Abstract
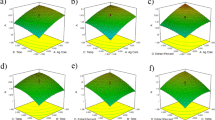
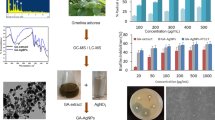
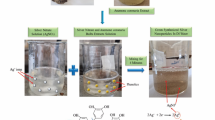
The green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using plant extracts presents a sustainable platform for multifunctional nanomaterials. This study reports the rapid, single-pot biosynthesis of AgNPs (B.gb-AgNPs) using the aqueous leaf extract of Barleria gibsonii. Phytoconstituents in the extract functioned as reducing and stabilizing agents, enabling efficient nanoparticle synthesis under optimized conditions. FT-IR, XRD, TEM, SEM, EDX, SAED, DLS, and zeta potential analyses confirmed the synthesis of predominantly spherical, face-centered cubic B.gb-AgNPs with nanoscale dimensions and biomolecular capping. The biosynthesized B.gb-AgNPs exhibited measurable antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, antioxidant capacity, and in vitro cytotoxic effects against MCF-7 breast cancer cells, with enhanced performance compared to the crude extract. In addition, the nanoparticles demonstrated effective catalytic activity in the degradation of methylene blue. Overall, this study extends current plant-mediated AgNP research by integrating phytochemical profiling, systematic synthesis optimization, and multifunctional evaluation, and identifies B. gibsonii as a promising bioresource warranting further investigation in sustainable nanotechnological research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahire, S. A. et al. The Augmentation of nanotechnology era: A concise review on fundamental concepts of nanotechnology and applications in material science and technology. Res. Chem. 4, 100633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2022.100633 (2022).
Khan, I., Saeed, K. & Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arabian J. Chem. 12, 908–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011 (2019).
Bayda, S., Adeel, M., Tuccinardi, T., Cordani, M. & Rizzolio, F. The history of nanoscience and nanotechnology: From chemical–physical applications to nanomedicine. Molecules 25(1), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010112 (2019).
Bhardwaj, B., Singh, P., Kumar, A., Kumar, S. & Budhwar, V. Eco-friendly greener synthesis of nanoparticles. Adv. Pharmaceut. Bull. 10, 566–576. https://doi.org/10.34172/apb.2020.067 (2020).
Sukhanova, A. et al. Dependence of nanoparticle toxicity on their physical and chemical properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 13(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2457-x (2018).
Rathod, S., Preetam, S., Pandey, C. & Bera, S. P. Exploring synthesis and applications of green nanoparticles and the role of nanotechnology in wastewater treatment. Biotechnol. Rep. 41, e00830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2024.e00830 (2024).
Barhoum, A. et al. Review on natural, incidental, bioinspired, and engineered nanomaterials: history, definitions, classifications, synthesis, properties, market, toxicities, risks, and regulations. Nanomaterials 12, 177 (2022).
Xia, Y., Campbell, C. T., Roldan Cuenya, B. & Mavrikakis, M. Introduction: Advanced materials and methods for catalysis and electrocatalysis by transition metals. Chem. Rev. 121, 563–566. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01269 (2021).
Baig, N., Kammakakam, I., Falath, W. & Kammakakam, I. Nanomaterials: A review of synthesis methods, properties, recent progress, and challenges. Mater. Adv. 2, 1821–1871. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ma00807a (2021).
Altammar, K. A. A review on nanoparticles: characteristics, synthesis, applications, and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1155622. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1155622 (2023).
Kumar, R. et al. Nanotoxicity unveiled: Evaluating exposure risks and assessing the impact of nanoparticles on human health. J. Trace Elements Minerals 13, 100252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemin.2025.100252 (2025).
Alshammari, B. H. et al. Organic and inorganic nanomaterials: Fabrication, properties and applications. RSC Adv. 13, 13735–13785. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ra01421e (2023).
Nagaraja, S. K., Chakraborty, B., Bhat, M. P. & Nayaka, S. Biofabrication of nano-silver composites from Indian catmint-Anisomeles ovata flower buds extract and evaluation of their potential in-vitro biological applications. Pharmacol. Res. Natural Product. 7, 100246 (2025).
Hanna, D. H. et al. Plant-derived nanoparticles: Green synthesis, factors, and bioactivities. Next Mater. 9, 101275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nxmate.2025.101275 (2025).
Kulkarni, D. et al. Biofabrication of nanoparticles: Sources, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1159193. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2023.1159193 (2023).
Karunakaran, G., Sudha, K. G., Ali, S. & Cho, E. B. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles from various biological sources and its biomedical applications. Molecules 28(11), 4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114527 (2023).
Pandit, C. et al. Biological agents for synthesis of nanoparticles and their applications. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 34, 101869 (2022).
Azadpour, A. & Khaleghi, S. Biosynthesized nanoparticles in pharmaceutical and biomedical sciences: Recent advances. Mater. Today Commun. 41, 110741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2024.110741 (2024).
Kalpana, M. et al. Actinobacteria mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Streptomyces diastaticus and their biological efficacy against human vector mosquitoes and agricultural insect pests. J. Nat. Pesticide Res. 10, 100091 (2024).
Cardoso, B., Nobrega, G., Afonso, I. S., Ribeiro, J. E. & Lima, R. A. Sustainable green synthesis of metallic nanoparticle using plants and microorganisms: A review of biosynthesis methods, mechanisms, toxicity, and applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 13, 116921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2025.116921 (2025).
El-Sheekh, M. M., Morsi, H. H., Hassan, L. H. S. & Ali, S. S. The efficient role of algae as green factories for nanotechnology and their vital applications. Microbiol. Res. 263, 127111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2022.127111 (2022).
Adeleke, B. S. et al. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles using microorganisms: A focus on endophytic fungi. Heliyon. 10, e39636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39636 (2024).
Moghaddam, A. B. et al. Nanoparticles biosynthesized by fungi and yeast: A review of their preparation, properties, and medical applications. Molecules 20, 16540–16565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200916540 (2015).
Nyabadza, A. et al. A review of physical, chemical and biological synthesis methods of bimetallic nanoparticles and applications in sensing, water treatment, biomedicine, catalysis and hydrogen storage. Adv. Coll. Interface Sci. 321, 103010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2023.103010 (2023).
Osman, A. I. et al. Synthesis of green nanoparticles for energy, biomedical, environmental, agricultural, and food applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 22, 841–887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01682-3 (2024).
Singh, H. et al. Revisiting the green synthesis of nanoparticles: Uncovering influences of plant extracts as reducing agents for enhanced synthesis efficiency and its biomedical applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 18, 4727–4750. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S419369 (2023).
Ayub, A. et al. Green nanoscience for healthcare: Advancing biomedical innovation through eco-synthesized nanoparticle. Biotechnol. Rep. 47, e00913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2025.e00913 (2025).
Kazemi, S. et al. Recent advances in green synthesized nanoparticles: From production to application. Mater. Today Sustain. 24, 100500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtsust.2023.100500 (2023).
Sati, A., Ranade, T. N., Mali, S. N., Ahmad Yasin, H. K. & Pratap, A. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs): Comprehensive insights into bio/synthesis, key influencing factors, multifaceted applications, and toxicity─ a 2024 update. ACS Omega 10(8), 7549–7582. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.4c11045 (2025).
Mehra, V., Kumar, S., Tamang, A. M. & Chandraker, S. K. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) by using plant extract and their biological application: A review. BioNanoScience 15, 18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-024-01703-7 (2025).
Kanwar, R., Rathee, J., Salunke, D. B. & Mehta, S. K. Green nanotechnology-driven drug delivery assemblies. ACS Omega 4, 8804–8815 (2019).
Malik, A. Q. et al. A review on the green synthesis of nanoparticles, their biological applications, and photocatalytic efficiency against environmental toxins. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 69796–69823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27437-9 (2023).
Ponnamma, D. et al. Green synthesized materials for sensor, actuator, energy storage and energy generation: A review. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 59, 1–62 (2020).
Comito, R., Darbyshire, I., Kiel, C., McDade, L. & Fisher, A. E. A RADseq phylogeny of Barleria (Acanthaceae) resolves fine-scale relationships. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 169, 107428 (2022).
Gangaram, S., Naidoo, Y., Dewir, Y. H. & El-Hendawy, S. Phytochemicals and biological activities of barleria (Acanthaceae). Plants 11, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11010082 (2022).
Keomanykham, O. et al. Prionitosides A and B—two iridoid glycosides with anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activities from Barleria prionitis. Phytochem. Lett. 60, 10–13 (2024).
Rodrigues, A. S. et al. Advances in silver nanoparticles: A comprehensive review on their potential as antimicrobial agents and their mechanisms of action elucidated by proteomics. Front. Microbiol. 15, 1440065. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1440065 (2024).
Zhang, W. et al. Effects of morphology and size of nanoscale drug carriers on cellular uptake and internalization process: A review. RSC Adv. 13, 80–114. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra06888e (2022).
Shao, F. et al. Bio-synthesis of Barleria gibsoni leaf extract mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles and their formulation gel for wound therapy in nursing care of infants and children. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 189, 267–273 (2018).
Mohsen Ali, S. S. & Robin, P. Comprehensive phytochemical profiling of bioactive compounds from Barleria prattensis for their antioxidant and cytotoxic capacity and its characterization using GC-MS. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 43, 102083 (2025).
Shaikh, J. R. & Patil, M. Qualitative tests for preliminary phytochemical screening: An overview. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 8, 603–608 (2020).
Gwada, C. A. et al. Phytochemical-assisted synthesis, optimization, and characterization of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv. 15, 14170–14181 (2025).
Ali, S. S. M., Aljawobaei, W., Rao, V. J., Nagar, P. S. & Robin, P. Sustainable synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Barleria prattensis extract: Characterization and evaluation of their biological and catalytic activities. Biomass. Convers. Biorefin. 15, 17811–17828 (2025).
Ali, S. S. M., Dawale, A. M. A., Samal, S., Robin, P. & Thakore, S. Barleria grandiflora leaf extract-driven silver nanoparticles: Assessment of their antibacterial, cytotoxicity, and catalysis. ChemistrySelect 10, e00764 (2025).
Manzoor, S. I. et al. Green synthesis of biocompatible silver nanoparticles using Trillium govanianum rhizome extract: Comprehensive biological evaluation and in silico analysis. Mater. Adv. 6, 682–702 (2024).
Bin-Asal, F. S. N., Saeed, A. A. & Yahia, A. R. A. B. Corallocarpus glomeruliflorus: Pharmacological potential revealed by phytochemical and in silico investigations. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 41, 101940 (2025).
Ansar, S. et al. Eco friendly silver nanoparticles synthesis by Brassica oleracea and its antibacterial, anticancer and antioxidant properties. Sci. Rep. 10, 18564 (2020).
Relva, M. et al. Electrophoretic deposition of green-synthesized hydroxyapatite on thermally oxidized titanium: enhanced bioactivity and antibacterial performance. Appl. Sci. 15, 8598 (2025).
Samal, S., Patel, M., Rohilla, A., Chandodwala, K. & Thakore, S. Sustainable synthesis of multifaceted copper oxide nanoparticles from Euphorbia tirucalli: Unveiling antimicrobial and catalytic potential. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 310, 117718 (2024).
Illanes Tormena, R. P. et al. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles obtained by microwave-assisted green synthesis using Handroanthus impetiginosus(Mart. ex DC.) Mattos underbark extract. RSC Adv. 10, 20676–20681 (2020).
Khan, S., Rukayadi, Y., Jaafar, A. H. & Ahmad, N. H. Antibacterial potential of silver nanoparticles (SP-AgNPs) synthesized from Syzygium polyanthum (Wight) Walp. against selected foodborne pathogens. Heliyon 9, (2023).
Bedlovičová, Z., Strapáč, I., Baláž, M. & Salayová, A. A brief overview on antioxidant activity determination of silver nanoparticles. Molecules 25, 3191. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143191 (2020).
Ručová, D. et al. Photoprotective and antioxidant properties of scytonemin isolated from Antarctic cyanobacterium Nostoc commune Vaucher ex Bornet & Flahault and its potential as sunscreen ingredient. J. Appl. Phycol. 35, 2839–2850 (2023).
Aljawobaei, W., Thippeswamy, N. B., Ali, S. S. M. & Achur, R. Evaluation of in vitro anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of Simarouba glauca leaf extract. Plant Sci. Today 12, 1–9 (2025).
Diab, T. A., Donia, T. & Saad-Allah, K. M. Characterization, antioxidant, and cytotoxic effects of some Egyptian wild plant extracts. Beni Suef. Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 10, 13 (2021).
Nagaraja, S. K., Niazi, S. K., Bepari, A., Assiri, R. A. & Nayaka, S. Leonotis nepetifolia flower bud extract mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles, their characterization, and in vitro evaluation of biological applications. Materials 15, 8990 (2022).
Soliman, M. K. Y., Salem, S. S., Abu-Elghait, M. & Azab, M. S. Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their efficacy towards antibacterial, antibiofilm, cytotoxicity, and antioxidant activities. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 195, 1158–1183 (2023).
Eze, F. N., Tola, A. J., Nwabor, O. F. & Jayeoye, T. J. Centella asiatica phenolic extract-mediated bio-fabrication of silver nanoparticles: Characterization, reduction of industrially relevant dyes in water and antimicrobial activities against foodborne pathogens. RSC Adv. 9, 37957–37970 (2019).
Hasan, K. M. F. et al. Functional silver nanoparticles synthesis from sustainable point of view: 2000 to 2023—A review on game changing materials. Heliyon 8, e12322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12322 (2022).
Javed, R. et al. Role of capping agents in the application of nanoparticles in biomedicine and environmental remediation: recent trends and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 18, 172. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-020-00704-4 (2020).
Arshad, F. et al. Bioinspired and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles for medical applications: A green perspective. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 196, 3636–3669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04719-z (2024).
Ahmed, S., Ahmad, M., Swami, B. L. & Ikram, S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 7, 17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2015.02.007 (2016).
Ayyankalai, N. K. et al. Green production of silver nanoparticles from Cassia occidentalis and Alternanthera pungens and evaluation of their nematicidal activity against Meloidogyne javanica. Sci. Rep. 15, 26228 (2025).
Rudrappa, M. et al. Plumeria alba-Mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles exhibits antimicrobial effect and anti-oncogenic activity against glioblastoma U118 MG cancer cell line. Nanomaterials 12, 493 (2022).
Peng, H. et al. Reduction of silver ions to silver nanoparticles by biomass and biochar: Mechanisms and critical factors. Sci. Total Environ. 779, 146326 (2021).
Tural, B., Ertaş, E., Batıbay, H. & Tural, S. The Impact of Pistacia khinjuk plant gender on silver nanoparticle synthesis: Are extracts of root obtained from female plants preferentially used?. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 746, 151257 (2025).
Chandraker, S. K. et al. Therapeutic potential of biogenic and optimized silver nanoparticles using Rubia cordifolia L. leaf extract. Sci. Rep. 12, 8831 (2022).
Pasieczna-Patkowska, S., Cichy, M. & Flieger, J. Application of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy in characterization of green synthesized nanoparticles. Molecules 30, 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030684 (2025).
Chandraker, S. K., Lal, M. & Shukla, R. DNA-binding, antioxidant, H2O2 sensing and photocatalytic properties of biogenic silver nanoparticles using: Ageratum conyzoides L. leaf extract. RSC Adv. 9, 23408–23417 (2019).
Gunagambhire, P. V., Rudrappa, M. & Nayaka, S. Myco-nanofabrication of silver nanoparticles from Clonostachys byssicola PSEF1: Characterization, and exploration of its antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory and anticancer property on liver cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 781, 152544 (2025).
Barabadi, H. et al. Trametes versicolor laccase-derived silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis, structural characterization and multifunctional biological properties. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 740, 150995 (2024).
Qing, Y. et al. Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies. Int. J. Nanomed. 13, 3311–3327. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S165125 (2018).
Hu, X. L. et al. Low-dimensional nanomaterials for antibacterial applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 9(17), 3640–3661. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1tb00033k (2021).
Elmehalawy, N. G., Zaky, M. M. M., Eid, A. M. & Fouda, A. Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Multifaceted antioxidant, antidiabetic, anticancer, and antimicrobial activities. Sci. Rep. 15, 37349 (2025).
De Mel, S. et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Magnolia alba leaf extracts and evaluating their antimicrobial, anticancer, antioxidant, and photocatalytic properties. Sci. Rep. 15, 23709 (2025).
Remya, R. R., Rajasree, S. R. R., Aranganathan, L. & Suman, T. Y. An investigation on cytotoxic effect of bioactive AgNPs synthesized using Cassia fistula flower extract on breast cancer cell MCF-7. Biotechnol. Rep. 8, 110–115 (2015).
Majeed, S., Bakhtiar, N. F. B., Danish, M., Mohamad Ibrahim, M. N. & Hashim, R. Green approach for the biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial and antitumor effect against osteoblast MG-63 and breast MCF-7 cancer cell lines. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 12, 100138 (2019).
Kavipriya, M., Selleswari, D. & Rajaganesh, R. Chitosan encapsulated silver nanoparticles by Brassica oleracea leaf extract: An in-vitro antioxidant, antimicrobial and anticancer activity on breast cancer MCF-7. Chem. Africa 7, 4875–4892 (2024).
Madakka, M., Jayaraju, N. & Rajesh, N. Evaluating the antimicrobial activity and antitumor screening of green synthesized silver nanoparticles compounds, using Syzygium jambolanum, towards MCF7 cell line (Breast cancer cell line). J. Photochem. Photobiol. 6, 100028 (2021).
Ahmad, T. et al. Biosynthesis, characterization and photo-catalytic degradation of methylene blue using silver nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proceed. 29, 1039–1043 (2020).
Saha, J., Begum, A., Mukherjee, A. & Kumar, S. A novel green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their catalytic action in reduction of Methylene Blue dye. Sustain. Environ. Res. 27, 245–250 (2017).
Somasundaram, C. K. et al. Sustainable synthesis of silver nanoparticles using marine algae for catalytic degradation of methylene blue. Catalysts 11, 1377 (2021).
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank Prof. Dhanesh Patel, Director of the Office of International Affairs (OIA), The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, for his support. The authors gratefully acknowledge the Gujarat Biodiversity Board, Gandhinagar, for granting permission (Ref. No. GBB/Legal/1-6/2025-26, dated 15 November 2025) to collect the plant material. The authors gratefully acknowledge Prof. Padmanabhi S. Nagar, Department of Botany, The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, for the taxonomic identification of the plant material, and Prof. Dharmendra Shah, In-Charge of the BARO Herbarium, for the authentication and deposition of the voucher specimen. We thank Dr. Vandana J. Rao for assistance with XRD analysis and Prof. Devarshi Gajjar, Department of Microbiology and Biotechnology Center, for providing the bacterial strains (S. aureus and E. coli). The Department of Chemistry, The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, is acknowledged for FT-IR support under the DST-FIST program, and MNIT Jaipur for conducting the DLS, zeta potential, and HRTEM characterizations. The authors acknowledge the Micro–Nano Research and Development Center, Parul University (NAAC A+ +), for providing SEM–EDX facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Saif Saleh Mohsen Ali: Writing—original draft, Visualization, Validation, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. Kanchan Dharmadhikari: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing—review & editing. Kamartaha I. Saiyed: Writing—review & editing, Resources, Investigation, Methodology. Harishree Vasava: Writing—review & editing, Investigation, Methodology. M. A. Jowhari: Formal analysis (nanomaterial characterization and biomedical interpretation); Validation; Writing; review & editing. Pushpa Robin: Writing review & editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
AI tools
Used exclusively for language refinement and proofreading, without involvement in data analysis or content creation.
Ethical approval
The article does not contain any studies involving human or animal participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, S.S.M., Dharmadhikari, K., Saiyed, K.I. et al. Ecofriendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Barleria gibsonii and evaluation of antibacterial antioxidant cytotoxic and catalytic activities. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37330-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37330-3