Abstract
Aim:
RNA-binding proteins are a large group of regulators (800–1000 in humans), some of which play significant roles in mRNA local translation. In this study, we analyzed the functions of the protein RNP-1, which was previously discovered in a genetic selection screen for nocodazole suppression.
Methods:
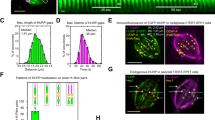
The growth rates and the microtubule networks of Dictyostelium cells were assessed with or without nocodazole (10 μmol/L) in suspension culture. Fluorescent images of RNP-1-GFP and RFP-tubulin were captured when cells were undergoing cytokinesis, then the GFP signal intensity and distance to the nearest centrosome were analyzed by using a computer program written in Matlab®. The RNP-1-GFP-expresseding cells were polarized, and the time-lapse images of cells were captured when cells were chemotaxing to a cAMP source.
Results:
Over-expression of RNP-1 rescued the growth defects caused by the microtubule-destabilizing agent nocodazole. Over-expression of RNP-1 protected microtubules from nocodazole treatment. In cells undergoing cytokinesis, the RNP-1 protein was localized to the polar regions of the cell cortex, and protein levels decreased proportionally as the power of the distance from the cell cortex to the nearest centrosome. In chemotactic cells, the RNP-1 protein localized to the leading edge of moving cells. Sequence analysis revealed that RNP-1 has two RNA-binding domains and is related to cytosolic poly(A)-binding proteins (PABPCs) in humans.
Conclusion:
RNP-1 has roles in protecting microtubules and in directing cortical movement during cytokinesis and cell migration in Dictyostelium cells. The sequence similarity of RNP-1 to human PABPCs suggests that PABPCs may have similar functions in mammalian cells, perhaps in regulating microtubule dynamics and functions during cortical movement in cytokinesis and cell migration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Kuspa A, Dingermann T, Nellen W . Analysis of gene function in Dictyostelium. Experientia 1995; 51: 1116–23.
Torija P, Robles A, Escalante R . Optimization of a large-scale gene disruption protocol in Dictyostelium and analysis of conserved genes of unknown function. BMC Microbiol 2006; 6: 75.
De Brabander MJ, Van de Veire RM, Aerts FE, Borgers M, Janssen PA . The effects of methyl (5-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl) carbamate, (R 17934; NSC 238159), a new synthetic antitumoral drug interfering with microtubules, on mammalian cells cultured in vitro. Cancer Res 1976; 36: 905–16.
Zhou Q, Kee YS, Poirier CC, Jelinek C, Osborne J, Divi S, et al. 14-3-3 coordinates microtubules, Rac, and myosin II to control cell mechanics and cytokinesis. Curr Biol 2010; 20: 1881–9.
Babinec P, Babincova M . Self-organized criticality and dynamic instability of microtubule growth. Z Naturforsch C 1995; 50: 739–40.
Mitchison T, Kirschner M . Dynamic instability of microtubule growth. Nature 1984; 312: 237–42.
Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO . Tracking the ends: a dynamic protein network controls the fate of microtubule tips. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 309–22.
Lansbergen G, Akhmanova A . Microtubule plus end: a hub of cellular activities. Traffic 2006; 7: 499–507.
Etienne-Manneville S . Microtubules in cell migration. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2013; 29: 471–99.
Daou P, Hasan S, Breitsprecher D, Baudelet E, Camoin L, Audebert S, et al. Essential and nonredundant roles for Diaphanous formins in cortical microtubule capture and directed cell migration. Mol Biol Cell 2014; 25: 658–68.
Li D, Gao J, Yang Y, Sun L, Suo S, Luo Y, et al. CYLD coordinates with EB1 to regulate microtubule dynamics and cell migration. Cell Cycle 2014; 13: 974–83.
Weng JH, Liang MR, Chen CH, Tong SK, Huang TC, Lee SP, et al. Pregnenolone activates CLIP-170 to promote microtubule growth and cell migration. Nat Chem Biol 2013; 9: 636–42.
Tang L, Franca-Koh J, Xiong Y, Chen MY, Long Y, Bickford RM, et al. tsunami, the Dictyostelium homolog of the Fused kinase, is required for polarization and chemotaxis. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 2278–90.
Dynes JL, Steward O . Arc mRNA docks precisely at the base of individual dendritic spines indicating the existence of a specialized microdomain for synapse-specific mRNA translation. J Comp Neurol 2012; 520: 3105–19.
Liu-Yesucevitz L, Bassell GJ, Gitler AD, Hart AC, Klann E, Richter JD, et al. Local RNA translation at the synapse and in disease. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 16086–93.
Jakobsen KR, Sorensen E, Brondum KK, Daugaard TF, Thomsen R, Nielsen AL . Direct RNA sequencing mediated identification of mRNA localized in protrusions of human MDA-MB-231 metastatic breast cancer cells. J Mol Signal 2013; 8: 9.
Lawrence JB, Singer RH . Intracellular localization of messenger RNAs for cytoskeletal proteins. Cell 1986; 45: 407–15.
Bassell GJ, Singer RH . Neuronal RNA localization and the cytoskeleton. Results Probl Cell Differ 2001; 34: 41–56.
Huttelmaier S, Zenklusen D, Lederer M, Dictenberg J, Lorenz M, Meng X, et al. Spatial regulation of beta-actin translation by Src-dependent phosphorylation of ZBP1. Nature 2005; 438: 512–5.
Rodriguez AJ, Shenoy SM, Singer RH, Condeelis J . Visualization of mRNA translation in living cells. J Cell Biol 2006; 175: 67–76.
Gu W, Katz Z, Wu B, Park HY, Li D, Lin S, et al. Regulation of local expression of cell adhesion and motility-related mRNAs in breast cancer cells by IMP1/ZBP1. J Cell Sci 2012; 125: 81–91.
Castello A, Fischer B, Eichelbaum K, Horos R, Beckmann BM, Strein C, et al. Insights into RNA biology from an atlas of mammalian mRNA-binding proteins. Cell 2012; 149: 1393–406.
Glisovic T, Bachorik JL, Yong J, Dreyfuss G . RNA-binding proteins and post-transcriptional gene regulation. FEBS Lett 2008; 582: 1977–86.
Castello A, Fischer B, Hentze MW, Preiss T . RNA-binding proteins in Mendelian disease. Trends Genet 2013; 29: 318–27.
Robinson DN, Spudich JA . Dynacortin, a genetic link between equatorial contractility and global shape control discovered by library complementation of a Dictyostelium discoideum cytokinesis mutant. J Cell Biol 2000; 150: 823–38.
Parent CA, Blacklock BJ, Froehlich WM, Murphy DB, Devreotes PN . G protein signaling events are activated at the leading edge of chemotactic cells. Cell 1998; 95: 81–91.
Octtaviani E, Effler JC, Robinson DN . Enlazin, a natural fusion of two classes of canonical cytoskeletal proteins, contributes to cytokinesis dynamics. Mol Biol Cell 2006; 17: 5275–86.
Gerald N, Dai J, Ting-Beall HP, De Lozanne A . A role for Dictyostelium racE in cortical tension and cleavage furrow progression. J Cell Biol 1998; 141: 483–92.
Journet A, Klein G, Brugiere S, Vandenbrouck Y, Chapel A, Kieffer S, et al. Investigating the macropinocytic proteome of Dictyostelium amoebae by high-resolution mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2012; 12: 241–5.
Newell-Litwa KA, Horwitz AR . Cell migration: PKA and RhoA set the pace. Curr Biol 2011; 21: R596–8.
Kermorgant S, Zicha D, Parker PJ . PKC controls HGF-dependent c-Met traffic, signalling and cell migration. EMBO J 2004; 23: 3721–34.
Delorme V, Cayla X, Faure G, Garcia A, Tardieux I . Actin dynamics is controlled by a casein kinase II and phosphatase 2C interplay on Toxoplasma gondii Toxofilin. Mol Biol Cell 2003; 14: 1900–12.
Pichon X, Wilson LA, Stoneley M, Bastide A, King HA . Somers J, et al. RNA binding protein/RNA element interactions and the control of translation. Curr Protein Pept Sci 2012; 13: 294–304.
Skoge M, Adler M, Groisman A, Levine H, Loomis WF, Rappel WJ . Gradient sensing in defined chemotactic fields. Integr Biol (Camb) 2010; 2: 659–68.
Iijima M, Devreotes P . Tumor suppressor PTEN mediates sensing of chemoattractant gradients. Cell 2002; 109: 599–610.
Yumura S, Fukui Y . Spatiotemporal dynamics of actin concentration during cytokinesis and locomotion in Dictyostelium. J Cell Sci 1998; 111: 2097–108.
Smith RW, Blee TK, Gray NK . Poly(A)-binding proteins are required for diverse biological processes in metazoans. Biochem Soc Trans 2014; 42: 1229–37.
Woods AJ, Roberts MS, Choudhary J, Barry ST, Mazaki Y . Sabe H, et al. Paxillin associates with poly(A)-binding protein 1 at the dense endoplasmic reticulum and the leading edge of migrating cells. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 6428–37.
Muddashetty R, Khanam T, Kondrashov A, Bundman M, Iacoangeli A . Kremerskothen J, et al. Poly(A)-binding protein is associated with neuronal BC1 and BC200 ribonucleoprotein particles. J Mol Biol 2002; 321: 433–45.
Chernov KG, Curmi PA, Hamon L, Mechulam A, Ovchinnikov LP, Pastre D . Atomic force microscopy reveals binding of mRNA to microtubules mediated by two major mRNP proteins YB-1 and PABP. FEBS Lett 2008; 582: 2875–81.
Jones LS, Yazzie B, Middaugh CR . Polyanions and the proteome. Mol Cell Proteomics 2004; 3: 746–69.
Acknowledgements
The majority of the bench experiments were performed in the laboratory of Dr Douglas N ROBINSON, and we thank him for his generous support. We also thank the NIH (R01 GM66817 to Douglas N ROBINSON) and AHA (Qiong-qiong ZHOU's fellowship) for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary information is available on the website of Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Movie S1
GFP-tubulin labeled 3D microtubule network in a Dictyostelium cell treated with 10 μmol/L of DMSO. (AVI 321 kb)
Supplementary Movie S2
GFP-tubulin labeled 3D microtubule network in a Dictyostelium cell treated with 10 μmol/L of nocodazole. (AVI 456 kb)
Supplementary Movie S3
RNP-1-GFP localization in Dictyostelium cells during chemotaxing toward cAMP needles. (AVI 171 kb)
Supplementary Movie S4
RNP-1-GFP localization in Dictyostelium cells during chemotaxing toward cAMP needles. (AVI 168 kb)
Supplementary Figure S1
Microtubule networks in the surface cultured cells after overnight nacodazole treatment. (JPG 1135 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ngo, T., Miao, X., Robinson, D. et al. An RNA-binding protein, RNP-1, protects microtubules from nocodazole and localizes to the leading edge during cytokinesis and cell migration in Dictyostelium cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37, 1449–1457 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.57
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.57