Abstract
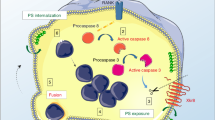
Differentiation of human placental villous trophoblast includes syncytial fusion of cytotrophoblast forming syncytiotrophoblast. Early stages of the apoptosis cascade were described to be involved in this differentiation process. We investigated the role of the initiator caspase 8 in syncytial fusion in vitro, cultivating placental villous explants with or without caspase 8 antisense oligonucleotides or peptide inhibitors for up to 120 h. Trophoblast fusion and differentiation were assessed by confocal microscopy, immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis. Culture with caspase 8 antisense oligonucleotides or peptide inhibitors reduced the fusion of cytotrophoblast with the syncytiotrophoblast, and resulted in multilayered cytotrophoblast. Caspase 8 expression was suppressed by antisense oligonucleotides and caspase 8 activities were reduced by peptide inhibitors. The organic anion-transporter hOAT-4 normally expressed in the cytotrophoblast and transferred into the syncytiotrophoblast by syncytial fusion was retained in the cytotrophoblast due to lack of fusion. We conclude that expression and activity of caspase 8 is a prerequisite for differentiation and syncytial fusion of cytotrophoblast cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ADAM:
-
a disintegrin and a metalloproteinase domain
- C3:
-
caspase 3
- C8:
-
caspase 8
- CT:
-
cytotrophoblast
- DEVD:
-
amino acids aspartic acid–glutamic acid–valine–aspartic acid
- DISC:
-
death-inducing signalling complex
- FADD:
-
Fas-associated death domain
- HIV-Env:
-
human immunodeficiency virus-envelope protein
- hOAT-4:
-
human organic anion transporter 4
- IETD:
-
amino acids isoleucine–glutamic acid–threonine–aspartic acid
- PCNA:
-
proliferative cell nuclear antigen
- PS:
-
phosphatidylserine
- ST:
-
syncytiotrophoblast
- TRADD:
-
TNF receptor-associated death domain
References
Benirschke K and Kaufmann P (2000) Pathology of the human placenta 4th edn (New York: Springer)
Pennica D, Nedwin GE, Hayflick JS, Seeburg PH, Derynck R, Palladino MA, Kohr WJ, Aggarwal BB and Goeddel DV (1984) Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature 312: 724–729
Yonehara S, Ishii A and Yonehara M (1989) A cell-killing monoclonal antibody (anti-Fas) to a cell surface antigen co-downregulated with the receptor of tumor necrosis factor. J. Exp. Med. 169: 1747–1756
Trauth BC, Klas C, Peters AM, Matzku S, Moller P, Falk W, Debatin KM and Krammer PH (1989) Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science 245: 301–305
Kischkel FC, Hellbardt S, Behrmann I, Germer M, Pawlita M, Krammer PH and Peter ME (1995) Cytotoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)-associated proteins form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) with the receptor. EMBO J. 14: 5579–5588
Lavrik I, Krueger A, Schmitz I, Baumann S, Weyd H, Krammer PH and Kirchhoff S (2003) The active caspase-8 heterotetramer is formed at the CD95 DISC. Cell Death Differ. 10: 144–145
Yui J, Garcia-Lloret M, Wegmann TG and Guilbert LJ (1994) Cytotoxicity of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and gamma-interferon against primary human placental trophoblasts. Placenta 15: 819–835
Phillips TA, Ni J and Hunt JS (2001) Death-inducing tumour necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily ligands and receptors are transcribed in human placentae, cytotrophoblasts, placental macrophages and placental cell lines. Placenta 22: 663–672
LeBrun DP, Warnke RA and Cleary ML (1993) Expression of bcl-2 in fetal tissues suggests a role in morphogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 142: 743–753
Huppertz B, Frank HG, Kingdom JCP, Reister F and Kaufmann P (1998) Villous cytotrophoblast regulation of the syncytial apoptotic cascade in the human placenta. Histochem. Cell Biol. 110: 495–508
Suzuki A, Umezawa A, Sano M, Nozawa S and Hata J (2000) Involvement of EAT/mcl-1, a bcl-2 related gene, in the apoptotic mechanisms underlying human placental development and maintenance. Placenta 21: 177–183
Huppertz B, Frank HG, Reister F, Kingdom J, Korr H and Kaufmann P (1999) Apoptosis cascade progresses during turnover of human trophoblast: analysis of villous cytotrophoblast and syncytial fragments in vitro. Lab. Invest. 79: 1687–1702
Yusuf K, Smith SD, Sadovsky Y and Nelson DM (2002) Trophoblast differentiation modulates the activity of caspases in primary cultures of term human trophoblasts. Pediatr. Res. 52: 411–415
Ishizaki Y, Jacobson MD and Raff MC (1998) A role for caspases in lens fiber differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 140: 153–158
Morioka K, Tone S, Mukaida M and Takano-Ohmuro H (1998) The apoptotic and nonapoptotic nature of the terminal differentiation of erythroid cells. Exp. Cell Res. 240: 206–217
Weil M, Raff MC and Braga VM (1999) Caspase activation in the terminal differentiation of human epidermal keratinocytes. Curr. Biol. 9: 361–364
Eckhart L, Declercq W, Ban J, Rendl M, Lengauer B, Mayer C, Lippens S, Vandenabeele P and Tschachler E (2000) Terminal differentiation of human keratinocytes and stratum corneum formation is associated with caspase-14 activation. J. Invest. Dermatol. 115: 1148–1151
Lippens S, Kockx M, Knaapen M, Mortier L, Polakowska R, Verheyen A, Garmyn M, Zwijsen A, Formstecher P, Huylebroeck D, Vandenabeele P and Declercq W (2000) Epidermal differentiation does not involve the pro-apoptotic executioner caspases, but is associated with caspase-14 induction and processing. Cell Death Differ. 7: 1218–1224
Chien AJ, Presland RB and Kuechle MK (2002) Processing of native caspase-14 occurs at an atypical cleavage site in normal epidermal differentiation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 296: 911–917
Martin SJ, O'Brien GA, Nishioka WK, McGahon AJ, Mahboubi A, Saido TC and Green DR (1995) Proteolysis of fodrin (non-erythroid spectrin) during apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 6425–6428
Greidinger EL, Miller DK, Yamin TT, Casciola-Rosen L and Rosen A (1996) Sequential activation of three distinct ICE-like activities in Fas-ligated Jurkat cells. FEBS Lett. 390: 299–303
Adler RR, Ng AK and Rote NS (1995) Monoclonal antiphosphatidylserine antibody inhibits intercellular fusion of the choriocarcinoma line, JAR. Biol. Reprod. 53: 905–910
Vogt E, Ng AK and Rote NS (1997) Antiphosphatidylserine antibody removes annexin-V and facilitates the binding of prothrombin at the surface of a choriocarcinoma model of trophoblast differentiation. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 177: 964–972
Rohn TT, Rissman RA, Davis MC, Kim YE, Cotman CW and Head E (2002) Caspase-9 activation and caspase cleavage of tau in the Alzheimer's disease brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 11: 341–354
Issa Y, Watts DC, Duxbury AJ, Brunton PA, Watson MB and Waters CM (2003) Mercuric chloride: toxicity and apoptosis in a human oligodendroglial cell line MO3.13. Biomaterials 24: 981–987
Vanden Hoek TL, Qin Y, Wojcik K, Li CQ, Shao ZH, Anderson T, Becker LB and Hamann KJ (2003) Reperfusion, not simulated ischemia, initiates intrinsic apoptosis injury in chick cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 284: H141–H150
McArthur C, Wang Y, Veno P, Zhang J and Fiorella R (2002) Intracellular trafficking and surface expression of SS-A (Ro), SS-B (La), poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and alpha-fodrin autoantigens during apoptosis in human salivary gland cells induced by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Arch. Oral Biol. 47: 443–448
Berg CP, Engels IH, Rothbart A, Lauber K, Renz A, Schlosser SF, Schulze-Osthoff K and Wesselborg S (2001) Human mature red blood cells express caspase-3 and caspase-8, but are devoid of mitochondrial regulators of apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 8: 1197–1206
Ugele R, St.Pierre MV, Pihusch M, Bahn A and Hantschmann P (2003) Characterization and identification of steroid sulphate transporters of human placenta. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 284: E390–E398
Caulin C, Salvesen GS and Oshima RG (1997) Caspase cleavage of keratin 18 and reorganization of intermediate filaments during epithelial cell apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 138: 1379–1394
MacFarlane M, Merrison W, Dinsdale D and Cohen GM (2000) Active caspases and cleaved cytokeratins are sequestered into cytoplasmic inclusions in TRAIL-induced apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 148: 1239–1254
Castellucci M, Kaufmann P and Bischof P (1990) Extracellular matrix influences hormone and protein production by human chorionic villi. Cell Tissue Res. 262: 135–142
Begum-Hasan J, Senterman M, Gillett P, LaPlante Branchaud C and Murphy BE (1993) Effect of maternal serum on viability and function of early human placental explants. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 29A: 505–511
Lappas M, Munns MJ, King RG and Rice GE (2001) Antisense oligonucleotide inhibition of type II phospholipase A2 expression, release and activity in vitro. Placenta 22: 418–424
Guilbert LJ, Winkler-Lowen B, Sherburne R, Rote NS, Li H and Morrish DW (2002) Preparation and functional characterization of villous cytotrophoblasts free of syncytial fragments. Placenta 23: 175–183
Shoeman RL, Hartig R, Huang Y, Grub S and Traub P (1997) Fluorescence microscopic comparison of the binding of phosphodiester and phosphorothioate (antisense) oligodeoxyribonucleotides to subcellular structures, including intermediate filaments, the endoplasmic reticulum, and the nuclear interior. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 7: 291–308
Pistritto G, Jost M, Srinivasula SM, Baffa R, Poyet JL, Kari C, Lazebnik Y, Rodeck U and Alnemri ES (2002) Expression and transcriptional regulation of caspase-14 in simple and complex epithelia. Cell Death Differ. 9: 995–1006
Nicholson DW and Thornberry NA (1997) Caspases: killer proteases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 22: 299–306
Salvesen GS and Dixit VM (1997) Caspases: intracellular signaling by proteolysis. Cell 91: 443–446
Sanders EJ and Parker E (2002) The role of mitochondria, cytochrome c and caspase-9 in embryonic lens fibre cell denucleation. J. Anat. 201: 121–135
Zou H, Li Y, Liu X and Wang X (1999) An APAF-1-cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that activates procaspase-9. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 11549–11556
Fernandes-Alnemri T, Armstrong RC, Krebs J, Srinivasula SM, Wang L, Bullrich F, Fritz LC, Trapani JA, Tomaselli KJ, Litwack G and Alnemri ES (1996) In vitro activation of CPP32 and Mch3 by Mch4, a novel human apoptotic cysteine protease containing two FADD-like domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 7464–7469
Muzio M, Chinnaiyan AM, Kischkel FC, O'Rourke K, Shevchenko A, Ni J, Scaffidi C, Bretz JD, Zhang M, Gentz R, Mann M, Krammer PH, Peter ME and Dixit VM (1996) FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death-inducing signaling complex. Cell 85: 817–827
Eckhart L, Henry M, Santos-Beneit AM, Schmitz I, Krueger A, Fischer H, Bach J, Ban J, Kirchhoff S, Krammer PH, Mollinedo F and Tschachler E (2001) Alternative splicing of caspase-8 mRNA during differentiation of human leukocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 289: 777–781
Secchiero P, Gonelli A, Mirandola P, Melloni E, Zamai L, Celeghini C, Milani D and Zauli G (2002) Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand induces monocytic maturation of leukemic and normal myeloid precursors through a caspase-dependent pathway. Blood 100: 2421–2429
Huppertz B, Frank HG and Kaufmann P (1999) The apoptosis cascade – morphological and immunohistochemical methods for its visualization. Anat. Embryol. 200: 1–18
Jaenicke RU, Ng P, Sprengart ML and Porter AG (1998) Caspase-3 is required for alpha-fodrin cleavage but dispensable for cleavage of other death substrates in apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 15540–15545
Chen X, Wan Y, Bai Q, Zhang W and Zhu H (2002) Sodium salicylate-triggered apoptosis in HL-60 cells depends on caspase-8 activation. Int. J. Hematol. 75: 407–411
Ferraro-Peyret C, Quemeneur L, Flacher M, Revillard JP and Genestier L (2002) Caspase-independent phosphatidylserine exposure during apoptosis of primary T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 169: 4805–4810
Wolfsberg TG and White JM (1996) ADAMs in fertilization and development. Dev. Biol. 180: 389–401
LaBranche CC, Galasso G, Moore JP, Bolognesi DP, Hirsch MS and Hammer SM (2001) HIV fusion and its inhibition. Antiviral Res. 50: 95–115
Huppertz B, Tews DS and Kaufmann P (2001) Apoptosis and syncytial fusion in human placental trophoblast and skeletal muscle. Int. Rev. Cytol. 205: 215–253
Dedieu S, Dourdin N, Dargelos E, Poussard S, Veschambre P, Cottin P and Brustis JJ (2002) Calpain and myogenesis: development of a convenient cell culture model. Biol. Cell 94: 65–76
Wang KK (2000) Calpain and caspase: can you tell the difference? Trends Neurosci. 23: 20–26
Berg CP, Engels IH, Rothbart A, Lauber K, Renz A, Schlosser SF, Schulze-Osthoff K and Wesselborg S (2001) Human mature red blood cells express caspase-3 and caspase-8, but are devoid of mitochondrial regulators of apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 8: 1197–1206
Formigli L, Papucci L, Tani A, Schiavone N, Tempestini A, Orlandini GE, Capaccioli S and Orlandini SZ (2000) Aponecrosis: morphological and biochemical exploration of a syncretic process of cell death sharing apoptosis and necrosis. J. Cell Physiol. 182: 41–49
Fernandes-Alnemri T, Litwack G and Alnemri ES (1994) CPP32, a novel human apoptotic protein with homology to Caenorhabditis elegans cell death protein CED-3 and mammalian interleukin-1-beta-converting enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 30761–30764
Kadyrov M, Kaufmann P and Huppertz B (2001) Expression of a cytokeratin 18 neo-epitope is a specific marker for trophoblast apoptosis in human placenta. Placenta 22: 44–48
Acknowledgements
The excellent technical assistance of Uta Zahn is gratefully acknowledged. PK and BH are funded by the Rockefeller Foundation, Grants No. RF96020#76 and RF99021#114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by J Tilly
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Black, S., Kadyrov, M., Kaufmann, P. et al. Syncytial fusion of human trophoblast depends on caspase 8. Cell Death Differ 11, 90–98 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401307
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401307
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
How trophoblasts fuse: an in-depth look into placental syncytiotrophoblast formation
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
Apoptosome-dependent myotube formation involves activation of caspase-3 in differentiating myoblasts
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
Mechanobiological regulation of placental trophoblast fusion and function through extracellular matrix rigidity
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Activated α2-macroglobulin binding to cell surface GRP78 induces trophoblastic cell fusion
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
The fine-tuning of endoplasmic reticulum stress response and autophagy activation during trophoblast syncytialization
Cell Death & Disease (2019)