Abstract
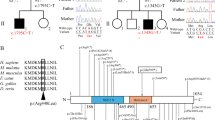
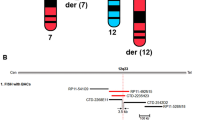
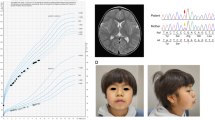
X-linked mental retardation (XLMR) is a common cause of inherited intellectual disability with an estimated prevalence of ∼1/1000 males. Most XLMR conditions are inherited as X-linked recessive traits, although female carriers may manifest usually milder symptoms. We have listed 215 XLMR conditions, subdivided according to their clinical presentation: 149 with specific clinical findings, including 98 syndromes and 51 neuromuscular conditions, and 66 nonspecific (MRX) forms. We also present a map of the 82 XLMR genes cloned to date (November 2007) and a map of the 97 conditions that have been positioned by linkage analysis or cytogenetic breakpoints. We briefly consider the molecular function of known XLMR proteins and discuss the possible strategies to identify the remaining XLMR genes. Final remarks are made on the natural history of XLMR conditions and on diagnostic issues.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Luckasson R, Borthwick-Duffy S, Buntinx WHE et al: Mental Retardation: Definition, Classification, and Systems of Supports 10th edn. American Association on Mental Retardation: Washington, DC, 2002.
Larson SA, Lakin KC, Anderson L, Kwak N, Lee JH, Anderson D : Prevalence of mental retardation and developmental disabilities: estimates from the 1994/1995 National Health Interview Survey Disability Supplements. Am J Ment Retard 2001; 106: 231–252.
Brosco JP, Mattingly M, Sanders LM : Impact of specific medical interventions on reducing the prevalence of mental retardation. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2006; 160: 302–309.
Schalock RL, Luckasson RA, Shogren KA et al: The renaming of mental retardation: understanding the change to the term intellectual disability. Intellect Dev Disabil 2007; 45: 116–124.
Chiurazzi P, Oostra BA : Genetics of mental retardation. Curr Opin Pediatr 2000; 12: 529–535.
Inlow JK, Restifo LL : Molecular and comparative genetics of mental retardation. Genetics 2004; 166: 835–881.
Chelly J, Khelfaoui M, Francis F, Cherif B, Bienvenu T : Genetics and pathophysiology of mental retardation. Eur J Hum Genet 2006; 14: 701–713.
Francis F, Meyer G, Fallet-Bianco C et al: Human disorders of cortical development: from past to present. Eur J Neurosci 2006; 23: 877–893.
Lehrke R : Theory of X-linkage of major intellectual traits. Am J Ment Defic 1972; 76: 611–619.
Plenge RM, Stevenson RA, Lubs HA, Schwartz CE, Willard HF : Skewed X-chromosome inactivation is a common feature of X-linked mental retardation disorders. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 168–173.
Amos-Landgraf JM, Cottle A, Plenge RM et al: X chromosome-inactivation patterns of 1,005 phenotypically unaffected females. Am J Hum Genet 2006; 79: 493–499.
Skuse DH : X-linked genes and mental functioning. Hum Mol Genet 2005; 14: R27–R32.
Herbst DS, Miller JR : Nonspecific X-linked mental retardation II: the frequency in British Columbia. Am J Med Genet 1980; 7: 461–469.
Fishburn J, Turner G, Daniel A, Brookwell R : The diagnosis and frequency of X-linked conditions in a cohort of moderately retarded males with affected brothers. Am J Med Genet 1983; 14: 713–724.
Mandel JL, Chelly J : Monogenic X-linked mental retardation: is it as frequent as currently estimated? The paradox of the ARX (Aristaless X) mutations. Eur J Hum Genet 2004; 12: 689–693.
Ropers HH, Hamel BC : X-linked mental retardation. Nat Rev Genet 2005; 6: 46–57.
Kleefstra T, Hamel BC : X-linked mental retardation: further lumping, splitting and emerging phenotypes. Clin Genet 2005; 67: 451–467.
Neri G, Gurrieri F, Gal A, Lubs HA : XLMR genes: update 1990. Am J Med Genet 1991; 38: 186–189.
Ryan SG, Chance PF, Zou CH, Spinner NB, Golden JA, Smietana S : Epilepsy and mental retardation limited to females: an X-linked dominant disorder with male sparing. Nat Genet 1997; 17: 92–95.
Moog U : The outcome of diagnostic studies on the etiology of mental retardation: considerations on the classification of the causes. Am J Med Genet A 2005; 137: 228–231.
Neri G, Chiurazzi P, Arena F, Lubs HA, Glass IA : XLMR genes: update 1992. Am J Med Genet 1992; 43: 373–382.
Neri G, Chiurazzi P, Arena JF, Lubs HA : XLMR genes: update 1994. Am J Med Genet 1994; 51: 542–549.
Lubs HA, Chiurazzi P, Arena JF, Schwartz C, Tranebjaerg L, Neri G : XLMR genes: update 1996. Am J Med Genet 1996; 64: 147–157.
Lubs H, Chiurazzi P, Arena J, Schwartz C, Tranebjaerg L, Neri G : XLMR genes: update 1998. Am J Med Genet 1999; 83: 237–247.
Chiurazzi P, Hamel BC, Neri G : XLMR genes: update 2000. Eur J Hum Genet 2001; 9: 71–81.
Chiurazzi P, Tabolacci E, Neri G : X-linked mental retardation (XLMR): from clinical conditions to cloned genes. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 2004; 41: 117–158.
Mulley JC, Kerr B, Stevenson R, Lubs H : Nomenclature guidelines for X-linked mental retardation. Am J Med Genet 1992; 43: 383–391.
Stromme P, Gilfillan G, Selmer KK et al: Mutations in SLC9A6 cause an Angelman syndrome like phenotype. In the Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Fragile X and X-linked mental retardation, Venice (Italy), 3–6 October 2007, Abstract 15.
Marco E, Abidi FE, Bristow J et al: ARHGEF9 disruption in a female patient is associated with X linked mental retardation and sensory hyperarousal. J Med Genet, September 2007; doi:10.1136/jmg.2007.052324.
Kalscheuer VM, Harvey K, Musante L et al: Truncation of ARHGEF9 encoding the RhoGEF collybistin by a de novo balanced translocation in a severely mentally retarded patient. Abstract 10. Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Fragile X and X-linked mental retardation, Venice (Italy), 3–6 October 2007, Abstract 15.
Froyen G, Corbett M, Vandewalle J et al: Submicroscopic duplications of the hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase HSD17B10 and the E3 ubiquitin ligase HUWE1 are associated with mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 2008, in press.
Meins M, Lehmann J, Gerresheim F et al: Submicroscopic duplication in Xq28 causes increased expression of the MECP2 gene in a boy with severe mental retardation and features of Rett syndrome. J Med Genet 2005; 42: e12.
Van Esch H, Bauters M, Ignatius J et al: Duplication of the MECP2 region is a frequent cause of severe mental retardation and progressive neurological symptoms in males. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 77: 442–453.
Friez MJ, Jones JR, Clarkson K et al: Recurrent infections, hypotonia, and mental retardation caused by duplication of MECP2 and adjacent region in Xq28. Pediatrics 2006; 118: e1687–e1695.
del Gaudio D, Fang P, Scaglia F et al: Increased MECP2 gene copy number as the result of genomic duplication in neurodevelopmentally delayed males. Genet Med 2006; 8: 784–792.
Froyen G, Van Esch H, Bauters M et al: Detection of genomic copy number changes in patients with idiopathic mental retardation by high-resolution X-array-CGH: important role for increased gene dosage of XLMR genes. Hum Mutat 2007; 28: 1034–1042.
Karim SA, Barrie JA, McCulloch MC et al: PLP overexpression perturbs myelin protein composition and myelination in a mouse model of Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease. Glia 2007; 55: 341–351.
Laumonnier F, Cuthbert PC, Grant SG : The role of neuronal complexes in human X-linked brain diseases. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 80: 205–220.
Chen W, Jensen LR, Gecz J et al: Mutation screening of brain-expressed X-chromosomal miRNA genes in 464 patients with nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation. Eur J Hum Genet 2007; 15: 375–378.
Gecz J : FMR3 is a novel gene associated with FRAXE CpG island and transcriptionally silent in FRAXE full mutations. J Med Genet 2000; 37: 782–784.
Santos-Reboucas CB, Abdalla CB, Fullston T, Campos Jr M, Pimentel MM, Gecz J : Lack of FMR3 expression in a male with non-syndromic mental retardation and a microdeletion immediately distal to FRAXE CCG repeat. Neurosci Lett 2006; 397: 245–248.
Ropers HH : X-linked mental retardation: many genes for a complex disorder. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2006; 16: 260–269.
Raymond FL, Tarpey P : The genetics of mental retardation. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: R110–R116.
Jensen LR, Lenzner S, Moser B et al: X-linked mental retardation: a comprehensive molecular screen of 47 candidate genes from a 7.4 Mb interval in Xp11. Eur J Hum Genet 2007; 15: 68–75.
Zalfa F, Eleuteri B, Dickson KS et al: A new function for the fragile X mental retardation protein in regulation of PSD-95 mRNA stability. Nat Neurosci 2007; 10: 578–587.
Moog U, Arens YH, van Lent-Albrechts JC et al: Subtelomeric chromosome aberrations: still a lot to learn. Clin Genet 2005; 68: 397–407.
de Vries BB, Pfundt R, Leisink M et al: Diagnostic genome profiling in mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 77: 606–616.
Menten B, Maas N, Thienpont B et al: Emerging patterns of cryptic chromosomal imbalance in patients with idiopathic mental retardation and multiple congenital anomalies: a new series of 140 patients and review of published reports. J Med Genet 2006; 43: 625–633.
Lugtenberg D, de Brouwer AP, Kleefstra T et al: Chromosomal copy number changes in patients with non-syndromic X linked mental retardation detected by array CGH. J Med Genet 2006; 43: 362–370.
Friedman JM, Baross A, Delaney AD et al: Oligonucleotide microarray analysis of genomic imbalance in children with mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 2006; 79: 500–513.
Zhang L, Jie C, Obie C et al: X chromosome cDNA microarray screening identifies a functional PLP2 promoter polymorphism enriched in patients with X-linked mental retardation. Genome Res 2007; 17: 641–648.
van Karnebeek CD, Scheper FY, Abeling NG et al: Etiology of mental retardation in children referred to a tertiary care center: a prospective study. Am J Ment Retard 2005; 110: 253–267.
Curry CJ, Stevenson RE, Aughton D et al: Evaluation of mental retardation: recommendations of a Consensus Conference: American College of Medical Genetics. Am J Med Genet 1997; 72: 468–477.
Moeschler JB, Shevell M, the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Genetics: Clinical genetic evaluation of the child with mental retardation or developmental delays. Pediatrics 2006; 117: 2304–2316.
Battaglia A, Carey JC : Diagnostic evaluation of developmental delay/mental retardation: an overview. Am J Med Genet C 2003; 117: 3–14.
van Karnebeek CD, Jansweijer MC, Leenders AG, Offringa M, Hennekam RC : Diagnostic investigations in individuals with mental retardation: a systematic literature review of their usefulness. Eur J Hum Genet 2005; 13: 6–25.
Mandel JL, Chelly J : Monogenic X-linked mental retardation: is it as frequent as currently estimated? The paradox of the ARX (Aristaless X) mutations. Eur J Hum Genet 2004; 12: 689–693.
de Brouwer AP, Yntema HG, Kleefstra T et al: Mutation frequencies of X-linked mental retardation genes in families from the EuroMRX consortium. Hum Mutat 2007; 28: 207–208.
Battaglia A : Neuroimaging studies in the evaluation of developmental delay/mental retardation. Am J Med Genet C 2003; 117: 25–30.
Kahler SG, Fahey MC : Metabolic disorders and mental retardation. Am J Med Genet C 2003; 117: 31–41.
Clark AJ, Rosenberg EH, Almeida LS et al: X-linked creatine transporter (SLC6A8) mutations in about 1% of males with mental retardation of unknown etiology. Hum Genet 2006; 119: 604–610.
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported in part by TELETHON grant (GGP06224), PRIN 2005 grant (no.2005060575) and a Conquer Fragile X Foundation grant to GN.; and by Grant HD26202 from NICHD and by the South Carolina Department of Disabilities and Special Needs to CES. This paper is dedicated to the memory of Libor Kozák (1960–2007) and of Ethan Francis Schwartz (1996–1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website (http://www.nature.com/ejhg)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiurazzi, P., Schwartz, C., Gecz, J. et al. XLMR genes: update 2007. Eur J Hum Genet 16, 422–434 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201994
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201994
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Calcium channelopathies and intellectual disability: a systematic review
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2021)
-
Estradiol-dependent axogenesis and Ngn3 expression are determined by XY sex chromosome complement in hypothalamic neurons
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Evaluating historical candidate genes for schizophrenia
Molecular Psychiatry (2015)
-
Copy number variation in schizophrenia in Sweden
Molecular Psychiatry (2014)
-
Neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders represent an interconnected molecular system
Molecular Psychiatry (2014)