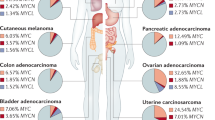
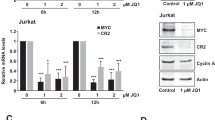
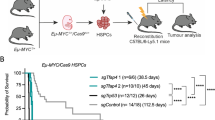
Abstract
C-myc gene is a member of the myc family of proto-oncogenes involved in proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Overexpression of c-myc in fibroblasts causes apoptosis under low serum conditions in a process that requires the interaction of CD95 and CD95L on the surface. We have previously reported an in vivo conditional model to inactivate the c-myc gene in B lymphocytes. Here, we show that c-Myc-deficient primary B lymphocytes are resistant to different apoptotic stimuli. Nonactivated c-Myc-deficient B cells are resistant to spontaneous cell death. Upon activation, c-Myc-deficient B lymphocytes express normal surface levels of activation markers, and show resistance to staurosporine and CD95-induced cell death.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- fl:
-
floxed allele
- Δ:
-
deleted allele
- AICD:
-
activation-induced cell death
- bHLHZip:
-
basic region/helix–loop–helix/leucine zipper
- GEP:
-
green fluorescence protein
References
Askew DS, Ashmun RA, Simmons BC and Cleveland JL (1991) Constitutive c-myc expression in an IL-3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis. Oncogene 6: 1915–1922
Evan GI, Wyllie AH, Gilbert CS, Littlewood TD, Land H, Brooks M, Waters CM, Penn LZ and Hancock DC (1992) Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell 69: 119–128
Waters CM, Littlewood TD, Hancock DC, Moore JP and Evan GI (1991) c-myc protein expression in untransformed fibroblasts. Oncogene 6: 797–805
Facchini LM and LZ P (1998) The molecular role of Myc in growth and transformation: recent discoveries lead to new insights. FASEB J 12: 633–651
Dang CV (1999) c-Myc target genes involved in cell growth, apoptosis, and metabolism. Mol Cell Biol 19: 1–11
Zimmerman Ka and Alt FW (1990) Expression and function of myc family genes. Crit Rev Oncog 2: 75–95
Campisi J, Gray HE, Pardee AB, Dean M and Sonenshein GE (1984) Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell 36: 241–247
Kelly K, Cochran BH, Stiles CD and Leder P (1983) Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell 35 (Part 2): 603–610
Thompson EB (1998) The many roles of c-Myc in apoptosis. Annu Rev Physiol 60: 575–600
Hueber AO, Zornig M, Lyon D, Suda T, Nagata S and Evan GI (1997) Requirement for the CD95 receptor-ligand pathway in c-Myc-induced apoptosis. Science 278: 1305–1309
Krammer PH (2000) CD95's deadly mission in the immune system. Nature 407: 789–795
Shi Y, Glynn JM, Guilbert LJ, Cotter TG, Bissonnette RP and Green DR (1992) Role for c-myc in activation-induced apoptotic cell death in T cell hybridomas. Science 257: 212–214
Brunner T, Mogil RJ, LaFace D, Yoo NJ, Mahboubi A, Echeverri F, Martin SJ, Force WR L, DH WC and DR G (1995) Cell-autonomous Fas (CD95)/Fas-ligand interaction mediates activation-induced apoptosis in T-cell hybridomas. Nature 373: 441–444
Dhein J, Walczak H, Baumler C, Debatin KM and PH K (1995) Autocrine T-cell suicide mediated by APO-1/. Nature 373: 438–441
Ju ST, Panka DJ, Cui H, Ettinger R, el-Khatib M, Sherr DH, Stanger BZ and Marshak-Rothstein A (1995) Fas(CD95)/FasL interactions required for programmed cell death after T-cell activation. Nature 373: 444–448
Genestier L, Kasibhatla S, Brunner T and Green DR (1999) Transforming growth factor beta1 inhibits fas ligand expression and subsequent activation-induced cell death in T cells via downregulation of c-Myc (in process citation). J Exp Med 189: 231–239
Brunner T, Kasibhatla S, Pinkoski MJ, Frutschi C, Yoo NJ, Echeverri F, Mahboubi A and Green DR (2000) Expression of Fas ligand in activated T cells is regulated by c-Myc. J Biol Chem 275: 9767–9772
Sonenshein GE (1997) Down-modulation of c-myc expression induces apoptosis of B lymphocyte models of tolerance via clonal deletion. J Immunol 158: 1994–1997
Wu M, Arsura M, Bellas RE, FitzGerald MJ, Lee H, Schauer SL, Sherr DH and Sonenshein GE (1996) Inhibition of c-myc expression induces apoptosis of WEHI 231 murine B cells. Mol Cell Biol 16: 5015–5025
DeFranco AL, Mittelstadt PR, Blum JH, Stevens TL, Law DA, Chan VW, Foy SP, Datta SK and Matsuuchi L (1994) Mechanism of B cell antigen receptor function: transmembrane signaling and triggering of apoptosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 365: 9–22
Rathmell JC, Townsend SE, Xu JC, Flavell RA and CC G (1996) Expansion or elimination of B cells in vivo: dual roles for CD40- and Fas (CD95)-ligands modulated by the B cell antigen receptor. Cell 87: 319–329
Rathmell JC, Cooke MP, Ho WY, Grein J, Townsend SE, Davis MM and Goodnow CC (1995) CD95 (Fas)-dependent elimination of self-reactive B cells upon interaction with CD4+ T cells. Nature 376: 181–184
Rothstein TL, Wang JK, Panka DJ, Foote LC, Wang Z, Stanger B, Cui H, Ju ST and Marshak-Rothstein A (1995) Protection against Fas-dependent Th1-mediated apoptosis by antigen receptor. Nature 374: 163–165
Davis AC, Wims M, Spotts GD, Hann SR and Bradley A (1993) A null c-myc mutation causes lethality before 10.5 days of gestation in homozygotes and reduced fertility in heterozygous female mice. Genes Dev 7: 671–682
de Alboran IM, O'Hagan RC, Gartner F, Malynn B, Davidson L, Rickert R, Rajewsky K, DePinho RA and Alt FW (2001) Analysis of C-MYC function in normal cells via conditional gene-targeted mutation. Immunity 14: 45–55
Mao X, Fujiwara Y, Chapdelaine A, Yang H and Orkin SH (2001) Activation of EGFP expression by Cre-mediated excision in a new ROSA26 reporter mouse strain. Blood 97: 324–326
Friedrich G and Soriano P (1991) Promoter traps in embryonic stem cells: a genetic screen to identify and mutate developmental genes in mice. Genes Dev 5: 1513–1523
Juin P, Hueber AO, Littlewood T and Evan G (1999) c-Myc-induced sensitization to apoptosis is mediated through cytochrome c release. Genes Dev 13: 1367–1381
Foote LC, Howard RG, Marshak-Rothstein A and Rothstein TL (1996) IL-4 induces Fas resistance in B cells. J Immunol 157: 2749–2753
Foote LC, Marshak-Rothstein A and Rothstein TL (1998) Tolerant B lymphocytes acquire resistance to Fas-mediated apoptosis after treatment with interleukin 4 but not after treatment with specific antigen unless a surface immunoglobulin threshold is exceeded. J Exp Med 187: 847–853
Tamaoki T, Nomoto H, Takahashi I, Kato Y, Morimoto M and Tomita F (1986) Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++ dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 135: 397–402
Malyguine A, Derby E, Brooks A, Reddy V, Baseler M and Sayers T (2002) Study of diverse mechanisms of cell-mediated cytotoxicity in gene-targeted mice using flow cytometric cytotoxicity assay. Immunol Lett 83: 55–59
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P, Hofmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer JL, Schroter M, Burns K, Mattmann C, Rimoldi D, French LE and Tschopp J (1997) Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature 388: 190–195
Delneste Y, Jeannin P, Sebille E, Aubry JP and Bonnefoy JY (1996) Thiols prevent Fas (CD95)-mediated T cell apoptosis by down-regulating membrane Fas expression. Eur J Immunol 26: 2981–2988
Los M, Van de Craen M, Penning LC, Schenk H, Westendorp M, Baeuerle PA, Droge W, Krammer PH, Fiers W and Schulze-Osthoff K (1995) Requirement of an ICE/CED-3 protease for Fas/APO-1-mediated apoptosis. Nature 375: 81–83
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Poirier GG and Earnshaw WC (1994) Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature 371: 346–347
Vooijs M, Jonkers J and Berns A (2001) A highly efficient ligand-regulated Cre recombinase mouse line shows that LoxP recombination is position dependent. EMBO Rep 2: 292–297
Lundy SK and Boros DL (2002) Fas ligand-expressing B-1a lymphocytes mediate CD4(+)-T-cell apoptosis during schistosomal infection: induction by interleukin 4 (IL-4) and IL-10. Infect Immun 70: 812–819
Acknowledgements
We thank CMA's lab members for their input, and X Mao and S Orkin for the EGFP reporter mice. IMA thanks FW Alt for his input and support. We are very grateful to all the staff of the animal facilities at CNB-CSIC for their help. IMA is supported by a Ramón y Cajal (RyC) fellowship, and EB by a predoc fellowship from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology and EU. The DIO was founded and is supported by the Spanish Council for Scientific Research (CSIC) and by PFIZER.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by SJ Martin
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Alborán, I., Baena, E. & Martinez-A, C. c-Myc-deficient B lymphocytes are resistant to spontaneous and induced cell death. Cell Death Differ 11, 61–68 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401319
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401319
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Crosstalk between hepatic tumor cells and macrophages via Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes M2-like macrophage polarization and reinforces tumor malignant behaviors
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
Toll-like receptor agonists induce apoptosis in mouse B-cell lymphoma cells by altering NF-κB activation
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2013)
-
Postnatal liver growth and regeneration are independent of c-myc in a mouse model of conditional hepatic c-myc deletion
BMC Physiology (2012)
-
Complex regulation of cell-cycle inhibitors by Fbxw7 in mouse embryonic fibroblasts
Oncogene (2010)
-
A Myc-regulated transcriptional network controls B-cell fate in response to BCR triggering
BMC Genomics (2009)