Abstract
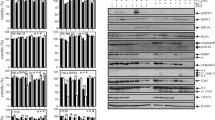
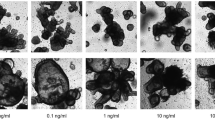
The HT29 adenocarcinoma is a common model of epithelial cell differentiation and colorectal cancer and its death is an oft-analyzed response to TNF family receptor signaling. The death event itself remains poorly characterized and here we have examined the involvement of caspases using pan-caspase inhibitors. zVAD-fmk did not block death of HT29 cells in response to activation of the Fas, TRAIL, TNF, TWEAK and LTβ receptors. The secondary induction of TNF or the other known bona fide death inducing ligands did not account for death following LTβ receptor activation indicating that TNF family receptors can trigger a caspase-independent death pathway regardless of the presence of canonical death domains in the receptor. To provide a frame of reference, the phenotype of HT29 death was compared to four other TNF family receptor triggered death events; Fas induced Jurkat cell apoptosis, TNF/zVAD induced L929 fibroblast necrosis, TNF induced death of WEHI 164 fibroblastoid cells and TNF/zVAD induced U937 death. The death of HT29 and U937 cells under these conditions is an intermediate form with both necrotic and apoptotic features. The efficient coupling of TNF receptors to a caspase-independent death event in an epithelial cell suggests an alternative approach to cancer therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AIF:
-
apoptosis inducing factor
- DAPI:
-
4,6 diaminophenyl-2-phenylindole
- IFNγ:
-
interferon-γ
- JNK:
-
cJun N terminal kinase
- LTβR:
-
lymphotoxin-β receptor
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl) 2,5 diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- PCD:
-
programmed cell death
- PI:
-
propidium iodide
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- TNFR:
-
tumor necrosis factor receptor
- TRAF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factors
- TRAIL-R:
-
TRAIL receptor
- 7AAD:
-
7-amino actinomycin D
References
Fiers W, Beyaert R, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P . 1999 More than one way to die: apoptosis, necrosis and reactive oxygen damage Oncogene 18: 7719–7730
Hengartner MO . 2000 The biochemistry of apoptosis Nature 407: 770–776
Wallach D, Varfolomeev EE, Malinin NL, Goltsev YV, Kovalenko AV, Boldin MP . 1999 Tumor necrosis factor receptor and Fas signaling mechanisms Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17: 331–367
Holler N, Zaru R, Micheau O, Thome M, Attinger A, Valitutti S, Bodmer JL, Schneider P, Seed B, Tschopp J . 2000 Fas triggers an alternative, caspase-8-independent cell death pathway using the kinase RIP as effector molecule Nat. Immunol. 1: 489–495
Matsumura H, Shimizu Y, Ohsawa Y, Kawahara A, Uchiyama Y, Nagata S . 2000 Necrotic death pathway in fas receptor signaling J. Cell. Biol. 151: 1247–1256
Khwaja A, Tatton L . 1999 Resistance to the cytotoxic effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha can be overcome by inhibition of a FADD/caspase-dependent signaling pathway J. Biol. Chem. 274: 36817–36823
Grell M, Zimmermann G, Gottfried E, Chen CM, Goenwald U, Huang DC, Lee YH, Duerkop H, Engelmann H, Scheurich P, Wajant H, Strasser A . 1999 Induction of cell death by tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 2, CD40 and CD30: a role for TNF-R1 activation by endogenous membrane- anchored TNF EMBO J. 18: 3034–3043
Schneider P, Schwenzer R, Haas E, Muhlenbeck F, Schubert G, Scheurich P, Tschopp J, Wajant H . 1999 TWEAK can induce cell death via endogenous TNF and TNF receptor 1 Eur. J. Immunol. 29: 1785–1792
Leist M, Jaattela M . 2001 Four deaths and a funeral: from caspases to alternative mechanisms Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2: 589–598
Kitanaka C, Kuchino Y . 1999 Caspase-independent programmed cell death with necrotic morphology Cell Death Differ. 6: 508–515
Zakerl Z, Bursch W, Tenniswood M, Lockshin RA . 1995 Cell death: programmed, apoptosis, necrosis or other? Cell Death Diff. 2: 87–96
Bidere N, Senik A . 2001 Caspase-independent apoptotic pathways in T lymphocytes: a minireview Apoptosis 6: 371–375
Margot T, Tschopp J . 2001 Regulation of lymphocyte proliferation and death by FLIP Nature Rev. Immunol. 1: 50–58
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, Stanford WL, Cho SK, Li CY, Sasaki T, Elia AJ, Cheng HY, Ravagnan L, Ferri KF, Zamzami N, Wakeham A, Hakem R, Yoshida H, Kong YY, Mak TW, Zuniga-Pflucker JC, Kroemer G, Penninger JM . 2001 Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in programmed cell death Nature 410: 549–554
Browning JL, Miatkowski K, Sizing I, Griffiths D, Zafari M, Benjamin CD, Meier W, Mackay F . 1996 Signaling through the lymphotoxin beta receptor induces the death of some adenocarcinoma tumor lines J. Exp. Med. 183: 867–878
Browning J, Ribolini A . 1989 Studies on the differing effects of tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin on the growth of several human tumor lines J. Immunol. 143: 1859–1867
Yonehara S, Ishii A, Yonehara M . 1989 A cell-killing monoclonal antibody (Anti-fas) to a cell surface antigen co-downregulated with the receptor of tumor necrosis factor J. Exp. Med. 169: 1747–1756
Abreu-Martin MT, Vidrich A, Lynch DH, Targan SR . 1995 Divergent induction of apoptosis and IL-8 secretion in HT-29 cells in response to TNF-α and ligation of Fas ligand J. Immunol. 155: 4147–4154
Ossina NK, Cannas A, Powers VC, Fitzpatrick PA, Knight JD, Gilbert JR, Shekhtman EM, Tomei LD, Umansky SR, Kiefer MC . 1997 Interferon-gamma modulates a p53-independent apoptotic pathway and apoptosis-related gene expression J. Biol. Chem. 272: 16351–16357
Chicheportiche Y, Bourdon PR, Xu H, Hsu YM, Scott H, Hession C, Garcia I, Browning JL . 1997 TWEAK, a new secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly induces apoptosis J. Biol. Chem. 272: 32401–32410
Rooney IA, Butrovich KD, Glass AA, Borboroglu S, Benedict CA, Whitbeck JC, Cohen GH, Eisenberg RJ, Ware CF . 2000 The lymphotoxin-beta receptor is necessary and sufficient for LIGHT-mediated apoptosis of tumor cells J. Biol. Chem. 275: 14307–14315
Sugarman BJ, Aggarwal BB, Hass PE, Figari IS, Palladino MA Jr, Shepard HM . 1985 Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro Science 230: 943–945
Fiers W, Brouckaert P, Devos R, Fransen L, Leroux-Roels G, Remaut E, Suffys P, Tavernier J, Van der Heyden J, Van Roy F . 1986 Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 51: 587–595
Mackay F, Bourdon PR, Griffiths DA, Lawton P, Zafari M, Sizing ID, Miatkowski K, Ngam-ek A, Benjamin CD, Hession C, Ambrose CM, Meier W, Browning JL . 1997 Cytotoxic activities of recombinant soluble murine lymphotoxin-alpha and lymphotoxin-alpha beta complexes J. Immunol. 159: 3299–3310
Eby MT, Jasmin A, Kumar A, Sharma K, Chaudhary PM . 2000 TAJ, a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family, activates the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and mediates caspase-independent cell death J. Biol. Chem. 275: 15336–15342
Kanda H, Igaki T, Kanuka H, Yagi T, Miura M . 2002 Wenger, a member of the drosophila TNF receptor superfamily, is required for Eiger signaling J. Biol. Chem. 277: 28372–28375
Sarin A, Williams MS, Alexander-Miller MA, Berzofsky JA, Zacharchuk CM, Henkart PA . 1997 Target cell lysis by CTL granule exocytosis is independent of ICE/Ced-3 family proteases Immunity 6: 209–215
Huet C, Sahuquillo-Merino C, Coudrier E, Louvard D . 1987 Absorptive and mucus-secreting subclones isolated from a multipotent intestinal cell line (HT-29) provide new models for cell polarity and terminal differentiation J. Cell. Biol. 105: 345–357
Velcich A, Palumbo L, Jarry A, Laboisse C, Racevskis J, Augenlicht L . 1995 Patterns of expression of lineage-specific markers during the in vitro- induced differentiation of HT29 colon carcinoma cells Cell Growth Differ. 6: 749–757
VanArsdale TL, Ware CF . 1994 TNF receptor signal transduction. Ligand-dependent stimulation of a serine protein kinase activity associated with (CD120a) TNFR60 J. Immunol. 153: 3043–3050
Vercammen D, Brouckaert G, Denecker G, Van de Craen M, Declercq W, Fiers W, Vandenabeele P . 1998 Dual signaling of the Fas receptor: initiation of both apoptotic and necrotic cell death pathways J. Exp. Med. 188: 919–930
Nicholson DW . 1999 Caspase structure, proteolytic substrates, and function during apoptotic cell death Cell Death Differ. 6: 1028–1042
Degli-Esposti MA, Davis-Smith T, Din WS, Smolak PJ, Goodwin RG, Smith CA . 1997 Activation of the lymphotoxin beta receptor by cross-linking induces chemokine production and growth arrest in A375 melanoma cells J. Immunol. 158: 1756–1762
Oberhammer F, Wilson JW, Dive C, Morris ID, Hickman JA, Wakeling AE, Walker PR, Sikorska M . 1993 Apoptotic death in epithelial cells: cleavage of DNA to 300 and/or 50 kb fragments prior to or in the absence of internucleosomal fragmentation EMBO J. 12: 3679–3684
Wright K, Kolios G, Westwick J, Ward SG . 1999 Cytokine-induced apoptosis in epithelial HT-29 cells is independent of nitric oxide formation. Evidence for an interleukin-13-driven phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent survival mechanism J. Biol. Chem. 274: 17193–17201
Dusenbury CE, Davis MA, Lawrence TS, Maybaum J . 1991 Induction of megabase DNA fragments by 5-fluorodeoxyuridine in human colorectal tumor (HT29) cells Mol. Pharmacol. 39: 285–289
Dealtry GB, Naylor MS, Fiers W, Balkwill FR . 1987 DNA fragmentation and cytotoxicity caused by tumor necrosis factor is enhanced by interferon-gamma Eur. J. Immunol. 17: 689–693
Tamura T, Aoyama N, Saya H, Futami S, Miyamoto M, Koh T, Ariyasu T, Tachi M, Kasugs M, Takahashi R . 1995 Induction of Fas-meidated apoptosis in p53-transfected human colon carcinoma cells Oncogene 11: 1939–1946
Vercammen D, Vandenabeele P, Beyaert R, Declercq W, Fiers W . 1997 Tumour necrosis factor-induced necrosis versus anti-Fas-induced apoptosis in L929 cells Cytokine 9: 801–808
Mashima T, Naito M, Kataoka S, Kawai H, Tsuruo T . 1995 Aspartate-based inhibitor of interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme prevents antitumor agent-induced apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia U937 cells Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 209: 907–915
Naito M, Nagashima K, Mashima T, Tsuruo T . 1997 Phosphatidylserine externalization is a downstream event of interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme family protease activation during apoptosis Blood 89: 2060–2066
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M, Zanin C, Vayssiere JL, Petit PX, Kroemer G . 1995 Reduction in mitochondrial potential constitutes an early irreversible step of programmed lymphocyte death in vivo J. Exp. Med. 181: 1661–1672
Bortner CD, Cidlowski JA . 1999 Caspase independent/dependent regulation of K(+), cell shrinkage, and mitochondrial membrane potential during lymphocyte apoptosis J. Biol. Chem. 274: 21953–21962
Hildeman DA, Mitchell T, Teague TK, Henson P, Day BJ, Kappler J, Marrack PC . 1999 Reactive oxygen species regulate activation -induced T cell apoptosis Immunity 10: 735–744
Bamji SX, Majdan M, Pozniak CD, Belliveau DJ, Aloyz R, Kohn J, Causing CG, Miller FD . 1998 The p75 neurotrophin receptor mediates neuronal apoptosis and is essential for naturally occurring sympathetic neuron death J. Cell. Biol. 140: 911–923
Hirano A, Longo DL, Taub DD, Ferris DK, Young LS, Eliopoulos AG, Agathanggelou A, Cullen N, Macartney J, Fanslow WC, Murphy WJ . 1999 Inhibition of human breast carcinoma growth by a soluble recombinant human CD40 ligand Blood 93: 2999–3007
Hess S, Engelmann H . 1996 A novel function of CD40: induction of cell death in transformed cells J. Exp. Med. 183: 159–167
Lee SY, Park CG, Choi Y . 1996 T cell receptor-dependent cell death of T cell hybridomas mediated by the CD30 cytoplasmic domain in association with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors J. Exp. Med. 183: 669–674
Prasad KVS, Ao Z, Yoon Y, Wu MX, Rizk M, Jacquot S, Schlossman SF . 1997 CD27, a member of the tumor necrosis receptor family, induces apoptosis and binds to siva, a proapoptotic protein Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 6346–6351
Gruss HJ, Boiani N, Williams DE, Armitage RJ, Smith CA, Goodwin RG . 1994 Pleiotropic effects of the CD30 ligand on CD30-expressing cells and lymphoma cell lines Blood 83: 2045–2056
Wu MY, Wang PY, Han SH, Hsieh SL . 1999 The cytoplasmic domain of the lymphotoxin-beta receptor mediates cell death in HeLa cells J. Biol. Chem. 274: 11868–11873
Wiley SR, Cassiano L, Lofton T, Davis-Smith T, Winkles JA, Lindner V, Liu H, Daniel TO, Smith CA, Fanslow WC . 2001 A novel TNF recpetor family member binds TWEAK and is implicated in angiogenesis Immunity 15: 837–846
Alexander-Miller MA, Derby MA, Sarin A, Henkart PA, Berzofsky JA . 1998 Supraoptimal peptide-major histocompatibility complex causes a decrease in bc1-2 levels and allows tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor II- mediated apoptosis of cytotoxic T lymphocytes J. Exp. Med. 188: 1391–1399
Chiarle R, Podda A, Prolla G, Podack ER, Thorbecke GJ, Inghirami G . 1999 CD30 overexpression enhances negative selection in the thymus and mediates programmed cell death via a Bcl-2-sensitive pathway J. Immunol. 163: 194–205
Kawahara A, Ohsawa Y, Matsumura H, Uchiyama Y, Nagata S . 1998 Caspase-independent cell killing by Fas-associated protein with death domain J. Cell. Biol. 143: 1353–1360
Lemaire C, Andreau K, Souvannavong V, Adam A . 1998 Inhibition of caspase activity induces a switch from apoptosis to necrosis FEBS Lett. 425: 266–270
Kataoka T, Budd RC, Holler N, Thome M, Martinon F, Irmler M, Burns K, Hahne M, Kennedy N, Kovacsovics M, Tschopp J . 2000 The caspase-8 inhibitor FLIP promotes activation of NF-kappaB and Erk signaling pathways Curr. Biol. 10: 640–648
Lorenzo HK, Susin SA, Penninger J, Kroemer G . 1999 Apoptosis inducing factor (AIF): a phylogenetically old, caspase- independent effector of cell death Cell Death Differ. 6: 516–524
Zamzami N, Kroemer G . 1999 Condensed matter in cell death [news; comment] Nature 401: 127–128
Sidoti-de Fraisse C, Rincheval V, Risler Y, Mignotte B, Vayssiere JL . 1998 TNF-alpha activates at least two apoptotic signaling cascades Oncogene 17: 1639–1651
Chen MC, Hsu TL, Luh TY, Hsieh SL . 2000 Overexpression of bcl-2 enhances LIGHT- and interferon-gamma -mediated J. Biol. Chem. 275: 38794–38801
Veldman RJ, Klappe K, Hoekstra D, Kok JW . 1998 Interferon-gamma-induced differentiation and apoptosis of HT29 cells: dissociation of (glucosyl)ceramide signaling Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 247: 802–808
Davis RJ . 2000 Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases Cell 103: 239–252
Wu YL, Jiang XR, Newland AC, Kelsey SM . 1998 Failure to activate cytosolic phospholipase A2 causes TNF resistance in human leukemic cells J. Immunol. 160: 5929–5935
Baker SJ, Reddy EP . 1998 Modulation of life and death by the TNF receptor superfamily Oncogene 17: 3261–3270
VanArsdale TL, VanArsdale SL, Force WR, Walter BN, Mosialos G, Kieff E, Reed JC, Ware CF . 1997 Lymphotoxin-beta receptor signaling complex: role of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 recruitment in cell death and activation of nuclear factor kappaB Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 2460–2465
Baud V, Karin M . 2001 Signal transduction by tumor necrosis and its relatives Trands Cell Biol. 11: 372–377
Nylandsted J, Rohde M, Brand K, Bastholm L, Elling F, Jaattela M . 2000 Selective depletion of heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) activates a tumor-specific death program that is independent of caspases and bypasses Bcl-2 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 7871–7876
Ravagnan L, Gurbuxani S, Susin SA, Maisse C, Daugas E, Zamzami N, Mak T, Jaattela M, Penninger JM, Garrido C, Kroemer G . 2001 Heat-shock protein 70 antagonizes apoptosis-inducing factor Nat. Cell. Biol. 3: 839–843
Browning JL, Miatkowski K, Griffiths DA, Bourdon PR, Hession C, Ambrose CM, Meier W . 1996 Preparation and characterization of soluble recombinant heterotrimeric complexes of human lymphotoxins alpha and beta J. Biol. Chem. 271: 8618–8626
Jakubowski A, Browning B, Lukashev M, Sizing I, Thompson JS, Benjamin CD, Hsu YM, Ambrose C, Zheng TS, Burkly LC . 2002 Dual role for TWEAK in angiogenic regulation J. Cell. Sci. 115: 267–274
Browning JL, Sizing ID, Lawton P, Bourdon PR, Rennert PD, Majeau GR, Ambrose CM, Hession C, Miatkowski K, Griffiths DA, Ngam-ek A, Meier W, Benjamin CD, Hochman PS . 1997 Characterization of lymphotoxin-alpha beta complexes on the surface of mouse lymphocytes J. Immunol. 159: 3288–3298
Martin SJ, Reutelingsperger CP, McGahon AJ, Rader JA, van Schie RC, LaFace DM, Green DR . 1995 Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus: inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl J. Exp. Med. 182: 1545–1556
Acknowledgements
We thank Jurg Tschopp for the Flag-TRAIL and TRAIL-R2-Ig preparations, Ya-hui Tu (Whitehead Institute) for the electron microscopy, Holly Prentice for helpful advice, Sukumari Mohan for FACS analysis, Irene Sizing for the blocking TWEAK mAb and Jennifer Gommerman, Tim Zheng and Matvey Lukashev for critical reading and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by B Osborne
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, C., Browning, J. Death of HT29 adenocarcinoma cells induced by TNF family receptor activation is caspase-independent and displays features of both apoptosis and necrosis. Cell Death Differ 9, 1321–1333 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401107
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401107
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Human CD4 cytotoxic T lymphocytes mediate potent tumor control in humanized immune system mice
Communications Biology (2023)
-
SMYD2 targets RIPK1 and restricts TNF-induced apoptosis and necroptosis to support colon tumor growth
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
An outline of necrosome triggers
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2016)
-
Pan-Bcl-2 inhibitor Obatoclax is a potent late stage autophagy inhibitor in colorectal cancer cells independent of canonical autophagy signaling
BMC Cancer (2015)
-
Regulated necrosis: the expanding network of non-apoptotic cell death pathways
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2014)