Abstract
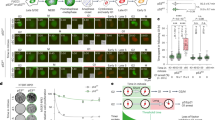
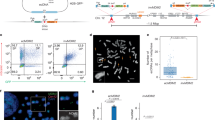
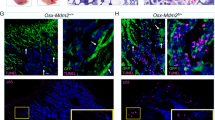
Mdm2, a regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor, is frequently overexpressed in lymphomas, including lymphomas that have inactivated p53. However, the biological consequences of Mdm2 overexpression in lymphocytes are not fully resolved. Here, we report that increased expression of Mdm2 in B cells augmented proliferation and reduced susceptibility to p53-dependent apoptosis, which was due to inhibition of p53 and suppression of p21 expression. Notably, developing and mature B cells from Mdm2 transgenic mice had an increased frequency of chromosomal/chromatid breaks and/or aneuploidy. This Mdm2-mediated genome instability occurred at a similar frequency as that in B cells overexpressing the oncogene c-Myc, but the chromosomal instability was not further enhanced when Mdm2 and c-Myc were overexpressed together. Elevated Mdm2 expression alone increased the occurrence of B-cell transformation in vivo and cooperated with c-Myc overexpression, resulting in an acceleration of B-cell lymphomagenesis. In addition, the frequency of p53 mutations was reduced, but not eliminated, in lymphomas arising in Mdm2/Eμ-myc double transgenic mice. Therefore, increased Mdm2 expression facilitated B-cell lymphomagenesis, in part, through regulation of p53 by altering B-cell proliferation and susceptibility to apoptosis, and by inducing chromosomal instability.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM, Harris AW, Pinkert CA, Corcoran LM, Alexander WS, Cory S et al. (1985). The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature 318: 533–538.
Alt JR, Bouska A, Fernandez MR, Cerny RL, Xiao H, Eischen CM . (2005). Mdm2 binds to Nbs1 at sites of DNA damage and regulates double strand break repair. J Biol Chem 280: 18771–18781.
Alt JR, Greiner TC, Cleveland JL, Eischen CM . (2003). Mdm2 haplo-insufficiency profoundly inhibits Myc-induced lymphomagenesis. EMBO J 22: 1442–1450.
Barak Y, Juven T, Haffner R, Oren M . (1993). Mdm2 expression is induced by wild type p53 activity. EMBO J 12: 461–468.
Canman CE, Lim DS, Cimprich KA, Taya Y, Tamai K, Sakaguchi K et al. (1998). Activation of the ATM kinase by ionizing radiation and phosphorylation of p53. Science 281: 1677–1679.
Capoulade C, Bressac-de Paillerets B, Lefrere I, Ronsin M, Feunteun J, Tursz T et al. (1998). Overexpression of MDM2, due to enhanced translation, results in inactivation of wild-type p53 in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Oncogene 16: 1603–1610.
Cross SM, Sanchez CA, Morgan CA, Schimke MK, Ramel S, Idzerda RL et al. (1995). A p53-dependent mouse spindle checkpoint. Science 267: 1353–1356.
Digweed M, Sperling K . (2004). Nijmegen breakage syndrome: clinical manifestation of defective response to DNA double-strand breaks. DNA Repair (Amst) 3: 1207–1217.
Eischen CM, Alt JR, Wang P . (2004). Loss of one allele of ARF rescues Mdm2 haploinsufficiency effects on apoptosis and lymphoma development. Oncogene 23: 8931–8940.
Eischen CM, Roussel MF, Korsmeyer SJ, Cleveland JL . (2001a). Bax loss impairs Myc-induced apoptosis and circumvents the selection of p53 mutations during Myc-mediated lymphomagenesis. Mol Cell Biol 21: 7653–7662.
Eischen CM, Weber JD, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ, Cleveland JL . (1999). Disruption of the ARF–Mdm2–p53 tumor suppressor pathway in Myc-induced lymphomagenesis. Genes Dev 13: 2658–2669.
Eischen CM, Woo D, Roussel MF, Cleveland JL . (2001b). Apoptosis triggered by Myc-induced suppression of Bcl-X(L) or Bcl-2 is bypassed during lymphomagenesis. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5063–5070.
Franco S, Alt FW, Manis JP . (2006). Pathways that suppress programmed DNA breaks from progressing to chromosomal breaks and translocations. DNA Repair (Amst) 5: 1030–1041.
Ghobrial IM, McCormick DJ, Kaufmann SH, Leontovich AA, Loegering DA, Dai NT et al. (2005). Proteomic analysis of mantle-cell lymphoma by protein microarray. Blood 105: 3722–3730.
Gumy-Pause F, Wacker P, Sappino AP . (2004). ATM gene and lymphoid malignancies. Leukemia 18: 238–242.
Honda R, Tanaka H, Yasuda H . (1997). Oncoprotein MDM2 is a ubiquitin ligase E3 for tumor suppressor p53. FEBS Lett 420: 25–27.
Jones SN, Hancock AR, Vogel H, Donehower LA, Bradley A . (1998). Overexpression of Mdm2 in mice reveals a p53-independent role for Mdm2 in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 15608–15612.
Levine AJ, Hu W, Feng Z . (2006). The P53 pathway: what questions remain to be explored? Cell Death Differ 13: 1027–1036.
Lundgren K, Montes de Oca Luna R, McNeill YB, Emerick EP, Spencer B, Barfield CR et al. (1997). Targeted expression of MDM2 uncouples S phase from mitosis and inhibits mammary gland development independent of p53. Genes Dev 11: 714–725.
Martins CP, Brown-Swigart L, Evan GI . (2006). Modeling the therapeutic efficacy of p53 restoration in tumors. Cell 127: 1323–1334.
Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D, Levine AJ . (1992). The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell 69: 1237–1245.
Strasser A, Harris AW, Cory S . (1993). E mu-bcl-2 transgene facilitates spontaneous transformation of early pre-B and immunoglobulin-secreting cells but not T cells. Oncogene 8: 1–9.
Vafa O, Wade M, Kern S, Beeche M, Pandita TK, Hampton GM et al. (2002). c-Myc can induce DNA damage, increase reactive oxygen species, and mitigate p53 function: a mechanism for oncogene-induced genetic instability. Mol Cell 9: 1031–1044.
Vassilev LT . (2007). MDM2 inhibitors for cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med 13: 23–31.
Wang P, Greiner TC, Lushnikova T, Eischen CM . (2006). Decreased Mdm2 expression inhibits tumor development induced by loss of ARF. Oncogene 25: 3708–3718.
Watanabe T, Ichikawa A, Saito H, Hotta T . (1996). Overexpression of the MDM2 oncogene in leukemia and lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 21: 391–397.
Weber JD, Taylor LJ, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ, Bar-Sagi D . (1999). Nucleolar ARF sequesters Mdm2 and activates p53. Nat Cell Biol 1: 20–26.
Wilda M, Bruch J, Harder L, Rawer D, Reiter A, Borkhardt A et al. (2004). Inactivation of the ARF–MDM-2–p53 pathway in sporadic Burkitt's lymphoma in children. Leukemia 18: 584–588.
Wu X, Bayle JH, Olson D, Levine AJ . (1993). The p53–mdm-2 autoregulatory feedback loop. Genes Dev 7: 1126–1132.
Acknowledgements
We thank Randy Fields, Dr Silvia Plaza, Greg Cochran, and Jane Kennedy for skilled technical assistance; Drs Jane Meza and William DuPont for statistical analyses. This work was supported by NCI Grants CA098139 and CA117935 (CME). TCG is a Lymphoma Research Foundation Mantle Cell Lymphoma Grantee. CME is a Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Scholar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Lushnikova, T., Odvody, J. et al. Elevated Mdm2 expression induces chromosomal instability and confers a survival and growth advantage to B cells. Oncogene 27, 1590–1598 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210788
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210788
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Targeting AKT with costunolide suppresses the growth of colorectal cancer cells and induces apoptosis in vitro and in vivo
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)
-
MDM2 promotes genome instability by ubiquitinating the transcription factor HBP1
Oncogene (2019)
-
Inactivation of ribosomal protein S27-like confers radiosensitivity via the Mdm2-p53 and Mdm2–MRN–ATM axes
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Activation of PERK-Nrf2 oncogenic signaling promotes Mdm2-mediated Rb degradation in persistently infected HCV culture
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Decoding critical long non-coding RNA in ovarian cancer epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Nature Communications (2017)