Abstract
Aim:
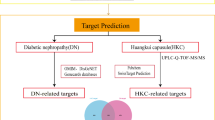
Xiao-Ke-An (XKA) is a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formula for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2D), and the effective ingredients and their targets as well as the mechanisms of XKA remain to be elucidated. In this study we investigated the therapeutic mechanisms of XKA in the treatment of T2D in mice using a Fangjiomics approach.
Methods:
KKAy mice feeding on a high-fat diet were used as models of T2D, and were orally treated with XKA (0.75 or 1.5 g·kg−1·d−1) for 32 d. Microarray mRNA expression data were obtained from the livers of the mice. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified by reverse rate analysis and ANOVA analysis. The compounds in XKA were identified by LC-MS analysis or collected from TCM databases. The relationships between the compounds and targets were established by combining the DEGs with information derived from mining literature or herb target databases. Relevant pathways were identified through a Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis using WebGestalt.
Results:
The compound-target-pathway network based on compounds identified by LC-MS analysis (NCA) included 20 constituent compounds, 46 targets and 36 T2D-related pathways, whereas the compound-target-pathway network based on compounds collected from databases (NCD) consisted of 40 compounds, 68 targets and 21 pathways. In the treatment of T2D, XKA might act mainly by improving carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, as well as ameliorating insulin resistance, inflammation and diabetic vascular complications.
Conclusion:
The network-based approach reveals complex therapeutic mechanisms of XKA in the treatment of T2D in mice that involve numerous compounds, targets, and signaling pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Qi L, Hu FB, Hu G . Genes, environment, and interactions in prevention of type 2 diabetes: a focus on physical activity and lifestyle changes. Curr Mol Med 2008; 8: 519–32.
Tahrani AA, Bailey CJ, Del Prato S, Barnett AH . Management of type 2 diabetes: new and future developments in treatment. Lancet 2011; 378: 182–97.
Yang Z, Yang J, Liu W, Wu L, Xing L, Wang Y, et al. T2D@ZJU: a knowledgebase integrating heterogeneous connections associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Database (Oxford) 2013; 2013: bat052.
Timmers S, Hesselink MK, Schrauwen P . Therapeutic potential of resveratrol in obesity and type 2 diabetes: new avenues for health benefits? Ann N Y Acad Sci 2013; 1290: 83–9.
Tian P . Convergence: where west meets east. Nature 2011; 480: S84–S6.
Nissen SE, Wolski K . Effect of rosiglitazone on the risk of myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. New Engl J Med 2007; 356: 2457–71.
Scarpello J, Hodgson E, Howlett H . Effect of metformin on bile salt circulation and intestinal motility in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 1998; 15: 651–6.
Owen M, DORAN E, Halestrap A . Evidence that metformin exerts its anti-diabetic effects through inhibition of complex 1 of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Biochem J 2000; 348: 607–14.
Tian P . CONVERGENCE Where West meets East. Nature 2011; 480: S84–S6.
Yang Z, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y . Bioassay-guided screening and isolation of alpha-glucosidase and tyrosinase inhibitors from leaves of Morus alba. Food Chem 2012; 131: 617–25.
Wang Z, Liu J, Cheng Y, Wang Y . Fangjiomics: in search of effective and safe combination therapies. J Clin Pharmacol 2011; 51: 1132–51.
Fang H, Harris SC, Su Z, Chen M, Qian F, Shi L, et al. ArrayTrack: an FDA and public genomic tool. Methods Mol Biol 2009; 563: 379–98.
Wang L, Li Z, Zhao X, Liu W, Liu Y, Yang J, et al. A network study of Chinese medicine Xuesaitong injection to elucidate a complex mode of action with multicompound, multitarget, and multipathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013; 2013: 652373.
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Tanabe M . KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res 2012; 40: D109–14.
Wang J, Duncan D, Shi Z, Zhang B . WEB-based GEne SeT AnaLysis Toolkit (WebGestalt): update 2013. Nucleic Acids Res 2013; 41: W77–83.
Chen X, Zhou H, Liu Y, Wang J, Li H, Ung C, et al. Database of traditional Chinese medicine and its application to studies of mechanism and to prescription validation. Br J Pharmacol 2006; 149: 1092–103.
Ye H, Ye L, Kang H, Zhang D, Tao L, Tang K, et al. HIT: linking herbal active ingredients to targets. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39: D1055–9.
Chen CYC . TCM Database@ Taiwan: the world's largest traditional Chinese medicine database for drug screening in silico. PloS One 2011; 6: e15939.
Xue R, Fang Z, Zhang M, Yi Z, Wen C, Shi T . TCMID: traditional Chinese medicine integrative database for herb molecular mechanism analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2013; 41: D1089–95.
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL, Ideker T . Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 2011; 27: 431–2.
Li H, Zhao L, Zhang B, Jiang Y, Wang X, Guo Y, et al. A network pharmacology approach to determine active compounds and action mechanisms of Ge-Gen-Qin-Lian decoction for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014; 2014: 495840.
Yu YL, Lu SS, Yu S, Liu YC, Wang P, Xie L, et al. Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction modulates glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2009; 124: 444–9.
Kong WJ, Zhang H, Song DQ, Xue R, Zhao W, Wei J, et al. Berberine reduces insulin resistance through protein kinase C-dependent up-regulation of insulin receptor expression. Metabolism 2009; 58: 109–19.
Zhang H, Wei J, Xue R, Wu JD, Zhao W, Wang ZZ, et al. Berberine lowers blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients through increasing insulin receptor expression. Metabolism 2010; 59: 285–92.
Kim SH, Shin EJ, Kim ED, Bayaraa T, Frost SC, Hyun CK . Berberine activates GLUT1-mediated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biol Pharm Bull 2007; 30: 2120–5.
Cok A, Plaisier C, Salie MJ, Oram DS, Chenge J, Louters LL . Berberine acutely activates the glucose transport activity of GLUT1. Biochimie 2011; 93: 1187–92.
Xing J, Kang L, Jiang Y . Effect of dietary betaine supplementation on lipogenesis gene expression and CpG methylation of lipoprotein lipase gene in broilers. Mol Biol Reports 2011; 38: 1975–81.
Guo HW, Yun CX, Hou GH, Du J, Huang X, Lu Y, et al. Mangiferin attenuates Th1/Th2 cytokine imbalance in an ovalbumin-induced asthmatic mouse model. PloS One 2014; 9: e100394.
Fu K, Piao T, Wang M, Zhang J, Jiang J, Wang X, et al. Protective effect of catalpol on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2014; 23: 400–6.
Liu Y, Qi W, Richardson A, Van Remmen H, Ikeno Y, Salmon AB . Oxidative damage associated with obesity is prevented by overexpression of CuZn-or Mn-superoxide dismutase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013; 438: 78–83.
Tinahones FJ, MurriPierri M, Garrido-Sánchez L, García-Almeida JM, García-Serrano S, García-Arnés J, et al. Oxidative stress in severely obese persons is greater in those with insulin resistance. Obesity 2009; 17: 240–6.
Muscogiuri G, Salmon AB, Aguayo-Mazzucato C, Li M, Balas B, Guardado-Mendoza R, et al. Genetic disruption of SOD1 gene causes glucose intolerance and impairs β-cell function. Diabetes 2013; 62: 4201–7.
Li Y, Bao Y, Jiang B, Wang Z, Liu Y, Zhang C, et al. Catalpol protects primary cultured astrocytes from in vitro ischemia-induced damage. Int J Develop Neurosci 2008; 26: 309–17.
Tang Y, Wang M, Le X, Meng J, Huang L, Yu P, et al. Antioxidant and cardioprotective effects of Danshensu (3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-propanoic acid from Salvia miltiorrhiza) on isoproterenol-induced myocardial hypertrophy in rats. Phytomedicine 2011; 18: 1024–30.
Sellamuthu PS, Arulselvan P, Kamalraj S, Fakurazi S, Kandasamy M . Protective nature of mangiferin on oxidative stress and antioxidant status in tissues of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. ISRN Pharmacol 2013; 2013.
Zhang YX, Wang L, Xiao EL, Li SJ, Chen JJ, Gao B, et al. Ginsenoside-Rd exhibits anti-inflammatory activities through elevation of antioxidant enzyme activities and inhibition of JNK and ERK activation in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol 2013; 17: 1094–100.
Bitar MS, Al-Mulla F . A defect in Nrf2 signaling constitutes a mechanism for cellular stress hypersensitivity in a genetic rat model of type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol-Endocrinol Metab 2011; 301: E1119–E29.
Chartoumpekis DV, Kensler TW . New player on an old field; the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway as a target for treatment of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Curr Diabetes Rev 2013; 9: 137.
Chong CM, Zhou ZY, Razmovski-Naumovski V, Cui GZ, Zhang LQ, Sa F, et al. Danshensu protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced damage of PC12 cells in vitro and dopaminergic neurons in zebrafish. Neuros Lett 2013; 543: 121–5.
Zhang H, Liu YY, Jiang Q, Li KR, Zhao YX, Cao C, et al. Salvianolic acid A protects RPE cells against oxidative stress through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Free Radical Biol Med 2014; 69: 219–28.
Zhou J, Qu XD, Li ZY, Liu Q, Ma YH, He JJ . Salvianolic acid B attenuates toxin-Induced neuronal damage via Nrf2-dependent glial cells-mediated protective activity in Parkinson's disease models. PloS One 2014; 9: e101668.
Kado S, Nagata N . Circulating intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and E-selectin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1999; 46: 143–8.
Otsuki M, Hashimoto K, Morimoto Y, Kishimoto T, Kasayama S . Circulating vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in atherosclerotic NIDDM patients. Diabetes 1997; 46: 2096–101.
Chen YH, Lin SJ, Ku HH, Shiao MS, Lin FY, Chen JW, et al. Salvianolic acid B attenuates VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression in TNF-alpha-treated human aortic endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem 2001; 82: 512–21.
Chai H, Wang Q, Huang L, Xie T, Fu Y . Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human endothelial cells. Biol Pharm Bull 2008; 31: 2050–6.
Al-Kateb H, Mirea L, Xie X, Sun L, Liu M, Chen H, et al. Multiple variants in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGFA) are risk factors for time to severe retinopathy in type 1 diabetes the DCCT/EDIC genetics study. Diabetes 2007; 56: 2161–8.
Abhary S, Burdon KP, Gupta A, Lake S, Selva D, Petrovsky N, et al. Common sequence variation in the VEGFA gene predicts risk of diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci 2009; 50: 5552–8.
Liu Y, Liu S, Liu Z . Eeffects of ginsenoside RbI on blood vessel regeneration after ischemia and reperfusion in rats. Chin J Histochem and Cytochem 2008; 17: 39–44.
Zhang YJ, Zhang XL, Li MH, Iqbal J, Bourantas CV, Li JJ, et al. The ginsenoside Rg1 prevents transverse aortic constriction-induced left ventricular hypertrophy and cardiac dysfunction by inhibiting fibrosis and enhancing angiogenesis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2013; 62: 50–7.
Shi AW, Wang XB, Lu FX, Zhu MM, Kong XQ, Cao KJ . Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes endothelial progenitor cell migration and proliferation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2009; 30: 299–306.
Lay IS, Chiu JH, Shiao MS, Lu WY, Wu CW . Crude extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza and salvianolic acid B enhance in vitro angiogenesis in murine SVR endothelial cell line. Planta Med 2003; 69: 26–32.
Hamsa TP, Kuttan G . Antiangiogenic activity of berberine is mediated through the downregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1, VEGF, and proinflammatory mediators. Drug Chem Toxicol 2012; 35: 57–70.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially financially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No 2012CB518405). The authors sincerely thank the Laboratory Animal Centre of Zhejiang University for technical assistance with the animal experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary information is available at the Acta Pharmacologica Sinica website.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Zz., Liu, W., Zhang, F. et al. Deciphering the therapeutic mechanisms of Xiao-Ke-An in treatment of type 2 diabetes in mice by a Fangjiomics approach. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36, 699–707 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2014.138
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2014.138
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Similarity of therapeutic networks induced by a multi-component herbal remedy, Ukgansan, in neurovascular unit cells
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Network Pharmacology in Research of Chinese Medicine Formula: Methodology, Application and Prospective
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine (2020)
-
Yangxin Tongmai Formula ameliorates impaired glucose tolerance in children with Graves' disease through upregulation of the insulin receptor levels
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2018)
-
A Bioactive Chemical Markers Based Strategy for Quality Assessment of Botanical Drugs: Xuesaitong Injection as a Case Study
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Combining Chemical Profiling and Network Analysis to Investigate the Pharmacology of Complex Prescriptions in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Scientific Reports (2017)