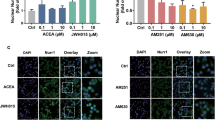
Abstract
Cyclin-dependent kinase-5 (Cdk5) is required for neuronal survival, but its targets in the apoptotic pathways remain unknown. Here, we show that Cdk5 kinase activity prevents neuronal apoptosis through the upregulation of Bcl-2. Treatment of SH-SY5Y cells with retinoid acid (RA) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) generates differentiated neuron-like cells. DNA damage triggers apoptosis in the undifferentiated cells through mitochondrial pathway; however, RA/BDNF treatment results in Bcl-2 upregulation and inhibition of the mitochondrial pathway in the differentiated cells. RA/BDNF treatment activates Cdk5-mediated PI3K/Akt and ERK pathways. Inhibition of Cdk5 inhibits PI3K/Akt and ERK phosphorylation and Bcl-2 expression, and thus sensitizes the differentiated cells to DNA-damage. Inhibition of ERK, but not PI3K/Akt, abrogates Cdk5-medidated Bcl-2 upregulation and the protection of the differentiated cells. This study suggests that ERK-mediated Bcl-2 upregulation contributes to BDNF-induced Cdk5-mediated neuronal survival.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- Cdk5:
-
cyclin-dependent kinase-5
- RA:
-
retinoid acid
- BDNF:
-
brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- PI3K:
-
phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- ERK:
-
extracellular-signal-regulated kinase
- NGF:
-
Nerve growth factor
- siRNA:
-
small interfering RNA
References
Lew J, Beaudette K, Litwin CM and Wang JH (1992) Purification and characterization of a novel proline-directed protein kinase from bovine brain. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 13383–13390
Tsai LH, Delalle I, Caviness Jr VS, Chae T and Harlow E (1994) p35 is a neural-specific regulatory subunit of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Nature 371: 419–423
Tang D, Yeung J, Lee KY, Matsushita M, Matsui H, Tomizawa K, Hatase O and Wang JH (1995) An isoform of the neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) activator. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 26897–26903
Hellmich MR, Pant HC, Wada E and Battey JF (1992) Neuronal cdc2-like kinase: a cdc2-related protein kinase with predominantly neuronal expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 10867–10871
Zheng M, Leung CL and Liem RK (1998) Region-specific expression of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (cdk5) and its activators, p35 and p39, in the developing and adult rat central nervous system. J. Neurobiol. 35: 141–159
Patrick GN, Zukerberg L, Nikolic M, de la Monte S, Dikkes P and Tsai LH (1999) Conversion of p35 to p25 deregulates Cdk5 activity and promotes neurodegeneration. Nature 402: 615–622
Wang J, Liu S, Fu Y, Wang JH and Lu Y (2003) Cdk5 activation induces hippocampal CA1 cell death by directly phosphorylating NMDA receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 6: 1039–1047
Song JH, Wang CX, Song DK, Wang P, Shuaib A and Hao C (2005) Interferon gamma induces neurite outgrowth by up-regulation of p35 neuron-specific cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator via activation of ERK1/2 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 280: 12896–12901
Chae T, Kwon YT, Bronson R, Dikkes P, Li E and Tsai LH (1997) Mice lacking p35, a neuronal specific activator of Cdk5, display cortical lamination defects, seizures, and adult lethality. Neuron 18: 29–42
Gupta A, Sanada K, Miyamoto DT, Rovelstad S, Nadarajah B, Pearlman AL, Brunstrom J and Tsai LH (2003) Layering defect in p35 deficiency is linked to improper neuronal-glial interaction in radial migration. Nat. Neurosci. 6: 1284–1291
Nikolic M, Chou MM, Lu W, Mayer BJ and Tsai LH (1998) The p35/Cdk5 kinase is a neuron-specific Rac effector that inhibits Pak1 activity. Nature 395: 194–198
Li BS, Ma W, Jaffe H, Zheng Y, Takahashi S, Zhang L, Kulkarni AB and Pant HC (2003) Cyclin-dependent kinase-5 is involved in neuregulin-dependent activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt activity mediating neuronal survival. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 35702–35709
Harada T, Morooka T, Ogawa S and Nishida E (2001) ERK induces p35, a neuron-specific activator of Cdk5, through induction of Egr1. Nat. Cell Biol. 3: 453–459
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM (1998) Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 281: 1305–1308
Newmeyer DD and Ferguson-Miller S (2003) Mitochondria: releasing power for life and unleashing the machineries of death. Cell 112: 481–490
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C and Wang X (1998) Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death receptors. Cell 94: 481–490
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X (1997) Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 91: 479–489
Stefanis L, Park DS, Friedman WJ and Greene LA (1999) Caspase-dependent and -independent death of camptothecin-treated embryonic cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. 19: 6235–6247
Huang EJ and Reichardt LF (2001) Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24: 677–736
Troy CM, Rabacchi SA, Hohl JB, Angelastro JM, Greene LA and Shelanski ML (2001) Death in the balance: alternative participation of the caspase-2 and -9 pathways in neuronal death induced by nerve growth factor deprivation. J. Neurosci. 21: 5007–5016
Encinas M, Iglesias M, Liu Y, Wang H, Muhaisen A, Cena V, Gallego C and Comella JX (2000) Sequential treatment of SH-SY5Y cells with retinoic acid and brain-derived neurotrophic factor gives rise to fully differentiated, neurotrophic factor-dependent, human neuron-like cells. J. Neurochem. 75: 991–1003
Chipuk JE, Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L, Droin NM, Newmeyer DD, Schuler M and Green DR (2004) Direct activation of Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. Science 303: 1010–1014
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ and Yuan J (1998) Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 94: 491–501
Hopkins-Donaldson S, Bodmer JL, Bourloud KB, Brognara CB, Tschopp J and Gross N (2000) Loss of caspase-8 expression in highly malignant human neuroblastoma cells correlates with resistance to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 60: 4315–4319
Liu X, Zou H, Slaughter C and Wang X (1997) DFF, a heterodimeric protein that functions downstream of caspase-3 to trigger DNA fragmentation during apoptosis. Cell 89: 175–184
Gross A, Jockel J, Wei MC and Korsmeyer SJ (1998) Enforced dimerization of BAX results in its translocation, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. EMBO J. 17: 3878–3885
Griffiths GJ, Dubrez L, Morgan CP, Jones NA, Whitehouse J, Corfe BM, Dive C and Hickman JA (1999) Cell damage-induced conformational changes of the pro-apoptotic protein Bak in vivo precede the onset of apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 144: 903–914
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ (1993) Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 74: 609–619
Yi X, Yin XM and Dong Z (2003) Inhibition of Bid-induced apoptosis by Bcl-2. tBid insertion, Bax translocation, and Bax/Bak oligomerization suppressed. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 16992–16999
Crews CM, Alessandrini A and Erikson RL (1992) The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science 258: 478–480
Franke TF, Yang SI, Chan TO, Datta K, Kazlauskas A, Morrison DK, Kaplan DR and Tsichlis PN (1995) The protein kinase encoded by the Akt proto-oncogene is a target of the PDGF-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell 81: 727–736
Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT and Saltiel AR (1995) PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 27489–27494
Vecil GG, Larsen PH, Corley SM, Herx LM, Besson A, Goodyer CG and Yong VW (2000) Interleukin-1 is a key regulator of matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in human neurons in culture and following mouse brain trauma in vivo. J. Neurosci. Res. 61: 212–224
Hetman M, Kanning K, Cavanaugh JE and Xia Z (1999) Neuroprotection by brain-derived neurotrophic factor is mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 22569–22580
Yao R and Cooper GM (1995) Requirement for phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in the prevention of apoptosis by nerve growth factor. Science 267: 2003–2006
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y and Greenberg ME (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91: 231–241
Liu YZ, Boxer LM and Latchman DS (1999) Activation of the Bcl-2 promoter by nerve growth factor is mediated by the p42/p44 MAPK cascade. Nucleic Acids Res. 27: 2086–2090
Riccio A, Ahn S, Davenport CM, Blendy JA and Ginty DD (1999) Mediation by a CREB family transcription factor of NGF-dependent survival of sympathetic neurons. Science 286: 2358–2361
Song JH, Song DK, Pyrzynska B, Petruk KC, Van Meir EG and Hao C (2003) TRAIL triggers apoptosis in human malignant glioma cells through extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. Brain Pathol. 13: 539–553
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Eric Sandberg for critically reading this manuscript. This work was supported in part by funds from the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at Emory University (CH) and the Canadian Institute of Health Research Grants (CW, AS and VWY). C Hao is the Georgia Cancer Coalition Distinguished Scholar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by P Nicotera
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Song, J., Song, D. et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase-5 prevents neuronal apoptosis through ERK-mediated upregulation of Bcl-2. Cell Death Differ 13, 1203–1212 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401804
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401804
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Somatostatin-Mediated Changes in Microtubule-Associated Proteins and Retinoic Acid–Induced Neurite Outgrowth in SH-SY5Y Cells
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2019)
-
Differentiation Induces Dramatic Changes in miRNA Profile, Where Loss of Dicer Diverts Differentiating SH-SY5Y Cells Toward Senescence
Molecular Neurobiology (2017)
-
Oral acetate supplementation attenuates N-methyl D-aspartate receptor hypofunction-induced behavioral phenotypes accompanied by restoration of acetyl-histone homeostasis
Psychopharmacology (2016)
-
Characterization of Apoptosis Signaling Cascades During the Differentiation Process of Human Neural ReNcell VM Progenitor Cells In Vitro
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2015)
-
Glutamate Excitotoxicity Activates the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway and Induces the Survival of Rat Hippocampal Neurons In Vivo
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2014)