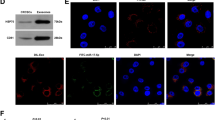
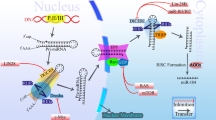
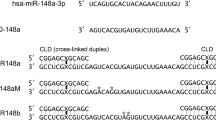Abstract
Apoptosis has a vital role in maintaining tissue homeostasis, and dysregulation of the apoptotic pathway is now widely recognized as a key step in tumourigenesis. Increasingly, evidence has demonstrated that microRNA (miRNA) can exert various biological functions in tumours by targeting oncogenes or tumour suppressors. Nevertheless, the role of miRNA in apoptosis remains unclear. Here we show that ectopical expression of miR-148a can induce apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. In addition, MYB can inhibit miR-148a by directly acting on the transcription factor binding site in miR-148a gene and miR-148a can posttranscriptionally silence Bcl-2. Subsequently, the intrinsic apoptosis pathway is activated by releasing cytochrome c, cleaving caspase 9, caspase 3 and PARP, which eventually induce cancer-cell apoptosis. These findings are part of a hitherto undocumented apoptotic regulatory pathway in which a pleiotropic transcription factor controls the expression of a miRNA and the miRNA inhibits the target, leading to activation of an intrinsic mitochondrial pathway and tumour apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- miR-NTC:
-
control vector
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- kb:
-
kilobase pairs
- TFBS:
-
transcription factor binding site
- TSS:
-
transcription start site
- ChIP:
-
chromatin immunoprecipitation
- EMSA:
-
electrophoresis mobility shift
- UTR:
-
untranslated region
- anti-148a:
-
anti-miR-148a or antisense oligonucleotides for miR-148a
- BLK:
-
blank
- siMYB:
-
MYB-siRNA or siRNA for MYB
- si-oligos:
-
control oligonucleotides
- Ago2:
-
Argonaute2
- RISC:
-
RNA-induced silencing complex
- ORF:
-
open reading frame
References
Cotter TG . Apoptosis and cancer: the genesis of a research field. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 501–507.
Erster S, Mihara M, Kim RH, Petrenko O, Moll UM . In vivo mitochondrial p53 translocation triggers a rapid first wave of cell death in response to DNA damage that can precede p53 target gene activation. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 6728–6741.
Green DR, Kroemer G . Cytoplasmic functions of the tumour suppressor p53. Nature 2009; 458: 1127–1130.
Hoffman B, Liebermann DA . Apoptotic signaling by c-MYC. Oncogene 2008; 27: 6462–6472.
Klefstrom J, Verschuren EW, Evan G . c-Myc augments the apoptotic activity of cytosolic death receptor signaling proteins by engaging the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 43224–43232.
Pelengaris S, Khan M, Evan GI . Suppression of Myc-induced apoptosis in beta cells exposes multiple oncogenic properties of Myc and triggers carcinogenic progression. Cell 2002; 109: 321–334.
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V . The C elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993; 75: 843–854.
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116: 281–297.
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009; 136: 215–233.
Carrington JC, Ambros V . Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science 2003; 301: 336–338.
Ambros V . MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 2003; 113: 673–676.
Chang TC, Wentzel EA, Kent OA, Ramachandran K, Mullendore M, Lee KH et al. Transactivation of miR-34a by p53 broadly influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol Cell 2007; 26: 745–752.
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 13944–13949.
Li J, Huang H, Sun L, Yang M, Pan C, Chen W et al. MiR-21 indicates poor prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinomas as an apoptosis inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 3998–4008.
Park JK, Lee EJ, Esau C, Schmittgen TD . Antisense inhibition of microRNA-21 or -221 arrests cell cycle, induces apoptosis, and sensitizes the effects of gemcitabine in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2009; 38: e190–e199.
Li T, Li D, Sha J, Sun P, Huang Y . MicroRNA-21 directly targets MARCKS and promotes apoptosis resistance and invasion in prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 383: 280–285.
Braconi C, Huang N, Patel T . MicroRNA-dependent regulation of DNA methyltransferase-1 and tumor suppressor gene expression by interleukin-6 in human malignant cholangiocytes. Hepatology 2010; 51: 881–890.
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, Ropero S, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Blanco D et al. A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 13556–13561.
Wingender E, Karas H, Knuppel R . TRANSFAC database as a bridge between sequence data libraries and biological function. Pac Symp Biocomput 1997: 477–485.
Ramsay RG, Gonda TJ . MYB function in normal and cancer cells. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 523–534.
Youle RJ, Strasser A . The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 47–59.
Cory S, Adams JM . The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 647–656.
Cory S, Huang DC, Adams JM . The Bcl-2 family: roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene 2003; 22: 8590–8607.
Chen Y, Song Y, Wang Z, Yue Z, Xu H, Xing C et al. Altered expression of MiR-148a and MiR-152 in gastrointestinal cancers and its clinical significance. J Gastrointest Surg 2010; 14: 1170–1179.
Takagi S, Nakajima M, Mohri T, Yokoi T . Post-transcriptional regulation of human pregnane X receptor by micro-RNA affects the expression of cytochrome P450 3A4. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 9674–9680.
Zhou J, Liu M, Zhai Y, Xie W . The antiapoptotic role of pregnane X receptor in human colon cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol 2008; 22: 868–880.
Masuyama H, Nakatsukasa H, Takamoto N, Hiramatsu Y . Down-regulation of pregnane X receptor contributes to cell growth inhibition and apoptosis by anticancer agents in endometrial cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol 2007; 72: 1045–1053.
Zucchini N, de Sousa G, Bailly-Maitre B, Gugenheim J, Bars R, Lemaire G et al. Regulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL anti-apoptotic protein expression by nuclear receptor PXR in primary cultures of human and rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 2005; 1745: 48–58.
Zhu W, Shan X, Wang T, Shu Y, Liu P . miR-181b modulates multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer Feb 16.
Hooper J, Maurice D, Argent-Katwala MJ, Weston K . Myb proteins regulate expression of histone variant H2A Z during thymocyte development. Immunology 2008; 123: 282–289.
Chen J, Kremer CS, Bender TP . The carbonic anhydrase I locus contains a c-Myb target promoter and modulates differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells. Oncogene 2006; 25: 2758–2772.
Wang DM, Sevcikova S, Wen H, Roberts S, Lipsick JS . v-Myb represses the transcription of Ets-2. Oncogene 2007; 26: 1238–1244.
Afroze T, Husain M . c-Myb-binding sites mediate G(1)/S-associated repression of the plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase-1 promoter. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 9062–9069.
Lang G, White JR, Argent-Katwala MJ, Allinson CG, Weston K . Myb proteins regulate the expression of diverse target genes. Oncogene 2005; 24: 1375–1384.
Wolff L, Schmidt M, Koller R, Haviernik P, Watson R, Bies J et al. Three genes with different functions in transformation are regulated by c-Myb in myeloid cells. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2001; 27: 483–488.
Zhao H, Kalota A, Jin S, Gewirtz AM . The c-myb proto-oncogene and microRNA-15a comprise an active autoregulatory feedback loop in human hematopoietic cells. Blood 2009; 113: 505–516.
Xue H, Lu B, Zhang J, Wu M, Huang Q, Wu Q et al. Identification of serum biomarkers for colorectal cancer metastasis using a differential secretome approach. J Proteome Res 2010; 9: 545–555.
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30770989, 81090421), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang province (D2080011), Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang province (2007C13020), Department of Education of Zhejiang Province (Y200908956) and National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the Eleventh Five-Year Plan Period of China (2006BAI0214 and 2009BAI80B00). We thank Dr Brian Eyden (Manchester, UK) for English language assistance.
Author ContributionsM Lai conceived the project and supervised research. H Zhang designed and performed experiments. Y Li performed DNA constructs. Q Hang collected tumour samples and executed immunohistochemistry. X Ren fulfilled statistical analysis. H Hu conducted apoptosis assay. H Sheng performed tumour cell xenograft study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by D Huang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Li, Y., Huang, Q. et al. MiR-148a promotes apoptosis by targeting Bcl-2 in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Differ 18, 1702–1710 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.28
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.28
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of miRNA-mRNA regulatory pairs associated with colorectal cancer and the role in tumor immunity
BMC Genomics (2023)
-
Chicken miR-148a-3p regulates immune responses against AIV by targeting the MAPK signalling pathway and IFN-γ
Veterinary Research (2023)
-
Mir-675-5p supports hypoxia-induced drug resistance in colorectal cancer cells
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
MicroRNAs as biomarkers for prostate cancer prognosis: a systematic review and a systematic reanalysis of public data
British Journal of Cancer (2022)
-
MicroRNAs and drug resistance in colorectal cancer with special focus on 5-fluorouracil
Molecular Biology Reports (2022)