Abstract
Objective: To investigate the potential of near-infrared reflectance (NIR) spectroscopy as a rapid and non-destructive method to determine total fat and protein in mixed, homogenized and freeze-dried human diets.
Design: 29 students collected duplicate portions of their diet for four consecutive days. In addition, a detailed food diary was kept. The duplicate portions were analysed for total protein and fat content both by traditional chemical analysis (Kjeldahl and Folch methods) and through the recently developed NIR spectroscopy method. In addition, traditional computerized estimation of nutrient composition was performed.
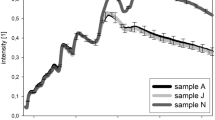
Results: Plotting of the NIR-predicted fat content against the chemically analysed fat content gave a correlation coefficient of 0.99. Plotting of the NIR-predicted protein content against the Kjeldahl-analysed protein gave a correlation coefficient of 0.81.
Conclusion: NIR-spectroscopy seems to be able to determine fat content in mixed, homogenized diets to a high degree of accuracy. In surveys involving duplicate portion sampling this will save time and money. The prediction accuracy for protein was less convincing, but acceptable depending on the need for accurate individual data.
Sponsorship: Norwegian Food Research Institute, Institute for Nutrition Research at the University of Oslo and the Research Society of the Norwegian Edible Fat Producers and the food company Mills DA.
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2000) 54, 20–23
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor: HM Meltzer.
Contributors: KA had the idea for the study, was responsible for the collaboration with industry and wrote the first version of the manuscript. HMM provided duplicate portion samples for the study, and wrote the final versions of the manuscript. JIP supervised Almendingen and Meltzer, and commented on the manuscript. BNN performed the NIR analysis and commented on the manuscript. MRE was responsible for the NIR analysis, part of the statistical analysis, and wrote selected parts of the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almendingen, K., Meltzer, H., Pedersen, J. et al. Near infrared spectroscopy—a potentially useful method for rapid determination of fat and protein content in homogenized diets. Eur J Clin Nutr 54, 20–23 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600886
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600886
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification key for selection of the matrix type to which a sample belongs within the context of GMO analysis
Accreditation and Quality Assurance (2021)
-
Direct determination of major components in human diets and baby foods
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2015)