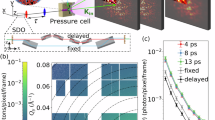
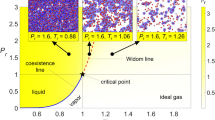
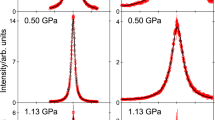
Abstract
Supercritical fluids are characterized by unique thermodynamic properties. One of these properties is the existence of two-component dynamics that is associated with distinct low-frequency and high-frequency vibrational responses of the fluid. However, the origin of this behavior remains unknown. By combining inelastic X-ray scattering and molecular dynamics simulations, we show that this behavior can be connected to density heterogeneities arising from molecular clusters. Analyses of measurements and molecular trajectories suggest that the two-component dynamics emerges due to distinct momentum fluctuations of clustered and unbound molecules. This connection between clusters and two-component dynamics highlights the importance of molecular-structural heterogeneities in supercritical fluids, colloids, and condensed-matter systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of the study are included in the main text and supplementary information files. Source data have been deposited in the Supplementary Material and Stanford Digital Repository52: https://doi.org/10.25740/sj299gg3375. Additional data are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
Code availability
The MD simulations were performed with the open-source software LAMMPS (release date 8 April, 2021). Code for the analysis of the experimental data is available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Correa, C. R. & Kruse, A. Supercritical water gasification of biomass for hydrogen production-review. J. Supercrit. Fluids 133, 573–590 (2018).
Kendall, J. L., Canelas, D. A., Young, J. L. & DeSimone, J. M. Polymerizations in supercritical carbon dioxide. Chem. Rev. 99, 543–564 (1999).
Brunner, G. Applications of supercritical fluids. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 1, 321–342 (2010).
Benson, S. M. & Cole, D. R. CO\(_2\) sequestration in deep sedimentary formations. Elements 4, 325–331 (2008).
Gallo, P., Corradini, D. & Rovere, M. Widom line and dynamical crossovers as routes to understand supercritical water. Nat. Commun. 5, 5806 (2014).
Simeski, F. & Ihme, M. Supercritical fluids behave as complex networks. Nat. Commun. 14, 1996 (2023).
Simeoni, G. G. et al. The Widom line as the crossover between liquid-like and gas-like behaviour in supercritical fluids. Nat. Phys. 6, 503–507 (2010).
Gorelli, F., Santoro, M., Scopigno, T., Krisch, M. & Ruocco, G. Liquidlike behavior of supercritical fluids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 245702 (2006).
Xu, L. et al. Relation between the Widom line and the dynamic crossover in systems with a liquid-liquid phase transition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 102, 16558–16562 (2005).
Brazhkin, V. V., Fomin, Y. D., Lyapin, A. G., Ryzhov, V. N. & Tsiok, E. N. Widom line for the liquid-gas transition in Lennard-Jones system. J. Phys. Chem. B 115, 14112–14115 (2011).
Brazhkin, V. V. et al. “Liquid-gas’’ transition in the supercritical region: Fundamental changes in the particle dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 145901 (2013).
Yang, C., Brazhkin, V. V., Dove, M. T. & Trachenko, K. Frenkel line and solubility maximum in supercritical fluids. Phys. Rev. E 91, 012112 (2015).
Fomin, Y. D., Ryzhov, V. N., Tsiok, E. N., Brazhkin, V. V. & Trachenko, K. Crossover of collective modes and positive sound dispersion in supercritical state. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 28, 43LT01 (2016).
Prescher, C. et al. Experimental evidence of the Frenkel line in supercritical neon. Phys. Rev. B 95, 134114 (2017).
Proctor, J., Pruteanu, C., Morrison, I., Crowe, I. & Loveday, J. Transition from gas-like to liquid-like behavior in supercritical \(\rm N_2\). J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10, 6584–6589 (2019).
Bryk, T. et al. Behavior of Supercritical Fluids across the “Frenkel Line’’. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8, 4995–5001 (2017).
Proctor, J. E., Bailey, M., Morrison, I., Hakeem, M. A. & Crowe, I. F. Observation of liquid-liquid phase transitions in ethane at 300 K. J. Phys. Chem. B 122, 10172–10178 (2018).
Ishii, R. et al. A neutron scattering study of the structure of supercritical carbon dioxide. Chem. Phys. Lett. 240, 84–88 (1995).
Nishikawa, K., Tanaka, I. & Amemiya, Y. Small-angle X-ray scattering study of supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Phys. Chem. 100, 418–421 (1996).
Morita, T., Nishikawa, K., Takematsu, M., Iida, H. & Furutaka, S. Structure study of supercritical CO\(_2\) near higher-order phase transition line by X-ray diffraction. J. Phys. Chem. B 101, 7158–7162 (1997).
Botti, A., Bruni, F., Ricci, M. A. & Soper, A. Neutron diffraction study of high density supercritical water. J. Chem. Phys. 109, 3180–3184 (1998).
Pipich, V. & Schwahn, D. Densification of supercritical carbon dioxide accompanied by droplet formation when passing the Widom line. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 145701 (2018).
Sator, N. Clusters in simple fluids. Phys. Rep. 376, 1–39 (2003).
Fan, J., Ly, N. & Ihme, M. Heterogeneous cluster energetics and nonlinear thermodynamic response in supercritical fluids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 133, 248001 (2024).
Maddox, M. W., Goodyear, G. & Tucker, S. C. Origins of atom-centered local density enhancements in compressible supercritical fluids. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 6248–6257 (2000).
Majumdar, A. et al. Direct observation of ultrafast cluster dynamics in supercritical carbon dioxide using X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 15, 10540 (2024).
Sun, P., Hastings, J. B., Ishikawa, D., Baron, A. Q. R. & Monaco, G. Two-component dynamics and the liquidlike to gaslike crossover in supercritical water. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 256001 (2020).
Boon, J. P. & Yip, S. Molecular Hydrodynamics (Courier Corporation, 1991).
Sun, P., Hastings, J., Ishikawa, D., Baron, A. Q. R. & Monaco, G. Universal two-component dynamics in supercritical fluids. J. Phys. Chem. B 125, 13494–13501 (2021).
Baron, A. Q. R. High-resolution inelastic x-ray scattering I: Context, spectrometers, samples, and superconductors. In Synchrotron Light Sources and Free-Electron Lasers: Accelerator Physics, Instrumentation and Science Applications (eds Jaeschke, E. et al.) 2131–2212 (Springer, 2020).
Lemmon, E. W., Bell, I. H., Huber, M. L. & McLinden, M. O. Thermophysical properties of fluid systems. In NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69 (eds Linstrom, P. J. & Mallard, W. G.) (National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2025).
Thompson, A. P. et al. LAMMPS-a flexible simulation tool for particle-based materials modeling at the atomic, meso, and continuum scales. Comput. Phys. Commun. 271, 108171 (2022).
Potoff, J. J. & Siepmann, J. I. Vapor-liquid equilibria of mixtures containing alkanes, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. AIChE J. 47, 1676–1682 (2001).
Aimoli, C. G., Maginn, E. J. & Abreu, C. R. A. Force field comparison and thermodynamic property calculation of supercritical CO\(_2\) and CH\(_4\) using molecular dynamics simulations. Fluid Ph. Equilib. 368, 80–90 (2014).
Bencivenga, F. et al. High-frequency dynamics of liquid and supercritical water. Phys. Rev. E 75, 051202 (2007).
Monaco, G., Cunsolo, A., Ruocco, G. & Sette, F. Viscoelastic behavior of water in the terahertz-frequency range: An inelastic x-ray scattering study. Phys. Rev. E 60, 5505 (1999).
Ishikawa, D. & Baron, A. Q. R. Interaction of acoustic and quasi-elastic modes in liquid water on nanometer length scales. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 90, 083602 (2021).
Sun, P. Molecular Dynamics of Supercritical Fluids. Ph.D. thesis, Stanford University (2021).
Sampoli, M., Ruocco, G. & Sette, F. Mixing of longitudinal and transverse dynamics in liquid water. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 1678 (1997).
Bolmatov, D., Zav’Yalov, D., Gao, M. & Zhernenkov, M. Structural evolution of supercritical CO\(_2\) across the Frenkel line. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5, 2785–2790 (2014).
Giordano, V. M. & Monaco, G. Fingerprints of order and disorder on the high-frequency dynamics of liquids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107, 21985–21989 (2010).
Scopigno, T., D’astuto, M., Krisch, M., Ruocco, G. & Sette, F. Observation of Umklapp processes in noncrystalline materials. Phys. Rev. B 64, 012301 (2001).
Muhunthan, P. et al. A self-consistent analysis of cluster morphology in supercritical carbon dioxide from small angle x-ray scattering. Chem. Phys. Lett. 142190 (2025).
Hill, T. L. Molecular clusters in imperfect gases. J. Chem. Phys. 23, 617–622 (1955).
Simdyankin, S. I., Taraskin, S. N., Dzugutov, M. & Elliott, S. R. Vibrational properties of the one-component \(\sigma\) phase. Phys. Rev. B 62, 3223 (2000).
Kittel, C. & McEuen, P. Introduction to Solid State Physics (Wiley, 2018).
Kalinichev, A. G. Molecular simulations of liquid and supercritical water: Thermodynamics, structure, and hydrogen bonding. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 42, 83–129 (2001).
Boero, M., Terakura, K., Ikeshoji, T., Liew, C. C. & Parrinello, M. Hydrogen bonding and dipole moment of water at supercritical conditions: A first-principles molecular dynamics study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 3245 (2000).
Rowlinson, J. S. & Swinton, F. L. Liquids and Liquid Mixtures (Butterworth-Heinemann, 2013).
Mattenet, M. et al. An X-Ray Thermo-Pressure Cell For Carbon Dioxide. In AIP Conference Proceedings, Vol. 1234, 111–114 (American Institute of Physics, 2010).
Walters, A. C. Using X-ray and neutron scattering to study the dynamics of low-dimensional systems. Ph.D. thesis, University College London (2009).
Majumdar, A. et al. Database for heterogeneity induced universal two-component dynamics in supercritical fluids, https://doi.org/10.25740/sj299gg3375 (2025).
Funding
Financial support from the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science under DOE (BES) Awards DE-SC0022222 and DE-SC0026165 (A.M. and M.I.) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.M.: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing original draft, Writing - review & editing; P.S.: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing - review & editing; M.S.: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing - review & editing; L.P.: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing - review & editing; A.B.: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing - review & editing; A.Q.R.B.: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing - review & editing; J.H.: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Project administration, Supervision, Writing - review & editing; M.I.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing - review & editing
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Majumdar, A., Sun, P., Singleton, M. et al. Two-component dynamics in supercritical \(\text {CO}_2\) from inelastic X-ray scattering. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38697-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38697-z