Abstract
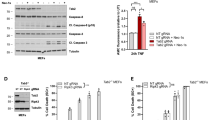
Tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), a proinflammatory cytokine, is a potent negative regulator of adipocyte differentiation. However, the mechanism of TNF-α-mediated antiadipogenesis remains incompletely understood. In this study, we first confirm that TNF-α inhibits adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes by preventing the early induction of the adipogenic transcription factors peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α (C/EBPα). This suppression coincides with enhanced expression of several reported mediators of antiadipogenesis that are also targets of the Wnt/β-catenin/T-cell factor 4 (TCF4) pathway. Indeed, we found that TNF-α enhanced TCF4-dependent transcriptional activity during early antiadipogenesis, and promoted the stabilisation of β-catenin throughout antiadipogenesis. We analysed the effect of TNF-α on adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells in which β-catenin/TCF signalling was impaired, either via stable knockdown of β-catenin, or by overexpression of dominant-negative TCF4 (dnTCF4). The knockdown of β-catenin enhanced the adipogenic potential of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and attenuated TNF-α-induced antiadipogenesis. However, β-catenin knockdown also promoted TNF-α-induced apoptosis in these cells. In contrast, overexpression of dnTCF4 prevented TNF-α-induced antiadipogenesis but showed no apparent effect on cell survival. Finally, we show that TNF-α-induced antiadipogenesis and stabilisation of β-catenin requires a functional death domain of TNF-α receptor 1 (TNFR1). Taken together these data suggest that TNFR1-mediated death domain signals can inhibit adipogenesis via a β-catenin/TCF4-dependent pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- TNF-α:
-
tumour necrosis factor-alpha
- TNFR1:
-
TNF-α receptor-1
- PPAR:
-
peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor
- C/EBP:
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein
- TCF4:
-
T-cell factor 4 (also known as TCF7L2)
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa B
References
Farmer SR . Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab 2006; 4: 263–273.
MacDougald OA, Mandrup S . Adipogenesis: forces that tip the scales. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2002; 13: 5–11.
Ross SE, Hemati N, Longo KA, Bennett CN, Lucas PC, Erickson RL et al. Inhibition of adipogenesis by Wnt signaling. Science 2000; 289: 950–953.
Xu H, Sethi JK, Hotamisligil GS . Transmembrane tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha inhibits adipocyte differentiation by selectively activating TNF receptor 1. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 26287–26295.
Huelsken J, Behrens J . The Wnt signalling pathway. J Cell Sci 2002; 115: 3977–3978.
Moldes M, Zuo Y, Morrison RF, Silva D, Park BH, Liu J et al. Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor gamma suppresses Wnt/beta-catenin signalling during adipogenesis. Biochem J 2003; 376: 607–613.
Yang X, Jansson PA, Nagaev I, Jack MM, Carvalho E, Sunnerhagen KS et al. Evidence of impaired adipogenesis in insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004; 317: 1045–1051.
Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig AJ . Thematic Review Series on Adipocyte Biology: Adipose tissue function and plasticity orchestrate nutritional adaptation. J Lipid Res 2007 (in press).
Xu H, Hotamisligil GS . Signaling pathways utilized by tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 in adipocytes to suppress differentiation. FEBS Lett 2001; 506: 97–102.
Chae GN, Kwak SJ . NF-kappaB is involved in the TNF-alpha induced inhibition of the differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells by reducing PPARgamma expression. Exp Mol Med 2003; 35: 431–437.
Suzawa M, Takada I, Yanagisawa J, Ohtake F, Ogawa S, Yamauchi T et al. Cytokines suppress adipogenesis and PPAR-gamma function through the TAK1/TAB1/NIK cascade. Nat Cell Biol 2003; 5: 224–230.
Berg AH, Lin Y, Lisanti MP, Scherer PE . Adipocyte differentiation induces dynamic changes in NF-kappaB expression and activity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2004; 287: E1178–1188.
Castro-Munozledo F, Beltran-Langarica A, Kuri-Harcuch W . Commitment of 3T3-F442A cells to adipocyte differentiation takes place during the first 24–36 h after adipogenic stimulation: TNF-alpha inhibits commitment. Exp Cell Res 2003; 284: 163–172.
Morrison RF, Farmer SR . Role of PPARgamma in regulating a cascade expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, p18(INK4c) and p21(Waf1/Cip1), during adipogenesis. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 17088–17097.
Burton GR, Nagarajan R, Peterson CA, McGehee Jr RE . Microarray analysis of differentiation-specific gene expression during 3T3-L1 adipogenesis. Gene 2004; 329: 167–185.
Tong Q, Dalgin G, Xu H, Ting CN, Leiden JM, Hotamisligil GS . Function of GATA transcription factors in preadipocyte–adipocyte transition. Science 2000; 290: 134–138.
Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Torti FM, Ringold GM . Tumor necrosis factor-induced c-myc expression in the absence of mitogenesis is associated with inhibition of adipocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 9611–9615.
Freytag S, Geddes TJ . Reciprocal regulation of adipogenesis by Myc and C/EBPalpha. Science 1992; 256: 379–382.
Fu M, Rao M, Bouras T, Wang C, Wu K, Zhang X et al. Cyclin D1 inhibits peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated adipogenesis through histone deacetylase recruitment. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 16934–16941.
Shi Y, Hon M, Evans RM . The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta, an integrator of transcriptional repression and nuclear receptor signaling. PNAS 2002; 99: 2613–2618.
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H, Zawel L, da Costa LT et al. Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science 1998; 281: 1509–1512.
Shtutman M, Zhurinsky J, Simcha I, Albanese C, D'Amico M, Pestell R et al. The cyclin D1 gene is a target of the beta -catenin/LEF-1 pathway. PNAS 1999; 96: 5522–5527.
He TC, Chan TA, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW . PPARdelta is an APC-regulated target of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Cell 1999; 99: 335–345.
Hagen T, Sethi JK, Foxwell N, Vidal-Puig A . Signalling activity of beta-catenin targeted to different subcellular compartments. Biochem J 2004; 379: 471–477.
Kolligs FT, Hu G, Dang CV, Fearon ER . Neoplastic transformation of RK3E by mutant beta-catenin requires deregulation of Tcf/Lef transcription but not activation of c-myc expression. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 5696–5706.
Bennett CN, Ross SE, Longo KA, Bajnok L, Hemati N, Johnson KW et al. Regulation of Wnt signaling during adipogenesis. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 30998–31004.
Gustafson B, Smith U . Cytokines promote WNT signaling and inflammation and impair the normal differentiation and lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 9507–9516.
Christodoulides C, Laudes M, Cawthorn WP, Schinner S, Soos M, O'Rahilly S et al. The Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 and its receptors are coordinately regulated during early human adipogenesis. J Cell Sci 2006; 119: 2613–2620.
Wu Z, Rosen ED, Brun R, Hauser S, Adelmant G, Troy AE et al. Cross-regulation of C/EBP alpha and PPAR gamma controls the transcriptional pathway of adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity. Mol Cell 1999; 3: 151–158.
Chen S, Guttridge DC, You Z, Zhang Z, Fribley A, Mayo MW et al. Wnt-1 signaling inhibits apoptosis by activating beta-catenin/T cell factor-mediated transcription. J Cell Biol 2001; 152: 87–96.
Orford K, Orford CC, Byers SW . Exogenous expression of beta-catenin regulates contact inhibition, anchorage-independent growth, anoikis, and radiation-induced cell cycle arrest. J Cell Biol 1999; 146: 855–868.
Korinek V, Barker N, Moerer P, van Donselaar E, Huls G, Peters PJ et al. Depletion of epithelial stem-cell compartments in the small intestine of mice lacking Tcf-4. Nat Genet 1998; 19: 379–383.
Cauchi S, Meyre D, Dina C, Choquet H, Samson C, Gallina S et al. Transcription factor TCF7L2 genetic study in the French population: expression in human beta-cells and adipose tissue and strong association with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2006; 55: 2903–2908.
Grant SF, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, Benediktsson R, Manolescu A, Sainz J et al. Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 320–323.
Saxena R, Gianniny L, Burtt NP, Lyssenko V, Giuducci C, Sjogren M et al. Common single nucleotide polymorphisms in TCF7L2 are reproducibly associated with type 2 diabetes and reduce the insulin response to glucose in nondiabetic individuals. Diabetes 2006; 55: 2890–2895.
Sharma C, Pradeep A, Wong L, Rana A, Rana B . Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation can regulate beta-catenin levels via a proteasome-mediated and Adenomatous Polyposis Coli-independent pathway. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 35583–35594.
Liu J, Farmer SR . Regulating the balance between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and beta-catenin signaling during adipogenesis. A glycogen synthase kinase 3beta phosphorylation-defective mutant of beta-catenin inhibits expression of a subset of adipogenic genes. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 45020–45027.
Lamberti C, Lin KM, Yamamoto Y, Verma U, Verma IM, Byers S et al. Regulation of beta-catenin function by the IkappaB kinases. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 42276–42286.
Carayol N, Wang CY . IKKalpha stabilizes cytosolic beta-catenin by inhibiting both canonical and non-canonical degradation pathways. Cell Signal 2006; 18: 1941–1946.
Ding Q, Xia W, Liu JC, Yang JY, Lee DF, Xia J et al. Erk Associates with and Primes GSK-3beta for Its Inactivation Resulting in Upregulation of beta-Catenin. Mol Cell 2005; 19: 159–170.
Tran SE, Holmstrom TH, Ahonen M, Kahari VM, Eriksson JE . MAPK/ERK overrides the apoptotic signaling from Fas, TNF, and TRAIL receptors. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 16484–16490.
Tartaglia LA, Ayres TM, Wong GH, Goeddel DV . A novel domain within the 55 kd TNF receptor signals cell death. Cell 1993; 74: 845–853.
Boone E, Vanden Berghe T, Van Loo G, De Wilde G, De Wael N, Vercammen D et al. Structure/Function analysis of p55 tumor necrosis factor receptor and fas-associated death domain. Effect on necrosis in L929sA cells. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 37596–37603.
Jiang Y, Woronicz JD, Liu W, Goeddel DV . Prevention of constitutive TNF receptor 1 signaling by silencer of death domains. Science 1999; 283: 543–546.
Nawaratne R, Gray A, Jorgensen CH, Downes CP, Siddle K, Sethi JK . Regulation of insulin receptor substrate 1 pleckstrin homology domain by protein kinase C: role of serine 24 phosphorylation. Mol Endocrinol 2006; 20: 1838–1852.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Toni Vidal-Puig, members of his laboratory, Gökhan Hotamisligil, Thilo Hagen and Dirk Hadaschik, for helpful discussions and/or reagents. This research was supported by a MRC studentship (WPC), a Studienstiftung des deutschen Volkes diploma studentship (FH), a Corpus Christi College-Brooke Scholarship (KH) and a Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council David Phillips Fellowship (JKS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by HU Simon
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cawthorn, W., Heyd, F., Hegyi, K. et al. Tumour necrosis factor-α inhibits adipogenesis via a β-catenin/TCF4(TCF7L2)-dependent pathway. Cell Death Differ 14, 1361–1373 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402127
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402127
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hypertonicity induces mitochondrial extracellular vesicles (MEVs) that activate TNF-α and β-catenin signaling to promote adipocyte dedifferentiation
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2023)
-
Knockout of ICAT in Adipose Tissue Alleviates Fibro-inflammation in Obese Mice
Inflammation (2023)
-
A STAT5-Smad3 dyad regulates adipogenic plasticity of visceral adipose mesenchymal stromal cells during chronic inflammation
npj Regenerative Medicine (2022)
-
Role of Inflammatory Cytokines, Growth Factors and Adipokines in Adipogenesis and Insulin Resistance
Inflammation (2022)
-
Metabolic Messengers: tumour necrosis factor
Nature Metabolism (2021)