Abstract
Acute kidney injury (AKI) has become a disease of global concern due to its high morbidity and mortality. This has highlighted the need for renoprotective agents. Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) is a saponin isolated from Astragalus membranaceus with good antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties. In this study, HK2 cells and rat model were utilized to explore the protective effect of AS-IV against cadmium chloride-induced oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. CdCl2-induced apoptosis, ROS production, and mitochondrial membrane potential alterations were significantly inhibited in AS-IV -treated HK2 cells. Expression of the mitochondria-associated apoptotic proteins Cleaved-Caspase3, Cleaved-Caspase9, and Cleaved-PARP was significantly reduced after AS-IV intervention. In addition, AS-IV inhibited Rat weight loss and also alleviated the symptoms of CdCl2-induced nephrotoxicity in a rat model of CdCl2-induced kidney injury. Further experiments showed that AS-IV suppresses heavy metal Cd-induced mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by regulating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. In conclusion, AS-IV could protect the kidney from heavy metal-induced toxicity and could be used as a nephroprotective agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
With the global industrial revolution, pollution of the environment by heavy metals has been increasing, and the production and consumption of heavy metals has also increased dramatically1. Cadmium pollution is particularly serious in industries such as nickel-cadmium batteries and pigment2. Atmosphere, water and soil are the three main pathways by which cadmium pollutes the environment3. Common modes of cadmium ingestion in humans are inhalation through breathing, dermal contact, and ingestion through water4. The kidney is the main excretory organ of the body, and cadmium is mainly excreted and retained through the kidney. Therefore, the kidneys have become one of the most serious organs damaged by cadmium5. Renal tubular epithelial cells are very sensitive to cadmium exposure. Cadmium-induced damage to renal tubular epithelial cells has been reported to be irreversible, and sustained exposure to cadmium increases the risk of developing total kidney injury6.
Cadmium as a transition metal mainly causes oxidative damage to tissues. Studies have shown that cellular biomolecules can be catalyzed by transition metals, followed by oxidative reactions, and that excessive accumulation of cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) destroys their own antioxidant defense system, resulting in oxidative stress7. Cadmium ions can cause transient or sustained accumulation of intracellular ROS through several pathways8. When cadmium ions enter the cell, the mitochondrial electron respiration transfer chain does not work properly, which leads to the accumulation of cellular ROS9. In addition, cadmium can indirectly induce ROS production. Cadmium induces an imbalance in the activity of intracellular antioxidant enzymes and a dysregulation of cellular free radical metabolism, resulting in oxidative stress10. For example, MT and GSH bind to cadmium and lose their reductive properties, resulting in the inability to scavenge intracellular ROS11. Following oxidative cellular injury, cells initiate a series of signaling pathways that culminate in apoptosis, causing AKI12. At present, however, chelation therapy for cadmium poisoning is not fully effective in removing cadmium from the body. Therefore, the use of natural antioxidants to reduce tissue damage caused by cadmium poisoning has become a focus of attention13.
Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) is the main bioactive substances in the traditional Chinese medicine Astragalus membranaceus14. AS-IV was found to possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antiviral and antitumor pharmacological effects. In recent years, As-IV has attracted attention in the prevention of renal diseases such as diabetic nephropathy15, renal fibrosis16 and launching renal injury17.However, the pharmacodynamic evaluation and mechanism of AS-IV on cadmium metal-induced renal injury are not clear.
In this study, the heavy metal cadmium (CdCl2) was used to model kidney injury. Cadmium-poisoned rats were gavaged with AS-IV, and the effectiveness of the drug was assessed by general symptoms, renal function indices and renal histopathology in rat. In in vitro experiments, we co-cultured CdCl2, AS-IV with renal epithelial cells and examined the effects of cell viability, ROS changes, apoptosis, and Nrf2/HO-1 pathway protein expression. To explore the mechanism of AS-IV anti- CdCl2 nephrotoxicity at the molecular level, it is hoped that this study will provide useful information for the research and development of AS-IV-based nutritional products and adjuvant drugs.
Materials and methods
The experiment was conducted in the experimental animal center of Chengdu University of traditional Chinese medicine and submitted to the Institutional Ethics Review Committee for approval (grant no: 2021-47). This study was conducted in strict accordance with the recommendations of the guide for the care and use of laboratory animals issued by the Ministry of science and technology of China. All experiments complied with the ARRIVE.
Reagents and antibodies
Astragaloside IV (purity ≥ 98%, cat: HY-N0431), N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC; purity, 99.88%) was purchased from MCE. cadmium chloride was purchased from Sigma (USA, cat: 233-296-7). Antibodies purchased from Proteintect were Nrf2 (China, cat: 16396-1-AP), HO-1 (China, 10701-1-AP), Cleaved-Caspase3 (China 19677-1-AP), Cleaved-Caspase9 (China, 66169-1-Ig), and Cleaved-PARP (China, 15613-1-AP). NQO1 (USA, cat: ab80588) was purchased from Abcam, USA. goat anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody HRP (China, Cat: A0208) and Goat anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody HRP (China, Cat: A0216) were purchased from Beyotime. GSH assay kit (Beyotime, China, Cat: S0053), MDA assay kit (Beyotime, China, Cat: S0131M) and SOD assay kit (Beyotime, China, Cat: S0101M) were used to assess the level of oxidative stress in fresh kidney homogenates and cultured cell supernatants. ELISA kits were used to detect tumor necrosis factor-α (Elabscience, China, Cat: E-EL-R2856), interleukin-1 β (Elabscience, China, E-EL-RB0013), and interleukin-6 (Elabscience, China, E-HSEL-R0004) supernatant Levels.
Animal models of kidney injury
We purchased 21 SD rats (100 g ± 20) from Chengdu Dashuo Co Ltd (Chengdu, China). All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (approval number:2021-47). After 1 week of acclimatization feeding, the rats were randomly divided into three groups: control (Con), Astragaloside IV group (AS-IV), CdCl2 group (CdCl2), Astragaloside IV low-dose group (AS-IV-L) and Astragaloside IV high-dose group (AS-IV-L). According to the previous protocol18,19, Saline was injected daily intraperitoneally in the control group. 5 mg/kg body weight of CdCl2 was injected daily in the CdCl2 group. 40 mg/kg Astragaloside IV intervention was added to the CdCl2 modeling process in the Astragaloside IV low-dose group. 80 mg/kg Astragaloside IV intervention. Body weight was assessed weekly throughout the experiment. In addition, 24-hour urine samples were collected using separate metabolic cages. 2 weeks later, all rats were sedated and then executed. Serum was collected for biochemical analysis. For pathologic analysis, kidney tissue was immersed in paraffin.
Serum and urine biochemistry
The collected serum and urine were submitted to the Laboratory Department of the Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine for the detection of serum urea nitrogen, creatinine, uric acid and 24-hour urinary protein by chemiluminescence.
HE detection
The embedded wax blocks were cut into sections with a thickness of 7 μm. Next, the samples were dewaxed and hydrated with xylene and graded concentrations of alcohol. After hematoxylin staining for 5 min, the sections were stained with eosin for 1 min. The sections were dehydrated using gradient concentrations of alcohol and xylene. Finally, the sections were sealed and the prepared sections were photographed and observed under a 40x lens.
Tunel analysis
Apoptosis was detected and quantified using the TUNEL Brighter Apoptosis Detection Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The nuclei of apoptotic cells showed green staining, while the nuclei of non-apoptotic cells showed blue color. Fluorescence intensity was detected using a fluorescence microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β assay
A portion of kidney tissue was homogenized with cold saline (1:9) containing 1% protease inhibitor on ice and the homogenate was retained. Levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β in the homogenate versus serum were assayed using an ELISA kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
GSH, MDA, SOD assay
Lipid MDA kit, GSH kit and SOD kit were used according to the manufacturer’s instructions to assay GSH, MDA content and SOD activity in kidney tissues of SD rats.
Histological evaluation and immunohistochemical analysis
As previously described20 assessment of symptoms of cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity. Cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity was evaluated. Rats were intervened as described above, and body weights were assessed every six days. After 2 weeks, all rats were executed, and the kidney tissues were subsequently immersed in paraffin. The embedded wax blocks were cut into sections of 7 μm thickness. Next, the samples were dewaxed and hydrated with xylene and graded concentrations of alcohol. After hematoxylin staining for 5 min, the sections were stained with eosin for 1 min. The sections were dehydrated using gradient concentrations of alcohol and xylene. Finally, the sections were sealed and the prepared sections were photographed and observed under a 40x lens.
Cell culture and cell modeling
Human proximal renal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2 cells) were provided by the Provincial Key Laboratory of the Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Cells were cultured in DMEM/F-12 containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% penicillin and streptomycin and placed in a 37 °C CO2 incubator. CdCl2 modeling was performed when the cell density reached 70–80%. Briefly, the cells were divided into control (Con) group, CdCl2 group and Astragaloside IV (0-100 µM) group. Cells in the Control group were placed in a 95% air, 5% CO2 incubator; cells in the CdCl2 group were incubated in medium supplemented with 30 µM CdCl2 for 24 h. Cells in the Astragaloside IV group were treated with different concentrations of Astragaloside IV at the same time as CdCl2 (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, and 100 µM) were incubated for 24 h in total.
Cell viability assay
The protective effect of AS-IV was assessed using CCK-8 (Apexbio, USA, cat: K1018). HK-2 cells were co-cultured with CdCl2 in 96-well plates at a density of 1 × 10 4 cells/mL for 24 h and different concentrations of AS-IV were added. finally, 10 µL of CCK-8 reagent was added to each well and the cells were incubated for 1 h. The cells were then incubated with CdCl2 for 1 h. The cells were then incubated for 1 h with CCK-8 reagent. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm by zymography and the experiment was repeated three times.
Flow cytometry
After treating the cells as described above, trypsin was added to digest the cells to obtain a single cell suspension. the supernatant was removed by centrifugation at 300 g for 5 min at 4 °C. The cells were washed with PBS and then centrifuged at 300 g for 5 min at room temperature. The cells were washed with PBS and centrifuged at 300 g for 5 min at room temperature, then the PBS was discarded. the cells were then loaded into sample tubes. The cells were resuspended with 1×Binding Buffer working solution. Subsequently, 5 µL of Annexin V-FITC and 10 µL of PI staining solution were added to each sample tube, gently vortexed, and incubated for 15 min at room temperature away from light, and the apoptosis rate was analyzed using flow cytometry.
ROS levels in cells were measured using the DCFH-DA (Abcam, USA, Cat: ab113851) assay kit. Briefly, single cells were incubated with 10 mM/l DCFH-DA for 30 min at 37 °C. Subsequently, the cells were washed by adding PBS and then centrifuged at 300 g for 5 min at room temperature before discarding the PBS. Finally, cellular reactive oxygen species levels were measured using flow cytometry.
The mitochondrial membrane potential of living cells was determined by JC-1 staining (Beyotime, China CAT: C2006). The intervened cells were aspirated off the original medium and the cells were washed with PBS buffer for 2 ~ 3 times. Subsequently, JC-1 staining solution was added, and the cells were incubated at 37 ℃ in an incubator for 30 min, the original staining solution was discarded, and the cells were washed with PBS buffer for 2 to 3 times. Finally, the ratio of cellular mitochondrial membrane potential was analyzed by flow cytometry.
Western blotting (WB)
The kidneys were homogenized in ice-cold RIPA lysis buffer with a mixture of protease and phosphatase inhibitors. The total protein concentration in the supernatant was determined using the BCA Protein Assay Kit. Aliquots of protein samples were separated on SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to PVDF membranes. The membrane was then closed in Tris-buffered saline suspended in 5% skim milk (containing 0.1% Tween 20) for 1 h at room temperature. Next, the PVDF membrane was incubated with the specific primary antibody overnight at 4 °C. After the PVDF membrane was washed with TBST buffer, it was incubated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-coupled secondary antibody for 60 min at room temperature. Finally, the immunoreactive signal was detected by chemiluminescence reagent (Biosharp, China, BL520A).
Statistical analysis
All data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. For normally distributed quantitative data, Student’s t-test was applied to compare difference between two groups. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and LSD post hoc tests were used to compare difference among three or more groups. For non-normally distributed data, Kruskal-Wallis test was used for comparing difference among different groups.
Result
Effect of AS-IV on CdCl2-induced renal injury
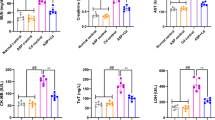
Rats were injected intraperitoneally with 5 mg/kg body weight of CdCl2 every other day and treated with AS-IV daily. Body weights of the rats were examined daily, and the CdCl2-treated rats showed a significant decrease in body weight, whereas AS-IV treatment reversed this trend of weight loss (Fig. 1A). The 24-hour proteinuria, Scr and BUN expression levels were significantly higher in CdCl2-intervened rats compared with the control group. However, 24-hour proteinuria, Scr and BUN, indicators of kidney injury, were decreased in rats treated with AS-IV (Fig. 1B-D). The rats were treated for two weeks and then executed. Subsequently, the gross morphology of the kidneys of the rats was examined. Compared with the control group, the morphology of the kidneys in the CdCl2 group was significantly impaired. It has been shown that cadmium poisoning will induce severe renal tubular injury characterized by tubular dilatation, loss of the tubular brush border, and detachment of tubular epithelial cells21. AS-IV was found to alleviate renal tubular dilatation with disappearance of tubular brush border by HE staining. In addition, AS-IV prevented inflammatory cell infiltration (Fig. 1E).
Effect of AS-IV on CdCl2-induced renal injury. (A) Changes in body weight of rats (n = 7). Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. (B) SCR levels in rats after 14 days. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. n = 7. Two-tailed t-test. p < 0.001, Con vs. CdCl2, p = 0.0237, AS-IV -L vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -H vs. CdCl2. (C) BUN levels in rats after 14 days. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. n = 7. Two-tailed t-test. p < 0.001, Con vs. CdCl2, p = 0.0879, AS-IV -L vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -H vs. CdCl2. (D) 24-hour urine protein levels in rats after 14 days. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. n = 7. Two-tailed t-test. p < 0.001, Con vs. CdCl2, p = 0.0276, AS-IV -L vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -H vs. CdCl2. (E) Morphologic observation and HE staining were used to observe histologic abnormalities in renal tissues. Scale bar, 50 μm.
To further confirm the cadmium-induced renal injury, we examined the nephrotoxicity markers fibronectin, collagen. as expected, the heavy metal cadmium promoted the expression of the nephrotoxicity markers fibronectin, collagen. After AS-IV treatment, fibronectin, collagen expression decreased significantly (Fig. 2A, B).
AS-IV reduces CdCl2-induced inflammatory factors. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Two weeks after exposure of rats to cadmium, blood was taken through the abdominal aorta and centrifuged to obtain rat serum. In addition, a portion of kidney tissue was homogenized with cold saline (1:9) containing 1% protease inhibitor on ice, and the homogenate was retained. The pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β were significantly elevated in the CdCl2 group of rats compared to the control group. The concentrations of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β were significantly decreased in rats treated with AS-IV (Fig. 3A-F). It was demonstrated that AS-IV significantly inhibited CdCl2-induced renal inflammatory response.
AS-IV reduces CdCl2-induced inflammatory factors. (A) Elisa for serum levels of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. n = 7. Two-tailed t-test. p < 0.001, Con vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -L vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -H vs. CdCl2. (B) Elisa for serum levels of inflammatory cytokines IL-6. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. n = 7. Two-tailed t-test. p < 0.001, Con vs. CdCl2, p = 0.419 AS-IV -L vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -H vs. CdCl2. (C) Elisa for serum levels of inflammatory cytokines IL-1β. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. n = 7. Two-tailed t-test. p < 0.001, Con vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -L vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -H vs. CdCl2. (D) Elisa for kidney tissue levels of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. n = 7. Two-tailed t-test. p < 0.001, Con vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -L vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -H vs. CdCl2. (E) Elisa for kidney tissue levels of inflammatory cytokines IL-6. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. n = 7. Two-tailed t-test. p < 0.001, Con vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -L vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -H vs. CdCl2. (F) Elisa for kidney tissue levels of inflammatory cytokines IL-1β. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. n = 7. Two-tailed t-test. p < 0.001, Con vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -L vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -H vs. CdCl2.
Effect of AS-IV on cadmium-induced apoptosis in rat kidney cells
To investigate the effect of AS-IV on apoptosis in rat kidney cells, we detected apoptosis in rat kidney tissues using Tunel assay. Apoptotic cells were significantly increased in the cadmium intervention group compared with the control group. However, apoptotic cells were significantly reduced after AS-IV treatment compared with the model group (Fig. 4A). Subsequently, the anti-apoptotic effect of AS-IV was further verified by Western blot.AS-IV blocked the expression of CdCl2-induced apoptotic proteins Cleaved-PARP, Cleaved-Caspase3 and Cleaved-Caspase9(Fig. 4B).
AS-IV ameliorates cadmium-induced renal cell apoptosis. (A) Tunel staining was used to determine the rate of apoptosis in renal tissues. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. (B) Measurement of Cleaved-PARP, Cleaved-Caspase3 and Cleaved-Caspase9 protein expression by WB. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Effect of AS-IV on oxidative stress
The effects of oxidative stress on renal injury are wide-ranging and cover all aspects of renal pathology as well as systemic complications22. Oxidative stress leads to renal injury and dysfunction by inducing apoptosis, necrosis, and inflammation in renal cells, and further leads to progressive decline in renal function23.Study finds long-term exposure to cadmium upsets oxidative and antioxidant balance, causing kidney damage. We used ELISA for superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH), and malondialdehyde (MDA) to assess oxidant product levels. As shown in Fig. 5A-C, MDA increased by approximately 300% and GSH and SOD decreased by 50% and 75%, respectively, in the CdCl2-treated group compared to the control group. When AS-IV was treated MDA, GSH & SOD expression levels were restored. To further assess the effect of AS-IV on oxidative stress, we measured the expression of oxidative stress-related proteins using WB. AS-IV activates the expression levels of Nrf2 and its downstream target proteins HO-1 and NQO1(Fig. 5D).
AS-IV activation of Nrf2 inhibits cadmium-induced oxidative stress in the kidney. (A) Quantification of GSH levels using ELISA assay. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. n = 7. Two-tailed t-test. p < 0.001, Con vs. CdCl2, p = 0.0395 AS-IV -L vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -H vs. CdCl2. (B) Quantification of MDA levels using ELISA assay. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. n = 7. Two-tailed t-test. p < 0.001, Con vs. CdCl2, p = 0.0614 AS-IV -L vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -H vs. CdCl2. (C) Quantification of SOD levels using ELISA assay. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. n = 7. Two-tailed t-test. p < 0.001, Con vs. CdCl2, p = 0.00274 AS-IV -L vs. CdCl2, p < 0.001 AS-IV -H vs. CdCl2. (D) Measurement of Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO1 protein expression by WB. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
AS-IV inhibits CdCl2-induced reduction in HK-2 cell viability and apoptosis
As cadmium poisoning will induce severe tubular damage leading to tubular cell apoptosis. To investigate the protective effect of AS-IV on the kidney in more detail, Renal tubular cells(HK2)were exposed to different concentrations of CdCl2 and AS-IV for 24 h respectively. CCK8 experiments revealed that cell viability decreased by 50% when CdCl2 reached 50 µM (Fig. 6A). HK2 cell growth will be inhibited at AS-IV concentrations up to 100 µM (Fig. 6B). Subsequently, HK2 cells were treated with 50 µM CdCl2 to induce apoptosis. The increase in cell viability after treatment with different concentrations of AS-IV was dose-dependent (Fig. 6C). To further prove the accuracy of the above results, we performed apoptosis experiments. As shown in Fig. 6D, the apoptosis rate was 30% in the CdCl2 group, and the apoptosis rate decreased to 10% after 70µM AS-IV intervention. Subsequently, the anti-apoptotic ability of AS-IV was further verified by Western blot.AS-IV blocked the expression of CdCl2-induced apoptotic proteins Cleaved-PARP, Cleaved-Caspase3 and Cleaved-Caspase9 (Fig. 6E).
AS-IV inhibits CdCl2-induced apoptosis in HK2 cells. ( A, B). HK-2 cells were incubated with different concentrations of CdCl2 and AS-IV for 24 h respectively. Cell viability was assessed using the CCK-8 assay. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. (C) HK-2 cells were co-cultured with different concentrations of AS-IV with 50 µM CdCl2 for 24 h and cell viability was assessed using the CCK-8 assay. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. (D) Apoptosis in HK2 cells was assessed by using flow cytometric assays. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. (E) Measurement of Cleaved-PARP, Cleaved-Caspase3 and Cleaved-Caspase9 protein expression by WB. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
AS-IV inhibits CdCl2-induced ROS production in HK2 cells with altered mitochondrial membrane potential through activation of the Nrf2 pathway
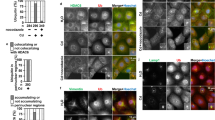
We further investigated the role of oxidative stress in cadmium-induced kidney injury in vitro. Mitochondria play a key role in energy metabolism as well as oxidative stress in kidney cells24. I used flow cytometry to determine the mitochondrial membrane potential changes and reactive oxygen species levels. The results showed that the fluorescence of JC-1 polymer had a decrease in intensity and the fluorescence of JC-1 monomer had an increase in intensity after CdCl2 intervention in HK2 cells, resulting in a significant increase in the fluorescence intensity of JC-1 polymer/monomer.AS-IV treatment reversed the mitochondrial membrane potential alteration (Fig. 7A, D). Similar to the JC-1 results there, AS-IV inhibited CdCl2-induced ROS accumulation (Fig. 7B, C). Subsequently, WB results showed that AS-IV was able to activate the expression levels of Nrf2 and its downstream target proteins HO-1 and NQO1 (Fig. 7E).
AS-IV prevents cadmium-induced oxidative stress in HK2 cells by activating Nrf2 (A, D) Mitochondrial membrane potential alteration detected by JC-1 kit. (B, C) Intracellular ROS levels were detected by flow cytometry after staining with DCFH-DA probe. E. Measurement of HK2 cells Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO1 protein expression by WB. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
To further recognize the therapeutic effect of AS-IV, we compared AS-IV with the antioxidant N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC). Subsequently, we co-cultured 35 µM AS-IV, 70 µM AS-IV, and 2 mM NAC with HK2, respectively. AS-IV was able to inhibit ROS production more effectively than the NAC intervention(Fig. 8A). AS-IV had a stronger ability to activate the expression of oxidative stress-related protein Nrf2 and its downstream target proteins HO-1 and NQO1(Fig. 8B). In addition, we examined mitochondrial dynamics and energy metabolism by an ATP kit. As shown in Fig. 8C, the ATP content, which was inhibited by CdCl2, was effectively protected by AS-IV treatment.
AS-IV has higher antioxidant capacity compared to NAC. (A) Intracellular ROS levels were detected by flow cytometry after staining with DCFH-DA probe. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. *** p < 0.001. (B) Measurement of Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO1 protein expression by WB. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. *** p < 0.001. (C) ATP content of HK2 cells. Measurement of Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO1 protein expression by WB. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed t-test. *** p < 0.001.
Discussion
With the development of economy and industry, heavy metal pollution is of great concern, people can ingest cadmium from the environment and food in the body accumulation, which leads to acute and chronic cadmium poisoning25.At present, there is no better means of antagonizing cadmium poisoning, when acute ingestion of cadmium poisoning occurs, mainly given a large number of rehydration, injection of atropine antiemetic and elimination of abdominal pain and other symptomatic treatment. Metal chelating agents, such as sodium edetate, can not antagonize cadmium toxicity, and even aggravate the toxic effect of the possible26.And it has been found that natural products such as dandelion flavonoids and garlic mixtures are effective in antagonizing cadmium poisoning27.Therefore, it is important to search for antidotes against cadmium toxicity from natural products.
Astragaloside IV (AS-IV), one of the main active components of Astragalus, is a cycloalkane triterpene glycoside28. In recent years, a large number of animal, cell and clinical experiments have shown that Astragalus has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, anti-fibrotic, anti-tumor, anti-neurological damage, and protection of cardiovascular and cerebral vascular effects, and it can be widely used in the treatment of various immune inflammation, diabetes mellitus, neurovascular diseases and so on29,30,31. Especially in renal disease, it has been confirmed that astragalus found different degrees of protective effects on cisplatin-induced renal injury, adriamycin-induced renal injury, streptozotocin-induced renal injury32,33,34AS-IV, as the main active ingredient of Astragalus, has been shown to be useful as a therapeutic or adjunctive agent for acute nephritis. However, the relationship between AS-IV and Cd-induced renal injury is not clear. Here, in order to fill the gap in this research field, we established a CdCl2-induced kidney injury rat model and a HK-2 cell model to investigate the possible role and potential mechanism of AS-IV in this process.
In this study, the body weight of the rats reflected the physical health of the animals. Long-term exposure to the heavy metal cadmium led to weight loss and the rats were no longer healthy compared to the control group. Since the kidney is the main excretory organ of the body, it is a target organ for cadmium accumulation35. Subsequently, I tested renal function markers in rats. The results showed that the kidneys were affected by chromium toxicity, with 2-hour proteinuria, elevated serum CRE and BUN levels, and impaired renal reabsorption and filtration. We dissected the rats and found that the kidneys showed congestion, edema and organ atrophy, etc. HE staining showed that the renal tissues showed massive inflammatory cell infiltration, loss of brush border, obvious formation of tubular pattern and dilatation of renal tubules. Tunel staining results showed that the toxic effects of cadmium were also manifested in apoptosis. Long-term exposure to the heavy metal cadmium leads to renal cell apoptosis. Inflammatory processes often occur throughout chronic kidney disease, and the inflammatory response is the body’s defense against inflammatory factors, in which the release of inflammatory factors plays a key role36. TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β were significantly higher in the serum of rats after heavy metal intervention compared to the control group. The above results indicate that the kidneys are susceptible to cadmium toxicity with long-term exposure to the heavy metal cadmium. As expected, when we used AS-IV to intervene in cadmium-intoxicated rats, the above deterioration of renal function was significantly improved by AS-IV. The improvement of CdCl2-induced acute kidney injury by AS-IV was demonstrated from a macroscopic morphologic point of view.
It has been suggested that kidney injury and proximal tubule cell apoptosis may be due to cadmium-induced oxidative stress37. However, the underlying mechanisms by which cadmium exposure causes oxidative stress in kidney and proximal tubule cells are unknown. Nrf2 is a typical anti-oxidative stress pathway38. We speculate that AS-IV significantly enhances the expression of Nrf2 and increases the activities of glutathione, peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase, resulting in cadmium-induced oxidative stress injury in renal tubular epithelial cells. We proved the conjecture by Elisa for SOD, GSH and MDA and WB for Nrf2 pathway proteins. To more fully verify the authenticity of our results. We performed a cellular model of CdCl2-induced HK2 injury in renal tubular cells. Consistent with the results of in vivo experiments AS-IV could effectively inhibit CdCl2-induced apoptosis. Notably, when the concentration of AS-IV exceeded 100 µM, AS-IV not only failed to resist apoptosis, but also promoted apoptosis. This result suggests that a higher dosage of AS-IV is not better when AS-IV is used clinically for the treatment of acute kidney injury due to Cd. Oxidative stress-related experiments revealed that CdCl2 would inhibit the Nrf2 pathway, inducing cellular reactive oxygen species accumulation and mitochondrial membrane potential alteration, contributing to apoptosis. In this study, we found that AS-IV could inhibit CdCl2-induced ROS production and mitochondrial membrane potential alteration in HK2 cells through activation of the Nrf2 pathway and thus treat acute kidney injury. However, this study still has shortcomings. First, although the role of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in mediating the protective effects of AS-IV was emphasized in this paper, more in-depth mechanistic studies were lacking due to time and resource constraints. Secondly, heavy metal cadmium has long-term effects on nephrotoxicity, and this experiment also failed to verify whether the protective effect of AS-IV could be sustained for a longer period of time. Therefore, we will further address these issues in subsequent studies.
In recent years, more and more Chinese herbs have attracted the attention of researchers for their diverse and multi-targeted effects. Astragalus, as a commonly used Chinese herb, has been used clinically for more than 2,000 years. AS-IV, as a star component of Astragalus, is widely used in herbal preparations for the treatment of diabetes, such as Astragalus injection and Ginseng Radix Hypoglycemic Granules. However, what role AS-IV has in heavy metal cadmium-induced acute kidney injury is not clear, and this paper fills the gap in this field. It suggests that AS-IV may be a potential drug for the clinical treatment of heavy metal cadmium poisoning.
Conclusion
The present study demonstrated that AS-IV effectively alleviated oxidative stress and renal tubular injury induced by heavy metal cadmium and protected the kidneys of cadmium-intoxicated rats. In addition, AS-IV attenuated renal tubular cell injury by activating the NRF2 pathway to inhibit CdCl2-induced ROS production and mitochondrial membrane potential alteration in HK2 cells. The results suggest that AS-IV has great potential as a viable therapeutic option as an antidote against cadmium toxicity.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Rani, A., Kumar, A., Lal, A. & Pant, M. Cellular mechanisms of cadmium-induced toxicity: A review. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 24, 378–399. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2013.835032 (2014).
Govil, P. K. et al. Soil contamination of heavy metals in the Katedan Industrial Development Area, Hyderabad, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 140, 313–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9869-x (2008).
Luevano, J. & Damodaran, C. A review of molecular events of cadmium-induced carcinogenesis. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncology: Official Organ. Int. Soc. Environ. Toxicol. Cancer 33, 183–194. https://doi.org/10.1615/jenvironpatholtoxicoloncol.2014011075 (2014).
Rafati Rahimzadeh, M., Rafati Rahimzadeh, M., Kazemi, S. & Moghadamnia, A. A. Cadmium toxicity and treatment: An update. Caspian J. Intern. Med. 8, 135–145. https://doi.org/10.22088/cjim.8.3.135 (2017).
Luo, B. et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress eIF2α-ATF4 pathway-mediated cyclooxygenase-2 induction regulates cadmium-induced autophagy in kidney. Cell Death Dis. 7, e2251. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.78 (2016).
Yan, L. J. & Allen, D. C. Cadmium-induced kidney injury: Oxidative damage as a unifying mechanism. Biomolecules 11, (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111575
Ercal, N., Gurer-Orhan, H. & Aykin-Burns, N. Toxic metals and oxidative stress part I: Mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 1, 529–539. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026013394831 (2001).
Thévenod, F. Cadmium and cellular signaling cascades: To be or not to be? Toxicol. Appl. Pharmcol. 238, 221–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.01.013 (2009).
Wang, Y., Fang, J., Leonard, S. S. & Rao, K. M. Cadmium inhibits the electron transfer chain and induces reactive oxygen species. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 36, 1434–1443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.03.010 (2004).
Nemmiche, S. Oxidative signaling response to Cadmium exposure. Toxicol. Sci. 156, 4–10. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfw222 (2017).
Hart, B. A., Potts, R. J. & Watkin, R. D. Cadmium adaptation in the lung - a double-edged sword? Toxicology 160, 65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0300-483x(00)00436-4 (2001).
Guo, Y. Y. et al. Mitochondrial GPX4 acetylation is involved in cadmium-induced renal cell ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 73, 103179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2024.103179 (2024).
Almeer, R. S. et al. Royal jelly attenuates cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity in male mice. Sci. Rep. 9, 5825. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42368-7 (2019).
Shi, Y., Shi, X., Zhao, M., Ma, S. & Zhang, Y. Pharmacological potential of Astragali Radix for the treatment of kidney diseases. Phytomedicine: Int. J. Phytotherapy Phytopharmacology 123, 155196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155196 (2024).
Liu, J. et al. Proteomic and lipidomic analysis of the mechanism underlying astragaloside IV in mitigating ferroptosis through hypoxia-inducible factor 1α/heme oxygenase 1 pathway in renal tubular epithelial cells in diabetic kidney disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 334, 118517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2024.118517 (2024).
Zhang, L. et al. Astragaloside IV alleviates renal fibrosis by inhibiting renal tubular epithelial cell pyroptosis induced by urotensin II through regulating the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway. PloS One 19, e0304365. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0304365 (2024).
Ding, Y., Liu, S., Zhang, M., Su, M. & Shao, B. Suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome activation by astragaloside IV via promotion of mitophagy to ameliorate radiation-induced renal injury in mice. Translational Androl. Urol. 13, 25–41. https://doi.org/10.21037/tau-23-323 (2024).
Huang, R. et al. Protective effect of quercetin on cadmium-induced renal apoptosis through cyt-c/caspase-9/caspase-3 signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 990993. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.990993 (2022).
Ju, Y. et al. Protective effects of Astragaloside IV on endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced renal tubular epithelial cells apoptosis in type 2 diabetic nephropathy rats. Biomed. Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine Pharmacotherapie. 109, 84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.041 (2019).
Zheng, J. et al. Icariin rReduces Cadmium-induced renal Injury in rats. Food Chem. Toxicology: Int. J. Published Br. Industrial Biol. Res. Association. 193, 114964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2024.114964 (2024).
Zhao, C. et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated autophagy activation is involved in cadmium-induced ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 175, 236–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.09.008 (2021).
Verma, S. et al. Implications of oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease: A review on current concepts and therapies. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 40, 183–193. https://doi.org/10.23876/j.krcp.20.163 (2021).
Krata, N., Zagożdżon, R., Foroncewicz, B. & Mucha, K. Oxidative stress in kidney diseases: The cause or the consequence? Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 66, 211–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-017-0496-0 (2018).
Kazeminia, S. & Eirin, A. Role of mitochondria in endogenous renal repair. Clin. Sci. (London England: 1979). 138, 963–973. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs20231331 (2024).
Johri, N., Jacquillet, G. & Unwin, R. Heavy metal poisoning: The effects of cadmium on the kidney. Biometals: Int. J. role Metal ions Biology Biochem. Med. 23, 783–792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9328-y (2010).
Esfandyari, F., Raeeszadeh, M. & Amiri, A. A. Comparative evaluation of Levamisole and broccoli in mitigating testicular oxidative stress and apoptotic alterations caused by cadmium and lead exposure in rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-024-04241-1 (2024).
Shati, A. A. Effects of Origanum majorana L. on cadmium induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in albino rats. Saudi Med. J. 32, 797–805 (2011).
Zhou, X. et al. Astragaloside IV from Astragalus Membranaceus ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis by inhibiting inflammation via TLR4/NF-кB in vivo and in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 42, 18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.11.006 (2017).
DiDonato, J. A., Mercurio, F. & Karin, M. NF-κB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 246, 379–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01099.x (2012).
Wang, J., Ke, J., Wu, X. & Yan, Y. Astragaloside prevents UV-induced keratinocyte injury by regulating TLR4/NF-κB pathway. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 21, 1163–1170. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.14174 (2022).
Qi, W., Niu, J., Qin, Q., Qiao, Z. & Gu, Y. Astragaloside IV attenuates glycated albumin-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by inhibiting oxidative stress in renal proximal tubular cells. Cell. Stress Chaperones. 19, 105–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-013-0438-7 (2014).
Zhu, Y. et al. Astragalus and its formulas as a therapeutic option for fibrotic diseases: Pharmacology and mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1040350. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1040350 (2022).
Lin, X. et al. Astragalus mongholicus Bunge and Panax notoginseng formula (A&P) improves renal mesangial cell damage in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting the inflammatory response of infiltrated macrophages. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 22 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-021-03477-x (2022).
Xie, K. H. et al. Hederagenin ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via inhibiting long non-coding RNA A330074k22Rik/Axin2/β-catenin signalling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 112, 109247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109247 (2022).
Mognetti, B., Franco, F., Castrignano, C., Bovolin, P. & Berta, G. N. Mechanisms of phytoremediation by resveratrol against cadmium toxicity. Antioxid. (Basel Switzerland) 13 https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070782 (2024).
Liang, Y. et al. Pharmacological effects of Astragaloside IV: A review. Molecules (Basel Switzerland) 28 https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166118 (2023).
Dong, W. et al. SIRT1 alleviates cd nephrotoxicity through NF-κB/p65 deacetylation-mediated pyroptosis in rat renal tubular epithelial cells. Sci. Total Environ. 929, 172392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.172392 (2024).
Huang, Q. et al. Targeting the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway: A novel therapeutic approach for acute lung injury. J. Inflamm. Res. 17, 4683–4700. https://doi.org/10.2147/jir.S467882 (2024).
Author information
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhou, J., Zhang, T. et al. Astragaloside IV attenuates cadmium induced nephrotoxicity in rats by activating Nrf2. Sci Rep 15, 2028 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-86312-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-86312-4