Abstract
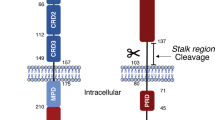
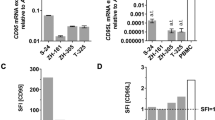
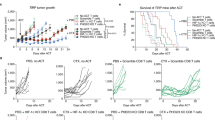
CD95 apoptosis resistance of tumor cells is often acquired through mutations in the death domain (DD) of one of the CD95 alleles. Furthermore, Type I cancer cells are resistant to induction of apoptosis by soluble CD95 ligand (CD95L), which does not induce efficient formation of the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). Here, we report that tumor cells expressing a CD95 allele that lacks a functional DD, splenocytes from heterozygous lprcg mice, which express one mutated CD95 allele, and Type I tumor cells stimulated with soluble CD95L can all die through CD95 when protein synthesis or nuclear factor kappa B is inhibited. This noncanonical form of CD95-mediated apoptosis is dependent on the enzymatic activity of procaspase-8 but does not involve fully processed active caspase-8 subunits. Our data suggest that it is possible to overcome the CD95 apoptosis resistance of many tumor cells that do not efficiently form a DISC through noncanonical activation of the caspase-8 proenzyme.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- Bio-zVAD:
-
biotinylated zVAD-fmk
- CD95L:
-
CD95 ligand
- CHX:
-
cycloheximide
- DD:
-
death domain
- ΔΨm:
-
change in mitochondrial inner membrane potential
- DISC:
-
death-inducing signaling complex
- FADD:
-
Fas-associated death domain
- FLIP:
-
FLICE-like inhibitory protein
- LzCD95L:
-
leucine zipper-tagged CD95L
- lpr:
-
lymphoproliferation
- mAb:
-
monoclonal antibody
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- NCI:
-
National Cancer Institute
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa B
- PARP:
-
poly (ADP ribose) polymerase
- RIP:
-
receptor interacting protein
- sCD95L:
-
soluble CD95L
- TNFα:
-
tumor necrosis factor alpha
References
Peter ME and Krammer PH (2003) The CD95(APO-1/Fas) DISC and beyond. Cell Death Differ. 10: 26–35
Barnhart BC, Alappat EC and Peter ME (2003) The CD95 type I/type II model. Semin. Immunol. 15: 185–193
Algeciras-Schimnich A, Pietras EM, Barnhart BC, Legembre P, Vijayan S, Holbeck SL and Peter ME (2003) Two CD95 tumor classes with different sensitivities to antitumor drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100: 11445–11450
Muschen M, Rajewsky K, Kronke M and Kuppers R (2002) The origin of CD95-gene mutations in B-cell lymphoma. Trends Immunol. 23: 75–80
Kischkel FC, Hellbardt S, Behrmann I, Germer M, Pawlita M, Krammer PH and Peter ME (1995) Cytotoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)-associated proteins form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) with the receptor. EMBO J. 14: 5579–5588
Siegel RM, Frederiksen JK, Zacharias DA, Chan FK, Johnson M, Lynch D, Tsien RY and Lenardo MJ (2000) Fas preassociation required for apoptosis signaling and dominant inhibition by pathogenic mutations. Science 288: 2354–2357
Natarajan K, Singh S, Burke Jr TR, Grunberger D and Aggarwal BB (1996) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester is a potent and specific inhibitor of activation of nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 9090–9095
Mori N, Yamada Y, Ikeda S, Yamasaki Y, Tsukasaki K, Tanaka Y, Tomonaga M, Yamamoto N and Fujii M (2002) Bay 11-7082 inhibits transcription factor NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines and primary adult T-cell leukemia cells. Blood 100: 1828–1834
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, Friesen C, Li F, Tomaselli KJ, Debatin KM, Krammer PH and Peter ME (1998) Two CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. EMBO J. 17: 1675–1687
Liu N, Raja SM, Zazzeroni F, Metkar SS, Shah R, Zhang M, Wang Y, Bromme D, Russin WA, Lee JC, Peter ME, Froelich CJ, Franzoso G and Ashton-Rickardt PG (2003) NF-kappaB protects from the lysosomal pathway of cell death. EMBO J. 22: 5313–5322
Lu T, Xu Y, Mericle MT and Mellgren RL (2002) Participation of the conventional calpains in apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1590: 16–26
Thorburn J, Bender LM, Morgan MJ and Thorburn A (2003) Caspase- and serine protease-dependent apoptosis by the death domain of FADD in normal epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 14: 67–77
Muschen M, Warskulat U and Beckmann MW (2000) Defining CD95 as a tumor suppressor gene. J. Mol. Med. 78: 312–325
Barnhart BC, Legembre P, Pietras EM, Bubici C, Franzoso G and Peter ME (2004) CD95 ligand induces motility and invasiveness of apoptosis resistant tumor cells. EMBO J. 23: 3175–3185
Delehanty LL, Payne JA, Farrow SN, Brown R and Champion BR (1997) Apoptosis in a Fas-resistant, T-cell receptor-sensitive human leukaemic T-cell clone. Immunology 90: 383–387
Cascino I, Papoff G, De Maria R, Testi R and Ruberti G (1996) Fas/Apo-1 (CD95) receptor lacking the intracytoplasmic signaling domain protects tumor cells from Fas-mediated apoptosis. J. Immunol. 156: 13–17
Matsuzawa A, Shimizu M, Takeda Y, Nagase H, Sayama K and Kimura M (2002) Significant role of Fas ligand-binding but defective Fas receptor (CD95) in lymph node hyperplasia composed of abnormal double-negative T cells. Immunology 106: 470–475
Salmena L, Lemmers B, Hakem A, Matysiak-Zablocki E, Murakami K, Au PY, Berry DM, Tamblyn L, Shehabeldin A, Migon E, Wakeham A, Bouchard D, Yeh WC, McGlade JC, Ohashi PS and Hakem R (2003) Essential role for caspase 8 in T-cell homeostasis and T-cell-mediated immunity. Genes Dev. 17: 883–895
Chang DW, Xing Z, Capacio VL, Peter ME and Yang X (2003) Interdimer processing mechanism of procaspase-8 activation. EMBO J. 22: 4132–4142
Stegh AH, Barnhart BC, Volkland J, Algeciras-Schimnich A, Ke N, Reed JC and Peter ME (2002) Inactivation of caspase-8 on mitochondria of Bcl-xL-expressing MCF7-Fas cells: role for the bifunctional apoptosis regulator protein. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 4351–4360
Medema JP, Scaffidi C, Kischkel FC, Shevchenko A, Mann M, Krammer PH and Peter ME (1997) FLICE is activated by association with the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). EMBO J. 16: 2794–2804
Zhou Q, Snipas S, Orth K, Muzio M, Dixit VM and Salvesen GS (1997) Target protease specificity of the viral serpin CrmA. Analysis of five caspases. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 7797–7800
Schneider P, Holler N, Bodmer JL, Hahne M, Frei K, Fontana A and Tschopp J (1998) Conversion of membrane-bound Fas(CD95) ligand to its soluble form is associated with downregulation of its proapoptotic activity and loss of liver toxicity. J. Exp. Med. 187: 1205–1213
Tanaka M, Itai T, Adachi M and Nagata S (1998) Downregulation of Fas ligand by shedding. Nat. Med. 4: 31–36
Leist M, Gantner F, Bohlinger I, Germann PG, Tiegs G and Wendel A (1994) Murine hepatocyte apoptosis induced in vitro and in vivo by TNF-alpha requires transcriptional arrest. J. Immunol. 153: 1778–1788
Fulda S, Meyer E and Debatin KM (2000) Metabolic inhibitors sensitize for CD95 (APO-1/Fas)-induced apoptosis by down-regulating Fas-associated death domain-like interleukin 1-converting enzyme inhibitory protein expression. Cancer Res. 60: 3947–3956
Holler N, Zaru R, Micheau O, Thome M, Attinger A, Valitutti S, Bodmer JL, Schneider P, Seed B and Tschopp J (2000) Fas triggers an alternative, caspase-8-independent cell death pathway using the kinase RIP as effector molecule. Nat. Immunol. 1: 489–495
Vercammen D, Brouckaert G, Denecker G, Van de Craen M, Declercq W, Fiers W and Vandenabeele P (1998) Dual signaling of the Fas receptor: initiation of both apoptotic and necrotic cell death pathways. J. Exp. Med. 188: 919–930
Desbarats J, Birge RB, Mimouni-Rongy M, Weinstein DE, Palerme JS and Newell MK (2003) Fas engagement induces neurite growth through ERK activation and p35 upregulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 5: 118–125
Alderson MR, Armitage RJ, Maraskovsky E, Tough TW, Roux E, Schooley K, Ramsdell F and Lynch DH (1993) Fas transduces activation signals in normal human T lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 178: 2231–2235
Scaffidi C, Volkland J, Blomberg I, Hoffmann I, Krammer PH and Peter ME (2000) Phosphorylation of FADD/MORT1 at serine 194 and association with a 70-kDa cell cycle-regulated protein kinase. J. Immunol. 164: 1236–1242
Scaffidi C, Medema JP, Krammer PH and Peter ME (1997) FLICE is predominantly expressed as two functionally active isoforms, caspase-8/a and caspase-8/b. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 26953–26958
Trauth BC, Klas C, Peters AM, Matzku S, Moller P, Falk W, Debatin KM and Krammer PH (1989) Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science 245: 301–305
Tanaka M, Suda T, Takahashi T and Nagata S (1995) Expression of the functional soluble form of human fas ligand in activated lymphocytes. EMBO J. 14: 1129–1135
Walczak H, Degli-Esposti MA, Johnson RS, Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Boiani N, Timour MS, Gerhart MJ, Schooley KA, Smith CA, Goodwin RG and Rauch CT (1997) TRAIL-R2: a novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for TRAIL. EMBO J. 16: 5386–5397
O'Reilly LA, Divisekera U, Newton K, Scalzo K, Kataoka T, Puthalakath H, Ito M, Huang DC and Strasser A (2004) Modifications and intracellular trafficking of FADD/MORT1 and caspase-8 after stimulation of T lymphocytes. Cell Death Differ. 11: 724–736
Algeciras-Schimnich A and Peter ME (2003) Actin dependent CD95 internalization is specific for Type I cells. FEBS Lett. 546: 185–188
Yasuda T, Zhang Y, Nagase H, Kaneko T, Sayama K, Hashimoto H and Matsuzawa A (2000) Immunological characterization of C3H mice congenic for Fas(lprcg), C3h/HeJ-Fas(lprcg)/Fas(lprcg). Lab. Anim. 34: 46–55
Peter ME, Legembre P and Barnhart BC . CD95 (APO-1/Fas), a tumor suppressor turned tumor promotor?
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs P Krammer and H Walczak for providing us with anti-APO-1 and LzCD95L, respectively. We are grateful for Drs R DeMaria, A Payne and V Dixit for the Hut78 and H9 mutant cells and the crmA-expressing BJAB cells, respectively. The expression construct for human soluble CD95L was kindly provided by Dr S Nagata and the anti-mouse caspase-8 antibody by Dr A Strasser. This work was funded by the NIH Grant GM61712. A A-S was supported by the Cancer Biology Training Program 5T32CA09594 and BC. Barnhart by the DOD Breast Cancer Research Program DAMD17-03-1-0200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by G Melino
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barnhart, B., Pietras, E., Algeciras-Schimnich, A. et al. CD95 apoptosis resistance in certain cells can be overcome by noncanonical activation of caspase-8. Cell Death Differ 12, 25–37 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401509
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401509
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Inhibition of NF-kappa B can enhance Fas-mediated apoptosis in leukemia cell line HL-60
Frontiers of Medicine in China (2010)