PacBio Sequel platform (PacBio, USA).
Transcriptome-based gene prediction
BRAKER3 (v 3.0.8) was used for gene prediction22,23. The RNA-seq and Iso-seq data were submitted to BRAKER3 separately24, and their respective prediction was finally merged by Tsebra25. The detailed information of transcriptome data was summarised in Table 1. Quality trimming for short read data was conducted using fastp (v 0.20.1)26 with following options: ‘-q 28 -l 80.’ Trimmed short read data were submitted to BRAKER3 using the ‘–rnaseq_sets_ids’ option. Then short reads were aligned to the genome assembly by hisat2 (v 2.2.1)27. The alignment rates of short read data to the genome assembly were summarised in Table 2. Iso-seq data were generated consensus for each read cluster according to the following procedure28: Iso-seq subreads were converted to circular consensus sequences (ccs) using ccs v 6.4.0 with options ‘–minLength 10–maxLength 100000–minPasses 0–minSnr 2.5–minPredictedAccuracy 0.0.’ lima (v 2.7.1) was used to remove primer sequences from the CCSs with options ‘–isoseq–peek-guess–ignore-biosamples.’ After the trimming of adaptors, PolyA tail trimming and concatemer removal were performed by isoseq. 3 v 3.8.2 in ‘refine’ mode with option ‘–require-polya.’ Finally, isoform-level clustering was conducted by isoseq. 3 in ‘cluster’ mode with option ‘–use-qvs.’ The resulting clustered.bam file was submitted to BRAKER3. Prior to gene prediction with Iso-seq data, BUSCO analysis on the genome assembly was conducted to obtain complete and single-copy BUSCO sequences5,29. Complete and single-copy BUSCO sequences were submitted to BRAKER3 together with Iso-seq derived bam file. Since we had two Iso-seq datasets (Table 1), we ran BRAKER3 for them separately. BUSCO analysis29 on the constructed gene models scored 98.6% of completeness (Fig. 2a). Basic statistics of the predicted gene models were summarised in Table 3.
Functional annotation of gene models
The deduced amino acid sequences of gene models were submitted to EnTAP6 for functional annotation. Protein similarity search was conducted against the latest complete UniProtKB/TrEMBL protein data set and complete UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot data set using diamond (v 0.9.14)30. Protein orthology search was also conducted against the EggNOG databases31 to assign Gene Ontology (GO), KEGG terms and protein domains from pfam32 and smart33. Additional family and domain search was performed against tigrfam34, sfld35, hamap36, cdd37, superfamily38, prints39, panther40, and gene3d41 using InterProScan (v 5.68–100)42. The results of functional annotation were summarised in Table 4. The top 10 GOs assigned to the gene models are shown in Fig. 3b without distinguishing between molecular function, biological process, and cellular component. The top 10 GOs for each category were shown in Fig. 3c–e.
BUSCO assessment and the top 10 GO assignments of transcriptome-based predicted gene models. (a) BUSCO scores of the gene models (top) and the genome assembly (bottom). (b) Overall top 10 GO assignments to gene models. (c) top 10 GO assignments of “biological process” in gene models. (d) top 10 GO assignments of “cellular component” in gene models. (e) top 10 GO assignments of “molecular function” in gene models.
ATAC library preparation and data processing
Another batch of early embryo samples subjected to RNA-seq, Iso-seq, and sRNA-seq were subjected to ATAC-seq. Fragmentation and amplification of the ATAC-seq libraries were conducted according to Buenrostro et al.43. The constructed libraries were sequenced on the Illumina HiSeq. ATAC-seq reads were pretreated with fastp and mapped to the genome with bwa-mem2 (v 2.2.1)44. Alignments containing mismatches were then removed using bamutils (v 0.5.9)45. Next, we removed duplicated reads using GATK MarkDuplicates (v 4.1.7)46. The resulting bam files were converted to bigwig files using deepTools bamCoverage with 10-bp width bin (v 3.5.1)47. The number of reads per bin was normalised by “reads per genomic content” (RPGC) method. Heatmap was created using deepTools computeMatrix with the starting point of the gene model being set to the reference point (Fig. 4).
Small RNA mapping
The small RNA reads were trimmed using Trim Galore v 0.6.6 (https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore) in small RNA mode. The trimmed small RNA reads were mapped to the assembled transcriptome, allowing up to 3 nucleotide mismatches using Hisat2 (v 2.1.0)27 and ngsutils (v 0.5.9)45. The information for each library was summarized in Table 1.
piRNA cluster detection
The piC detection was performed as previously described5. proTRAC (v 2.4.4)48 was used with options ‘-clsize 5000 -pimin 23 -pimax 29 -1Tor10A 0.3 -1Tand10A 0.3 -clstrand 0.0 -clsplit 1.0 -distr 1.0–99.0 -spike 90–1000 -nomotif -pdens 0.05.’ As a result, we successfully identified a total of 517 piRNA clusters in the three tissues (Fig. 5). The identity of a piC is defined by the two nearest (upstream and downstream) gene models. If multiple piCs were predicted between the two gene pair, such piCs were treated as a single piC. The genomic positions of piCs identified in testes, ovaries, and early embryos were visualized by RIdeogram (v 0.2.2)49 (Fig. 5a). The aggregation relationship of those piCs was visualized by ComplexUpset (v 1.3.3)50 (Fig. 5b).
piRNA clusters on T. varians genome. (a) piCs distribution of detected in early embryos (box), pupal ovary (circle), and pupal testis (triangle). (b) UpSet plot visualising piCs that are each assigned to each tissue. The vertical bars correspond to the intersections. When the circles corresponding to tissues are connected by a line, the bar above circles represents the number of piCs commonly identified in concerning tissues. The identity of piCs was defined by the nearest two gene models: When comparing piCs identified in different tissues, if the nearest upstream and downstream gene models are the same, those piCs were treated as the same piC.
Data Records
The raw sequence data reported in this paper have been deposited in DDBJ. RNA-seq data and Iso-seq data derived from tissues other than early embryos were registered across the accession code PRJDB941951. Embryonic Iso-seq and Embryonic RNA-seq data, small RNA-seq data, and ATAC-seq data are available under the accession code PRJDB1395552 [DRR396187, DRR396188, DRR396189, DRR396190, DRR396191, DRR515037]. Annotated gene models have been deposited in the figshare repository53.
Technical Validation
To assess the quality of gene models, BUSCO v. 5.4.66 with lepidoptera_odb10 lineage dataset was used. For comparison, the results are summarized in Fig. 2, together with the results of BUSCO analysis for the genome assembly. 98.58% of the complete and single-copy BUSCO sequences were present in the gene models, while 98.66% of the complete and single-copy BUSCO sequences were present in the genome assembly. BUSCO completeness scores were almost the same between the genome assembly and the gene model, suggesting that the gene prediction process is highly accurate across all genome regions. The mapping rates of RNA-seq data to genome assembly were summarized in Table 1. The mapping rates ranged between 87.5–93.7% for all samples. The mapping rates and the above-mentioned BUSCO completeness scores demonstrate the RNA-seq data quality and the genome assembly quality.
Code availability
Programs exploited in this study were executed with the default parameters except where otherwise specified in the Methods section. No custom code was used during this study.
References
Kishida, Y. Trilocha varians(Walker)(Bombycidae)from Ishigaki Island, the Ryukyu. Japan Heterocerist’s J. 219, 370 (2002).
Soloyevyev, A. V. & Witt, T. J. The Limacodidae of Vietnam (Lepidoptera). Entomofauna 16, 33–229 (2009).
Daimon, T. et al. Molecular Phylogeny, Laboratory Rearing, and Karyotype of the Bombycid Moth, Trilocha varians. J. Insect Sci. 12, 1–17 (2012).
Lee, J. et al. The genome sequence of Samia ricini, a new model species of lepidopteran insect. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 21, 327–339 (2021).
Lee, J. et al. W chromosome sequences of two bombycid moths provide an insight into the origin of Fem. Mol. Ecol. 33, 1–12 (2024).
NCBI GenBank https://identifiers.org/ncbi/insdc.gca:GCA_030269945.2 (2023).
Hart, A. J. et al. EnTAP: Bringing faster and smarter functional annotation to non-model eukaryotic transcriptomes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 20, 591–604 (2020).
Jain, S. et al. TALEN outperforms Cas9 in editing heterochromatin target sites. Nat. Commun. 12, 4–13 (2021).
Aravin, A. et al. A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature 442, 203–207 (2006).
Girard, A., Sachidanandam, R., Hannon, G. J. & Carmell, M. A. A germline-specific class of small RNAs binds mammalian Piwi proteins. Nature 442, 199–202 (2006).
Grivna, S. T., Beyret, E., Wang, Z. & Lin, H. A novel class of small RNAs in mouse spermatogenic cells. Genes Dev. 20, 1709–1714 (2006).
Vagin, V. V. et al. A Distinct Small RNA Pathway Silences Selfish Genetic Elements in the Germline. Science (80-.). 313, 320–324 (2006).
Kiuchi, T. et al. A single female-specific piRNA is the primary determiner of sex in the silkworm. Nature 509, 633–636 (2014).
Harvey-Samuel, T. et al. Silencing RNAs expressed from W-linked PxyMasc “retrocopies” target that gene during female sex determination in Plutella xylostella. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 119, 1–11 (2022).
NCBI Sequence Read Archive https://identifiers.org/ncbi/insdc.sra:DRR452104 (2023).
Marçais, G. & Kingsford, C. A fast, lock-free approach for efficient parallel counting of occurrences of k-mers. Bioinformatics 27, 764–770 (2011).
Vurture, G. W. et al. GenomeScope: Fast reference-free genome profiling from short reads. Bioinformatics 33, 2202–2204 (2017).
Flynn, J. M. et al. RepeatModeler2 for automated genomic discovery of transposable element families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 117, 9451–9457 (2020).
Gu, Z., Gu, L., Eils, R., Schlesner, M. & Brors, B. Circlize implements and enhances circular visualization in R. Bioinformatics 30, 2811–2812 (2014).
Okumura, A. et al. Construction of a bacterial artificial chromosome library of Endoclita excrescens as a tool for comparative gene mapping in Lepidoptera. Entomol. Sci. 22, 167–172 (2019).
Yoshido, A., Sahara, K. & Yasukochi, Y. Protocols for cytogenetic mapping of arthropod genomes. in Protocols for Cytogenetic Mapping of Arthropod Genomes 381–438, https://doi.org/10.1201/b17450-12 (CRC Press, 2014).
Stanke, M., Schöffmann, O., Morgenstern, B. & Waack, S. Gene prediction in eukaryotes with a generalized hidden Markov model that uses hints from external sources. BMC Bioinformatics 7, 62 (2006).
Stanke, M., Diekhans, M., Baertsch, R. & Haussler, D. Using native and syntenically mapped cDNA alignments to improve de novo gene finding. Bioinformatics 24, 637–644 (2008).
Lomsadze, A., Burns, P. D. & Borodovsky, M. Integration of mapped RNA-Seq reads into automatic training of eukaryotic gene finding algorithm. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, 1–8 (2014).
Gabriel, L., Hoff, K. J., Brůna, T., Borodovsky, M. & Stanke, M. TSEBRA: transcript selector for BRAKER. BMC Bioinformatics 22, 1–12 (2021).
Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y. & Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, i884–i890 (2018).
Kim, D., Langmead, B. & Salzberg, S. L. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 12, 357–360 (2015).
Brůna, T., Gabriel, L. & Hoff, K. J. Navigating Eukaryotic Genome Annotation Pipelines: A Route Map to BRAKER, Galba, and TSEBRA. (2024).
Manni, M., Berkeley, M. R., Seppey, M., Simão, F. A. & Zdobnov, E. M. BUSCO Update: Novel and Streamlined Workflows along with Broader and Deeper Phylogenetic Coverage for Scoring of Eukaryotic, Prokaryotic, and Viral Genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 38, 4647–4654 (2021).
Buchfink, B., Xie, C. & Huson, D. H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 12, 59–60 (2014).
Huerta-Cepas, J. et al. EggNOG 5.0: A hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically annotated orthology resource based on 5090 organisms and 2502 viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, D309–D314 (2019).
Mistry, J. et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, D412–D419 (2021).
Letunic, I. & Bork, P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, D493–D496 (2018).
Haft, D. H. et al. TIGRFAMs: A protein family resource for the functional identification of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 41–43 (2001).
Akiva, E. et al. The Structure-Function Linkage Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, 521–530 (2014).
Pedruzzi, I. et al. HAMAP in 2015: Updates to the protein family classification and annotation system. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, D1064–D1070 (2015).
Wang, J. et al. The conserved domain database in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, D384–D388 (2023).
Pandurangan, A. P., Stahlhacke, J., Oates, M. E., Smithers, B. & Gough, J. The SUPERFAMILY 2.0 database: A significant proteome update and a new webserver. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, D490–D494 (2019).
Attwood, T. K. et al. The PRINTS database: A fine-grained protein sequence annotation and analysis resource-its status in 2012. Database 2012, 1–9 (2012).
Mi, H., Muruganujan, A., Ebert, D., Huang, X. & Thomas, P. D. PANTHER version 14: More genomes, a new PANTHER GO-slim and improvements in enrichment analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, D419–D426 (2019).
Lewis, T. E. et al. Gene3D: Extensive prediction of globular domains in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, D435–D439 (2018).
Jones, P. et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 30, 1236–1240 (2014).
Buenrostro, J., Wu, B., Chang, H. & Greenleaf, W. ATAC-seq method. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2015, 1–10 (2016).
Vasimuddin, M., Misra, S., Li, H. & Aluru, S. Efficient Architecture-Aware Acceleration of BWA-MEM for Multicore Systems. 2019 IEEE Int. Parallel Distrib. Process. Symp. 314–324 (2019).
Breese, M. R. & Liu, Y. NGSUtils: A software suite for analyzing and manipulating next-generation sequencing datasets. Bioinformatics 29, 494–496 (2013).
van der Auwera, G. & O’Connor, B. D. Genomics in the Cloud: Using Docker, GATK, and WDL in Terra. (O’Reilly Media, Incorporated, 2020).
Ramírez, F. et al. deepTools2: a next generation web server for deep-sequencing data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, W160–W165 (2016).
Rosenkranz, D. & Zischler, H. proTRAC - a software for probabilistic piRNA cluster detection, visualization and analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 13, 5 (2012).
Hao, Z. et al. RIdeogram: Drawing SVG graphics to visualize and map genome-wide data on the idiograms. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 6, 1–11 (2020).
Krassowski, M., Arts, M., Lagger, C. & Max. krassowski/complex-upset: v1.3.5. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7314197 (2022).
NCBI Sequence Read Archive http://identifiers.org/ncbi/insdc.sra:DRP008708 (2022).
NCBI Sequence Read Archive https://identifiers.org/ncbi/insdc.sra:DRP009926 (2023).
Lee, J. Trilocha varians comprehensive genome annotation information, including gene model, its functional annotation result, and piRNA cluster maps. figshare https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.23648115 (2024).
Acknowledgements
Insects were donated from Kyushu University and Shinshu University according to a Grant-in Aid “National Bio Resource Project (NBRP, RR2002), Silkworm Genetic Resources” for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan. This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 24K17900 and 20K15535 to J.L, and JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number J18H03949 to T.S. This study was also supported by the 2022 Gakushuin University Computer Centre Collaborative Research Program to J.L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.L. designed the research plan, performed RNA extraction, analyzed the obtained data, and wrote the manuscript. T.S. also designed this research plan and performed the data analysis. T.F. and K.S. performed BAC-clone selection and chromosome imaging. K.Y. and S.S. were in charge of managing the progress of the study and checking and revising the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Fujimoto, T., Yamaguchi, K. et al. Comprehensive genome annotation of Trilocha varians, a new model species of Lepidopteran insects. Sci Data 12, 124 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-025-04411-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-025-04411-3