Abstract
Aim:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is a major polyphenol in green tea. In this study, we investigated the effects of EGCG on insulin resistance and insulin clearance in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) mice.
Methods:
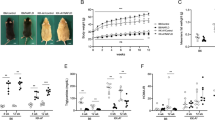
Mice were fed on a high-fat diet for 24 weeks. During the last 4 weeks, the mice were injected with EGCG (10, 20 and 40 mg·kg−1·d−1, ip). Glucose tolerance, insulin tolerance and insulin clearance were assessed. After the mice were euthanized, blood samples and tissue specimens were collected. Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion was examined in isolated pancreatic islets. The progression of NAFLD was evaluated histologically and by measuring lipid contents. Insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) protein expression and enzyme activity were detected using Western blot and immunocapture activity assays, respectively.
Results:
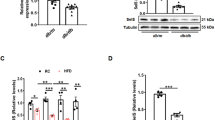
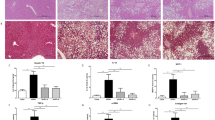
The high-fat diet significantly increased the body weight and induced grade 2 or 3 liver fatty degeneration (steatosis, lobular inflammation and ballooning) accompanied by severe hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in the model mice. Administration of EGCG dose-dependently ameliorated the hepatic morphology and function, reduced the body weight, and alleviated hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in NAFLD mice. Furthermore, EGCG dose-dependently enhanced insulin clearance and upregulated IDE protein expression and enzyme activity in the liver of NAFLD mice.
Conclusion:
EGCG dose-dependently improves insulin resistance in NAFLD mice not only by reducing body weight but also through enhancing the insulin clearance by hepatic IDE. The results suggest that IDE be a potential drug target for the treatment of NAFLD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Wang Y, Li YY, Nie YQ, Zhou YJ, Cao CY, Xu L . Association between metabolic syndrome and the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Exp Ther Med 2013; 6: 77–84.
Birkenfeld AL, Shulman GI . Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Hepatology 2014; 59: 713–23.
Marin-Juez R, Jong-Raadsen S, Yang S, Spaink HP . Hyperinsulinemia induces insulin resistance and immune suppression via Ptpn6/Shp1 in zebrafish. J Endocrinol 2014; 222: 229–41.
Kim B, McLean LL, Philip SS, Feldman EL . Hyperinsulinemia induces insulin resistance in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Endocrinology 2011; 152: 3638–47.
Lorenzo C, Hanley AJ, Wagenknecht LE, Rewers MJ, Stefanovski D, Goodarzi MO, et al. Relationship of insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion, and adiposity with insulin clearance in a multiethnic population: the insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis study. Diabetes Care 2013; 36: 101–3.
Fernandez-Gamba A, Leal MC, Morelli L, Castano EM . Insulin-degrading enzyme: structure-function relationship and its possible roles in health and disease. Curr Pharm Des 2009; 15: 3644–55.
Haque R, Nazir A . Insulin-degrading enzyme: a link between Alzheimer's and type 2 diabetes mellitus. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2014; 13: 259–64.
Farris W, Mansourian S, Leissring MA, Eckman EA, Bertram L, Eckman CB, et al. Partial loss-of-function mutations in insulin-degrading enzyme that induce diabetes also impair degradation of amyloid beta-protein. Am J Pathol 2004; 164: 1425–34.
Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, Lindsley L, Eckman EA, Frosch MP, et al. Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003; 100: 4162–7.
Bril F, Lomonaco R, Orsak B, Ortiz-Lopez C, Webb A, Tio F, et al. Relationship between disease severity, hyperinsulinemia, and impaired insulin clearance in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2014; 59: 2178–87.
Kim HS, Quon MJ, Kim JA . New insights into the mechanisms of polyphenols beyond antioxidant properties; lessons from the green tea polyphenol, epigallocatechin 3-gallate. Redox Biol 2014; 2: 187–95.
Li Y, Zhao S, Zhang W, Zhao P, He B, Wu N, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCG) attenuates FFAs-induced peripheral insulin resistance through AMPK pathway and insulin signaling pathway in vivo. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2011; 93: 205–14.
Jang HJ, Ridgeway SD, Kim JA . Effects of the green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate on high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2013; 305: E1444–51.
Ueno T, Torimura T, Nakamura T, Sivakumar R, Nakayama H, Otabe S, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate improves nonalcoholic steatohepatitis model mice expressing nuclear sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c in adipose tissue. Int J Mol Med 2009; 24: 17–22.
Ren Y, Deng F, Zhu H, Wan W, Ye J, Luo B . Effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on iron overload in mice with alcoholic liver disease. Mol Biol Rep 2011; 38: 879–86.
Katz A, Nambi SS, Mather K, Baron AD, Follmann DA, Sullivan G, et al. Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index: a simple, accurate method for assessing insulin sensitivity in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 2402–10.
Del Prato S . Loss of early insulin secretion leads to postprandial hyperglycaemia. Diabetologia 2003; 46: M2–8.
Castell-Auvi A, Cedo L, Pallares V, Blay M, Ardevol A, Pinent M . The effects of a cafeteria diet on insulin production and clearance in rats. Br J Nutr 2012; 108: 1155–62.
Lee CC, Haffner SM, Wagenknecht LE, Lorenzo C, Norris JM, Bergman RN, et al. Insulin clearance and the incidence of type 2 diabetes in Hispanics and African Americans: the IRAS Family Study. Diabetes Care 2013; 36: 901–7.
Vozarova B, Stefan N, Lindsay RS, Saremi A, Pratley RE, Bogardus C, et al. High alanine aminotransferase is associated with decreased hepatic insulin sensitivity and predicts the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2002; 51: 1889–95.
Wiernsperger N . Hepatic function and the cardiometabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2013; 6: 379–88.
Hassan K, Bhalla V, Ezz El Regal M, HH AK . Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A comprehensive review of a growing epidemic. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20: 12082–101.
Chen YK, Cheung C, Reuhl KR, Liu AB, Lee MJ, Lu YP, et al. Effects of green tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on newly developed high-fat/Western-style diet-induced obesity and metabolic syndrome in mice. J Agric Food Chem 2011; 59: 11862–71.
Kochi T, Shimizu M, Terakura D, Baba A, Ohno T, Kubota M, et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and preneoplastic lesions develop in the liver of obese and hypertensive rats: suppressing effects of EGCG on the development of liver lesions. Cancer Lett 2014; 342: 60–9.
Sae-Tan S, Grove KA, Kennett MJ, Lambert JD . (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate increases the expression of genes related to fat oxidation in the skeletal muscle of high fat-fed mice. Food Funct 2011; 2: 111–6.
Kievit P, Halem H, Marks DL, Dong JZ, Glavas MM, Sinnayah P, et al. Chronic treatment with a melanocortin-4 receptor agonist causes weight loss, reduces insulin resistance, and improves cardiovascular function in diet-induced obese rhesus macaques. Diabetes 2013; 62: 490–7.
Ballesteros-Pomar MD, Calleja S, Diez-Rodriguez R, Calleja-Fernandez A, Vidal-Casariego A, Nunez-Alonso A, et al. Inflammatory status is different in relationship to insulin resistance in severely obese people and changes after bariatric surgery or diet-induced weight loss. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2014; 122: 592–6.
Kotronen A, Vehkavaara S, Seppala-Lindroos A, Bergholm R, Yki-Jarvinen H . Effect of liver fat on insulin clearance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2007; 293: E1709–15.
Goto T, Onuma T, Takebe K, Kral JG . The influence of fatty liver on insulin clearance and insulin resistance in non-diabetic Japanese subjects. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1995; 19: 841–5.
Strang BD, Bertics SJ, Grummer RR, Armentano LE . Relationship of triglyceride accumulation to insulin clearance and hormonal responsiveness in bovine hepatocytes. J Dairy Sci 1998; 81: 740–7.
Abdul-Hay SO, Kang D, McBride M, Li L, Zhao J, Leissring MA . Deletion of insulin-degrading enzyme elicits antipodal, age-dependent effects on glucose and insulin tolerance. PLoS One 2011; 6: e20818.
Du J, Zhang L, Liu S, Zhang C, Huang X, Li J, et al. PPARgamma transcriptionally regulates the expression of insulin-degrading enzyme in primary neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 383: 485–90.
Zhang L, Ding Q, Wang Z . Nuclear respiratory factor 1 mediates the transcription initiation of insulin-degrading enzyme in a TATA box-binding protein-independent manner. PLoS One 2012; 7: e42035.
Leal MC, Surace EI, Holgado MP, Ferrari CC, Tarelli R, Pitossi F, et al. Notch signaling proteins HES-1 and Hey-1 bind to insulin degrading enzyme (IDE) proximal promoter and repress its transcription and activity: implications for cellular Aβ metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012; 1823: 227–35.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 31070687) and Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (No 9451051501002535) and Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (No 2013B031800004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary information is available at website of Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information, Table S1
The composition in 100 g chow (DOC 29 kb)
Supplementary Information, Figure S1
Effects of EGCG on HOMA–ISI (A) and HOMA–IRI (B) by homeostatic model assessment. (DOC 107 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, L., Meng, Zj., Xiong, Rb. et al. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates insulin resistance in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36, 597–605 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.11
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.11
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Alisol B 23-acetate protects against non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice via farnesoid X receptor activation
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2017)
-
Intestinal Metrnl released into the gut lumen acts as a local regulator for gut antimicrobial peptides
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2016)
-
New Insights into Epigenetic and Pharmacological Regulation of Amyloid-Degrading Enzymes
Neurochemical Research (2016)