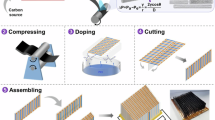
Carbon nanotubes weave their way into a range of imaginative macroscopic applications.
Abstract
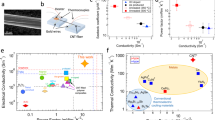
The creation of continuous yarns made out of carbon nanotubes would enable macroscopic nanotube devices and structures to be constructed1,2. Here we show that carbon nanotubes can be self-assembled into yarns of up to 30 cm in length simply by being drawn out from superaligned arrays of carbon nanotubes, and that the strength and conductivity of these yarns can be enhanced by heating them at high temperatures. Our findings should help to translate the remarkable mechanical, electrical and thermal properties of carbon nanotubes to a macroscopic scale.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vigolo, B. et al. Science 290, 1331–1334 (2000).
Ball, P. Nature 414, 142–144 (2001).
de Heer, W. A. et al. Science 268, 845–847 (1995).
Li, W. Z. et al. Science 274, 1701–1703 (1996).
Ren, Z. F. et al. Science 282, 1105–1107 (1998).
Fan, S. S. et al. Science 283, 512–514 (1999).
Wang, J. F., Gudiksen, M. S., Duan, X. F., Cui, Y. & Lieber, C. M. Science 293, 1455–1457 (2001).
Li, Z. M. et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 1274011–1274014 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, K., Li, Q. & Fan, S. Spinning continuous carbon nanotube yarns. Nature 419, 801 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/419801a
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/419801a
This article is cited by
-
Influence of purity and level of disorder on the spinnability of CNTs yarn derived from the CNTs forest grown by a parametrically tuned CVD
Journal of Materials Science (2024)
-
Preparation of carbon nanotube films towards mechanical and electrochemical energy storage
Nano Research (2023)
-
Failure-analysis of carbon nanotubes and their extreme applications
Nano Research (2023)
-
Feasibility of wear reduction for soft nanostructured thin film through enhanced elastic recoverability and contact stress relief
Friction (2023)
-
Soft-lock drawing of super-aligned carbon nanotube bundles for nanometre electrical contacts
Nature Nanotechnology (2022)