Abstract
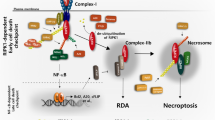
Necroptosis is a type of programmed necrosis regulated by receptor interacting protein kinase 1 (RIP1) and RIP3. Necroptosis is found to be accompanied by an overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), but the role of ROS in regulation of necroptosis remains elusive. In this study, we investigated how shikonin, a necroptosis inducer for cancer cells, regulated the signaling leading to necroptosis in glinoma cells in vitro. Treatment with shikonin (2–10 μmol/L) dose-dependently triggered necrosis and induced overproduction of intracellular ROS in rat C6 and human SHG-44, U87 and U251 glioma cell lines. Moreover, shikonin treatment dose-dependently upregulated the levels of RIP1 and RIP3 and reinforced their interaction in the glioma cells. Pretreatment with the specific RIP1 inhibitor Nec-1 (100 μmol/L) or the specific RIP3 inhibitor GSK-872 (5 μmol/L) not only prevented shikonin-induced glioma cell necrosis but also significantly mitigated the levels of intracellular ROS and mitochondrial superoxide. Mitigation of ROS with MnTBAP (40 μmol/L), which was a cleaner of mitochondrial superoxide, attenuated shikonin-induced glioma cell necrosis, whereas increasing ROS levels with rotenone, which improved the mitochondrial generation of superoxide, significantly augmented shikonin-caused glioma cell necrosis. Furthermore, pretreatment with MnTBAP prevented the shikonin-induced upregulation of RIP1 and RIP3 expression and their interaction while pretreatment with rotenone reinforced these effects. These findings suggest that ROS is not only an executioner of shikonin-induced glioma cell necrosis but also a regulator of RIP1 and RIP3 expression and necrosome assembly.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Stavrovskaya AA, Shushanov SS, Rybalkina EY . Problems of glioblastoma multiforme drug resistance. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2016; 81: 91–100.
Kang JI, Hong JY, Choi JS, Lee SK . Columbianadin inhibits cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis and necroptosis in HCT116 colon cancer cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 2016; 24: 320–7.
Shahsavari Z, Karami-Tehrani F, Salami S . Shikonin induced necroptosis via reactive oxygen species in the T-47D breast cancer cell line. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2015; 16: 7261–6.
Diao Y, Ma X, Min W, Lin S, Kang H, Dai Z, et al. Dasatinib promotes paclitaxel-induced necroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma with phosphorylated caspase-8 by c-Src. Cancer Lett 2016; 379: 12–23.
Han W, Li L, Qiu S, Lu Q, Pan Q, Gu Y, et al. Shikonin circumvents cancer drug resistance by induction of a necroptotic death. Mol Cancer Ther 2007; 6: 1641–9.
McComb S . Aguadé-Gorgorió J, Harder L, Marovca B, Cario G, Eckert C, et al. Activation of concurrent apoptosis and necroptosis by SMAC mimetics for the treatment of refractory and relapsed ALL. Sci Transl Med 2016; 8: 339ra70.
Kaiser WJ, Sridharan H, Huang C, Mandal P, Upton JW, Gough PJ, et al. Toll-like receptor 3-mediated necrosis via TRIF, RIP3, and MLKL. J Biol Chem 2013; 88: 31268–79.
Qin D, Wang X, Li Y, Yang L, Wang R, Peng J, et al. MicroRNA-223-5p and -3p cooperatively suppress necroptosis in ischemic/reperfused hearts. J Biol Chem 2016; 291: 20247–59.
Cai Z, Liu ZG . Execution of RIPK3-regulated necrosis. Mol Cell Oncol 2014; 1: e960759.
Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao D, et al. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3 kinase. Cell 2012; 148: 213–27.
Zhao J, Jitkaew S, Cai Z, Choksi S, Li Q, Luo J, et al. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like is a key receptor interacting protein 3 downstream component of TNF-induced necrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012; 109: 5322–7.
Wang H, Sun L, Su L, Rizo J, Liu L, Wang LF, et al. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein MLKL causes necrotic membrane disruption upon phosphorylation by RIP3. Mol Cell 2014; 54: 133–46.
Cai Z, Jitkaew S, Zhao J, Chiang HC, Choksi S, Liu J, et al. Plasma membrane translocation of trimerized MLKL protein is required for TNF-induced necroptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2014; 16: 55–65.
Huang C, Luo Y, Zhao J, Yang F, Zhao H, Fan W, et al. Shikonin kills glioma cells through necroptosis mediated by RIP-1. PLoS One 2013; 8: e66326.
Wada N, Kawano Y, Fujiwara S, Kikukawa Y, Okuno Y, Tasaki M, et al. Shikonin, dually functions as a proteasome inhibitor and a necroptosis inducer in multiple myeloma cells. Int J Oncol 2015; 46: 963–72.
Fu Z, Deng B, Liao Y, Shan L, Yin F, Wang Z, et al. The anti-tumor effect of shikonin on osteosarcoma by inducing RIP1 and RIP3 dependent necroptosis. BMC Cancer 2013; 13: 580.
Rohde K, Kleinesudeik L, Roesler S, Löwe O, Heidler J, Schröder K, et al. A Bak-dependent mitochondrial amplification step contributes to Smac mimetic/glucocorticoid-induced necroptosis. Cell Death Differ 2017; 24: 83–97.
Ma YM, Peng YM, Zhu QH, Gao AH, Chao B, He QJ, et al. Novel CHOP activator LGH00168 induces necroptosis in A549 human lung cancer cells via ROS-mediated ER stress and NF-κB inhibition. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2016; 37: 1381–90.
Zhao H, Wang C, Lu B, Zhou Z, Jin Y, Wang Z, et al. Pristimerin triggers AIF-dependent programmed necrosis in glioma cells via activation of JNK. Cancer Lett 2016; 374: 136–48.
Ma D, Lu B, Feng C, Wang C, Wang Y, Luo T, et al. Deoxypodophyllotoxin triggers parthanatos in glioma cells via induction of excessive ROS. Cancer Lett 2016; 371: 194–204.
Pokrzywinski KL, Biel TG, Kryndushkin D, Rao VA . Therapeutic targeting of the mitochondria initiates excessive superoxide production and mitochondrial depolarization causing decreased mtDNA integrity. PLoS One 2016; 11: e0168283.
Hanson B . Necroptosis: A new way of dying? Cancer Biol Ther 2016; 17: 899–910.
Chan FK, Moriwaki K, De Rosa MJ . Detection of necrosis by release of lactate dehydrogenase activity. Methods Mol Biol 2013; 979: 65–70.
Miki Y, Akimoto J, Moritake K, Hironaka C, Fujiwara Y . Photodynamic therapy using talaporfin sodium induces concentration-dependent programmed necroptosis in human glioblastoma T98G cells. Lasers Med Sci 2015; 30: 1739–45.
Das A, McDonald DG, Dixon-Mah YN, Jacqmin DJ, Samant VN . Vandergrift WA 3rd et al. RIP1 and RIP3 complex regulates radiation-induced programmed necrosis in glioblastoma. Tumour Biol 2016; 37: 7525–34.
Melo-Lima S, Celeste Lopes M, Mollinedo F . Necroptosis is associated with low procaspase-8 and active RIPK1 and -3 in human glioma cells. Oncoscience 2014; 1: 649–64.
Pasupuleti N, Leon L . Carraway KL 3rd, Gorin F . 5-Benzylglycinyl-amiloride kills proliferating and nonproliferating malignant glioma cells through caspase-independent necroptosis mediated by apoptosis-inducing factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2013; 344: 600–15.
Dasgupta A, Nomura M, Shuck R, Yustein J . Cancer's achilles' heel: apoptosis and necroptosis to the rescue. Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18: 23.
Voss P, Grune T . The nuclear proteasome and the degradation of oxidatively damaged proteins. Amino Acids 2007; 32: 527–34.
Kim YS, Morgan MJ, Choksi S, Liu ZG . TNF-induced activation of the Nox1 NADPH oxidase and its role in the induction of necrotic cell death. Mol Cell 2007; 26: 675–87.
Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ, Lin SC, et al. RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis. Science 2009; 325: 332–6.
Yang JT, Li ZL, Wu JY, Lu FJ, Chen CH . An oxidative stress mechanism of shikonin in human glioma cells. PLoS One 2014; 9: e94180.
Su Z, Yang Z, Xie L, DeWitt JP, Chen Y . Cancer therapy in the necroptosis era. Cell Death Differ 2016; 23: 748–56.
Belizário J, Vieira-Cordeiro L, Enns S . Necroptotic cell death signaling and execution pathway: lessons from knockout mice. Mediators Inflamm 2015; 2015: 128076.
Hannes S, Abhari BA, Fulda S . Smac mimetic triggers necroptosis in pancreatic carcinoma cells when caspase activation is blocked. Cancer Lett 2016; 380: 31–8.
Piao JL, Cui ZG, Furusawa Y, Ahmed K, Rehman MU, Tabuchi Y, et al. The molecular mechanisms and gene expression profiling for shikonin-induced apoptotic and necroptotic cell death in U937 cells. Chem Biol Interact 2013; 205: 119–27.
Zhang Y, Su SS, Zhao S, Yang Z, Zhong CQ, Chen X, et al. RIP1 autophosphorylation is promoted by mitochondrial ROS and is essential for RIP3 recruitment into necrosome. Nat Commun 2017; 8: 14329.
Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray TD, Guildford M, et al. Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell 2009; 137: 1112–23.
Xu X, Chua CC, Kong J, Kostrzewa RM, Kumaraguru U, Hamdy RC, et al. Necrostatin-1 protects against glutamate-induced glutathione depletion and caspase-independent cell death in HT-22 cells. J Neurochem 2007; 103: 2004–14.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81372697), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-12-0233), the Changbaishan Scholar Project of Jilin Province (2013026), the Scientific Research Foundation of Jilin province (20150414013GH and 20160101127JC), and the Bethune Project B of Jilin University (No 2012203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary information is available at the website of Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Material Figure S1
Representative images of shikonin-induced morphological changes captured with a transmission electron microscope. (JPG 298 kb)
Supplementary Material Figure S2
(A) Statistical analysis of shikonin-induced changes in the RIP1 and RIP3 protein levels at 2 h of incubation. (JPG 1039 kb)
Supplementary Material Figure S3
(A and B) Representative fluorescence microscopic images of SHG-44 cells detected by the mitochondrial superoxide probe Mitosox Red and the ROS probe DCFH-DA, respectively (20×). (JPG 282 kb)
Supplementary Material Figure S4
(A) Representative images of SHG-44 cells under a fluorescence microscope showed that MnTBAP pretreatment mitigated the rotenone-induced production of mitochondrial superoxide (20×). (JPG 333 kb)
Supplementary Material Figure S5
(A) Statistical analysis of the shikonin-induced upregulation of RIP1 and RIP3 in cells pretreated with rotenone. (JPG 238 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LU, B., GONG, X., WANG, Zq. et al. Shikonin induces glioma cell necroptosis in vitro by ROS overproduction and promoting RIP1/RIP3 necrosome formation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38, 1543–1553 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.112
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.112
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Shikonin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma cells by upregulating p53 and promoting miR-361-5p level to suppress ZEB1 expression
BMC Neuroscience (2025)
-
FGD3 mediates lytic cell death, enhancing efficacy and immunogenicity of chemotherapy agents in breast cancer
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2025)
-
A novel approach to glioblastoma multiforme treatment using modulation of key pathways by naturally occurring small molecules
Inflammopharmacology (2025)
-
Acute Administration of Edaravone Improves Cognitive Impairment in a Mouse Model of mPFC Ischemia: Crosstalk Between Necroptosis, Neuroinflammation, and Antioxidant Defense
Molecular Neurobiology (2025)
-
Amplification of tumor oxidative stresses with Shikonin-Fe(II) liposomal nanomedicine for enhanced anticancer treatment
Journal of Materials Science (2025)