Abstract
Asian cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) is the most important cultivated species in the AA genome species of the genus Oryza. basmati is a special and famous subgroup in Asian cultivated rice, and temperate japonica is one of the most important cultivated subgroup, too. However, hybrid sterility hinders the introgression of favorable traits and the utilization of hybrid vigour between the two subgroups. The genetic basis of intraspecific hybrid sterility between temperate japonica and basmati remained elusive. In this study, a novel hybrid sterility locus S67 was identified, which caused hybrid male sterility in hybrids between the temperate japonica rice variety Dianjingyou 1 (DJY1) and the basmati rice variety Dom-sufid. Initial mapping with BC1F1, BC4F1, BC4F2 populations and DNA markers located S67 between RM5362 and K1-40.6 on the long arm of chromosome 1. Genetic analysis confirmed that S67 caused a transmission advantage for the temperate japonica rice S67-te allele in the hybrid offsprings. This result not only fills the gap in the research on hybrid sterility between basmati and temperate japonica, but also lays a good foundation for the systematic study of the genetic nature of hybrid sterility between basmati and other subgroups, as well as the full exploration and utilization of this subgroup through the creation of wide or specific compatibility lines to overcome hybrid sterility. In addition, this result can also help us broaden our understanding of genetic differentiation within Asian cultivated rice and hybrid sterility between inter-subgroups.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Rice is one of the most important food crops in the world, feeding more than half of the global population1. The utilization of heterosis played a significant role in improving rice yield per unit area2. However, the growth of rice yield entered a bottleneck period, the fundamental reason is that the genetic diversity of hybrid rice parents is narrow3. Asian cultivated rice, the most important cultivated species in the AA genome rice species of the genus Oryza, mainly comprises two subspecies, indica and japonica4,5, and some relatively small ecological subgroups. Currently, most studies classified Asian cultivated rice into five subgroups based on molecular biology, genomics, and other characteristics: temperate japonica, tropical japonica, indica, aus and basmati6,7,8,9,10,11,12. Numerous studies and breeding practices shown that the hybridization-introgression of subgroups within Asian cultivated rice played a very important role and had great potential for the utilization of heterosis and the improvement of rice yield, quality, and resistance10,11,13,14,15. Thus, fully mining and introgression of favorable alleles from minor subgroups of Asian cultivated rice is an important way to enrich the genetic diversity of existing breeding populations.
Basmati is a unique subgroup of Asian cultivated rice, mainly distributed in countries in South Asia, Southeast Asia, Central Asia, and West Asia such as Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Iran, etc.8,16,17,18,19. It is one of the important agricultural trade commodities in these regions20,21. The main feature of basmati rice exhibits its excellent longitudinal elongation of rice grains during cooking (about twice as much as before), and the soft and fluffy texture of cooked rice, with a unique nutty aroma, known as the "king of rice". basmati rice is rich in trace elements such as zinc and iron, and has a low blood sugar index19. In addition, basmati rice also contains rich WA-CMS restorer resources and significant potential for nitrogen efficient utilization and storage tolerance22,23,24,25. Therefore, basmati rice not only has very high economic value and international trade status, but also has a very important position and significance in the classification, genetic research, and breeding application in Asian cultivated rice. Temperate japonica is one of the main subgroup of Asian cultivated rice, mainly distributed in a few countries and regions such as East Asia, the Mediterranean, Europe, and North America, including China, Japan, South Korea, Egypt, North Korea, the United States, etc. The annual planting area of temperate japonica accounts for about 9% of the world’s total rice area, and the total yield accounts for about 14% of the world’s total rice production. Given the excellent quality, its market demand continues to increase. However, the breeding and production of temperate japonica rice also faces serious problems, such as insufficient genetic diversity of germplasm resources. basmati is a very excellent germplasm resource, which can be used for genetic improvement by hybridizing with temperate japonica varieties, which helps breed rice varieties with better yield, quality, and adaptability. Unfortunately, the severe hybrid sterility between these two subgroups limits the utilization of heterosis and introgression breeding between them26. Identifying and analyzing the hybrid sterility genes between them can help overcome hybrid sterility and better understand the nature of this reproductive barrier, and promote the application of distant parents in hybrid breeding.
Hybrid sterility is the most common form of postzygotic reproductive isolation in plant species. The hybrid sterility between Asian cultivated rice indica and japonica subgroups is the most classic case of postzygotic reproductive isolation and has always been a focus of genetic research. So far, more than 30 genes/QTL conferring sterility in inter-subspecific hybrids in Asian cultivated rice were reported12,27,28,29, of which seven hybrid sterility loci (S5, Sa, hsa1, S7, Sc, RHS12/Pf12/Se, DPL1/DPL2) were cloned26,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37. Twenty-two hybrid sterility loci were described between indica and temperate japonica cultivars, including major genes such as S5, Sa, Sc, RHS12/Pf12/Se12. In addition to indica and temperate japonica, some hybrid sterility loci were also found in other subgroups of Asian cultivated rice. DPL1/DPL2 resulted in male gametes abortion and qSIG3.1, qSIG3.2, qSIG6.1 and qSIG12.1 resulted in female gametes abortion in the crosses between temperate japonica and aus33,38,S7 and S15 were responsible for female gamete sterility in the hybrid between indica and aus37,39, S8, S9, S16, S17, S29, S31, S32, qSS-2, and qSS-8b gave rise to female gametes abortion in the hybrid between tropical japonica and temperate japonica40,41,42,43,44,45,46, S7, S8, S9, and S35(t) led to the female sterility in the cross between tropical japonica and indica39,47,48, S7 and S9 controlled the hybrid female sterility between tropical japonica and aus39,49. These hybrid sterility genes or QTL identified in the different subgroups will lay the foundation for elucidating the genetic and molecular mechanisms of hybrid sterility in Asian cultivated rice, and for breeding utilization. But, so far, due to the severe hybrid sterility between basmati and other subgroups, the hybrid introgression and utilization of favorable agronomic traits are very limited. A few of research was also limited to describing the phenomenon of hybrid sterility between basmati and other subgroups or the coincidental utilization of single hybrid sterility gene50,51,52. At present, there are no systematic studies on hybrid sterility between basmati and other subgroups, and no hybrid sterility genes or QTL were identified in the cross between them.
In the present study, a major inter-subgroup hybrid male sterility locus S67 in the hybrids between basmati and temperate japonica in Asian cultivated rice that conferred selective abortion of male gametes carrying the basmati allele, giving a transmission advantage to the temperate japonica allele, was identified. S67 was delimited between RM5362 and K1-40.6 on the long arm of chromosome 1 by linkage analysis. In addition, the degree of segregation distortion and the mode of gamete transmission were analysed by developing reciprocal test crosses between the plants with the NIL-S67(H) genotype in BC4F2 and recurrent parent DJY1. Judging from the locus location and action mode, this locus was confirmed as a new finding of hybrid sterility between basmati and temperate japonica.
Results
The confirmation of hybrid sterility between basmati and temperate japonica rice
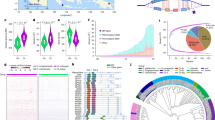
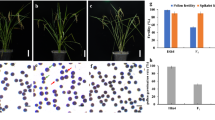
Severe pollen and spikelet sterility was observed in the F1 obtained between basmati accession Dom-sufid and temperate japonica cultivar DJY1 (Fig. 1). The pollen and spikelet fertility distribution of BC1F1 to BC3F1 was continuous, fertile, semi-sterility, and sterility plants could still be found, and gradually showing a bimodal distribution with the increase of backcross generations (Fig. 2a–c), while BC4F1 only had fertile and semi sterility plants (Fig. 2d).
F1 (DJY1/Dom-sufid) exhibits pollen and spikelet sterility. Pollen fertility of DJY1, Dom-sufid and F1 plants was determined based on the average value of five independent florets from DJY1, Dom-sufid and F1 plants. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 5). Spikelet fertility of DJY1, Dom-sufid and F1 plants was determined based on the average value of five independent panicles from DJY1, Dom-sufid and F1 plants. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 5).
Detection of QTL for hybrid sterility in BC1F1
The linkage map comprised of 663 polymorphic SNP markers and spans 2311.93 cM. The mean interval between markers was about 3.49 cM. QTL for pollen and spikelet fertility analyzed by composite interval mapping was presented in Table 1. Two QTL (qSS3, qSS6) for spikelet fertility were detected on chromosomes 3 and 6, explained 8.48% and 20.35% of the total spikelet fertility variation, respectively, and accounted for 28.83% of the total variation. Three QTL (qPS1.1 and qPS1.2, qPS2) for pollen fertility were detected on chromosomes 1, and 2. These QTL individually explained 5.52%–53.80% of the total phenotypic variation, and accounted for 66.14% of the total variation. Among these QTL, qPS1.2 was the most effective QTL, which explained 53.80% of the total pollen fertility variation, and was selected for in-depth mapping and genetic analysis in this study. Then, based on the molecular marker RM5362 (https://archive.gramene.org/markers/) genotypes (Table 2), tightly linked to qPS1.2 locus, and the phenotypes in each generation, continuous backcross to obtain BC4F1 was made.
Genetic linkage analysis and mapping of the S67 locus
In BC4F1, only two type plants: fertile and semi-sterility could be found, and they were used to detect for genetic background and target fragments introgression using Rice 6 k Chips53. The results showed that about 97% of the genetic background of BC4F1 plants was the same as that of their recurrent parent DJY1 (Fig. 3), and introgression fragments of the qPS1.2 locus was also detected in 5 semi-sterility pollen grain plants, 136-1-1, 136-1-5, 136-1-6, 136-1-7, 136-1-10. To map qPS1.2, one of the semi-sterility individual 136-1-1, which had a clean background and carried the qPS1.2 locus in BC4F1, was selected to self and form BC4F2 mapping population.
Rice 6k Chips detection of genetic background and target fragment introgression. The first column is the individual plant code of BC4F1 in 2021 Late Crop Season in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan province, P. R. China. Green represents the homozygous genotype of DJY1; Red represents the heterozygous genotype of DJY1 and Dom-sufid; Yellow represents the homozygous genotype of Dom-sufid. The black wireframe represents the area where the target locus is located. The individual with the blue line below had the least background interference and was selected to selfing to form the BC4F2 mapping population.
Among 390 plants in the BC4F2 population, pollen fertility showed bimodal distribution, divided into semi-sterility and fertile and spikelet fertility of all plant was normal (Figs. 4 and 5). By means of linkage analysis using phenotypic data and six polymorphic molecular markers (Table 2), qPS1.2 was located in a 2.95 cM region flanked by RM5362 and K1-40.6 on the long arm of chromosome 1 (Fig. 6).
Segregation distortion and gametes transmission of the S67 locus
To clarify the relationship between the introgression segments and the semi-sterility phenotype, the pollen fertility of 390 BC4F2 plants and the segregation of their genotypes of the closely linked molecular marker RM5362 was analysed. One hundred and eighty-six plants exhibited semi-sterility pollen grain and 204 plants exhibited fully fertile pollen grain in BC4F2 were found. All plants that exhibited semi-sterility carried heterozygous genotypes and all plants that showed fully fertile pollen grain harbored the homozygous temperate japonica DJY1 genotype, which were deteceted with molecular markers RM5362. No any plants with homozygous basmati Dom-sufid genotype was found in this population. In this segregating population, the segregation ratio of fertile and semi-sterility was 1:1, which did not conform to classical Mendelian inheritance and was a typical hybrid sterility (Table 3). In fact, no plants with homozygous basmati Dom-sufid genotype were detected in another large population of 1344 BC4F3 plants (Additional file 1: Table S1). By reviewing previous studies, qPS1.2 was a novel pollen grain hybrid sterility locus, and was named as S67. Plants with heterozygous S67 (S67-te/S67-b) genotype in BC4F2 were selected as a near isogenic line, NIL-S67(H).
For the convenience of description, the basmati S67 allele was named as S67-b and the temperate japonica DJY1 S67 allele as S67-te. Given that no homozygous plants having the S67-b/S67-b genotype using the SSR Marker RM5362 in BC4F2 population were found (Table 3), therefore reciprocal test crosses between the NIL-S67(H) and DJY1 were made to further analyze the gametes transmission. When the NIL-S67(H) was used as the female parent, the segregation ratios of the NIL-S67(H) genotype plants and DJY1 genotype plants fitted a 1:1 ratio (Table 3). This indicates that both the S67-te and S67-b female gametes in the NIL-S67(H) were normally fertile, which corresponds to the normal seed setting of the field plants. Nevertheless, when the NIL-S67(H) was used as the male parent in a cross with DJY1, only DJY1 genotype F1 plants were obtained (Table 3 and Fig. 7). This observation showed that the S67-b type male gametes in the NIL-S67(H) are fully sterile, and S67-te has a strong transmission advantage.
Discussion
Hybrid sterility was always considered as a very complex quantitative trait, and the efficiency of using different strategies to map hybrid sterility locus varies greatly. QTL mapping can be performed in low backcross generations, such as BC1F1, to prevent the loss of hybrid sterility loci with smaller effects. However, it is important to avoid using the F2 population as much as possible, as there may be interference from hybrid breakdown. Due to their susceptibility to environmental factors, QTLs that are sensitive to the environment and have minimal effects are often prone to be false positives. Another strategy is to not conduct QTL testing in the low generation, but to select sterile plants in the population through continuous backcrossing based on phenotype, ultimately transforming quantitative traits into qualitative traits. In this study, we found that the pollen and spikelet fertility distribution of BC1F1 to BC3F1 was continuous, fertile, semi-sterility, and sterility plants could still be found, and gradually showing a bimodal distribution with the increase of backcross generations (Fig. 2a–c), while BC4F1 only had fertile and semi sterility plants (Fig. 2d). The results showed that inter-subgroup hybrid sterility between temperate japonica and basmati in Asian cultivated rice controlled by multiple genes in the preliminary populations was gradually decomposed into a simple inheritance trait, and a significant amount of genetic noise was removed after four generations phenotypic selection and continuous backcrossing, which facilitated the detection and confirmation of loci in the advanced backcrossing population.
Basmati is a very special and famous subgroups of the Asian cultivated rice germplasm, but it was not fully utilized yet, and the main reason is that the relationship between basmati and other groups in Asian cultivated rice is unclear. In terms of grain morphology, some varieties of this group had slender grains, and some had short round grains17,19. Some scholars believed that it belonged to the indica54, while others classified them as the japonica type50. Numerous studies on the genome classified basmati as japonica or similar to japonica7,10,11,55. In terms of origin and evolution, some studies suggested that basmati was derived from hybridization-introgression between aus from South Asia and japonica6,12,56. Some scholars also believed that basmati was formed through domestication and selection of ancient japonica rice from China to South Asia after being transmitted57,58,59. There were also views that basmati was directly domesticated from local O. rufipogon in South Asia60. In short, different research led to distinct results. So, as indication of species formation, the relationship between basmati and other subgroups from the vision of reproductive isolation is the key to know the difference. In the present study, severe hybrid sterility between basmati and temperate japonica was found, and a novel hybrid male sterility locus S67 was identified, which will greatly help understand the hybridization compatibility between basmati and other subgroups from a new perspective, and will also help us fully understand the genetic differentiation of Asian cultivation rice from the perspective of reproductive isolation. However, in order to comprehensively and scientifically explain the hybrid sterility relationship between basmati and other subgroups, it is necessary to further systematically map and analyze the corresponding hybrid sterility genes.
To this day, about 50 hybrid sterility loci/QTL were discovered and reported, with more than 30 responsible for the crosses between Asian cultivated rice two subspecies, and these loci mainly contributed to the hybrid sterility between indica and temperate japonica12,27,28. But there are no reports on the hybrid sterility loci of basmati. In this study, a new hybrid male sterility locus, S67, was discovered in hybrids between the basmati variety Dom-sufid and the temperate japonica variety DJY1, and mapped between RM5362 and K1-40.6 on the long arm of chromosome 1. In this chromosomal region, previous studies reported one inter-subspecific hybrid sterility locus, S16, between indica and japonica, which was a hybrid sterility locus affecting female gametes43. Another locus S58 controlled the hybrid male sterility in Asian–African cultivated rice hybrids was reported, too61. Unlike the gamete elimination of S162, the finding showed that male gametes carrying the S58-g allele (African rice-type S58 allele) were eliminated, resulting in the male gametes with the S58-s (Asian rice-type S58 allele) allele gaining a transmission advantage. Both S67 and S58 are hybrid sterility sites that affect male gametes, and the type of pollen sterility is stained abortion type. The difference is that they lead to hybrid sterility between different subgroups and species, respectively. Interestingly, if we assume that they are different haplotypes on the same locus, the differentiation under different conditions leads to reproductive isolation between basmati and temperate japonica, O.sativa and O. glaberrima. In addition, what is the haplotype differentiation of this locus in indica, aus, tropical japonica, and other wild relatives of Asian cultivated rice? It is speculated that in-depth study of the vertical homology relationship of this gene is of great significance and role in understanding the origin and evolution of the AA genome species in the rice genus. This result not only fills the gap in the research on hybrid sterility between basmati and temperate japonica, but also lays a good foundation for the systematic study of the genetic rules of hybrid sterility between basmati and other subgroups.
Basmati is a very excellent germplasm resource with rich genetic variation and great potential for increasing yield, improving quality and adaptability. However, the heterosis generated by hybridization between basmati and other subgroups is limited by hybrid sterility, thus overcoming the reproductive barrier by adopting different methods and technical means is the key step to use the diversity of basmati. Varieties carrying natural or artificial neutral alleles of hybrid sterility loci are important germplasm resources for overcoming the hybrid sterility28. Previous studies have shown that the main hybrid sterility genes between indica and japonica subspecies are Sb, Sc, Sd, Se, f5, pf12, and S5. The indica-compatible japonica lines developed by pyramiding the indica allele (S-i) at Sb, Sc, Sd and Se loci and the neutral allele (S–n) at S5 locus in japonica genetic background through marker-assisted selection are compatible with indica rice in pollen fertility and in spikelet fertility63. Some researchers constructed and assembled different combinations of naturally compatible alleles of four loci, S5, Sc, pf12, and f5, and the improved lines can fully recover pollen and embryo-sac fertility in testcrossed F1s, thereby completely fulfilling the demands of inter-subspecific hybrid spikelet fertility in production36. Cloning hybrid sterility genes and clarifying their genetic mechanisms are prerequisites for creating widely compatible lines. In this study, only the preliminary localization of S67 was completed, and the research on cloning and genetic mechanisms is ongoing. But before that, we still have other methods to overcome hybrid sterility between basmati and temperate japonica. The “bridge parents” developed by fixing the basmati allele at S67 loci in temperate japonica genetic background by repeatedly backcrossing and molecular assisted selection is one way to recover the fertility of hybrid offspring between two subgroups. Nine NILs, including NILs with O. glaberrima fragment at six hybrid sterile loci under O. sativa genetic background, two lines harboring two hybrid sterile loci, one line harboring three hybrid sterile loci, were used to test cross with O.glaberrima accessions. The results showed that compared to single-locus-NILs, the multiple-loci-NILs showed increasing effect on pollen fertility when test crossing with O. glaberrima accessions. Further backcrossing can improve the fertility of pollen grain and spikelet of interspecific hybrids, too64. Certainly, we need to identify as many major hybrid sterility loci as possible between basmati and temperate japonica, and analyze their molecular mechanisms. Ultimately, we can overcome the hybrid sterility completely through gene editing plus target chromosome fragment replacement. In addition, extensive test cross can be conducted in temperate japonica germplasm to unearth widely compatible varieties carrying natural neutral alleles of S67 as “bridge parents” for hybridization with basmati to overcome hybrid sterility.
Materials and methods
Materials
One basmati variety named Dom-sufid introduced from the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) was as the donor parent, one O. sativa ssp. temperate japonica variety, Dianjingyou 1 (DJY1), from Yunnan province, P. R. China, as the maternal, were used to obtain F1. Afterwards, selected the sterility plants in each generation as female parent and continuously backcrossed with DJY1 were made until BC4F1. The cultivation of all relevant populations was completed in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan province, P. R. China. In the BC1F1, 148 plants were used for QTL detection. Meanwhile, after phenotypic evaluation and marker-assisted selection, sterility individuals (pollen fertility below 90% and the genotype is heterozygous) were randomly selected as the maternal for continuous backcrossing until BC4F1. A total of 5 pollen grain semi-sterility plants were selected in the backcross line 136 of BC4F1 (Fig. 3). The background and target fragment introgression of plants in BC4F1 were screened by using Rice 6 k Chips53. BC4F2, obtained by selfing of the target individual from the BC4F1 population, was used for target locus mapping and near isogenic line raising. To study the gamete elimination and transmission pattern, reciprocal crosses were made between heterozygous individual in BC4F2 and recurrent parent to obtain F1.
Observation of pollen grain and spikelet fertility
Anthers were collected from spikelet of the upper and middle parts of the main panicle at 1 to 2 days before anthesis, fixed and stored in 70% ethanol for determining pollen fertility65. Pollen fertility was estimated based on the percentage of pollen grains stained with 1% (w/v) iodine-potassium iodide solution. The pollen grain sterility types were classified as typical, spherical and stained abortion types. Observation requires at least three independent microscopic fields, at least 100 pollen grains in each field were scored for counting the percentage of fertile pollen grains in each plant. Spikelet fertility was calculated as a percentage of fertilized spikelet per panicle for each of the individuals involved.
Detection of QTL and DNA analysis
To detect the QTL, a linkage map of the BC1F1 population was constructed using QTL IciMapping Version 4.266, with a minimum LOD score of 3.0. Composite interval analysis was conducted to determine QTL related to the tested traits. The experiment-wide LOD (log of the odds ratio) threshold significant level was determined from 1000 permutation tests67, as implemented by QTL IciMapping. The genotype data of BC1F1 was obtained using rice 10 K Liquid Chips by Boradi Biotechnology Co., Ltd, Shijiazhuang, Hebei. BC4F2 population was used to target gene mapping and genetic analysis. QTL IciMapping Version 4.2 and MapChart 2.32 were used to construct linkage groups and map hybrid sterility loci.
Ten days after transplanting, fresh leaves from each individual were sampled for extraction of genomic DNA using the CTAB method68. SSR and KASP markers, distributed throughout the entire rice genome were used for polymorphism screening and genotyping. Rice 6 k Chips was used to detect target fragments infiltration and background replacement. The protocol of Rice 6 k Chips as Infinium HD Assay Ultra Protocol Guide (https://support.illumina.com.cn/downloads/infinium_hd_ultra_assay_protocol_guide_(11328087_b).html) was used. GGT 2.0 software was used to map and view the infiltration of target trait related fragments and background replacement.
Genetic and gametic transmission assay
To determine the genetic and gametic transmission nature of S67, the segregation ratios of the S67-b (from basmati) and the S67-te (from temperate japonica) alleles were investigated in three populations: BC4F2, NIL-S67(H)/DJY1 and DJY1/NIL-S67(H). The S67 genotypes in these populations were checked using the SSR marker RM5362 (Table 3), allowing to analyze the transmission rates to offspring of the S67-b allele and the S67-te allele.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author (taody12@aliyun.com) on reasonable request.
References
Fukagawa, N. K. & Ziska, L. H. Rice: Importance for global nutrition. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 65, S2–S3 (2019).
Yu, S. B. et al. Hybrid rice and green super rice. Sci. Bull. 61, 3797–3803 (2016).
Tang, H. W. et al. Advances in understanding the molecular mechanisms of cytoplasmic male sterility and restoration in rice. Plant Reprod. 30, 179–184 (2017).
Kato, S. On the affinity of the cultivated varieties of rice plants Oryza sativa L. J. Dept. Agric. Kyushu Imperial Univ. 2, 241–276 (1930).
Oka, H. Phylogenetic differentiation of the cultivated rice plant II. Intervarietal hybrid sterility. Jpn. J. Breed. 3, 50–63 (1952).
Civáň, P. et al. Three geographically separate domestications of Asian rice. Nat. Plants 1, 1–5 (2015).
Garris, A. J. et al. Genetic structure and diversity in Oryza sativa L. Genetics 169, 1631–1638 (2005).
Glaszmann, J. C. Isozymes and classification of Asian rice varieties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 74, 21–30 (1987).
Kishor, D. S. et al. Evaluation of whole-genome sequence, genetic diversity, and agronomic traits of Basmati rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front. Genet. 11, 86 (2020).
McNally, K. L. et al. Genome-wide SNP variation reveals relationships among landraces and modern varieties of rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 12273–12278 (2009).
Wang, W. S. et al. Genomic variation in 3010 diverse accessions of Asian cultivated rice. Nature 557, 43–49 (2018).
Zhang, Y. et al. Understanding the nature of hybrid sterility and divergence of Asian cultivated rice. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 908342. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.908342 (2022).
Bai, S. W. et al. Retrospective and perspective of rice breeding in China. J. Genet. Genom. 45, 603–612 (2018).
Brar, D. S. & Khush, G. S. Wild relatives of rice: a valuable genetic resource for genomics and breeding research. In The Wild Oryza Genomes, Compendium of Plant Genomes (eds Mondal, T. K. & Henry, R. J.) 1–25 (Springer International Publishing AG, 2018).
Kiran, B. G. et al. Deployment of wild relatives for genetic improvement in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Breed. 140, 23–52 (2020).
Choi, J. Y. et al. Nanopore sequencing-based genome assembly and evolutionary genomics of circumbasmati rice. Genome Biol. 21, 21 (2020).
Civáň, P. et al. Origin of the aromatic group of cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) traced to the Indian subcontinent. Genome Biol. Evol. 11, 832–843 (2019).
Khin, M. M. et al. Specific patterns of genetic diversity among aromatic rice varieties in Myanmar. Rice 5, 1–13 (2012).
Khush, G. S. Taxonomy and Origin of Rice 5–13 (Oxford & IBH Publishing, 2000).
Ashfaq, M. et al. Basmati rice a class apart (a review). Rice Res. Open Access 3, 156. https://doi.org/10.4172/2375-4338.1000156 (2015).
Satishkumar, M., Harishkumar, H. & Rangegowda, R. Growth export performance and competitiveness of basmati and non-basmati rice of India-an Markov chain approach. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 9, 305–311 (2016).
Ashok, K. S. et al. Introgression of multiple disease resistance into a maintainer of basmati rice CMS line by marker assisted backcross breeding. Euphytica 203, 97–107 (2015).
Foster-Powell, K., Holt, S. H. A. & Brand-Miller, J. C. International table of glycemic index and glycemic load values. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 76, 5–56 (2002).
Liu, Y. Q. et al. Genomic basis of geographical adaptation to soil nitrogen in rice. Nature 590, 600–605 (2021).
Wang, H. R. et al. The power of inbreeding: NGS-based GWAS of rice reveals convergent evolution during rice domestication. Mol. Plant 9, 975–985 (2016).
Wang, C. L. et al. A natural gene drive system confers reproductive isolation in rice. Cell 186, 1–16 (2023).
Ouyang, Y. D. Understanding and breaking down the reproductive barrier between Asian and African cultivated rice: a new start for hybrid rice breeding. Sci. China Life Sci. 62, 1–3 (2019).
Xie, Y. Y. et al. Molecular mechanisms of hybrid sterility in rice. Sci. China Life Sci. 62, 737–743 (2019).
Zhang, G. Q. Prospects of utilization of inter-subspecific heterosis between indica and japonica rice. J. Integr. Agric. 19, 1–10 (2020).
Chen, J. J. et al. A triallelic system of S5 is a major regulator of the reproductive barrier and compatibility of indica-japonica hybrids in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 11436–11441 (2008).
Kubo, T. et al. Two tightly linked genes at the hsa1 locus cause both F1 and F2 hybrid sterility in rice. Mol. Plant 9, 221–232 (2016).
Long, Y. et al. Hybrid male sterility in rice controlled by interaction between divergent alleles of two adjacent genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 18871–18876 (2008).
Mizuta, Y., Harushima, Y. & Kurata, N. Rice pollen hybrid incompatibility caused by reciprocal gene loss of duplicated genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107, 20417–20422 (2010).
Shen, R. X. et al. Genomic structural variation-mediated allelic suppression causes hybrid male sterility in rice. Nat. Commun. 8, 1310 (2017).
Yang, J. et al. A killerprotector system regulates both hybrid sterility and segregation distortion in rice. Science 337, 1336–1340 (2012).
Zhou, P. H. et al. A minimal genome design to maximally guarantee fertile inter-subspecific hybrid rice. Mol. Plant 16, 726–738 (2023).
Yu, Y. et al. Hybrid sterility in rice (Oryza sativa L.) involves the tetratricopeptide repeat domain containing protein. Genetics 203, 1439–1451 (2016).
Rao, J. L. et al. Genetic analysis of S5-interacting genes regulating hybrid sterility in rice. Rice 14, 11 (2021).
Wan, J. C. et al. Two new loci for hybrid sterility in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 92, 183–190 (1996).
Li, D. T. et al. Mapping for a new locus causing hybrid sterility in a China landrace (Oryza sativa L.). Rice Genet. Newslett. 22, 20 (2005).
Li, D. T. et al. Fine mapping of S32(t), a new gene causing hybrid embryo sac sterility in a Chinese landrace rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 114, 515–524 (2007).
Wan, J. M. et al. Mapping of hybrid sterility gene S17 of rice (Oryza sativa L.) by isozyme and RFLP markers. Rice Genet. Newslett. 15, 151–154 (1998).
Wan, J. M. & Ikehashi, H. Identification of a new locus S-16 causing hybrid sterility in native rice varieties (Oryza sativa L.) from Tai-hu lake region and Yunnan Province, China. Breed. Sci. 45, 446–470 (1995).
Wang, C. M. et al. Mapping segregation distortion loci and quantitative trait loci for spikelet sterility in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genet. Res. 86, 97–106 (2005).
Zhao, Z. G. et al. Fine mapping of S31, a gene responsible for hybrid embryo-sac abortion in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta 226, 1087–1096 (2007).
Zhu, S. S. et al. A new gene located on chromosome 2 causing hybrid sterility in a remote cross of rice. Plant Breed. 124, 440–445 (2005).
Chen, M. J. et al. A new gene controlling hybrid sterility in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 184, 15–22 (2012).
Wan, J. M. et al. Multiple alleles at a new locus causing hybrid sterility between a Korean indica variety and a javanica variety in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Jpn. J. Breed. 43, 507–516 (1993).
Yanagihara, S., Kato, H. & Ikehashi, H. A new locus for multiple alleles causing hybrid sterility between an Aus variety and javanica varieties in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 90, 182–188 (1992).
Cheng, K. S., Huang, N. W. & Zhang, Y. Z. Research on that sickle-shaped rice is an another king of intermediate type. Southw. China J. Agric. Sci. 3, 102–103 (1990).
Dolores, R. C., Chang, T. T. & Ramirez, D. A. Cytogenetics of sterility in F2 hybrids of indica×indica and indica×javanica varieties of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Cytologia 40, 639–647 (1975).
Xu, N. et al. Introgression of a complex genomic structural variation causes hybrid male sterility in GJ Rice (Oryza sativa L.) subspecies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 1–10 (2022).
Thomson, M. J. et al. Large-scale deployment of a rice 6 K SNP array for genetics and breeding applications. Rice 10, 40 (2017).
Regina, C. D., Chang, T. T. & Ramirez, D. A. Cytogenetics of sterility in F2 hybrids of indica×indica and indica×javanica varieties of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Cytologia 40, 639–647 (1975).
Zhao, K. Y. et al. Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa. Nat. Commun. 2, 92–100 (2011).
Zhou, J. W. et al. Interspecific hybridization is an important driving force for origin and diversification of Asian cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L). Front. Plant Sci. 13, 932737. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.932737 (2022).
Chen, R. Z. et al. Rice functional genomics: decades’ efforts and roads ahead. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 33–92 (2022).
Huang, X. H. et al. A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice. Nature 490, 497–501 (2012).
Xie, L. et al. RiceENCODE: A comprehensive epigenomic database as a rice Encyclopedia of DNA Elements. Mol. Plant 14, 1604–1606 (2021).
Zhang, F. et al. The landscape of gene-CDS-haplotype diversity in rice: Properties, population organization, footprints of domestication and breeding, and implications for genetic improvement. Mol. Plant 14, 787–804 (2021).
Feng, Y. M. et al. Characterization and fine-mapping of a new Asian rice selfish genetic locus S58 in Asian-African rice hybrids. Theor. Appl. Genet. 136, 87 (2023).
Xie, Y. Y. et al. Interspecific hybrid sterility in rice is mediated by OgTPR1 at the S1 locus encoding a peptidase-like protein. Mol. Plant 10, 1137–1140 (2017).
Guo, J. et al. Overcoming inter-subspecific hybrid sterility in rice by developing indica-compatible japonica lines. Sci. Rep. 6, 26878 (2016).
Li, J. et al. Improving bridge effect to overcome interspecific hybrid sterility by pyramiding hybrid sterile loci from Oryza glaberrima. Sci. Rep. 13, 23057 (2023).
Doi, K., Yoshimura, A. & Iwata, N. RFLP mapping and QTL analysis of heading date and pollen sterility using backcross population between Oryza sativa L. and Oryza glaberrima Steud. Breed. Sci. 48, 395–399 (1998).
Lei, M. et al. QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J. 3, 269–283 (2015).
Churchill, G. A. & Doerge, R. W. Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138, 963–971 (1994).
Rogers, S. O. & Bendich, A. J. Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol. Biol. 5, 69–76 (1985).
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31991221, 32160489); Basic Research Foundation of Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department, China (Grant Nos. 202401AT070090, 202101AT070193, 202101AS070036, 202001AS070003, 202201AS070072, 202205AR070001-04); Yunnan Provincial Government (YNWR-QNBJ-2018-359); Technology Talent and Platform program of Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department, China (Grant Nos. 202205AC160057); and the Yunnan Seed Laboratory Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.T and Y.Z conceived and designed the experiments. Y.L participated in phenotyping, genotyping, drafting the manuscript. J.L and Y.Y participated in phenotyping and genotyping. Q.P, J.Z, and X.D participated in phenotyping. D.T and Y.Z corrected manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics declarations
The plant collection and use was in accordance with all the relevant guidelines.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Y., Li, J., Yang, Y. et al. Identification of a novel hybrid sterility locus S67 between temperate japonica subgroup and basmati subgroup in Oryza sativa L. Sci Rep 14, 28619 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-80011-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-80011-2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Molecular mapping of a novel locus S68 for intrasubspecific hybrid sterility in indica-indica hybrid
Scientific Reports (2025)