Abstract
This study examined the moderating effect of self-compassion on the relationship between post-traumatic symptoms (PTS) and post-traumatic growth (PTG) among adults with trauma exposure. A sample of 413 participants (254 women, 155 men) aged 18 to 81 years (M = 33.8; SD = 12.9) completed questionnaires assessing trauma exposure, PTS, PTG, and self-compassion. The results indicated that women reported significantly higher PTS and lower self-compassion than men, while no significant gender differences were found for PTG. Correlational analyses revealed a significant positive association between PTS and PTG, and a significant negative association between PTS and self-compassion. Moderation analysis demonstrated that self-compassion significantly moderated the relationship between PTS and PTG, with higher levels of self-compassion linked to greater PTG, even at elevated levels of PTS. These findings underscore the importance of self-compassion as a protective factor in trauma recovery, promoting positive psychological transformation despite the presence of distress.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Definition and impact of trauma
Exposure to trauma, whether a single incident, recurring events, or prolonged circumstances perceived as life-threatening or harmful1,2, can lead to diverse psychological outcomes. Trauma results from experiences or events that are overwhelming and involve significant threats to an individual’s emotional, physical, or psychological well-being and safety, leading to psychological distress and impairment3.
PTSD, PTS, and PTG: understanding the spectrum of trauma responses
While frequently associated with adverse consequences such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), trauma can also catalyse positive psychological transformations, including post-traumatic growth (PTG)4,5,6,7. PTSD is a recognised clinical diagnosis that requires a set of specific criteria to be met. PTSD symptoms include intrusive thoughts, avoidance behaviours, negative alterations in cognition and mood, and marked alterations in arousal and reactivity that persist for more than a month and cause significant distress or impairment in functioning8. Post-traumatic growth (PTG) refers to the positive psychological change experienced as a result of the struggle with highly challenging life circumstances. This concept suggests that individuals can develop beyond their previous levels of functioning after encountering a traumatic event. PTG involves not merely a return to baseline, but rather an improvement in various areas of life4,5,7.
Theoretical models of post-traumatic growth
Theoretical models of PTG emphasise the role of cognitive processing of the traumatic event, specifically meaning-making and cognitive reappraisal, as crucial mechanisms7. This stands in contrast to the distress and dysfunction characteristic of PTSD. Despite substantial research investigating the relationship between PTSD and PTG9,10, the factors influencing this complex interplay remain inadequately understood11.
According to Rutten et al.'s12 theoretical framework, individuals experience distinct trajectories of risk and resilience in psychopathology following trauma exposure. These trajectories can range from persistent mental health decline to an initial decline, followed by a recovery that surpasses pre-trauma well-being, a hallmark of PTG. PTG is believed to result from cognitive processing initiated when traumatic events disrupt existing worldviews and schemas7, with empirical evidence highlighting the critical role of positive reappraisal, acceptance, and deliberate meaning-making in fostering PTG13,14,15,16. Ultimately, PTG occurs when individuals successfully process their trauma, derive meaning from it, and cultivate a renewed and empowered perspective on life12. The pathway to PTG, however, is rarely straightforward. Trauma exposure can also precipitate PTSD symptoms, including intrusive thoughts, avoidance behaviours, negative mood alterations, and hyperarousal17, which can significantly impair daily functioning and interpersonal relationships. Importantly, PTSD does not necessarily preclude PTG. Some research suggests the two can co-occur, with PTSD potentially acting as a catalyst for transformative growth4.
While the idea of PTG as gaining strength through adversity is compelling and deeply rooted in humanistic psychology and cultural narratives, Infurna and Jayawickreme18 highlight the need for caution in interpreting PTG as evidence of profound psychological change. PTG could sometimes represent adaptive narratives individuals create to make sense of their trauma, without necessarily indicating deep internal change. Retrospective self-perceived measures of PTG may partly indicate meaningful personality change, but they can also encompass maladaptive reality distortions, selective appraisals, coping mechanisms, personality traits, interpretations of emotional states, reflections of implicit theories of change, and beliefs that one’s past self was worse than it truly was18. Despite these alternative interpretations of PTG, PTG remains an essential concept in trauma studies, as it offers valuable insights into how individuals navigate adversity, construct meaning, and find pathways toward resilience and recovery.
Risk and resilience: factors influencing PTSD and PTG
Research has identified numerous individual and contextual factors influencing the development of both PTSD and PTG. Risk factors for PTSD include trauma severity, perceived threat, inadequate social support, and personality traits such as neuroticism19. Conversely, factors associated with greater PTG include engagement in active coping strategies, higher levels of subjective well-being, and personality traits such as openness to experience and extraversion20,21,22,23. Intriguingly, research suggests a potential curvilinear relationship between PTSD and PTG, with moderate PTSD levels associated with the highest levels of PTG, while both low and high levels correspond to lower PTG4.
The role of self-compassion in trauma recovery
Within this complex interplay, self-compassion, a core construct within positive psychology24,25, has emerged as a potentially salient factor. Self-compassion, defined as a kind, understanding, and non-judgemental orientation towards oneself in the face of suffering, comprises three core components: self-kindness, common humanity, and mindfulness. A growing body of research has linked self-compassion to numerous adaptive outcomes, including reduced PTSD symptoms, lower levels of anxiety and depression, enhanced well-being, and the utilisation of more effective coping strategies2,26,27,28,29. Several studies have specifically demonstrated a negative relationship between PTSD and self-compassion2,30,31,32,33.
Higher levels of self-compassion appear to mitigate PTSD symptoms and facilitate PTG. Self-compassion may help individuals reframe their experience of suffering as part of the shared human experience, thereby potentially aiding in the reappraisal of the traumatic event and facilitating PTG24,25,34. Mindfulness, a key component of self-compassion, may promote calmer responses to traumatic memories and experiences, further correlating with higher PTG35.
While relatively few studies have explicitly investigated the tripartite relationship between self-compassion, PTSD, and PTG, preliminary findings are promising. Research suggests that self-compassion correlates with the adaptive cognitive processes associated with increased PTG36, mediates the relationship between trauma and PTG in bereaved parents37, and is positively correlated with distress tolerance and PTG38. Furthermore, self-compassion has been found to mediate the relationship between PTSD and PTG in students who experienced a natural disaster39.
As mentioned earlier, previous research has indicated a connection between self-compassion and positive outcomes. These outcomes include a reduction in symptoms of PTSD, decreased levels of anxiety and depression, improved well-being, and better coping skills. Furthermore, there seems to be a strong relationship or even overlap between self-compassion and neuroticism. In a study conducted by Pfattheicher and colleagues40, significant correlations were found between the neuroticism factor of the Five Factor Model of personality (FFM) and both the positive and negative aspects of self-compassion. The correlations between facets of neuroticism, such as Anxiety (r = 0.85), Depression (r = 0.90), and Self-consciousness (r = 0.85) from the NEO-PI-R, were so high that self-compassion and FFM neuroticism can be considered virtually identical constructs40. This suggests that while self-compassion may, in part, overlap with dimensions of neuroticism, its distinct framing and practical application remain invaluable for addressing trauma, mitigating post-traumatic symptoms, and fostering post-traumatic growth.
Earlier literature about the effects of traumatic evets and PTG focus mostly on PTSD. Not all people develop PTSD following exposure to trauma while still showing post-traumatic stress (PTS) symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, and sleep disturbances33,41. These PTS symptoms may resolve over time without intervention41. Furthermore, research has shown that recent PTS symptoms can predict future post-traumatic stress symptoms42. This indicates that, while PTS may not be as severe as PTSD, PTS symptoms can be seen as “subthreshold” PTSD, which can have lasting effects on individuals8,42. The present study focuses on PTS symptoms, which are naturally more common among trauma survivors than diagnosed PTSD43.
Gender differences in trauma responses
Research has highlighted gender differences in psychological responses to trauma, including both PTSD and PTG. Women show a greater likelihood of developing PTSD after trauma, possibly explained by differences in the type of trauma experienced, coping mechanisms, and hormonal effects44,45,46,47. On the other hand, studies suggest that women also report higher levels of PTG compared to men, potentially reflecting greater engagement in meaning-making processes and social support networks7,48. This research emphasizes the complex interaction of biological, psychological, and sociocultural elements in influencing trauma responses based on gender. It is thus important to understand the gender differences in the development of PTSD, PTG as well as the role of self-compassion in order to design gender appropriate treatments.
The current study
Above-described findings underscore the complex and nuanced interplay between the negative and positive outcomes of trauma and the importance of self-compassion in the trauma recovery process. While the independent relationships between self-compassion and both PTS and PTG have been explored, a critical gap remains in understanding the potential interplay between these constructs. Specifically, does self-compassion moderate the relationship between PTS and PTG, influencing the extent to which individuals experience positive growth even in the face of trauma-related distress? This study directly addresses this question by examining the moderating role of self-compassion on the relationship between PTS and PTG within a diverse sample of adults who have experienced trauma.
Method
Procedure
Sixty university student volunteers, selected through a convenience sampling method, distributed 600 questionnaire packets within their social networks, targeting a diverse range of age groups. Each packet contained four questionnaires designed to measure exposure to trauma, post-traumatic stress (PTS), post-traumatic growth (PTG), and self-compassion. Additionally, each packet included a consent form and detailed instructions. Participants were asked to sign the consent form before completing the questionnaires and returning the completed packets to the volunteers. The distribution was primarily conducted in person, with follow-up reminders to ensure a high return rate. The study received approval from the institutional research ethics committee, and all ethical guidelines, including those outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki, were strictly followed to protect participant confidentiality and well-being.
Participants
Out of the 600 distributed packets, 494 (82%) were returned. The final sample consisted of 299 women (60.5%) and 189 men (38.3%), with ages ranging from 18 to 81 years old (M = 34.7, SD = 13.41). All participants were Greek-speaking Cypriots residing in the government-controlled areas of Cyprus. Educational backgrounds were varied: 26% had primary or secondary education, 48.6% had college or university education, 25% had post-graduate education, and one participant had no formal education. Regarding marital status, 38% were married, 51% were single, and 9.6% were divorced, widowed, or separated. Participants rated their socioeconomic status (SES) on a 10-point Likert scale (1 = worst possible SES, 10 = best possible SES), with a normal distribution (M = 5.94, SD = 1.36).
A priori power analysis was conducted using GPower (version 3.1.9.70 to calculate the necessary sample size for a multiple regression model. The model included three predictors and was set to detect a small effect size (f2 = 0.02) with a significance level of 0.05. The analysis determined that a sample size of 485 participants would be required to achieve a power of 0.80.
Measures
Life Events Checklist for DSM-5 (LEC-5)
The LEC-5, or Life Events Checklist for DSM-549, is a self-report questionnaire designed to collect information on potentially traumatic events in a person’s life. For this study, the questionnaire was translated into Greek. Participants specified whether each event occurred to them personally, to a close family member or friend, to someone they witnessed, as part of their job, or if they were unsure or it did not apply. The translated version was validated through a pilot study with 50 participants to ensure cultural relevance and comprehension. Participants reported that the items were clear and unambiguous, with no confusion about what was being asked.
PTSD Checklist, Civilian Version (PCL-C)
The PCL-C50 is a self-report instrument designed to measure post-traumatic stress symptoms. This study utilised the Greek version51. The 17-item scale employs a five-point severity scale (1 = not at all, 5 = extremely) to assess symptoms experienced over the past month. Total scores range from 17 to 85, with higher scores indicating more severe post-traumatic stress. The internal reliability of this measure, as indicated by Cronbach’s α, was 0.93. The validity of the Greek version has been confirmed through previous studies51.
Posttraumatic Growth Inventory (PTGI)
The PTGI52 is a self-report measure evaluating positive outcomes following trauma. This study used the Greek version53. The 21-item scale encompasses five domains: new possibilities, personal strength, spiritual change, relating to others, and appreciation of life. Participants were asked to reflect on their most traumatic event and to rate each of the 21 items on a six-point Likert scale, ranging from 0 (no change) to 5 (very great change). The internal reliability of this measure, indicated by Cronbach’s α, was 0.97. The validity of the Greek version has been established in prior research53.
Self-Compassion Scale (SCS)
The SCS24,25 is a self-report measure designed to assess self-compassion. This study utilized the Greek version54. The 26-item scale evaluates six elements: common humanity, self-kindness, self-judgment, mindfulness, over-identification, and isolation. The self-kindness subscale measures the ability to be kind and understanding toward oneself (e.g., “I try to be loving towards myself when I’m feeling emotional pain”), while the self-judgement subscale assesses the tendency to be critical of oneself (e.g., “I’m disapproving and judgemental about my own flaws and inadequacies”). Common humanity reflects the recognition that suffering and personal inadequacy are part of the shared human experience (e.g., “I try to see my failings as part of the human condition”), and isolation measures feelings of being alone in one’s struggles and failures (e.g., “When I think about my inadequacies, it tends to make me feel more separate and cut off from the rest of the world”). The mindfulness subscale evaluates the ability to hold one’s painful thoughts and feelings in balanced awareness (e.g., “When something painful happens, I try to take a balanced view of the situation”), while over-identification captures the tendency to become absorbed in negative emotions (e.g., “When I’m feeling down, I tend to obsess and fixate on everything that’s wrong”). Participants rate each item on a five-point Likert scale (1 = almost never, 5 = almost always), with higher scores indicating greater self-compassion. The internal reliability of this measure, as indicated by Cronbach’s α, was 0.86. The validity of the Greek version has been supported by previous validation studies54.
Data handling and data analysis
All collected data were anonymised and securely stored in a password-protected database, accessible only to authorised researchers. The data were independently entered by two different research assistants. Any discrepancies identified were resolved by consulting the original questionnaires, ensuring complete accuracy of the data. Data analysis was conducted using version 26 of the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS). Descriptive statistics and independent samples t-tests were performed to examine gender differences in study variables. Pearson correlations assessed the bivariate relationships between PTS, PTG, and self-compassion. To explore the moderating effect of self-compassion on the relationship between PTS and PTG, a moderation analysis was conducted using the PROCESS macro for SPSS55. PTS was entered as the independent variable, self-compassion as the moderator, and PTG as the dependent variable. All variables were mean centred prior to analysis to reduce multicollinearity.
Results
Descriptive statistics and gender differences
Among the 494 participants, 413 (84%) reported experiencing at least one traumatic event. Consequently, all subsequent analyses were performed exclusively on data from these individuals, with sample sizes ranging from 366 to 487 depending on responses to different instruments (Table 1). The most common trauma types were transportation accidents (36%), severe human suffering (36%), and natural disasters (29%; Fig. 1). Sixty-seven (13.6%) individuals reported sexual abuse, 141 (28.5%) reported physical abuse, and 346 (70%) reported situational trauma. Women were overrepresented for sexual abuse, and situational trauma, while men were overrepresented for physical abuse (Table 2).
Independent samples t-tests indicated that women reported significantly higher PTS (t(481) = − 3.54, p < 0.001) and lower self-compassion (t(481) = 3.44, p < 0.001) compared to men. No significant gender differences emerged for PTG (Table 3).
Correlations
Pearson correlations revealed a significant positive relationship between PTS and PTG (r = 0.32, p < 0.001), indicating that individuals reporting higher levels of PTS also reported greater PTG. Additionally, PTS was significantly negatively correlated with self-compassion (r = − 0.42, p < 0.001), suggesting that individuals with higher PTS tended to report lower levels of self-compassion. The correlation between PTG and self-compassion was not statistically significant (r = 0.04, p = 0.42).
Moderation analysis
A simple moderation analysis, using PROCESS 3.3 with 5000 bootstrap samples and 95% confidence intervals, was conducted to investigate the moderation effect of self-compassion on the relationship between PTS (IV) and PTG (DV). Predictors were centred to correct for multicollinearity and only participants who reported exposure to at least one traumatic event were included (n = 413).
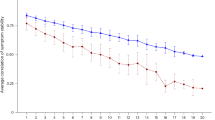
The analysis revealed a significant interaction effect of PTS and self-compassion on PTG (b = 0.02, 95% CI [0.02, 0.03], p < 0.001), accounting for 16% of the variance in PTG (F(3, 342) = 22.29, p < 0.001). The interaction plot (Fig. 2) illustrated that at higher levels of self-compassion, the positive relationship between PTS and PTG was strengthened. At higher levels of self-compassion, the positive relationship between post-traumatic stress (PTS) and post-traumatic growth (PTG) was strengthened. Specifically, to determine these effects, self-compassion was assessed at three levels: one standard deviation above the mean (high), at the mean (medium), and one standard deviation below the mean (low). Individuals reporting high levels of both PTS and self-compassion demonstrated significantly higher PTG (β = 1.32, 95% CI [0.94, 1.72]) compared to those with medium levels (β = 1.07, 95% CI [0.81, 1.33]) or low levels of both PTS and self-compassion (β = 0.86, 95% CI [0.58, 1.14]).
Discussion
This study examined how self-compassion influences the relationship between posttraumatic symptoms (PTS) and posttraumatic growth (PTG) among adult trauma survivors. The study highlights a correlation between self-compassion and recovery from trauma, suggesting its potential importance in promoting psychological adaptation and development. This study builds on previous research supporting the notion that self-compassion plays an important role in promoting positive psychological change after a traumatic event2,32.
An important finding of the current study is that people who display higher levels of self-compassion tend to experience stronger PTG, even in situations where they experience high levels of PTS. This is consistent with Tedeschi and Calhoun’s7 model of PTG, which emphasizes the importance of cognitive processes, such as reappraisal and meaning making, in the recovery process after trauma. Self-compassion is thought to enhance these processes by encouraging a non-judgemental and emotionally regulated response to trauma, which in turn supports psychological development24,25.
The moderation analysis revealed that self-compassion enhances the positive correlation between post-traumatic symptoms (PTS) and post-traumatic growth (PTG), aligning with Kleim and Ehlers’s4 findings that moderate levels of PTSD correlate with increased PTG. Self-compassion serves as a buffer against the adverse effects of trauma, aiding individuals in finding meaning and personal growth despite distressing experiences7,24,25. It not only alleviates the negative impacts of PTS but also increases the potential for PTG, particularly for individuals with high levels of both PTS and self-compassion, who report stronger PTG compared to those with lower self-compassion. By enabling individuals to adopt a broader perspective, reduce self-criticism, and enhance emotion regulation, self-compassion fosters the psychological conditions necessary for growth despite severe stress. This suggests that interventions promoting self-compassion, such as compassion-focused therapy and mindful self-compassion training, may be particularly effective for those with high PTS, fostering resilience, emotional development, and psychological well-being56,57. The significant moderating role of self-compassion underscores its importance in trauma recovery interventions58.
Consistent with previous research, this study found significant gender differences in PTS and self-compassion59,60, although the effect sizes were rather small. Women demonstrated higher levels of PTS and less self-compassion compared to men. This is consistent with previous research indicating that women are more likely to experience increased psychological distress following trauma and may have lower levels of self-compassion due to societal expectations and gender norms46,60,61. Socialisation processes often encourage women to prioritise caregiving and victimisation, which may explain their relatively lower levels of self-compassion45,61. No significant gender differences in PTG were observed, indicating that both men and women are capable of experiencing personal growth after a traumatic event, although the specific processes may differ. This finding contrasts with meta-analytical findings based on 70 studies that report small to moderate gender differences in PTG62. This lack of gender differences in PTG might be due to cultural differences or other sample characteristics. Since the study was conducted exclusively in Cyprus, and cross-cultural comparisons were not possible, it is challenging to determine why gender differences were not observed.
Individuals who reported high levels of both PTS and self-compassion experienced stronger PTG compared to those who reported lower levels of self-compassion. This suggests that self-compassion played a significant role in moderating the relationship between PTS and PTG. This finding suggests that self-compassion may enhance emotional resilience and development by promoting effective coping mechanisms and emotional control following a traumatic event24,25,57. Findings highlight the importance of self-compassion as a mitigating factor in trauma recovery interventions58.
Practical implications
The results of this study have significant implications for clinical practice both clinical practice and public health strategies. First, self-compassion’s moderation of the relationship between PTS and PTG suggests that trauma recovery programs could benefit from self-compassion-based interventions. Interventions such as compassion-focused therapy56 and mindful self-compassion training57 can be particularly effective in enhancing trauma survivors’ capacity to process distress and foster psychological growth. By cultivating self-compassion, physicians and psychologists can help survivors not only alleviate suffering, but also promote good psychological development, thus promoting a more holistic trauma healing process. Second, the gender differences observed in self-compassion and PTS suggest the importance of tailoring interventions to address unique needs based on gender. Third, the findings highlight the potential role of self-compassion in fostering resilience among individuals in high-risk professions, such as healthcare workers, first responders, and military personnel, who frequently face traumatic events. Training programs that focus on developing self-compassion can equip these individuals with tools to manage PTS while promoting long-term psychological well-being and growth. Fourth, self-compassion training in educational settings such as schools and in community centers could help individuals to better cope with traumatic experience and foster a culture of resilience. Finally, policymakers and mental health organizations could consider funding and promoting large-scale programs focused on self-compassion to address trauma recovery on a broader scale. Given the growing body of evidence supporting its efficacy, self-compassion training has the potential to significantly reduce the societal burden of trauma-related mental health challenges, improving both individual and community outcomes.
Limitations
This study has some limitations. The reliance on self-report measures can introduce biases, such as the tendency to provide socially desirable responses and potential misinformation. Including observational or physiological data in future studies may enhance the validity of the results. Additionally, the current study employed a cross-sectional design, which cannot establish true causality or track changes over time. Longitudinal studies could provide valuable insights into the development of PTS, PTG, and self-compassion throughout the trauma healing process.
The number of participants who reported experiencing a traumatic event was lower than the target sample size estimated in the power analysis. As a result, the study’s statistical power was marginally below the desired threshold, potentially reducing its ability to detect significant effects or associations. This limitation should be taken into account when interpreting the results. The geographic and cultural homogeneity of the sample also limits the generalisability of the results to the wider population. Future research should aim to replicate these findings in diverse cultural settings and examine additional factors that may influence the relationship between PTS post-traumatic growth, and self-compassion.
Conclusions
This research contributes to the expanding understanding of the psychological processes that foster resilience and growth following trauma. The study underscores the importance of self-compassion in moderating the relationship between PTS and PTG, suggesting that self-compassion plays a crucial role in the trauma healing process. Future research should aim to replicate these findings in diverse populations and identify additional factors that influence the relationship between trauma symptoms, self-compassion, and personal growth. This will ultimately enhance the understanding of trauma recovery and aid in the development of more effective treatment approaches.
Data availability
Data available at: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.27931476.
References
Krupnik, V. Trauma or adversity?. Traumatology 25(4), 256–261. https://doi.org/10.1037/trm0000169 (2018).
Winders, S. J., Murphy, O., Looney, K. & O’Reilly, G. Self-compassion, trauma, and posttraumatic stress disorder: A systematic review. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 27(3), 300–329. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.2429 (2020).
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5th edn. (American Psychiatric Association, 2013).
Kleim, B. & Ehlers, A. Evidence for a curvilinear relationship between posttraumatic growth and posttrauma depression and PTSD in assault survivors. J. Traumatic Stress 22(1), 45–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.20378 (2009).
Koliouli, F. & Canellopoulos, L. Dispositional optimism, stress, post-traumatic stress disorder and post-traumatic growth in greek general population facing the COVID-19 crisis. Eur. J. Trauma Dissoc. 5(2), 100209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejtd.2021.100209 (2021).
Shakespeare-Finch, J. & Lurie-Beck, J. A meta-analytic clarification of the relationship between posttraumatic growth and symptoms of posttraumatic distress disorder. J. Anxiety Disord. 28(2), 223–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2013.10.005 (2014).
Tedeschi, R. G. & Calhoun, L. G. Posttraumatic growth: Conceptual foundations and empirical evidence. Psychol. Inq. 15(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327965pli1501_01 (2004).
Uddin, M. et al. Epigenetic and immune function profiles associated with posttraumatic stress disorder. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107(20), 9470–9475. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0910794107 (2010).
Bonanno, G. A. & Mancini, A. D. Beyond resilience and PTSD: Mapping the heterogeneity of responses to potential trauma. Psychol. Trauma Theory Res. Pract. Policy 4(1), 74–83. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0017829 (2012).
Friedman, M. J. et al. (eds) Handbook of PTSD: Science and Practice (Guilford Press, 2007).
Solomon, Z. & Dekel, R. Posttraumatic stress disorder and posttraumatic growth among Israeli ex-pows. J. Traumatic Stress 20(3), 303–312. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.20216 (2007).
Rutten, B. P. F. et al. Resilience in mental health: Linking psychological and neurobiological perspectives. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 128(1), 3–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/acps.12095 (2013).
Cadell, S. et al. Posttraumatic growth in parents caring for a child with a life-limiting illness: A structural equation model. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 84(2), 123–133. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0099384 (2014).
Park, C. L. & Fenster, J. R. Stress-related growth: Predictors of occurrence and correlates with psychological adjustment. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 23(2), 195–215. https://doi.org/10.1521/jscp.23.2.195.31019 (2004).
Schmidt, S. D., Blank, T. O., Bellizzi, K. M. & Park, C. L. The relationship of coping strategies, social support, and attachment style with posttraumatic growth in cancer survivors. J. Health Psychol. 17(7), 1033–1040. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359105311429203 (2012).
Tang, S. T. et al. Threatened with death but growing: Changes in and determinants of posttraumatic growth over the dying process for Taiwanese terminally ill cancer patients. Psycho-Oncology 24(2), 147–154. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.3616 (2015).
Giordano, A. L. et al. Addressing trauma in substance abuse treatment. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 60(2), 55–71 (2016).
Infurna, F. J. & Jayawickreme, E. Fixing the growth illusion: New directions for research in resilience and posttraumatic growth. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 28(2), 152–158. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721419827017 (2019).
Jeon, S. W. et al. Posttraumatic growth and resilience: Assessment and clinical implications. J. Korean Neuropsychiatr. Assoc. 54(1), 32–32. https://doi.org/10.4306/jknpa.2015.54.1.32 (2015).
Aslam, N. & Kamal, A. Coping strategies as a predictors of psychological distress and post traumatic growth among flood affected individuals. J. Alcohol. Drug Depend. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-6488.1000181 (2015).
Dell’Osso, L., Lorenzi, P., Nardi, B., Carmassi, C. & Carpita, B. Post traumatic growth (PTG) in the frame of traumatic experiences. Natl. Inst. Health 19(6), 390–393. https://doi.org/10.36131/cnfioritieditore20220606 (2022).
Sheikhi, M., Matinnia, N. & Yazdi-Ravandi, S. Predicting post-traumatic growth in COVID-19 survivors based on five major personality traits in Ilam City. Thrita https://doi.org/10.5812/thrita-137609 (2023).
Wild, N. D. & Paivio, S. C. Psychological adjustment, coping, and emotion regulation as predictors of posttraumatic growth. J. Aggress. Maltreat. Trauma 8(4), 97–122. https://doi.org/10.1300/J146v08n04_05 (2003).
Neff, K. Self-compassion: An alternative conceptualization of a healthy attitude toward oneself. Self Identity 2(2), 85. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298860309032 (2003).
Neff, K. D. The development and validation of a scale to measure self-compassion. Self Identity 2(3), 223–250. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298860309027 (2003).
MacBeth, A. & Gumley, A. Exploring compassion: A meta-analysis of the association between self-compassion and psychopathology. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 32(6), 545–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2012.06.003 (2012).
Mosewich, A. D., Crocker, P. R. E., Kowalski, K. C. & DeLongis, A. Applying self-compassion in sport: An intervention with women athletes. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 35(5), 514–524. https://doi.org/10.1123/jsep.35.5.514 (2013).
Serrão, C., Valquaresma, A., Rodrigues, A. R. & Duarte, I. Mediation of self-compassion on pathways from stress and anxiety to depression among portuguese higher education students. Healthcare 11(18), 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11182494 (2023).
Smeets, E., Neff, K. D., Alberts, H. & Peters, M. Meeting suffering with kindness: Effects of a brief self-compassion intervention for female college students. J. Clin. Psychol. 70(8), 794–807. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.22076 (2014).
Harman, R. & Lee, D. The role of shame and self-critical thinking in the development and maintenance of current threat in post-traumatic stress disorder. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 17(1), 13–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.636 (2010).
Kearney, D. J., McManus, C., Martinez, M. E., Felleman, B. & Simpson, T. L. Loving-kindness meditation for posttraumatic stress disorder: A pilot study. J. Traumatic Stress 26(4), 426–434. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.21832 (2013).
Seligowski, A. V., Miron, L. R. & Orcutt, H. K. Relations among self-compassion, PTSD symptoms, and psychological health in a trauma-exposed sample. Mindfulness 6(5), 1033–1041. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-014-0351-x (2015).
Thompson, B. L. & Waltz, J. Self-compassion and PTSD symptom severity. J. Traumatic Stress 21(6), 556–558. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.20374 (2008).
Heffernan, M., Quinn Griffin, M. T., McNulty, S. R. & Fitzpatrick, J. J. Self-compassion and emotional intelligence in nurses. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 16(4), 366–373. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-172X.2010.01853.x (2010).
Hanley, A. W., Garland, E. L. & Tedeschi, R. G. Relating dispositional mindfulness, contemplative practice, and positive reappraisal with posttraumatic cognitive coping, stress, and growth. Psychol. Trauma Theory Res. Pract. Policy 9(5), 526–536. https://doi.org/10.1037/tra0000208 (2017).
Wong, C. C. Y. & Yeung, N. C. Y. Self-compassion and posttraumatic growth: Cognitive processes as mediators. Mindfulness 8(4), 1078–1087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-017-0683-4 (2017).
Khursheed, M. & Shahnawaz, M. G. Trauma and post-traumatic growth: Spirituality and self-compassion as mediators among parents who lost their young children in a protracted conflict. J. Relig. Health 59(5), 2623–2637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-020-00980-2 (2020).
Basharpoor, S., Mowlaie, M. & Sarafrazi, L. The relationships of distress tolerance, self-compassion to posttraumatic growth, the mediating role of cognitive fusion. J. Aggress. Maltreat. Trauma 30(1), 70–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/10926771.2019.1711279 (2021).
Yuhan, J., Wang, D., Canada, A. & Schwartz, J. Growth after trauma: The role of self-compassion following Hurricane Harvey. Trauma Care 1(2), 119–129. https://doi.org/10.3390/traumacare1020011 (2021).
Pfattheicher, S., Geiger, M., Hartung, J., Weiss, S. & Schindler, S. Old wine in new bottles? The case of self-compassion and neuroticism. Eur. J. Person. 31(2), 160–169. https://doi.org/10.1002/per.2097 (2017).
Elliott, R., McKinley, S., Fien, M. V. & Elliott, D. Posttraumatic stress symptoms in intensive care patients: an exploration of associated factors. Rehabil. Psychol. 61(2), 141–150. https://doi.org/10.1037/rep0000074 (2016).
Wani, A. H. et al. The impact of psychopathology, social adversity and stress-relevant DNA methylation on prospective risk for post-traumatic stress: a machine learning approach. J. Affect. Disord. 282, 894–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2020.12.076 (2021).
Lunkenheimer, F., Garatva, P., Steubl, L. & Baumeister, H. Prevalence and incidence of post-traumatic stress disorder and symptoms in people with chronic somatic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 14, 1107144. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1107144 (2023).
Dorte, C. & Ask, E. Sex differences in PTSD. In Post Traumatic Stress Disorders in a Global Context (ed. Emilio, O.) (IntechOpen, 2012). https://doi.org/10.5772/28363.
Olff, M., Langeland, W., Draijer, N. & Gersons, B. P. R. Gender differences in posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychol. Bull. 133(2), 183–204. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.133.2.183 (2007).
Tolin, D. F. & Foa, E. B. Sex differences in trauma and posttraumatic stress disorder: A quantitative review of 25 years of research. Psychol. Bull. 132(6), 959–992. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.132.6.959 (2006).
Vieweg, W. V. et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder: clinical features, pathophysiology, and treatment. Am. J. Med. 119(5), 383–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.09.027 (2006).
Morris, B. A. & Shakespeare-Finch, J. Cancer diagnostic group differences in posttraumatic growth: accounting for age, gender, trauma severity, and distress. J. Loss Trauma 16(3), 229–242. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325024.2010.519292 (2011).
Weathers, F. W. & Keane, T. M. The criterion A problem revisited: Controversies and challenges in defining and measuring psychological trauma. J. Traumatic Stress 20(2), 107–121. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts (2007).
Blanchard, E. B., Jones-Alexander, J., Buckley, T. C. & Forneris, C. A. Psychometric properties of the PTSD checklist (PCL). Behav. Res. Ther. 34(8), 669–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-7967(96)00033-2 (1996).
Calbari, E. & Anagnostopoulos, F. Exploratory factor analysis of the Greek adaptation of the PTSD checklist—Civilian version. J. Loss Trauma 15(4), 339–350. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325024.2010.491748 (2010).
Tedeschi, R. G. & Calhoun, L. G. The posttraumatic growth inventory: Measuring the positive legacy of trauma. J. Traumatic Stress 9(3), 455–471. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.2490090305 (1996).
Mystakidou, K., Tsilika, E., Parpa, E., Galanos, A. & Vlahos, L. Post-traumatic growth in advanced cancer patients receiving palliative care. Br. J. Health Psychol. 13(4), 633–646. https://doi.org/10.1348/135910707X246177 (2008).
Mantzios, M., Wilson, J. C. & Giannou, K. Psychometric properties of the Greek versions of the self-compassion and mindful attention and awareness scales. Mindfulness 6(1), 123–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-013-0237-3 (2015).
Hayes, A. F. Partial, conditional, and moderated moderated mediation: Quantification, inference, and interpretation. Commun. Monogr. 85(1), 4–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/03637751.2017.1352100 (2018).
Gilbert, P. Compassion Focused Therapy: Distinctive Features (Taylor & Francis Group, 2010).
Neff, K. D. & Germer, C. K. A pilot study and randomized controlled trial of the mindful self-compassion program. J. Clin. Psychol. 69(1), 28–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.21923 (2013).
Yadavaia, J. E., Hayes, S. C. & Vilardaga, R. Using acceptance and commitment therapy to increase self-compassion: A randomized controlled trial. J. Context. Behav. Sci. 3(4), 248–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcbs.2014.09.002 (2014).
Hourani, L. L., Williams, J., Bray, R. M. & Kandel, D. B. Gender differences in the expression of PTSD symptoms among active duty military personnel. J. Anxiety Disord. 29, 101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2014.11.007 (2014).
Yarnell, L. M. et al. Meta-analysis of gender differences in self-compassion. Self Identity 14(5), 499–520. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298868.2015.1029966 (2015).
Yarnell, L. M., Neff, K. D., Davidson, O. A. & Mullarkey, M. Gender differences in self-compassion: Examining the role of gender role orientation. Mindfulness 10(6), 1136–1152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-018-1066-1 (2019).
Vishnevsky, T., Cann, A., Calhoun, L. G., Tedeschi, R. G. & Demakis, G. J. Gender differences in self-reported posttraumatic growth: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Women Q. 34(1), 110–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-6402.2009.01546.x (2010).
Funding
Open access funding provided by NTNU Norwegian University of Science and Technology (incl St. Olavs Hospital - Trondheim University Hospital)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.L and M. A. designed the study. M.L. collected the data. M.L. and M.A. conducted the analyses. T.L. and M.S. wrote the main manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical standards
The study was reviewed by the University of Nicosia Research Ethics Committee.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Adonis, M., Loucaides, M., Sullman, M.J.M. et al. The protective role of self compassion in trauma recovery and its moderating impact on post traumatic symptoms and post traumatic growth. Sci Rep 15, 8145 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-91819-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-91819-x