Abstract
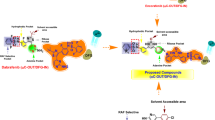
The mutation of B-RafV600E is widespread in a variety of human cancers. Its inhibitors vemurafenib and dabrafenib have been launched as drugs for treating unresectable melanoma, demonstrating that B-RafV600E is an ideal drug target. This study focused on developing novel B-RafV600E inhibitors as drug leads against various cancers with B-RafV600E mutation. Using molecular modeling approaches, 200 blockbuster drugs were spliced to generate 283 fragments followed by molecular docking to identify potent fragments. Molecular structures of potential inhibitors of B-RafV600E were then obtained by fragment reassembly followed by docking to predict the bioactivity of the reassembled molecules. The structures with high predicted bioactivity were synthesized, followed by in vitro study to identify potent B-RafV600E inhibitors. A highly potent fragment binding to the hinge area of B-RafV600E was identified via a docking-based structural splicing approach. Using the fragment, 14 novel structures were designed by structural reassembly, two of which were predicted to be as strong as marketed B-RafV600E inhibitors. Biological evaluation revealed that compound 1m is a potent B-RafV600E inhibitor with an IC50 value of 0.05 μmol/L, which was lower than that of vemurafenib (0.13 μmol/L). Moreover, the selectivity of 1m against B-RafWT was enhanced compared with vemurafenib. In addition, 1m exhibits desirable solubility, bioavailability and metabolic stability in in vitro assays. Thus, a highly potent and selective B-RafV600E inhibitor was designed via a docking-based structural splicing and reassembly strategy and was validated by medicinal synthesis and biological evaluation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Li HF, Chen Y, Rao SS, Chen XM, Liu HC, Qin JH, et al. Recent advances in the research and development of B-Raf inhibitors. Curr Med Chem 2010; 17: 1618–34.
Maik-Rachline G, Seger R . The ERK cascade inhibitors: towards overcoming resistance. Drug Resist Updates 2016; 25: 1–12.
Uehling DE, Harris PA . Recent progress on MAP kinase pathway inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2015; 25: 4047–56.
Menzies AM, Haydu LE, Visintin L, Carlino MS, Howle JR, Thompson JF, et al. Distinguishing clinicopathologic features of patients with V600E and V600K BRAF-mutant metastatic melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 3242–9.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell 2014; 159: 676–90.
Yokota T, Ura T, Shibata N, Takahari D, Shitara K, Nomura M, et al. BRAF mutation is a powerful prognostic factor in advanced and recurrent colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2011; 104: 856–62.
Fransen K, Klintenas M, Osterstrom A, Dimberg J, Monstein HJ, Soderkvist P . Mutation analysis of the BRAF, ARAF and RAF-1 genes in human colorectal adenocarcinomas. Carcinogenesis 2004; 25: 527–33.
DeFazio A, Moujaber T, Etemadmoghadam D, Kennedy C, Chiew YE, Balleine RL, et al. Abstract A25: BRAFV600E mutations in serous ovarian cancer and response to the BRAF inhibitor, dabrafenib. Clin Cancer Res 2016; 22: A25.
Brastianos PK, Taylor-Weiner A, Manley PE, Jones RT, Dias-Santagata D, Thorner AR, et al. Exome sequencing identifies BRAF mutations in papillary craniopharyngiomas. Nat Genet 2014; 46: 161–5.
Fiskus W, Mitsiades N . B-Raf inhibition in the clinic: present and future. Annu Rev Med 2016; 67: 29–43.
Qin J, Xie P, Ventocilla C, Zhou G, Vultur A, Chen Q, et al. Identification of a novel family of BRAFV600E inhibitors. J Med Chem 2012; 55: 5220–30.
Xu Z, Yan G, Wang G, Li B, Zhu J, Sun P, et al. Combining pharmacophore, docking and substructure search approaches to identify and optimize novel B-RafV600E inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2012; 22: 5428–37.
Bollag G, Hirth P, Tsai J, Zhang J, Ibrahim PN, Cho H, et al. Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nature 2010; 467: 596–9.
Flaherty KT, Yasothan U, Kirkpatrick P . Vemurafenib. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2011; 10: 811–2.
Zhang C, Spevak W, Zhang Y, Burton EA, Ma Y, Habets G, et al. RAF inhibitors that evade paradoxical MAPK pathway activation. Nature 2015; 526: 583–6.
Sun XX, Yu Q . Intra-tumor heterogeneity of cancer cells and its implications for cancer treatment. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2015; 36: 1219–27.
Akritopoulou-Zanze I, Hajduk PJ . Kinase-targeted libraries: the design and synthesis of novel, potent, and selective kinase inhibitors. Drug Discov Today 2009; 14: 291–7.
Zhang J, Yang PL, Gray NS . Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 28–39.
Hoi PM, Li S, Vong CT, Tseng HH, Kwan YW, Lee SM . Recent advances in structure-based drug design and virtual screening of VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Methods 2015; 71: 85–91.
Pemovska T, Johnson E, Kontro M, Repasky GA, Chen J, Wells P, et al. Axitinib effectively inhibits BCR-ABL1(T315I) with a distinct binding conformation. Nature 2015; 519: 102–5.
Kumar A, Voet A, Zhang KY . Fragment based drug design: from experimental to computational approaches. Curr Med Chem 2012; 19: 5128–47.
Roberts AW, Davids MS, Pagel JM, Kahl BS, Puvvada SD, Gerecitano JF, et al. Targeting BCL2 with venetoclax in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2016; 374: 311–22.
Joseph-McCarthy D, Campbell AJ, Kern G, Moustakas D . Fragment-based lead discovery and design. J Chem Inf Model 2014; 54: 693–704.
Radoux CJ, Olsson TS, Pitt WR, Groom CR, Blundell TL . Identifying interactions that determine fragment binding at protein hotspots. J Med Chem 2016; 59: 4314–25.
Pipeline Pilot; Accelrys Software Inc: San Diego, CA, USA.
LigPrep, version 2.4, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2010.
Epik, version 2.1; Schro dinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2010.
Shelley JC, Cholleti A, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Timlin MR, Uchimaya M . Epik: a software program for pKa prediction and protonation state generation for drug-like molecules. J Comput Aided Mol Des 2007; 21: 681–91.
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Klicic JJ, Mainz DT, et al. Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem 2004; 47: 1739–49.
Halgren TA, Murphy RB, Friesner RA, Beard HS, Frye LL, Pollard WT, et al. Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. J Med Chem 2004; 47: 1750–9.
Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Halgren TA, et al. Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J Med Chem 2006; 49: 6177–96.
Tolosa L, Donato MT, Gomez-Lechon MJ . General cytotoxicity assessment by means of the MTT assay. Methods Mol Biol 2015; 1250: 333–48.
Xie P, Streu C, Qin J, Bregman H, Pagano N, Meggers E, et al. The crystal structure of BRAF in complex with an organoruthenium inhibitor reveals a mechanism for inhibition of an active form of BRAF kinase. Biochemistry 2009; 48: 5187–98.
Tsai J, Lee JT, Wang W, Zhang J, Cho H, Mamo S, et al. Discovery of a selective inhibitor of oncogenic B-Raf kinase with potent antimelanoma activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008; 105: 3041–6.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81273435, 81302699 and 81321092), the National Science and Technology Major Project (2013ZX09103001001), the Ministry of Science and Technology (2012AA01A305), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai, China (14ZR1447800), the State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs (K20150205) and the Special Program for Applied Research on Super Computation of the NSFC-Guangdong Joint Fund (the second phase).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary information is available at the Acta Pharmacologica Sinica's website.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Docking-Based Structural Splicing and Reassembly Strategy to Develop Novel Deazapurine Derivatives as Potent B-RafV600E Inhibitors (PDF 1905 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Gm., Wang, X., Zhu, Jm. et al. Docking-based structural splicing and reassembly strategy to develop novel deazapurine derivatives as potent B-RafV600E inhibitors. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38, 1059–1068 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.173
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.173