Abstract
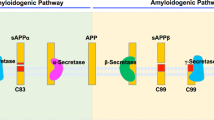
Dysregulation of β-site APP-cleaving enzyme (BACE) and/or γ-secretase leads to anomalous production of amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) and contributes to the etiology of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Since these secretases mediate proteolytic processing of numerous proteins, little success has been achieved to treat AD by secretase inhibitors because of inevitable undesired side effects. Thus, it is of importance to unravel the regulatory mechanisms of these secretases. Here, we show that δ-opioid receptor (DOR) promotes the processing of Aβ precursor protein (APP) by BACE1 and γ-secretase, but not that of Notch, N-cadherin or APLP. Further investigation reveals that DOR forms a complex with BACE1 and γ-secretase, and activation of DOR mediates the co-endocytic sorting of the secretases/receptor complex for APP endoproteolysis. Dysfunction of the receptor retards the endocytosis of BACE1 and γ-secretase and thus the production of Aβ. Consistently, knockdown or antagonization of DOR reduces secretase activities and ameliorates Aβ pathology and Aβ-dependent behavioral deficits, but does not affect the processing of Notch, N-cadherin or APLP in AD model mice. Our study not only uncovers a molecular mechanism for the formation of a DOR/secretase complex that regulates the specificity of secretase for Aβ production but also suggests that intervention of either formation or trafficking of the GPCR/secretase complex could lead to a new strategy against AD, potentially with fewer side effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Albert MS . Cognitive and neurobiologic markers of early Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93:13547–13551.
Selkoe DJ . Alzheimer's disease: genotypes, phenotypes, and treatments. Science 1997; 275:630–631.
Selkoe DJ . Deciphering the genesis and fate of amyloid β-protein yields novel therapies for Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest 2002; 110:1375–1381.
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ . The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002; 297:353–356.
Selkoe DJ . Clearing the brain's amyloid cobwebs. Neuron 2001; 32:177–180.
Kang J, Lemaire HG, Unterbeck A, et al. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature 1987; 325:733–736.
Sinha S, Anderson JP, Barbour R, et al. Purification and cloning of amyloid precursor protein β-secretase from human brain. Nature 1999; 402:537–540.
Takasugi N, Tomita T, Hayashi I, et al. The role of presenilin cofactors in the gamma-secretase complex. Nature 2003; 422:438–441.
Vassar R, Bennett BD, Babu-Khan S, et al. Beta-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein by the transmembrane aspartic protease BACE. Science 1999; 286:735–741.
Sinha S, Lieberburg I . Cellular mechanisms of beta-amyloid production and secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96:11049–11053.
De Strooper B . Aph-1, Pen-2, and Nicastrin with Presenilin generate an active gamma-secretase complex. Neuron 2003; 38:9–12.
Lichtenthaler SF, Wang R, Grimm H, Uljon SN, Masters CL, Beyreuther K . Mechanism of the cleavage specificity of Alzheimer's disease γ-secretase identified by phenylalanine-scanning mutagenesis of the transmembrane domain of the amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96:3053–3058.
Ling Y, Morgan K, Kalsheker N . Amyloid precursor protein (APP) and the biology of proteolytic processing: relevance to Alzheimer's disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2003; 35:1505–1535.
Iwata N, Tsubuki S, Takaki Y, et al. Metabolic regulation of brain Abeta by neprilysin. Science 2001; 292:1550–1552.
Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, et al. Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid β-protein, and the β-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100:4162–4167.
Eckman EA, Watson M, Marlow L, Sambamurti K, Eckman CB . Alzheimer's disease β-amyloid peptide is increased in mice deficient in endothelin-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem 2003; 278:2081–2084.
Hemming ML, Selkoe DJ . Amyloid β-protein is degraded by cellular angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and elevated by an ACE inhibitor. J Biol Chem 2005; 280:37644–37650.
Blennow K, de Leon MJ, Zetterberg H . Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 2006; 368:387–403.
Nitsch RM, Slack BE, Wurtman RJ, Growdon JH . Release of Alzheimer amyloid precursor derivatives stimulated by activation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Science 1992; 258:304–307.
Xu H, Gouras GK, Greenfield JP, et al. Estrogen reduces neuronal generation of Alzheimer β-amyloid peptides. Nat Med 1998; 4:447–451.
Weggen S, Eriksen JL, Das P, et al. A subset of NSAIDs lower amyloidogenic Aβ42 independently of cyclooxygenase activity. Nature 2001; 414:212–216.
Cai D, Netzer WJ, Zhong M, et al. Presenilin-1 uses phospholipase D1 as a negative regulator of β-amyloid formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103:1941–1946.
Ni Y, Zhao, X, Bao G, et al. Activation of β2-adrenergic receptor stimulates γ-secretase activity and accelerates amyloid plaque formation. Nat Med 2006; 12:1390–1396.
Thathiah A, Spittaels K, Hoffmann M, et al. The orphan G protein-coupled receptor 3 modulates amyloid-β peptide generation in neurons. Science 2009; 323:946–951.
Bramham CR, Milgram NW, Srebro B . Delta opioid receptor activation is required to induce LTP of synaptic transmission in the lateral perforant path in vivo. Brain Res 1991; 567:42–50.
Wagner JJ, Terman GW, Chavkin C . Endogenous dynorphins inhibit excitatory neurotransmission and block LTP induction in the hippocampus. Nature 1993; 363:451–454.
Gallagher M, King RA, Young NB . Opiate antagonists improve spatial memory. Science 1983; 221:975–976.
Izquierdo I, Paiva AC, Elisabetsky E . Post-training intraperitoneal administration of leu-enkephalin and β-endorphin causes retrograde amnesia for two different tasks in rats. Behav Neural Biol 1980; 28:246–250.
Reisberg B, Ferris SH, Anand R, et al. Effects of naloxone in senile dementia: a double-blind trial. N Engl J Med 1983; 308:721–722.
Tariot PN, Sunderland T, Murphy DL, et al. Design and interpretation of opiate antagonist trials in dementia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 1986; 10:611–626.
Pomara N, Roberts R, Rhiew HB, Stanley M, Gershon S . Multiple, single-dose naltrexone administrations fail to effect overall cognitive functioning and plasma cortisol in individuals with probable Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 1985; 6:233–236.
Serby M, Resnick R, Jordan B, Adler J, Corwin J, Rotrosen JP . Naltrexone and Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 1986; 10:587–590.
Kieffer BL, Gaveriaux-Ruff C . Exploring the opioid system by gene knockout. Prog Neurobiol 2002; 66:285–306.
Mathieu-Kia AM, Fan LQ, Kreek MJ, Simon EJ, Hiller JM . Mu-, delta- and κ-opioid receptor populations are differentially altered in distinct areas of postmortem brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. Brain Res 2001; 893:121–134.
Risser D, You ZB, Cairns N, et al. Endogenous opioids in frontal cortex of patients with Down syndrome. Neurosci Lett 1996; 203:111–114.
Meilandt WJ, Yu GQ, Chin J, et al. Enkephalin elevations contribute to neuronal and behavioral impairments in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 2008; 28:5007–5017.
Marks N, Berg MJ . Neurosecretases provide strategies to treat sporadic and familial Alzheimer disorders. Neurochem Int 2008; 52:184–215.
Schroeter EH, Kisslinger JA, Kopan R . Notch-1 signalling requires ligand-induced proteolytic release of intracellular domain. Nature 1998; 393:382–386.
Karlstrom H, Bergman A, Lendahl U, Naslund J, Lundkvist J . A sensitive and quantitative assay for measuring cleavage of presenilin substrates. J Biol Chem 2002; 277:6763–6766.
Allen JA, Halverson-Tamboli RA, Rasenick MM . Lipid raft microdomains and neurotransmitter signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci 2007; 8:128–140.
Sargiacomo M, Lisanti M, Graeve L, Le Bivic A, Rodriguez-Boulan E . Integral and peripheral protein composition of the apical and basolateral membrane domains in MDCK cells. J Membr Biol 1989; 107:277–286.
von Arnim CA, Tangredi MM, Peltan ID, et al. Demonstration of BACE (β-secretase) phosphorylation and its interaction with GGA1 in cells by fluorescence-lifetime imaging microscopy. J Cell Sci 2004; 117:5437–5445.
Kaether C, Lammich S, Edbauer D, et al. Presenilin-1 affects trafficking and processing of βAPP and is targeted in a complex with nicastrin to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol 2002; 158:551–561.
Whistler JL, Enquist J, Marley A, et al. Modulation of postendocytic sorting of G protein-coupled receptors. Science 2002; 297:615–620.
Finn AK, Whistler JL . Endocytosis of the mu opioid receptor reduces tolerance and a cellular hallmark of opiate withdrawal. Neuron 2001; 32:829–839.
Afify EA, Law PY, Riedl M, Elde R, Loh HH . Role of carboxyl terminus of mu-and δ-opioid receptor in agonist-induced down-regulation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1998; 54:24–34.
Portoghese PS, Sultana M, Takemori AE . Naltrindole, a highly selective and potent non-peptide δ opioid receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 1988; 146:185–186.
Ward SJ, Portoghese PS, Takemori AE . Pharmacological characterization in vivo of the novel opiate, β-funaltrexamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1982; 220:494–498.
Waldhoer M, Bartlett SE, Whistler JL . Opioid receptors. Annu Rev Biochem 2004; 73:953–990.
Dhawan BN, Cesselin F, Raghubir R, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XII. Classification of opioid receptors. Pharmacol Rev 1996; 48:567–592.
Fernandez B, Antelo MT, Kitchen I, Viveros MP . Effects of neonatal naltrindole treatment on antinociceptive and behavioral responses to mu and kappa agonists in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1999; 62:145–149.
Jankowsky JL, Slunt HH, Ratovitski T, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Borchelt DR . Co-expression of multiple transgenes in mouse CNS: a comparison of strategies. Biomol Eng 2001; 17:157–165.
Garcia-Alloza M, Robbins EM, Zhang-Nunes SX, et al. Characterization of amyloid deposition in the APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol Dis 2006; 24:516–524.
Reiserer RS, Harrison FE, Syverud DC, McDonald MP . Impaired spatial learning in the APPSwe + PSEN1ΔE9 bigenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Genes Brain Behav 2007; 6:54–65.
Kitchen I, Pinker SR . Antagonism of swim-stress-induced antinociception by the δ-opioid receptor antagonist naltrindole in adult and young rats. Br J Pharmacol 1990; 100:685–688.
Berrendero F, Maldonado R . Involvement of the opioid system in the anxiolytic-like effects induced by δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2002; 163:111–117.
Matsuzawa S, Suzuki T, Misawa M, Nagase H . Involvement of mu- and δ-opioid receptors in the ethanol-associated place preference in rats exposed to foot shock stress. Brain Res 1998; 803:169–177.
Negus SS, Henriksen SJ, Mattox A, et al. Effect of antagonists selective for mu, δ and κ opioid receptors on the reinforcing effects of heroin in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1993; 265:1245–1252.
Cao D, Lu H, Lewis TL, Li L . Intake of sucrose-sweetened water induces insulin resistance and exacerbates memory deficits and amyloidosis in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 2007; 282:36275–6282.
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Tago H, McGeer EG . Reactive microglia in patients with senile dementia of the Alzheimer type are positive for the histocompatibility glycoprotein HLA-DR. Neurosci Lett 1987; 79:195–200.
Simard AR, Soulet D, Gowing G, Julien JP, Rivest S . Bone marrow-derived microglia play a critical role in restricting senile plaque formation in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 2006; 49:489–502.
Eggert S, Paliga K, Soba P, et al. The proteolytic processing of the amyloid precursor protein gene family members APLP-1 and APLP-2 involves α-, β-, γ-, and epsilon-like cleavages: modulation of APLP-1 processing by N-glycosylation. J Biol Chem 2004; 279:18146–18156.
Chishti MA, Yang DS, Janus C, et al. Early-onset amyloid deposition and cognitive deficits in transgenic mice expressing a double mutant form of amyloid precursor protein 695. J Biol Chem 2001; 276:21562–21570.
Qin XF, An DS, Chen IS, Baltimore D . Inhibiting HIV-1 infection in human T cells by lentiviral-mediated delivery of small interfering RNA against CCR5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100:183–188.
Westerman MA, Cooper-Blacketer D, Mariash A, et al. The relationship between Aβ and memory in the Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 2002; 22:1858–1867.
Lazarov O, Robinson J, Tang YP, et al. Environmental enrichment reduces Aβ levels and amyloid deposition in transgenic mice. Cell 2005; 120:701–713.
Farmery MR, Tjernberg LO, Pursglove SE, Bergman A, Winblad B, Naslund J . Partial purification and characterization of γ-secretase from post-mortem human brain. J Biol Chem 2003; 278:24277–24284.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr David Westaway (University of Alberta) for TgCRND8 mice, Dr David Baltimore (California Institute of Technology) for lentiviral constructs, Dr Raphael Kopan (Washington University) for the plasmid of myc-tagged NotchΔE and Dr Johan Lundkvist (Karolinska Institutet) for the plasmid of Gal4-driven luciferase reporter gene, the plasmid of APP/CTFβ-GVP and NΔE-GVP. We appreciate Shunmei Xin, Shan Chen and Xianglu Zeng for their technical assistance. We thank all members of the lab for sharing reagents and advice. This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (2009ZX09103-684), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30621091, 30625014, 30623003, 30871285 and 90713047), the Shanghai Municipal Commission for Science and Technology (07PJ14099 and 09JC1416400), and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2007KIP204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, Figure S1
DOR and MORDT but not MOR or DORMT enhances BACE and PS1 endocytic trafficking. (PDF 125 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S2
The effect of NTI treatment on mice. (PDF 138 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teng, L., Zhao, J., Wang, F. et al. A GPCR/secretase complex regulates β- and γ-secretase specificity for Aβ production and contributes to AD pathogenesis. Cell Res 20, 138–153 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2010.3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2010.3
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
G-protein coupled receptor, PI3K and Rho signaling pathways regulate the cascades of Tau and amyloid-β in Alzheimer’s disease
Molecular Biomedicine (2021)
-
A tricyclic antidepressant, amoxapine, reduces amyloid-β generation through multiple serotonin receptor 6-mediated targets
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Rab21, a Novel PS1 Interactor, Regulates γ-Secretase Activity via PS1 Subcellular Distribution
Molecular Neurobiology (2017)
-
Exploring novel mechanistic insights in Alzheimer’s disease by assessing reliability of protein interactions
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
TRPC6 specifically interacts with APP to inhibit its cleavage by γ-secretase and reduce Aβ production
Nature Communications (2015)