Abstract
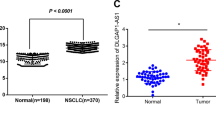
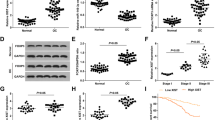
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are associated with the occurrence, development and prognoses of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In the present study, we investigated the functional mechanisms of the lncRNA XIST in two human NSCLC cell lines, A549 and NCI-H1299. In all the 5 NSCLC cell lines (NL9980, NCI-H1299, NCI-H460, SPC-A-1 and A549) tested, the expression levels of XIST were significantly elevated, as compared with those in normal human bronchial epithelial cell line BEAS-2B. In A549 and NCI-H1299 cells, knockdown of XIST by siRNA significantly inhibited the cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and promoted cell apoptosis. Furthermore, XIST knockdown elevated the expression of E-cadherin, and suppressed the expression of Bcl-2. Moreover, knockdown of XIST significantly suppressed the tumor growth in NSCLC A549 xenograft mouse model. Bioinformatic analysis and luciferase reporter assays revealed that XIST was negatively regulated by miR-449a. We further identified reciprocal repression between XIST and miR-449a, which eventually influenced the expression of Bcl-2: XIST functioned as a miRNA sponge of miR-449a, which was a negative regulator of Bcl-2. These data show that expression of the lncRNA XIST is associated with an increased growth rate and metastatic potential in NSCLC A549 and NCI-H1299 cells partially through miR-449a, and suggest that XIST may be a potential prognostic factor and therapeutic target for patients with NSCLC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Change history
01 March 2017
This article has been corrected since Advanced Online Publication, and an erratum is also printed in this issue.
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D . Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 69–90.
Goldstraw P, Ball D, Jett JR, Le CT, Lim E, Nicholson AG, et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 2011; 378: 1727–40.
Verdecchia A, Francisci S, Brenner H, Gatta G, Micheli A, Mangone L, et al. Recent cancer survival in Europe: a 2000-02 period analysis of EUROCARE-4 data. Lancet Oncol 2007; 8: 784–96.
Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001; 409: 860–921.
Carninci P, Kasukawa T, Katayama S, Gough J, Frith MC, Maeda N, et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science 2005; 309: 1559–63.
An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012; 489: 57–74.
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Sunkin SM, Mehler MF, Mattick JS . Specific expression of long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008; 105: 716–21.
Ravasi T, Suzuki H, Pang KC, Katayama S, Furuno M, Okunishi R, et al. Experimental validation of the regulated expression of large numbers of non-coding RNAs from the mouse genome. Genome Res 2006; 16: 11–9.
Clemson CM, Hutchinson JN, Sara SA, Ensminger AW, Fox AH, Chess A, et al. An architectural role for a nuclear noncoding RNA: NEAT1 RNA is essential for the structure of paraspeckles. Mol Cell 2009; 33: 717–26.
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H, Spector DL . Long noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev 2009; 23: 1494–504.
Ji P, Diederichs S, Wang W, Böing S, Metzger R, Schneider PM, et al. MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2003; 22: 8031–41.
Gibb EA, Brown CJ, Lam WL . The functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol Cancer 2011; 10: 38.
Han L, Kong R, Yin DD, Zhang EB, Xu TP, De W, et al. Low expression of long noncoding RNA GAS6-AS1 predicts a poor prognosis in patients with NSCLC. Med Oncol 2013; 30: 694.
Thai P, Statt S, Chen CH, Liang E, Campbell C, Wu R . Characterization of a novel long noncoding RNA, SCAL1, induced by cigarette smoke and elevated in lung cancer cell lines. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2013; 49: 204–11.
Gendrel AV, Heard E . Fifty years of X-inactivation research. Development 2011; 138: 5049–55.
Weakley SM, Wang H, Yao Q, Chen C . Expression and function of a large non-coding RNA gene XIST in human cancer. World J Surg 2011; 35: 1751–6.
Yao Y, Ma J, Xue Y, Wang P, Li Z, Liu J, et al. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA XIST exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human glioblastoma stem cells by up-regulating miR-152. Cancer Lett 2015; 359: 75–86.
You J, Zhang Y, Liu B, Li Y, Fang N, Zu L, et al. MicroRNA-449a inhibits cell growth in lung cancer and regulates long noncoding RNA nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1. Indian J Cancer 2014; 51 Suppl 3: e77–81.
Han D, Wang M, Ma N, Xu Y, Jiang Y, Gao X . Long noncoding RNAs: novel players in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett 2015; 361: 13–21.
Roth A, Diederichs S . Long noncoding RNAs in lung cancer. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2016; 394: 57–110.
Zequn N, Xuemei Z, Wei L, Zongjuan M, Yujie Z, Yanli H, et al. The role and potential mechanisms of LncRNA-TATDN1 on metastasis and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016; 7: 18219–28.
Nie FQ, Sun M, Yang JS, Xie M, Xu TP, Xia R, et al. Long noncoding RNA ANRIL promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by silencing KLF2 and P21 expression. Mol Cancer Ther 2015; 14: 268–77.
Zhou C, Ye L, Jiang C, Bai J, Chi Y, Zhang H . Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR, a hypoxia-inducible factor-1α activated driver of malignancy, enhances hypoxic cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol 2015; 36: 9179–88.
Guo F, Guo L, Li Y, Zhou Q, Li Z . MALAT1 is an oncogenic long non-coding RNA associated with tumor invasion in non-small cell lung cancer regulated by DNA methylation. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015; 8: 15903–10.
Lv J, Qiu M, Xia W, Liu C, Xu Y, Wang J, et al. High expression of long non-coding RNA SBF2-AS1 promotes proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2016; 35: 75.
Yildirim E, Kirby JE, Brown DE, Mercier FE, Sadreyev RI, Scadden DT, et al. Xist RNA is a potent suppressor of hematologic cancer in mice. Cell 2013; 152: 727–42.
Chen Q, Gao S, He W, Kou X, Zhao Y, Wang H, et al. Xist repression shows time-dependent effects on the reprogramming of female somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 2014; 32: 2642–56.
Guttman M, Amit I, Garber M, French C, Lin MF, Feldser D, et al. Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 2009; 458: 223–7.
Wang R, Chen X, Xu T, Xia R, Han L, Chen W, et al. MiR-326 regulates cell proliferation and migration in lung cancer by targeting phox2a and is regulated by HOTAIR. Am J Cancer Res 2016; 6: 173–86.
Prensner JR, Chen W, Han S, Iyer MK, Cao Q, Kothari V, et al. The long non-coding RNA PCAT-1 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation through cMyc. Neoplasia 2014; 16: 900–8.
Renhua G, Yue S, Shidai J, Jing F, Xiyi L . 165P: Long noncoding RNA LUCAT1 is associated with poor prognosis in human non-small cell lung cancer and affects cell proliferation via regulating p21 and p57 expression. J Thorac Oncol 2016; 11: S129.
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP . A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language. Cell 2011; 146: 353–8.
You J, Zhang Y, Li Y, Fang N, Liu B, Zu L, et al. MiR-449a suppresses cell invasion by inhibiting MAP2K1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Cancer Res 2015; 5: 2730–44.
Chen J, Zhou J, Chen X, Yang B, Wang D, Yang P, et al. miRNA-449a is downregulated in osteosarcoma and promotes cell apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Tumour Biol 2015; 36: 8221–9.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education Fund Priority to the Development of Instructions of Higher Leading Doctoral Degree Field (No 20131202130001, to Qing-hua ZHOU), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81572288, to Qing-hua ZHOU; No 81302002, to Xue-bing LI), the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (No 14JCQNJC12300, to Xue-bing LI) and the “New Century” Talent Training Project of Tianjin Medical University General Hospital (2014, to Xue-bing LI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary information is available on the website of Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Table 1
Sequences of siRNA for knockdown of XIST. (DOC 29 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Sequences of shRNA embedded in lentivirus for knockdown of XIST. (DOC 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Yl., Li, Xb., Hou, Yx. et al. The lncRNA XIST exhibits oncogenic properties via regulation of miR-449a and Bcl-2 in human non-small cell lung cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38, 371–381 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.133
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.133
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Unraveling LncRNAs: the future of lung cancer treatment
Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute (2025)
-
Potential roles of lncRNA-XIST/miRNAs/mRNAs in human cancer cells
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2023)
-
Targeting lncRNAs in programmed cell death as a therapeutic strategy for non-small cell lung cancer
Cell Death Discovery (2022)
-
Long non-coding RNA XIST: a novel oncogene in multiple cancers
Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
LncRNA GAS5 modulates the progression of non-small cell lung cancer through repressing miR-221-3p and up-regulating IRF2
Diagnostic Pathology (2021)