Abstract
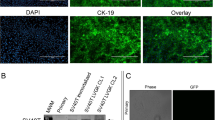
Phenotypic change of adult pancreatic islets has been implicated in the development of certain pancreatic cancers and in islet transplant failure. The aim of this study was to characterize intracellular events that mediate changes in adult islet phenotype. Using an in vitro islet-to-duct transformation model, canine islets were induced to undergo phenotypic transformation to duct-like epithelial structures through a two-stage process. Stage one was characterized by widespread islet cell apoptosis associated with the formation of cavitary spaces within the islets. During this stage, c-Jun N-terminal regulated kinase (JNK) and caspase-3 activities were elevated, while extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Akt activities were decreased. The second stage of the process was characterized by an inversion in the balance in activity between these signal transduction pathways and by a concomitant decrease in apoptosis. The transformed islets were no longer immunoreactive for islet cell hormones, but expressed the duct epithelial cell marker CK-AE1/AE3. In contrast to islet cells, these duct epithelial cells were highly proliferative. To clarify the role of the identified changes in signal transduction events, we performed additional studies using pharmacological inhibitors of enzyme activity and demonstrated that inhibition of JNK and caspase-3 activity prevented cystic transformation. Our results indicate that the balance in signaling activity between ERK/Akt and JNK/caspase-3 appears to be an important regulator of islet cell death and differentiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- ERK:
-
extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal regulated kinase
- PI3K:
-
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- IHC:
-
immunohistochemistry
- ELISA:
-
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- TUNEL:
-
terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling
- MTT:
-
(3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide)
- BrdU:
-
5-bromo-2' deoxyuridine
References
Ju Q, Edelstein D, Brendel MD, Brandhorst D, Brandhorst H, Bretzel RG and Brownlee M (1998) Transduction of non-dividing adult human pancreatic beta cells by an integrating lentiviral vector. Diabetologia 41: 736–739
Arias AE and Bendayan M (1993) Differentiation of pancreatic acinar cells into duct-like cells in vitro. Lab. Invest. 69: 518–530
Hall PA and Lemoine NR (1992) Rapid acinar to ductal transdifferentiation in cultured human exocrine pancreas. J. Pathol. 166: 97–103
Scarpelli DG and Rao MS (1981) Differentiation of regenerating pancreatic cells into hepatocyte-like cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78: 2577–2581
Yuan SY, Rosenberg L, Paraskevas S, Agapitos D and Duguid WP (1996) Transdifferentiation of human islets to pancreatic ductal cells in collagen matrix culture. Differentiation 61: 67–75
Kerr-Conte J, Pattou F, Lecomte-Houcke M, Xia Y, Boilly B, Proye C and Lefebvre J (1996) Ductal cyst formation in collagen-embedded adult human islet preparations. A means to the reproduction of nesidioblastosis in vitro. Diabetes 45: 1108–1114
Schmied BM, Ulrich A, Matsuzaki H, Li CH and Pour PM (1999) In vitro pancreatic carcinogenesis. Ann. Oncol. 10 (Suppl 4): 41–45
Wang RN and Rosenberg L (1999) Maintenance of beta-cell function and survival following islet isolation requires re-establishment of the islet–matrix relationship. J. Endocrinol. 163: 181–190
Murakamai M, Satou H, Kimara T, Kobayashi T, Yamaguchi A, Nagagawara G and Iwata H (2000) Effects of micro-encapsulation on morphology and endocrine function of cryopreserved neonatal porcine islet-like cell clusters. Transplantation 70: 1143–1108
Lungren T, Bennet W, Tibell J and Korsgen O (2001) Soluble complement receptor 1 (TP10) preserves adult porcine islet morphology after intraportal transplantation into cynomolgus monkeys. Transplant. Proc. 33: 725
Jaeger C, Wohrle M, Freerlin K and Bretzel RG (1995) Pancreatic islet xenografts at two different transplantation sites (renal subcapsular versus intraportal): comparison of graft survival and morphology. Exp & Clin Endosc Diabetes 102 (Suppl 2): 123–128
Rutzky L, Kloc M, Bilinski T, Phan T, Zhang H, Stepkowski SM and Katz S (2001) Microgravity culture conditions decreases immunogenicity but maintains excellent morphology of pancreatic islets. Transplant. Proc. 33: 388
Ling Z, Van de Catseele M, Eizirik DL and Pipeleers DG (2000) Interleukin-1beta-induced alteration in a beta-cell phenotype can reduce cellular sensitivity to conditions that necrosis but not to cytokine induced apoptosis. Diabetes 49: 340–345
Wang R, Li J and Rosenberg L (2001) Factors mediating the transdifferentiation of islets of Langerhans to duct epithelial-like structures. J. Endocrinol. 171: 309–318
Meredith JE, Fazeli B and Schwartz MA (1993) The extracellular matrix as a cell survival factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 4: 953–961
Streuli C (1999) Extracellular matrix remodelling and cellular differentiation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11: 634–640
Miettinen PJ, Huotari M, Koivisto T, Ustinov J, Palgi J, Rasilainen S, Lehtonen E, Keski-Oja J and Otonkoski T (2000) Impaired migration and delayed differentiation of pancreatic islet cells in mice lacking EGF-receptors. Development 127(12): 2617–2627
Miralles F, Battelino T, Czernichow P and Scharfmann R (1998) TGF-beta plays a key role in morphogenesis of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans by controlling the activity of the matrix metalloproteinase MMP-2. J. Cell Biol. 143: 827–836
Jiang FX, Cram DS, De Aizpurua HJ and Harrison LC (1999) Laminin-1 promotes differentiation of fetal mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 48: 722–730
Bergmann A, Tugentman M, Shilo BZ and Steller H (2002) Regulation of cell number by MAPK-dependent control of apoptosis: a mechanism for trophic survival signaling. Dev. Cell 2: 159–170
Lee SE, Woo KM, Kim SY, Kim HM, Kwack K, Lee ZH and Kim HH (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p38, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways are involved in osteoclast differentiation. Bone 30: 71–77
Davis RJ (2000) Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103: 239–252
Nagata Y and Todokoro K (1999) Requirement of activation of JNK and p38 for environmental stress-induced erythroid differentiation and apoptosis and of inhibition of ERK for apoptosis. Blood 94: 853–863
Damodar Reddy C, Marwaha S, Patti R, Raghunath M, Duhaime AC, Sutton L and Phillips PC (2001) Role of MAP kinase pathways in primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Anticancer Res. 21: 2733–2738
Yoon SO, Kim MM, Park SJ, Kim D, Chung J and Chung AS (2002) Selenite suppresses hydrogen peroxide-induced cell apoptosis through inhibition of ASK1/JNK and activation of PI3-K/Akt pathways. FASEB J. 16: 111–113
Hong F, Kwon SJ, Jhun BS, Kim SS, Ha J, Kim SJ, Sohn NW, Kang C and Kang I (2001) Insulin-like growth factor-1 protects H9c2 cardiac myoblasts from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. Life Sci. 68: 1095–1105
Porter AG and Janicke RU (1999) Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6: 99–104
Han H, Wang H, Long H, Nattel S and Wang Z (2001) Oxidative preconditioning and apoptosis in L-cells. Roles of protein kinase B and mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 26357–26364
Kops GJ and Burgering BM (1999) Forkhead transcription factors: new insights into protein kinase B (c-akt) signaling. J. Mol. Med. 77: 656–665
Pour PM, Weide L, Liu G, Kazakoff K, Scheetz M, Toshkov I, Ikematsu Y, Fienhold MA and Sanger W (1997) Experimental evidence for the origin of ductal-type adenocarcinoma from the islets of Langerhans. Am. J. Pathol. 150: 2167–2180
Meszoely IM, Means AL, Scoggins CR and Leach SD (2001) Developmental aspects of early pancreatic cancer. Cancer J. 7: 242–250
Aikin R, Rosenberg L and Maysinger D (2000) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling to Akt mediates survival in isolated canine islets of Langerhans. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 277: 455–461
Paraskevas S, Aikin R, Maysinger D, Lakey JR, Cavanagh TJ, Hering B, Wang R and Rosenberg L (1999) Activation and expression of ERK, JNK, and p38 MAP-kinases in isolated islets of Langerhans: implications for cultured islet survival. FEBS Lett. 455: 203–208
Coucouvanis E and Martin GR (1995) Signals for death and survival: a two-step mechanism for cavitation in the vertebrate embryo. Cell 83: 279–287
Boudreau N, Sympson CJ, Werb Z and Bissell MJ (1995) Suppression of ICE and apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by extracellular matrix. Science 267: 891–893
Streuli C (1999) Extracellular matrix remodelling and cellular differentiation. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 11: 634–640
Hisaoka M, Haratake J and Hashimoto H (1993) Pancreatic morphogenesis and extracellular matrix organization during rat development. Differentiation 53: 163–172
Menko AS, Kreidberg JA, Ryan TT, Van Bockstaele E and Kukuruzinska MA (2001) Loss of alpha3beta1 integrin function results in an altered differentiation program in the mouse submandibular gland. Dev. Dyn. 220: 337–349
Widmann C, Gibson S and Johnson GL (1998) Caspase-dependent cleavage of signaling proteins during apoptosis. A turn-off mechanism for anti-apoptotic signals. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 7141–7147
Abu-Qare AW and Abou-Donia MB (2001) Biomarkers of apoptosis: release of cytochrome c, activation of caspase-3, induction of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine, increased 3-nitrotyrosine, and alteration of p53 gene. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 4: 313–332
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S and Reed JC (1998) Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 282: 1318–1321
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y and Greenberg ME (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91: 231–241
del Peso L, Gonzalez-Garcia M, Page C, Herrera R and Nunez G (1997) Interleukin-3-induced phosphorylation of BAD through the protein kinase Akt. Science 278: 687–689
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J and Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96: 857–868
Paradis S and Ruvkun G (1998) Caenorhabditis elegans Akt/PKB transduces insulin receptor-like signals from AGE-1 PI3 kinase to the DAF-16 transcription factor. Genes Dev. 12: 2488–2498
Levresse V, Butterfield L, Zentrich E and Heasley LE (2000) Akt negatively regulates the cJun N-terminal kinase pathway in PC12 cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 62: 799–808
Hazrati A, Jamal AM and Rosenberg L (2002) The role of TGF- in the transdifferentiation of islets of langerhans to duct-like epithelial structures. Diabetes 51 (Suppl 2): 376–377
Ilan N, Mahooti S and Madri JA (1998) Distinct signal transduction pathways are utilized during the tube formation and survival phases of in vitro angiogenesis. J. Cell. Sci. 111: 3621–3631
Bernal-Mizrachi E, Wen W, Stahlhut S, Welling CM and Permutt MA (2001) Islet beta cell expression of constitutively active Akt1/PKB alpha induces striking hypertrophy, hyperplasia, and hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Invest. 108: 1631–1638
Tuttle RL, Gill NS, Pugh W, Lee JP, Koeberlein B, Furth EE, Polonsky KS, Naji A and Birnbaum MJ (2001) Regulation of pancreatic beta-cell growth and survival by the serine/threonine protein kinase Akt1/PKBalpha. Nature Medicine 7: 1133–1137
Murray P and Edgar D (2000) Regulation of programmed cell death by basement membranes in embryonic development. J. Cell. Biol. 150: 1215–1221
Chen Y, Li X, Eswarakumar VP, Seger R and Lonai P (2000) Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling through PI 3-kinase and Akt/PKB is required for embryoid body differentiation. Oncogene 19: 3750–3756
Horaguchi A and Merrell RC (1981) Preparation of viable islet cells from dogs by a new method. Diabetes 30: 455–461
Ricordi C (1992) The automated method for islet isolation. In Pancreatic Islet Cell Transplantation, Ricordi C, ed (Austin: R.G. Landes Co.) pp. 99–112
London NJM, James RFL and Bell PRF (1992) Islet purification. In Pancreatic Islet Cell Transplantation, Ricordi C, ed (Austin: R.G. Landes Co.) pp. 99–112
Trauth BC, Klas B, Peters AM, Matzku S, Moller P, Falk W, Debatin KM and Krammer PH (1989) Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science 245: 301–305
Wang RN, Bouwens L and Kloppel G (1994) Beta-cell proliferation in normal and streptozotocin-treated newborn rats: site, dynamics and capacity. Diabetologia 37: 1088–1096
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by CJ Thiele
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamal, AM., Lipsett, M., Hazrati, A. et al. Signals for death and differentiation: a two-step mechanism for in vitro transformation of adult islets of Langerhans to duct epithelial structures. Cell Death Differ 10, 987–996 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401266
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401266
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Molecular signaling in pancreatic ductal metaplasia: emerging biomarkers for detection and intervention of early pancreatic cancer
Cellular Oncology (2022)
-
Cellular origins of adult human islet in vitro dedifferentiation
Laboratory Investigation (2008)
-
The role of Islet Neogenesis-Associated Protein (INGAP) in islet neogenesis
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2007)
-
Morphogenetic plasticity of adult human pancreatic islets of Langerhans
Cell Death & Differentiation (2005)