Abstract
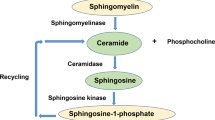
Activation of acid and neutral sphingomyelinases, and the ensuing generation of ceramide, contributes to the biological effects of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), one of which is apoptosis. While the mechanisms of activation of sphingomyelinases by the cytokine are being unravelled, less is known about regulation of their activity. Nitric oxide has previously been shown to exert a cyclic GMP-dependent inhibition of early apoptotic events triggered by TNF-α in the U937 monocytic cell line. We therefore investigated whether inhibition of sphingomyelinases by nitric oxide plays a role in regulating such early events. We found that activation of both acid and neutral sphingomyelinases, triggered in the first minutes after U937 cell stimulation with TNF-α, is regulated in an inhibitory fashion by nitric oxide, working through generation of cyclic GMP and activation of protein kinase G. Using a range of inhibitors selective for either sphingomyelinase we found that the acid sphingomyelinase contributes to activation of the initiator caspase-8 and early DNA fragmentation and that inhibition of the acid enzyme by nitric oxide accounts for cyclic GMP-dependent early protection from apoptosis. We also found that the protective effect by both cGMP and acid sphingomyelinase inhibitors progressively disappeared at later stages of the apoptotic process. Inhibition of sphingomyelinases represents a novel action of nitric oxide, which might be of physiological relevance in regulating initial phases of apoptosis as well as other biological actions of ceramide.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- TNF-α and TNF-RI:
-
tumour necrosis factor-α and its p55 kDa receptor
- A-SMase and N-SMase:
-
acid and neutral sphingomyelinases
- cGMP:
-
cyclic GMP
- SNAP,S-nitroso-acetylpenicillamine; ODQ:
-
H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-α]- quinoxalin-1-one
- D609:
-
tricyclodecan-9-yl xanthate
- CHX:
-
cycloheximide
References
Zimmermann KC, Bonzen C, Reed DR . 2001 The machinery of programmed cell death Pharmacol. Ther. 92: 57–70
Borner C, Monney L, Olivier R, Rosse T, Hacki J, Conus S . 1999 Life and death in a medieval atmosphere Cell Death Differ. 6: 201–206
Liu L, Stamler JS . 1999 NO: an inhibitor of cell death Cell Death Differ. 6: 937–942
Takuma K, Phuagphong P, Lee E, Mori K, Baba A, Matsuda T . 2001 Anti-apoptotic effect of cGMP in cultured astrocytes: inhibition by cGMP-dependent protein kinase of mitochondrial permeable transition pore J. Biol. Chem. 276: 48093–48099
Zamora R, Alarcon L, Vodovotz Y, Betten B, Kim PK, Gibson KF, Billiar TR . 2001 Nitric oxide suppresses the expression of Bcl-2 binding protein BNIP3 in hepatocytes J. Biol. Chem. 276: 46887–46895
De Nadai C, Sestili P, Cantoni O, Liévremont JP, Sciorati C, Barsacchi R, Moncada S, Meldolesi J, Clementi E . 2000 Nitric oxide inhibits tumor necrosis factor-α-induced apoptosis by reducing the generation of ceramide Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 97: 5480–5485
Kolesnick RN, Krönke M . 1998 Regulation of ceramide production and apoptosis Annu. Rev. Physiol. 60: 643–665
Perry DK, Hannun YA . 1998 The role of ceramide in cell signaling Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1436: 233–243
Levade T, Jaffrézou J-P . 1999 Signalling sphingomyelinases: which, where, how and why? Biophys. Acta 1438: 1–17
Sciorati C, Rovere P, Ferrarini M, Heltai S, Manfredi AA, Clementi E . 1997 Autocrine nitric oxide modulates CD95-induced apoptosis in γδ T lymphocytes J. Biol. Chem. 272: 23211–23215
Sciorati C, Rovere P, Ferrarini M, Paolucci C, Heltai S, Vaiani R, Clementi E, Manfredi AA . 1999 Generation of nitric oxide by the inducible nitric oxide synthase protects γδ T cells from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced apoptosis J. Immunol. 163: 1570–1576
Schütze S, Machleidt T, Adam D, Schwandner R, Wiegmann K, Kruse ML, Heinrich M, Wickel M, Krönke M . 1999 Inhibition of receptor internalization by monodansylcadaverine selectively blocks p55 tumor necrosis factor receptor death domain signaling J. Biol. Chem. 274: 10203–10212
Stasch JP, Becker EM, Alonso-Alija C, Apeler H, Dembowsky K, Feurer A, Gerzer R, Minuth T, Perzborn E, Pleiss U, Schroder H, Schroeder W, Stahl E, Steinke W, Straub A, Schramm M . 2001 NO-independent regulatory site on soluble guanylate cyclase Nature 410: 212–215
Moncada S, Higgs EA . 1995 Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies related to nitric oxide FASEB J. 9: 1319–1330
Gadbois DM, Crissman HA, Tobey RA, Bradbury EM . 1992 Multiple kinase arrest points in the G1 phase of nontransformed mammalian cells are absent in transformed cells Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 89: 8626–8630
Lozano J, Menendez S, Morales A, Ehleiter D, Liao WC, Wagman R, Haimovitz-Friedman A, Fuks Z, Kolesnick R . 2001 Cell autonomous apoptosis defects in acid sphingomyelinase knockout fibroblasts J. Biol. Chem. 276: 442–448
Ségui B, Cuvillier O, Adam-Klages S, Garcia V, Malagarie-Cazenave S, Lévéque S, Caspar-Bauguil S, Coudert J, Salvayre R, Krönke M, Levade T . 2001 Involvement of FAN in TNF-induced apoptosis J. Clin. Invest. 108: 143–151
Jensen JM, Schütze S, Forl M, Krönke M, Proksch E . 1999 Roles for tumor necrosis factor receptor p55 and sphingomyelinase in repairing the cutaneous permeability barrier J. Clin. Invest. 104: 1761–1770
Garcìa-Ruiz C, Mari M, Morales A, Colell A, Ardite E, Fernandez-Checa JC . 2000 Human placenta sphingomyelinase, an exogenous acidic pH-optimum sphingomyelinase, induces oxidative stress, glutathione depletion, and apoptosis in rat hepatocytes Hepatol. 32: 56–65
Tanaka M, Nara F, Suzuki-Konagai K, Hosoya T, Ogita T . 1997 Structural elucidation of scyphostatin, an inhibitor of membrane-bound neutral sphingomyelinase J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116: 7871–7872
Andrieu-Abadie N, Jaffrézou JP, Hatem S, Laurent G, Levade T, Mercaider JJ . 1999 L-carnitine prevents doxorubicin-induced apoptosis of cardiac myocytes: role of inhibition of ceramide generation FASEB J. 13: 1501–1510
Brenner B, Ferlinz K, Grassmé H, Weller M, Koppenhoefer U, Dichgans J, Sandhoff K, Lang F, Gulbins E . 1998 Fas/CD95/Apo-I activates the acidic sphingomyelinase via caspases Cell Death Differ. 5: 29–37
Schwandner R, Wiegmann K, Bernardo K, Kreder D, Krönke M . 1998 TNF receptor death domain-associated proteins TRADD and FADD signal activation of acid sphingomyelinase J. Biol. Chem. 273: 5916–5922
Dbaibo GS, Perry DK, Gamard CJ, Platt R, Poirier GG, Obeid LM, Hannun YA . 1997 Cytokine response modifier A (CrmA) inhibits ceramide formation in response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α: CrmA and Bcl-2 target distinct components in the apoptotic pathway J. Exp. Med. 85: 481–490
Jayadev S, Hayter HL, Andrieu N, Gamard CJ, Liu B, Balu R, Hayakawa M, Ito F, Hannun Y . 1997 Phospholipase A2 is necessary for tumor necrosis factor α-induced ceramide generation in L929 cells J. Biol. Chem. 272: 17196–17203
Mansat V, Laurent G, Levade T, Bettaieb A, Jaffrézou JP . 1997 The protein kinase C activators phorbol esters and phosphatidylserine inhibit neutral sphingomyelinase activation, ceramide generation, and apoptosis triggered by daunorubicin Cancer Res. 57: 5300–5304
Ségui B, Bezombes C, Uro-Coste E, Medin JA, Andrieu-Abadie N, Auge N, Brouchet A, Laurent G, Salvayre R, Jaffrézou JP, Levade T . 2000 Stress-induced apoptosis is not mediated by endolysosomal ceramide FASEB J. 14: 36–47
Grassmé H, Jekle A, Riehle A, Schwarz H, Berger J, Sandhoff K, Kolesnick R, Gulbins E . 2001 CD95 signaling via ceramide-rich membrane rafts J. Biol. Chem. 276: 20589–20596
Birbes H, El Bawab S, Hannun YA, Obeid LM . 2001 Selective hydrolysis of a mitochondrial pool of sphingomyelin induces apoptosis FASEB J. 15: 2669–2679
Garcìa-Ruiz C, Colell A, Mari M, Morales A, Fernandez-Checa JC . 1997 Direct effect of ceramide on the mitochondrial electron transport chain leads to generation of reactive oxygen species. Role of mitochondrial glutathione J. Biol. Chem. 272: 11369–11377
Ghafourifar P, Klein SD, Schucht O, Schenk U, Pruschy M, Rocha S, Richter C . 1999 Ceramide induces cytochrome c release from isolated mitochondria. Importance of mitochondrial redox state J. Biol. Chem. 274: 6080–6088
Beltràn B, Mathur A, Duchen MR, Erusalimsky JD, Moncada S . 2000 The effect of nitric oxide on cell respiration: A key to understanding its role in cell survival or death Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 97: 14602–14607
Brown GC . 1999 Nitric oxide and mitochondrial respiration Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1411: 351–369
Bulotta S, Barsacchi R, Rotiroti D, Borgese N, Clementi E . 2001 Activation of the endothelial nitric-oxide synthase by tumor necrosis factor-α. A novel feedback mechanism regulating cell death J. Biol. Chem. 276: 6529–6536
Li XA, Titlow WB, Jackson BA, Giltiay N, Nikolova-Karakashian M, Uittenbogaard A, Smart EJ . 2002 High-density lipoprotein binding to scavenger receptor class B, type I activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase in a ceramide-dependent manner J. Biol. Chem. 277: 11058–11063
Acknowledgements
We thank Annie Higgs and Jacopo Meldolesi for their critical revision of the manuscript, and Céline De Nadai for her help in the initial phases of the project. This work was supported by grants from: Italian Association for Cancer Research (E Clementi); Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Target Project Biotechnology and Agenzia 2000 (E Clementi); cofinanziamento 2001 from the Ministero dell'Istruzione, dell'Università e della Ricerca (E Clementi and Jacopo Meldolesi).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by G Melino
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barsacchi, R., Perrotta, C., Sestili, P. et al. Cyclic GMP-dependent inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase by nitric oxide: an early step in protection against apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 9, 1248–1255 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401095
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401095
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ATF3 reduces migration capacity by regulation of matrix metalloproteinases via NFκB and STAT3 inhibition in glioblastoma
Cell Death Discovery (2017)
-
Nitric oxide released from JS-K induces cell death by mitotic catastrophe as part of necrosis in glioblastoma multiforme
Cell Death & Disease (2016)
-
The emerging role of Acid Sphingomyelinase in autophagy
Apoptosis (2015)
-
Acid sphingomyelinase determines melanoma progression and metastatic behaviour via the microphtalmia-associated transcription factor signalling pathway
Cell Death & Differentiation (2014)
-
Acid sphingomyelinase in macrophage biology
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2011)