Abstract
There is limited information on new-onset mental disorders in adults with metabolic diseases following the COVID-19 pandemic. Here, we aimed to examine the changes in mental health following the COVID-19 pandemic and identify factors associated with the development of new-onset mental disorders. Among 90,580 UK Biobank participants diagnosed with COVID-19 between Jan 31, 2020 and Oct 31, 2022, those who completed both baseline and follow-up mental health questionnaires in 2016–2017 and 2022–2023 were included in the analysis. New-onset depression, anxiety, and alcohol use disorder following the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as changes in mental health scores, were assessed. Furthermore, their association with sociodemographic, clinical, and self-perceived emotional state-related exposures was examined. Prevalent metabolic diseases were significantly associated with a higher risk of new-onset depression (hypertension: odds ratio [OR], 1.22; 95% CI 1.01–1.47; diabetes: OR 1.8; 95% CI 1.25–2.6; obesity: OR 1.66; 95% CI 1.43–1.95) and anxiety (hypertension: OR 1.32; 95% CI 1.06–1.63; diabetes: OR 1.66; 95% CI 1.06–2.62; obesity: OR 1.2; 95% CI 0.99–1.44) following COVID-19 pandemic. There was a significant increase of Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9; beta, 0.32; 95% CI 0.29–0.35) and Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7; beta, 0.10; 95% CI 0.06–0.13) scores throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, while Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT) score decreased over time (beta, − 0.24; 95% CI − 0.30 to − 0.18). Preexisting metabolic diseases were associated with the accelerated increase in the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 scores following the pandemic. Adults with metabolic diseases are associated with an increased risk of new-onset depression, anxiety, and alcohol use disorders following the COVID-19 pandemic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Mental disorders are a global health issue that cause a substantial socioeconomic burden and is related to unfavorable health outcomes1,2. Mental health is profoundly affected by environmental factors, and the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has threatened global mental health via a huge shift in public policy aimed at suppressing viral spread-outs by enforcing physical and societal restrictions (e.g., mask requirements, lockdowns, and physical distancing)3,4. In the context of COVID-19 itself, neuropsychiatric sequelae, such as fatigue, depression, anxiety, and cognitive dysfunctions, could manifest potentially in relation to neuroinflammation or central nervous system invasion5,6.
Apparently, individuals with metabolic diseases, including diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, are at increased risk for mental disorders due to the complex interactions of physical, socioeconomical, and genetic factors, which is also linked to serious short- and long-term complications and adverse outcomes7,8,9,10. Identifying patterns of mental health change following the pandemic in patients with metabolic diseases and understanding their socioeconomic implications is therefore crucial to mitigate disease burden, prevent the worsening of mental health, and guide targeted intervention. A systematic review of mental health problems in the pandemic period revealed significant increases in anxiety, depression, sleep problems, and a substance use disorders; however, most studies were conducted in the general population, students, and health-care workers and focused on short-term prevalence after COVID-19 infection4,11,12,13,14,15. Large-scale, well-controlled longitudinal studies that examine the link between peri-pandemic mental distress in patients with metabolic diseases at the demographic, clinical, and societal levels remain scarce.
UK Biobank is a prospective study that involves comprehensive data on demographic, biochemical, and genetic information, including a recently released 6-year interval longitudinal follow-up mental well-being questionnaire16. Factors such as social interaction and self-perceived emotional state (e.g., loneliness or resilience), which are also available in the study, are worth investigating to demonstrate the nature of peri-COVID-19 mental health, given the significance of the social environment in the development of mental disorders and the circumstances surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic17.
In this study, we examined longitudinal changes in mental health throughout the COVID-19 pandemic and explored a comprehensive set of factors associated with the development of new-onset mental disorders in ~ 60,000 UK Biobank participants. We hypothesized that individuals with prevalent metabolic diseases would be at an increased risk of new-onset mental disorders and worsening of mental health.
Methods
Study setting and participants
The UK Biobank is a prospective cohort study consisting of 502,536 participants aged 37–69 years when recruited in 2006–201016. The baseline assessment included comprehensive phenotypic and genotypic information obtained from touch-screen questionnaire and interview (e.g., lifestyle, health, and socioeconomic status), physical and functional measures, biochemical assays, and genotyping. Health-related outcomes were obtained from self-reported data or linkage to electronic health records in national datasets.
Mental health web-questionnaire (MHQ) is a set of self-report questions to capture symptoms of possible mental disorders—mainly depression and anxiety—even in people who did not receive a formal diagnosis or have medical records in the linked national health datasets. Baseline MHQ including domains of current depression, anxiety disorder, and alcohol misuse, was completed by ~ 1/3 of participants during 2016–2017. Follow-up questionnaires were sent to approximately 330,000 participants during 2022–2023 to identify change in mental health-related experiences and psychiatric symptoms throughout time.
Among participants diagnosed with COVID-19 infection between Jan 1, 2020 (the date of the first diagnosed COVID-19 case in the UK) and Oct 31, 2022 (two weeks prior to the initiation of the follow-up MHQ survey) (Supplementary Fig. 1), a subset of participants who completed both baseline and follow-up MHQ were include in the study to assess the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health and to explore the factors involved in new-onset mental disorder. (Fig. 1).
Assessment of depression, anxiety, and alcohol use disorder
Assessments of depression, anxiety, and alcohol use disorder were conducted using MHQ at baseline and follow-up, which incorporates established screening and severity assessment tools to evaluate the mental health status of the participants. The Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) is a widely used, 9-item questionnaire to evaluate the likely presence or absence and severity of current depression, and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) is a validated screening tool comprising 7-items for symptoms of generalized anxiety disorders18,19,20. The Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT) is a 10-item screening tool to assess hazardous alcohol use by examining alcohol consumption patterns and the problematic consequences of drinking21. These scales were employed to identify the presence of relevant mental disorders and measure the degree of mental distress at the baseline and follow-up. Details of the items in each scale are available in Supplementary Data 1.
Ascertainment of exposures
Demographic, clinical, and occupational exposures included age, sex, smoking status (current, former, never), alcohol consumption frequency (less than once a week, 1–2, 3–4, 7 times/week), body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, systolic blood pressure (BP), biochemical assays, prevalent comorbidity, shift work (never, sometimes–always), and current employment status (employed, retired). Social interaction-related exposures included frequency of seeing friends and family in person and frequency of speaking to friends and family on a voice call. Factors related to loneliness and resilience were taken from 3-item UCLA loneliness scale22,23 and Brief Resilience Scales24. Details of collected variables are described in Supplementary Data 2.
Statistical analyses
Baseline characteristics were presented as percentages for categorical variables, means with SDs, or medians with interquartile ranges.
In the cohort of participants who completed both baseline and follow-up questionnaires, participants with baseline PHQ-9, GAD-7, or AUDIT scores < 10—indicative of a lower likelihood of preexisting mental health issues before the COVID-19 pandemic—were included in the analysis to identify the factors related to the new-onset mental disorders and worsening of mental health post-pandemic. New-onset depression, anxiety disorder, and alcohol use disorders were defined as follow-up scores ≥ 10 on each assessment scale18,19,21,25. Logistic regression models were used to assess the association between the exposures and new-onset mental disorders post-pandemic. The exposures were analyzed individually, with adjustments made for age, sex, BMI, smoking status, alcohol consumption, hypertension, diabetes, hemoglobin, serum glucose, and creatinine-based eGFR at baseline. Participants with missing covariates were excluded from the analysis.
The longitudinal changes of mental health-assessment scales across the COVID-19 pandemic were assessed using linear regression models. Time was determined as a binary variable (baseline, follow-up). Worsening of mental health was defined as the significant increase in PHQ-9, GAD-7, or AUDIT score. Then, to test whether there were subgroups of distinct mental health changes over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic, linear regression models were fitted in subgroups (Supplementary Data 3). The rate of change over the COVID-19 pandemic was assessed using interaction term between the variable of interest and time. To ensure the robustness of the main analysis, sensitivity analyses were conducted after excluding participants who had been diagnosed with a mental disorder by a professional at baseline. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05. All statistical analyses were performed using R software (version 4.2.3).
Results
Characteristics of participants
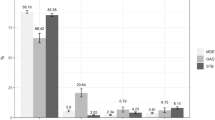
Of 502,356 UKB participants, 90,580 participants diagnosed with COVID-19 in Jan 2020–Oct 2022 were included in the study. Characteristics of the study population are provided in Table 1. Briefly, participants were aged 55 (48–60) year-old and 58.8% were male, with prevalence of hypertension (13.5%), diabetes (2.5%), obesity (10.8%), depression (11.2%), and anxiety disorder (3.9%). Among the participants who completed both baseline and follow-up assessments for the PHQ-9, GAD-7, and AUDIT questionnaires (59,935 [66.1%], 59,937 [66.1%], and 28,736 [31.7%], respectively), the proportion with the scores less than 10 accounted for 95.2%, 96.3%, and 73.4% on each scale at baseline. In the follow-up, participants with a PHQ-9 score less than 10 slightly decreased (95.2% to 94.6%), while those with a GAD-7 score less than 10 remained stable at 96.3%, and participants with an AUDIT score less than 10 were increased over time (73.4% to 76.3%).
Associated factors of new-onset depression, anxiety, and alcohol use disorder
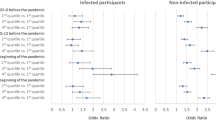
The associations of the factors and new-onset depression, anxiety, or alcohol use disorder are examined. In the multivariable-adjusted models, being 60 years or younger (OR [95% CI], 1.4 [1.18–1.66]), being female (OR 1.64 [1.41–1.92]), being current or former smoker (OR 1.36 [1.21–1.54]), being obese (OR 1.66 [1.43–1.92]), prevalent hypertension (OR 1.22 [1.01–1.47]), diabetes (OR 1.8 [1.25–2.6]), and current main job involving shift work (OR 1.56 [1.3–1.87]) were significantly associated with a higher risk of new-onset depression following COVID-19 pandemic (Figs. 2 and 3). Risk factors of new-onset anxiety also included the factors mentioned above, as well as being retired (OR 1.45 [1.18–1.79]). Younger age (OR 1.52 [1.33–1.74]), being male (OR 1.43 [1.25–1.63], being current or former smoker (OR 1.5 [1.35–1.66]), being obese (OR 1.17 [1.02–1.35]), and prevalent hypertension (OR 1.2 [1.02–1.42]) were significantly associated with higher risk of new-onset alcohol use disorder.
Multivariable-adjusted results of the association between demographic factors and new-onset mental disorders. Models were adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, smoking status, alcohol consumption, prevalent hypertension, diabetes, hemoglobin, serum glucose, and creatinine-based eGFR at baseline. AUD, alcohol use disorder; OR odds ratio; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval.
Multivariable-adjusted results of the associations between comorbidity and new-onset mental disorders. Obesity was defined as baseline body mass index > 30 kg/m2. Models were adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, smoking status, alcohol consumption, prevalent hypertension, diabetes, hemoglobin, serum glucose, and creatinine-based eGFR at baseline. AUD, alcohol use disorder; OR, odds ratio; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval.
Next, we examined whether the patterns of social interaction, loneliness and resilience were associated with the risk of new-onset mental disorder (Fig. 4). Participants who have not had regular contact with their friends and family were associated with higher risk of new-onset depression (OR 2.45 [1.69–3.55]) and anxiety (OR 2.81 [1.86–4.24]). Frequent feeling of being left out was markedly associated with a higher risk of new-onset depression (OR 28 [20.8–37.7]), anxiety (OR 15.8 [11.3–22.2]), and alcohol use disorder (OR 1.7 [1.12–2.57]); frequent feeling of “in tune” with the people around was associated with lower risk of all three mental disorders (depression, OR 0.08 [0.05–0.12]; anxiety, OR 0.1 [0.06–0.17]; alcohol use disorder, OR 0.47 [0.27–0.82]). Regarding resilience, participants who reported difficulty recovering from stressful events or who tended to take a long time to recover were more likely to develop mental disorders post-pandemic, while those who reported quick recovery from stressful events had a significantly lower risk of those.
Association between social interaction, loneliness, and resilience and new-onset mental disorders. Models were adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, smoking status, alcohol consumption, prevalent hypertension, diabetes, hemoglobin, serum glucose, and creatinine-based eGFR at baseline. AUD, alcohol use disorder; OR, odds ratio; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval.
Factors related to accelerated worsening of mental health
Multivariable-adjusted linear regression models demonstrated the increase of PHQ-9 (beta [95% CI], 0.32 [0.29–0.35]) and GAD-7 scores (beta, 0.10 [0.06–0.13]) throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, while AUDIT score decreased over time (beta, -0.24 [-0.30– -0.18]) (Table 2).
Several factors, particularly baseline comorbidity, were associated with the rate of worsening mental health during the era (Table 3 and Fig. 5). Participants with hypertension showed significant increase of both PHQ-9 and GAD-7 scores over time, showing greater degree of increase compared to those without hypertension (hypertension vs. those without, beta [95% CI]; PHQ-9, 0.43 [0.34–0.53] vs. 0.3 [0.27–0.34]; GAD-7, 0.19 [0.1–0.29] vs. 0.08 [0.05–0.12]; P for interaction, < 0.001). Obese participants also exhibited a steeply increasing slope of PHQ-9 (obesity vs. those without, beta [95% CI]; 0.49 [0.4–0.58] vs. 0.28 [0.25–0.32]; P for interaction, < 0.001) and GAD-7 scores over time (obesity, those without, beta [95% CI]; 0.16 [0.08–0.25] vs. 0.08 [0.05–0.12]; P for interaction, 0.20) compared to those without obesity. Similar patterns were identified in participants with diabetes and dyslipidemia, while no significant interaction was observed between subgroups in each group with respect to GAD-7.
The change in average mental health scores over time in subgroups of metabolic diseases. The interaction plots show the change in average PHQ-9, GAD-7, and AUDIT scores (y-axis) across baseline and follow-up timepoints (x-axis) within each comorbidity subgroups. Beta coefficients, indicating the slope between the average mental health scores at the specified timepoints, and P-values for these associations (P for interaction) are presented as indicators of statistical significance in each subgroup. Models were adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, smoking status, alcohol consumption, prevalent hypertension, diabetes, hemoglobin, serum glucose, and creatinine-based eGFR at baseline. PHQ-9, Patient Health Questionnaire-9; GAD-7, Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7; AUDIT, Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test.
In adjusted models, participants who lacked regular contact with friends or family and frequently experienced a sense of companionship or isolation showed a greater increase in both PHQ-9 and GAD-7 scores. Conversely, participants who responded they often feel “in tune” with others or exhibit quick recovery from stressful events showed a significantly lower degree of increase in these scores.
Sensitivity analysis
To test the robustness of the relationship between the change in mental health and several factors across the COVID-19 pandemic, we conducted sensitivity analysis for the subset of 72,167 participants who were free of mental disorders at baseline. The associations between new-onset mental disorder and the factors examined in the main analysis mostly remained significant in the fully-adjusted models (Supplementary Table 1). The patterns of change in mental health assessment scores, such as the increase in PHQ-9 and GAD-7 scores and the decrease in AUDIT scores, were consistently observed in the sensitivity analysis (Supplementary Table 2). In the interaction term analysis, participants being female, current/former smokers, engaged in shift work, having prevalent comorbidities, and being emotionally vulnerable had greater increases in PHQ-9 scores (Supplementary Table 3).
Discussion
In this study, we explored the change in mental health following the COVID-19 pandemic, the factors associated with new-onset depression, anxiety, and alcohol use disorder, as well as the accelerated worsening of mental health in ~ 60,000 participants diagnosed with COVID-19 in the UK Biobank. We identified that adults with prevalent metabolic diseases, including hypertension, diabetes, and obesity, were more likely to develop new-onset depression, anxiety, and alcohol use disorder across the pandemic, compared to those without such comorbidities. On average, PHQ-9 and GAD-7 scores increased over time, while AUDIT scores were decreased. Patients with metabolic disease presented a marked increase in the rate of deterioration of PHQ-9 and GAD-7 scores. Social interactions, loneliness, and resilience were significantly linked to a reduced risk of new-onset mental disorder and worsening of mental health.
The COVID-19 pandemic reshaped the global landscape of mental health, causing significant increases in the prevalence of depression and anxiety compared to pre-pandemic era26,27,28,29. Accumulating evidence on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health indicates an association between comorbidities and an increased risk of mental illness12,30,31,32. Particularly, patients with preexisting comorbidities are more exposed to a burden from social disconnection and financial instabilities, which can lead to much detrimental effects on mental health33,34. The people with metabolic diseases are not only at a higher risk of mental disorders in peri-pandemic era35,36,37,38, but being complicated with mental disorders in these patients exacerbates adverse biological responses, such as elevated blood pressure39,40, insulin resistance41,42, and activation of inflammatory and stress signaling43, potentially leading to unfavorable outcomes. As the world is slowly recovering from the aftermath of the pandemic, it is necessary to demonstrate the longitudinal change of mental health throughout the COVID-19 era, identify high-risk groups and modifiable risk factors of new-onset mental disorders to risk-stratify the population, conduct effective interventions, and establish post-pandemic public health strategies.
Our study has several strengths. First, several studies and systematic reviews focused on the short-term consequences of COVID-19 on mental health or were conducted in a cross-sectional design11,12,44,45; we observed longitudinal patterns of mental health in a large population over an extended period (2016–2017 to 2022–2023) in the UK Biobank dataset to broaden the scope in understanding the change in mental health pre- and post-COVID-19 era. Second, we used well-established scales, including PHQ-9 (depression)19, GAD-7 (anxiety disorder),18 and AUDIT (alcohol use disorder)21, and employed validated cut-off values in defining cases of mental disorders, as in previous studies. Measure for loneliness and resilience were also taken form established scoring system, such as 3-item UCLA loneliness scale22,23 and Brief Resilience Scales24. Third, in addition to observing a change in the overall mental health of the study population, we also focused on the rate of worsening mental health in several subgroups—females, adults aged < 60-year-old, those with comorbidities, shift workers, those vulnerable to loneliness, and those lacking resilience—to determine whether these subgroups require interventions at an earlier stage than those who do not.
In this study, females and participants aged < 60-year-old were associated with a greater risk of depression and anxiety compared to males and those with older age, which was in line with the previous observations30,44,46. Remarkably, we identified that prevalent hypertension, diabetes, and obesity were associated with an increased risk of new-onset depression and anxiety post-pandemic. These patients were already at higher preexisting risks for mental disorders before the pandemic; it is noticeable that the preexisting risks significantly accelerated during the pandemic, leading to substantial deterioration in mental health and an increase in new-onset mental disorders following the pandemic. Patients with metabolic diseases are more predisposed to developing severe diseases and increased mortality rates associated with COVID-1947. Obese individuals are 1.75 times more likely to be hospitalized in the intensive care unit48, and patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension have a 2.88 and 1.74 times higher likelihood, respectively, of developing severe COVID-1949,50. They face unprecedented somatic and social challenges, which significantly complicate the management of the preexisting comorbidities30,42,47. These findings support that post-pandemic mental health management strategies should be initiated at an earlier stage for patients with metabolic diseases. In addition, through an analysis of the association between mental health, social interactions with family or friends, and self-perceived emotional states, our study demonstrated that these factors are significantly associated with post-pandemic changes in mental well-being. Individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 often experience social isolation and disruptions in interpersonal connections. However, even within this cohort, differences in the extent of social interaction were linked to varying risks of mental disorders. These findings underscore the critical role of social engagement and self-perceived emotional status in mitigating psychological distress and highlighting the need for tailored interventions to support mental well-being in affected populations.
During the early period of the COVID-19 pandemic, several studies reported a significant rise in alcohol use disorder and related mortality51,52. The greatest increase in high-risk drinking was observed among individuals who were under lockdown or stay-at-home restrictions, potentially because of the increased emotional strains due to confinement with other family members53; however, our study shows a contradictory results of a decrease in AUDIT score throughout the pandemic. This could be explained by the different timing of data collection, as most studies were implemented during the lockdown period or when social restrictions were stringent. In contrast, the current study examined the longitudinal change in alcohol misuse between pre- and post-pandemic. Our study suggests, while the risk of alcohol use disorder was increased during the pandemic, relaxation of social restrictions and public efforts to improve alcohol-related disorders may have contributed to the overall decrease of alcohol use disorder following the pandemic.
There are some limitations to this study. First, it should be noted that the findings may not be representative of global changes in mental health, as the study only included participants from the UK Biobank. Second, using mental health-assessment scales in defining cases of mental illnesses can possibly overestimate the prevalence of mental disorders in patients with metabolic diseases to some extent9. However, considering the cohort size of over 300,000 participants who completed the MHQ from the UK Biobank, and given the diagnostic validity of using a cut-off score of 10 or higher18,19,20,21, our study effectively demonstrates a population-based longitudinal patterns of mental health change following the COVID-19 pandemic. Additionally, the reciprocal impact of mental disorders on the progression of metabolic diseases was not examined in the present study. Given the well-established associations between mental and metabolic disorders—mediated by behavioral54,55, pharmacological56, genetic57, and healthcare factors58—it is plausible that the new-onset mental disorders may exacerbate the severity of preexisting metabolic diseases and contribute to adverse health outcomes. However, further research is warranted to elucidate the bidirectional relationship between these conditions.
In summary, we found that patients with metabolic diseases showed an increased risk for new-onset depression and anxiety disorders and accelerated rate of mental health worsening following the COVID-19 pandemic. Modifiable risk factors include social interactions, as well as self-perceived emotional status. Increased attention to the risk stratification and intervention for mental health in these patients is a public health priority.
Data availability
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are available in the UK Biobank (www.ukbiobank.ac.uk; study accession no, 53,799).
References
Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry 9, 137–150 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/s2215-0366(21)00395-3
Walker, E. R., McGee, R. E. & Druss, B. G. Mortality in mental disorders and global disease burden implications: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiat. 72, 334–341. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.2502 (2015).
Penninx, B., Benros, M. E., Klein, R. S. & Vinkers, C. H. How COVID-19 shaped mental health: from infection to pandemic effects. Nat. Med. 28, 2027–2037. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-02028-2 (2022).
Al-Aly, Z., Xie, Y. & Bowe, B. High-dimensional characterization of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19. Nature 594, 259–264. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03553-9 (2021).
Szcześniak, D., Gładka, A., Misiak, B., Cyran, A. & Rymaszewska, J. The SARS-CoV-2 and mental health: From biological mechanisms to social consequences. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 104, 110046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.110046 (2021).
Ceban, F. et al. Fatigue and cognitive impairment in Post-COVID-19 Syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 101, 93–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2021.12.020 (2022).
Young-Hyman, D. et al. Psychosocial care for people with diabetes: A position statement of the American diabetes association. Diabetes Care 39, 2126–2140. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc16-2053 (2016).
Bădescu, S. V. et al. The association between diabetes mellitus and depression. J. Med. Life 9, 120–125 (2016).
Li, Z., Li, Y., Chen, L., Chen, P. & Hu, Y. Prevalence of depression in patients with hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Baltimore 94, 1317. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000001317 (2015).
Anderson, R. J., Freedland, K. E., Clouse, R. E. & Lustman, P. J. The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 24, 1069–1078. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.24.6.1069 (2001).
Cénat, J. M. et al. The global evolution of mental health problems during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J. Affect. Disord. 315, 70–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2022.07.011 (2022).
Robinson, E., Sutin, A. R., Daly, M. & Jones, A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies comparing mental health before versus during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. J. Affect. Disord. 296, 567–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.09.098 (2022).
Cénat, J. M. et al. Prevalence of symptoms of depression, anxiety, insomnia, posttraumatic stress disorder, and psychological distress among populations affected by the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 295, 113599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113599 (2021).
Racine, N. et al. Global prevalence of depressive and anxiety symptoms in children and adolescents during COVID-19: A meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 175, 1142–1150. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.2482 (2021).
Zhao, Y. J. et al. The prevalence of psychiatric comorbidities during the SARS and COVID-19 epidemics: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Affect. Disord. 287, 145–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.03.016 (2021).
Sudlow, C. et al. UK biobank: An open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med 12, e1001779. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001779 (2015).
Karmakar, M., Lantz, P. M. & Tipirneni, R. Association of social and demographic factors with COVID-19 incidence and death rates in the US. JAMA Netw. Open 4, e2036462. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.36462 (2021).
Spitzer, R. L., Kroenke, K., Williams, J. B. & Löwe, B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The GAD-7. Arch. Intern. Med. 166, 1092–1097. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092 (2006).
Kroenke, K., Spitzer, R. L. & Williams, J. B. The PHQ-9: Validity of a brief depression severity measure. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 16, 606–613. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-1497.2001.016009606.x (2001).
Moriarty, A. S., Gilbody, S., McMillan, D. & Manea, L. Screening and case finding for major depressive disorder using the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9): A meta-analysis. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 37, 567–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2015.06.012 (2015).
Conigrave, K. M., Hall, W. D. & Saunders, J. B. The AUDIT questionnaire: Choosing a cut-off score. Alcohol use disorder identification test. Addiction 90, 1349–1356. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1360-0443.1995.901013496.x (1995).
Hughes, M. E., Waite, L. J., Hawkley, L. C. & Cacioppo, J. T. A short scale for measuring loneliness in large surveys: Results from two population-based studies. Res. Aging 26, 655–672. https://doi.org/10.1177/0164027504268574 (2004).
Steptoe, A., Shankar, A., Demakakos, P. & Wardle, J. Social isolation, loneliness, and all-cause mortality in older men and women. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 110, 5797–5801. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1219686110 (2013).
Smith, B. W. et al. The brief resilience scale: Assessing the ability to bounce back. Int. J. Behav. Med. 15, 194–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705500802222972 (2008).
Nadkarni, A. et al. Auditing the AUDIT: A systematic review of cut-off scores for the alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT) in low- and middle-income countries. Drug. Alcohol. Depend. 202, 123–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2019.04.031 (2019).
Wang, C. et al. Immediate psychological responses and associated factors during the initial stage of the 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) epidemic among the general population in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051729 (2020).
Ahmed, M. Z. et al. Epidemic of COVID-19 in China and associated psychological problems. Asian J. Psychiatr 51, 102092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajp.2020.102092 (2020).
Lei, L. et al. Comparison of prevalence and associated factors of anxiety and depression among people affected by versus people unaffected by quarantine during the COVID-19 epidemic in Southwestern China. Med. Sci. Monit. 26, 924609. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.924609 (2020).
Huang, Y. & Zhao, N. Generalized anxiety disorder, depressive symptoms and sleep quality during COVID-19 outbreak in China: A web-based cross-sectional survey. Psychiatry Res. 288, 112954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2020.112954 (2020).
Raina, P. et al. A longitudinal analysis of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health of middle-aged and older adults from the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Nat. Aging 1, 1137–1147. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-021-00128-1 (2021).
Mukhopadhyay, S. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health of people with obesity. Stress Health https://doi.org/10.1002/smi.3359 (2023).
García-Lara, R. A. et al. Anxiety, distress and stress among patients with diabetes during COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Pers. Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091412 (2022).
Ducat, L., Rubenstein, A., Philipson, L. H. & Anderson, B. J. A review of the mental health issues of diabetes conference. Diabetes Care 38, 333–338. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc14-1383 (2015).
Mukhtar, S. & Mukhtar, S. Letter to the editor: Mental health and psychological distress in people with diabetes during COVID-19. Metabolism 108, 154248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154248 (2020).
Schaare, H. L. et al. Associations between mental health, blood pressure and the development of hypertension. Nat. Commun. 14, 1953. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37579-6 (2023).
Pan, A. et al. Bidirectional association between depression and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Diabetes Care 35, 1171–1180. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-2055 (2012).
Ducat, L., Philipson, L. H. & Anderson, B. J. The mental health comorbidities of diabetes. JAMA 312, 691–692. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.8040 (2014).
Leutner, M. et al. Obesity as pleiotropic risk state for metabolic and mental health throughout life. Transl. Psychiatry 13, 175. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-023-02447-w (2023).
Zhang, S. et al. Anxiety, home blood pressure monitoring, and cardiovascular events among older hypertension patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. Hypertens Res. 45, 856–865. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-022-00852-0 (2022).
Nagai, M., Kato, M. & Keigo, D. Anxiety and hypertension in the COVID-19 era: How is the central autonomic network linked?. Hypertens Res. 45, 922–923. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-022-00864-w (2022).
Deleskog, A. et al. Severity of depression, anxious distress and the risk of type 2 diabetes: A population-based cohort study in Sweden. BMC Public Health 19, 1174. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-7322-z (2019).
Bahrmann, A. et al. Psychological insulin resistance in geriatric patients with diabetes mellitus. Patient Educ. Couns. 94, 417–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2013.11.010 (2014).
Steenblock, C. et al. COVID-19 and metabolic disease: Mechanisms and clinical management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 9, 786–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(21)00244-8 (2021).
Sun, Y. et al. Comparison of mental health symptoms before and during the covid-19 pandemic: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis of 134 cohorts. BMJ 380, 1074224. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj-2022-074224 (2023).
Salanti, G. et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and associated control measures on the mental health of the general population: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med 175, 1560–1571. https://doi.org/10.7326/m22-1507 (2022).
Leung, C. M. C. et al. Mental disorders following COVID-19 and other epidemics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 12, 205. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-022-01946-6 (2022).
Dissanayake, H. COVID-19 and metabolic syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 37, 101753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2023.101753 (2023).
Raeisi, T. et al. The negative impact of obesity on the occurrence and prognosis of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eat. Weight Disord. 27, 893–911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-021-01269-3 (2022).
Kastora, S., Patel, M., Carter, B., Delibegovic, M. & Myint, P. K. Impact of diabetes on COVID-19 mortality and hospital outcomes from a global perspective: An umbrella systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 5, e00338. https://doi.org/10.1002/edm2.338 (2022).
Khairy, Y., Naghibi, D., Moosavi, A., Sardareh, M. & Azami-Aghdash, S. Prevalence of hypertension and associated risks in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis of meta-analyses with 1468 studies and 1,281,510 patients. Syst. Rev. 11, 242. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-022-02111-2 (2022).
White, A. M., Castle, I. P., Powell, P. A., Hingson, R. W. & Koob, G. F. Alcohol-related deaths during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA 327, 1704–1706. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.4308 (2022).
Grossman, E. R., Benjamin-Neelon, S. E. & Sonnenschein, S. Alcohol consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional survey of US Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249189 (2020).
Killgore, W. D. S., Cloonan, S. A., Taylor, E. C., Lucas, D. A. & Dailey, N. S. Alcohol dependence during COVID-19 lockdowns. Psychiatry Res. 296, 113676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113676 (2021).
Fagiolini, A. & Goracci, A. The effects of undertreated chronic medical illnesses in patients with severe mental disorders. J. Clin. Psychiatry 70(Suppl 3), 22–29. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.7075su1c.04 (2009).
Chwastiak, L. A., Rosenheck, R. A. & Kazis, L. E. Association of psychiatric illness and obesity, physical inactivity, and smoking among a national sample of veterans. Psychosomatics 52, 230–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psym.2010.12.009 (2011).
Meltzer, H. Y., Davidson, M., Glassman, A. H. & Vieweg, W. V. Assessing cardiovascular risks versus clinical benefits of atypical antipsychotic drug treatment. J. Clin. Psychiatry 63(Suppl 9), 25–29 (2002).
Amare, A. T., Schubert, K. O., Klingler-Hoffmann, M., Cohen-Woods, S. & Baune, B. T. The genetic overlap between mood disorders and cardiometabolic diseases: A systematic review of genome wide and candidate gene studies. Transl. Psychiatry 7, e1007. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.261 (2017).
Mackin, P., Bishop, D. R. & Watkinson, H. M. A prospective study of monitoring practices for metabolic disease in antipsychotic-treated community psychiatric patients. BMC Psychiatry 7, 28. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-244x-7-28 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The corresponding author attests that all of the listed authors meet the authorship criteria and that no others meeting the criteria have been omitted. JMC, JO, JHK, MK, SGK, SC, SL, YK, YCK, SSH, and HL performed the main statistical analysis including data curation, formal analysis, and investigation. JMC, JO, JHK, MK, and SGK contributed to the investigation and methodology. KWJ, YSK, DKK, and SP contributed to the conceptualization and design of the study. SP advised on statistical aspects and interpreted the data. DKK and SP offer advice regarding the data interpretation and supervised. SP supervised the overall project. All of the authors participated in drafting the manuscript. All of the authors reviewed the manuscript and approved the final version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) reporting guideline. UK Biobank (no. 53799) and Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital (IRB No. 2402-003-1506) approved this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the study participants before collecting any bio-specimens or clinical information.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, J.M., Oh, Ji., Koh, J.H. et al. New-onset mental disorders increase among patients with metabolic diseases after the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci Rep 15, 16021 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-99280-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-99280-6