Abstract
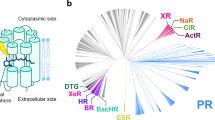
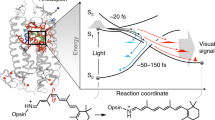
Individual biological molecules can be imaged under physiological conditions by atomic force microscopy. Our results from AFM, supported by electron microscopy, revealed distinct rows of rhodopsin dimers and paracrystalline arrays in native murine disc membranes1,2. This supramolecular arrangement was also found for the light-activated form, opsin1. We counted 30,000–55,000 rhodopsin molecules per square micrometre, a packing density comparable to that measured by optical methods in amphibian discs3. From the lattice vectors describing the paracrystalline arrays, a maximum possible packing density of 62,900 rhodopsin molecules per square micrometre was calculated. The rhodopsin dimers seen in AFM topographs2 have cytosolic protrusions separated by 3.8 nm, providing an ideal docking platform for arrestin, which has two binding grooves that are separated by 3.8 nm as well1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang, Y. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 21655–21662 (2003).
Fotiadis, D. et al. Nature 421, 127–128 (2003).
Liebman, P. A. & Entine, G. Science 185, 457–459 (1974).
Miljanich, G. P., Brown, M. F., Mabrey-Gaud, S., Dratz, E. A. & Sturtevant, J. M. J. Membr. Biol. 85, 79–86 (1985).
Suzuki, E., Katayama, E. & Hirosawa, K. J. Electron Microsc. (Tokyo) 42, 178–184 (1993).
Kajimura, N., Harada, Y. & Usukura, J. J. Electron Microsc. (Tokyo) 49, 691–697 (2000).
Bouvier, M. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 2, 274–286 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fotiadis, D., Liang, Y., Filipek, S. et al. Is rhodopsin dimeric in native retinal rods?. Nature 426, 31 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/426031a
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/426031a