Abstract
Aim:
Streptozotocin (STZ) is widely used to induce oxidative damage and to impair glucose metabolism, apoptosis, and tau/Aβ pathology, eventually leading to cognitive deficits in both in vitro and in vivo models of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In this study, we constructed a cell-based platform using STZ to induce stress conditions mimicking the complicated pathologies of AD in vitro, and evaluated the anti-amyloid effects of a small molecule, N-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-[5-chloro-2-methoxy(phenylsulfonyl)anilino]acetamide (LX2343) in the amelioration of cognitive deficits in AD model mice.
Methods:
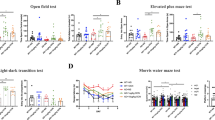
Cell-based assays for screening anti-amyloid compounds were established by assessing Aβ accumulation in HEK293-APPsw and CHO-APP cells, and Aβ clearance in primary astrocytes and SH-SY5Y cells after the cells were treated with STZ in the presence of the test compounds. Autophagic flux was observed using confocal laser scanning microscopy. APP/PS1 transgenic mice were administered LX2343 (10 mg·kg−1·d−1, ip) for 100 d. After LX2343 administration, cognitive ability of the mice was evaluated using Morris water maze test, and senile plaques in the brains were detected using Thioflavine S staining. ELISA assay was used to evaluate Aβ and sAPPβ levels, while Western blot analysis was used to measure the signaling proteins in both cell and animal brains.
Results:
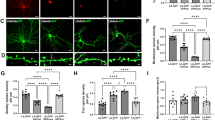
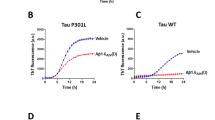
LX2343 (5–20 μmol/L) dose-dependently decreased Aβ accumulation in HEK293-APPsw and CHO-APP cells, and promoted Aβ clearance in SH-SY5Y cells and primary astrocytes. The anti-amyloid effects of LX2343 were attributed to suppressing JNK-mediated APPThr668 phosphorylation, thus inhibiting APP cleavage on one hand, and inhibiting BACE1 enzymatic activity with an IC50 value of 11.43±0.36 μmol/L, on the other hand. Furthermore, LX2343 acted as a non-ATP competitive PI3K inhibitor to negatively regulate AKT/mTOR signaling, thus promoting autophagy, and increasing Aβ clearance. Administration of LX2343 in APP/PS1 transgenic mice significantly ameliorated cognitive deficits and markedly ameliorated the Aβ pathology in their brains.
Conclusion:
LX2343 ameliorates cognitive dysfunction in APP/PS1 transgenic mice via both Aβ production inhibition and clearance promotion, which highlights the potential of LX2343 in the treatment of AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Change history
29 April 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01273-0
References
Hardy J . A hundred years of Alzheimer's disease research. Neuron 2006; 52: 3–13.
Thies W, Bleiler L, Alzheimer's A . 2013 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 2013; 9: 208–45.
Musiek ES, Holtzman DM . Three dimensions of the amyloid hypothesis: time, space and 'wingmen'. Nat Neurosci 2015; 18: 800–6.
Hardy J, Allsop D . Amyloid deposition as the central event in the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 1991; 12: 383–8.
Huang Y, Mucke L . Alzheimer mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell 2012; 148: 1204–22.
Bero AW, Yan P, Roh JH, Cirrito JR, Stewart FR, Raichle ME, et al. Neuronal activity regulates the regional vulnerability to amyloid-beta deposition. Nat Neurosci 2011; 14: 750–6.
Guo X, Jiang W, Li C, Zhu Z, Shen X . Abeta regulation-based multitarget strategy for drug discovery against Alzheimer's disease. Rev Neurosci 2015; 26: 13–30.
Vincent B, Govitrapong P . Activation of the alpha-secretase processing of AbetaPP as a therapeutic approach in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2011; 24: 75–94.
Pettersson M, Stepan AF, Kauffman GW, Johnson DS . Novel gamma-secretase modulators for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: a review focusing on patents from 2010 to 2012. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2013; 23: 1349–66.
Nie Q, Du XG, Geng MY . Small molecule inhibitors of amyloid beta peptide aggregation as a potential therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer's disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2011; 32: 545–51.
Lichtenthaler SF . alpha-secretase in Alzheimer's disease: molecular identity, regulation and therapeutic potential. J Neurochem 2011; 116: 10–21.
Forman M, Tseng J, Palcza J, Leempoels J, Ramael S, Krishna G, et al. The novel BACE inhibitor MK-8931 dramatically lowers CSF A beta peptides in healthy subjects: results from a rising single dose study. Neurology 2012; 78.
Schneider LS, Mangialasche F, Andreasen N, Feldman H, Giacobini E, Jones R, et al. Clinical trials and late-stage drug development for Alzheimer's disease: an appraisal from 1984 to 2014. J Intern Med 2014; 275: 251–83.
Hardy J, Bogdanovic N, Winblad B, Portelius E, Andreasen N, Cedazo-Minguez A, et al. Pathways to Alzheimer's disease. J Intern Med 2014; 275: 296–303.
Schellenberg GD, Montine TJ . The genetics and neuropathology of Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 2012; 124: 305–23.
Buccafusco JJ . Terry AV Jr. Multiple central nervous system targets for eliciting beneficial effects on memory and cognition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2000; 295: 438–46.
Clark TA, Lee HP, Rolston RK, Zhu X, Marlatt MW, Castellani RJ, et al. Oxidative stress and its implications for future treatments and management of Alzheimer disease. Int J Biomed Sci 2010; 6: 225–7.
Kim GH, Kim JE, Rhie SJ, Yoon S . The role of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Neurobiol 2015; 24: 325–40.
Guan ZZ . Cross-talk between oxidative stress and modifications of cholinergic and glutaminergic receptors in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2008; 29: 773–80.
Tiraboschi P, Hansen LA, Thal LJ, Corey-Bloom J . The importance of neuritic plaques and tangles to the development and evolution of AD. Neurology 2004; 62: 1984–9.
Salkovic-Petrisic M, Knezovic A, Hoyer S, Riederer P . What have we learned from the streptozotocin-induced animal model of sporadic Alzheimer's disease, about the therapeutic strategies in Alzheimer's research. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2013; 120: 233–52.
Biswas J, Goswami P, Gupta S, Joshi N, Nath C, Singh S . Streptozotocin induced neurotoxicity involves Alzheimer's related pathological markers: a study on N2A cells. Mol Neurobiol 2016; 53: 2794–806.
Yang S, Xia C, Li S, Du L, Zhang L, Hu Y . Mitochondrial dysfunction driven by the LRRK2-mediated pathway is associated with loss of Purkinje cells and motor coordination deficits in diabetic rat model. Cell Death Dis 2014; 5: e1217.
Zhu Z, Yan J, Jiang W, Yao XG, Chen J, Chen L, et al. Arctigenin effectively ameliorates memory impairment in Alzheimer's disease model mice targeting both beta-amyloid production and clearance. J Neurosci 2013; 33: 13138–49.
Deeds MC, Anderson JM, Armstrong AS, Gastineau DA, Hiddinga HJ, Jahangir A, et al. Single dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes: considerations for study design in islet transplantation models. Lab Anim 2011; 45: 131–40.
Jiang Q, Lee CY, Mandrekar S, Wilkinson B, Cramer P, Zelcer N, et al. ApoE promotes the proteolytic degradation of Abeta. Neuron 2008; 58: 681–93.
Cramer PE, Cirrito JR, Wesson DW, Lee CY, Karlo JC, Zinn AE, et al. ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models. Science 2012; 335: 1503–6.
Zhu Z, Li C, Wang X, Yang Z, Chen J, Hu L, et al. 2,2′,4′-trihydroxychalcone from Glycyrrhiza glabra as a new specific BACE1 inhibitor efficiently ameliorates memory impairment in mice. J Neurochem 2010; 114: 374–85.
Malumbres M, Mangues R, Ferrer N, Lu S, Pellicer A . Isolation of high molecular weight DNA for reliable genotyping of transgenic mice. Biotechniques 1997; 22: 1114–9.
Reiserer RS, Harrison FE, Syverud DC, McDonald MP . Impaired spatial learning in the APPSwe+PSEN1DeltaE9 bigenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Genes Brain Behav 2007; 6: 54–65.
Colombo A, Bastone A, Ploia C, Sclip A, Salmona M, Forloni G, et al. JNK regulates APP cleavage and degradation in a model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis 2009; 33: 518–25.
Yoon SO, Park DJ, Ryu JC, Ozer HG, Tep C, Shin YJ, et al. JNK3 perpetuates metabolic stress induced by Abeta peptides. Neuron 2012; 75: 824–37.
Mazzitelli S, Xu P, Ferrer I, Davis RJ, Tournier C . The loss of c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase activity prevents the amyloidogenic cleavage of amyloid precursor protein and the formation of amyloid plaques in vivo. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 16969–76.
Klionsky DJ, Emr SD . Autophagy as a regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science 2000; 290: 1717–21.
Chan EY, Kir S, Tooze SA . siRNA screening of the kinome identifies ULK1 as a multidomain modulator of autophagy. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 25464–74.
Nave BT, Ouwens M, Withers DJ, Alessi DR, Shepherd PR . Mammalian target of rapamycin is a direct target for protein kinase B: identification of a convergence point for opposing effects of insulin and amino-acid deficiency on protein translation. Biochem J 1999; 344: 427–31.
Memmott RM, Dennis PA . Akt-dependent and -independent mechanisms of mTOR regulation in cancer. Cell Signal 2009; 21: 656–64.
Franke TF, Kaplan DR, Cantley LC, Toker A . Direct regulation of the Akt proto-oncogene product by phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate. Science 1997; 275: 665–8.
Xiao T, Guan X, Nie L, Wang S, Sun L, He T, et al. Rapamycin promotes podocyte autophagy and ameliorates renal injury in diabetic mice. Mol Cell Biochem 2014; 394: 145–54.
Zhao Y, Zhang L, Qiao Y, Zhou X, Wu G, Wang L, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 prevents cardiac dysfunction in streptozotocin-diabetic mice by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis and enhancing autophagy. PLoS One 2013; 8: e75927.
Matthews JA, Belof JL, Acevedo-Duncan M, Potter RL . Glucosamine-induced increase in Akt phosphorylation corresponds to increased endoplasmic reticulum stress in astroglial cells. Mol Cell Biochem 2007; 298: 109–23.
Bjorkoy G, Lamark T, Brech A, Outzen H, Perander M, Overvatn A, et al. p62/SQSTM1 forms protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J Cell Biol 2005; 171: 603–14.
Kimura S, Noda T, Yoshimori T . Dissection of the autophagosome maturation process by a novel reporter protein, tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3. Autophagy 2007; 3: 452–60.
Kimura T, Takabatake Y, Takahashi A, Isaka Y . Chloroquine in cancer therapy: a double-edged sword of autophagy. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 3–7.
Lee JJ, Loh K, Yap YS . PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in breast cancer. Cancer Biol Med 2015; 12: 342–54.
Ikeda H, Hideshima T, Fulciniti M, Perrone G, Miura N, Yasui H, et al. PI3K/p110{delta} is a novel therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Blood 2010; 116: 1460–8.
Araujo DM, Cotman CW . Beta-amyloid stimulates glial cells in vitro to produce growth factors that accumulate in senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 1992; 569: 141–5.
Rai S, Kamat PK, Nath C, Shukla R . Glial activation and post-synaptic neurotoxicity: the key events in Streptozotocin (ICV) induced memory impairment in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2014; 117: 104–17.
Valtorta F, Pennuto M, Bonanomi D, Benfenati F . Synaptophysin: leading actor or walk-on role in synaptic vesicle exocytosis? Bioessays 2004; 26: 445–53.
Jirillo E, Candore G, Magrone T, Caruso C . A scientific approach to anti-ageing therapies: state of the art. Curr Pharm Des 2008; 14: 2637–42.
Simonsen A, Cumming RC, Brech A, Isakson P, Schubert DR, Finley KD . Promoting basal levels of autophagy in the nervous system enhances longevity and oxidant resistance in adult Drosophila. Autophagy 2008; 4: 176–84.
Harrison DE, Strong R, Sharp ZD, Nelson JF, Astle CM, Flurkey K, et al. Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in genetically heterogeneous mice. Nature 2009; 460: 392–5.
Castello MA, Jeppson JD, Soriano S . Moving beyond anti-amyloid therapy for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. BMC Neurol 2014; 14: 169.
Puzzo D, Gulisano W, Arancio O, Palmeri A . The keystone of Alzheimer pathogenesis might be sought in Abeta physiology. Neuroscience 2015; 307: 26–36.
Herrup K . The case for rejecting the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Nat Neurosci 2015; 18: 794–9.
Daviglus ML, Bell CC, Berrettini W, Bowen PE . Connolly ES Jr, Cox NJ, et al. National institutes of health state-of-the-science conference statement: preventing alzheimer disease and cognitive decline. Ann Intern Med 2010; 153: 176–81.
Herrup K . Reimagining Alzheimer's disease — an age-based hypothesis. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 16755–62.
Castello MA, Soriano S . On the origin of Alzheimer's disease. Trials and tribulations of the amyloid hypothesis. Ageing Res Rev 2014; 13: 10–2.
Stranahan AM, Mattson MP . Recruiting adaptive cellular stress responses for successful brain ageing. Nat Rev Neurosci 2012; 13: 209–16.
Gordon J, Amini S, White MK . General overview of neuronal cell culture. Methods Mol Biol 2013; 1078: 1–8.
Groemer TW, Thiel CS, Holt M, Riedel D, Hua Y, Huve J, et al. Amyloid precursor protein is trafficked and secreted via synaptic vesicles. PLoS One 2011; 6: e18754.
Kovalevich J, Langford D . Considerations for the use of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells in neurobiology. Methods Mol Biol 2013; 1078: 9–21.
Bhat R, Crowe EP, Bitto A, Moh M, Katsetos CD, Garcia FU, et al. Astrocyte senescence as a component of Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One 2012; 7: e45069.
Acevedo KM, Opazo CM, Norrish D, Challis LM, Li QX, White AR, et al. Phosphorylation of amyloid precursor protein at threonine 668 is essential for its copper-responsive trafficking in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 2014; 289: 11007–19.
Suzuki T, Nakaya T . Regulation of amyloid beta-protein precursor by phosphorylation and protein interactions. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 29633–7.
Mehan S, Meena H, Sharma D, Sankhla R . JNK: a stress-activated protein kinase therapeutic strategies and involvement in Alzheimer's and various neurodegenerative abnormalities. J Mol Neurosci 2011; 43: 376–90.
Cai H, Wang Y, McCarthy D, Wen H, Borchelt DR, Price DL, et al. BACE1 is the major beta-secretase for generation of Abeta peptides by neurons. Nat Neurosci 2001; 4: 233–4.
He LQ, Lu JH, Yue ZY . Autophagy in ageing and ageing-associated diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2013; 34: 605–11.
Nixon RA, Yang DS . Autophagy failure in Alzheimer's disease — locating the primary defect. Neurobiol Dis 2011; 43: 38–45.
Hochfeld WE, Lee S, Rubinsztein DC . Therapeutic induction of autophagy to modulate neurodegenerative disease progression. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2013; 34: 600–4.
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof Hai-yun SONG (Institute for Nutritional Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China) for help with the lifespan experiments in Drosophila melanogaster. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81220108025, 81473141, and 81273556), NSFC-TRF collaboration projects (81561148011 and DBG5980001) and the Drug Innovation Project of SIMM (CASIMM0120154035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Figures are available on the website of Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figure S1
Both LX2343 and Idelalisib increased Aβ clearance by promoting autophagy. (DOC 2033 kb)
Supplementary Figure S2
Effects of LX2343 on body weight, liver function and swimming speed in mice. (DOC 362 kb)
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Xd., Sun, Gl., Zhou, Tt. et al. Small molecule LX2343 ameliorates cognitive deficits in AD model mice by targeting both amyloid β production and clearance. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37, 1281–1297 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.80
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.80
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer's disease investigation by one-dimensional plasmonic grating chip
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Autophagy and apoptosis cascade: which is more prominent in neuronal death?
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
Long Non-Coding RNA BACE1-AS Modulates Isoflurane-Induced Neurotoxicity to Alzheimer’s Disease Through Sponging miR-214-3p
Neurochemical Research (2020)
-
Lack of insulin resistance in response to streptozotocin treatment in neuronal SH-SY5Y cell line
Journal of Neural Transmission (2020)
-
Knockdown of miR-429 Attenuates Aβ-Induced Neuronal Damage by Targeting SOX2 and BCL2 in Mouse Cortical Neurons
Neurochemical Research (2018)