Abstract
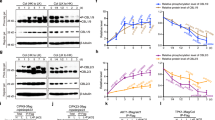
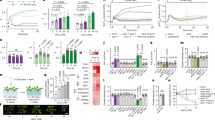
Potassium (K+) channel function is fundamental to many physiological processes. However, components and mechanisms regulating the activity of plant K+ channels remain poorly understood. Here, we show that the calcium (Ca2+) sensor CBL4 together with the interacting protein kinase CIPK6 modulates the activity and plasma membrane (PM) targeting of the K+ channel AKT2 from Arabidopsis thaliana by mediating translocation of AKT2 to the PM in plant cells and enhancing AKT2 activity in oocytes. Accordingly, akt2, cbl4 and cipk6 mutants share similar developmental and delayed flowering phenotypes. Moreover, the isolated regulatory C-terminal domain of CIPK6 is sufficient for mediating CBL4- and Ca2+-dependent channel translocation from the endoplasmic reticulum membrane to the PM by a novel targeting pathway that is dependent on dual lipid modifications of CBL4 by myristoylation and palmitoylation. Thus, we describe a critical mechanism of ion-channel regulation where a Ca2+ sensor modulates K+ channel activity by promoting a kinase interaction-dependent but phosphorylation-independent translocation of the channel to the PM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Xu J, Li HD, Chen LQ et al. A protein kinase, interacting with two calcineurin B-like proteins, regulates K+ transporter AKT1 in Arabidopsis. Cell 2006; 125:1347–1360.
Lee SC, Lan WZ, Kim BG et al. A protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation network regulates a plant potassium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104:15959–15964.
Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Grant JJ, et al. Two calcineurin B-like calcium sensors, interacting with protein kinase CIPK23, regulate leaf transpiration and root potassium uptake in Arabidopsis. Plant J 2007; 52:223–239.
Batistič O, Kudla J . Plant calcineurin B-like proteins and their interacting protein kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1793:985–992.
Weinl S, Kudla J . The CBL-CIPK Ca2+-decoding signaling network: function and perspectives. New Phytol 2009; 184:517–528.
Albrecht V, Ritz O, Linder S, Harter K, Kudla J . The NAF domain defines a novel protein-protein interaction module conserved in Ca2+-regulated kinases. EMBO J 2001; 20:1051–1063.
Batistič O, Kudla J . Integration and channeling of calcium signaling through the CBL calcium sensor/CIPK protein kinase network. Planta 2004; 219:915–924.
Kudla J, Batistič O, Hashimoto K . Calcium signals: the lead currency of plant information processing. Plant Cell 2010; 22:541–563.
Albrecht V, Weinl S, Blazevic D, et al. The calcium sensor CBL1 integrates plant responses to abiotic stresses. Plant J 2003; 36:457–470.
D'Angelo C, Weinl S, Batistič O, et al. Alternative complex formation of the Ca2+-regulated protein kinase CIPK1 controls abscisic acid-dependent and independent stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J 2006; 48:857–872.
Kim BG, Waadt R, Cheong YH, et al. The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 2007; 52:473–484.
Batistič O, Sorek N, Schultke S, Yalovsky S, Kudla J . Dual fatty acyl modification determines the localization and plasma membrane targeting of CBL/CIPK Ca2+ signaling complexes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2008; 20:1346–1362.
Marten I, Hoth S, Deeken R, et al. AKT3, a phloem-localized K+ channel, is blocked by protons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96:7581–7586.
Lacombe B, Pilot G, Michard E, et al. A shaker-like K+ channel with weak rectification is expressed in both source and sink phloem tissues of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2000; 12:837–851.
Dreyer I, Michard E, Lacombe B, Thibaud JB . A plant Shaker-like K+ channel switches between two distinct gating modes resulting in either inward-rectifying or “leak” current. FEBS Lett 2001; 505:233–239.
Cherel I, Michard E, Platet N, et al. Physical and functional interaction of the Arabidopsis K+ channel AKT2 and phosphatase AtPP2CA. Plant Cell 2002; 14:1133–1146.
Michard E, Dreyer I, Lacombe B, Sentenac H, Thibaud JB . Inward rectification of the AKT2 channel abolished by voltage-dependent phosphorylation. Plant J 2005; 44:783–797.
Michard E, Lacombe B, Poree F, et al. A unique voltage sensor sensitizes the potassium channel AKT2 to phosphoregulation. J Gen Physiol 2005; 126:605–617.
Ma D, Jan LY . ER transport signals and trafficking of potassium channels and receptors. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2002; 12:287–292.
Hasdemir B, Fitzgerald DJ, Prior IA, Tepikin AV, Burgoyne RD . Traffic of Kv4 K+ channels mediated by KChIP1 is via a novel post-ER vesicular pathway. J Cell Biol 2005; 171:459–469.
Mikosch M, Kaberich K, Homann U . ER export of KAT1 is correlated to the number of acidic residues within a triacidic motif. Traffic 2009; 10:1481–1487.
Xicluna J, Lacombe B, Dreyer I, et al. Increased functional diversity of plant K+ channels by preferential heteromerization of the shaker-like subunits AKT2 and KAT2. J Biol Chem 2007; 282:486–494.
Ishitani M, Liu J, Halfter U, et al. SOS3 function in plant salt tolerance requires N-myristoylation and calcium binding. Plant Cell 2000; 12:1667–1678.
Dennison KL, Robertson WR, Lewis BD, et al. Functions of AKT1 and AKT2 potassium channels determined by studies of single and double mutants of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 2001; 127:1012–1019.
Deeken R, Geiger D, Fromm J, et al. Loss of the AKT2/3 potassium channel affects sugar loading into the phloem of Arabidopsis. Planta 2002; 216:334–344.
Quintero FJ, Ohta M, Shi H, Zhu JK, Pardo JM . Reconstitution in yeast of the Arabidopsis SOS signaling pathway for Na+ homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99:9061–9066.
Fujii H, Zhu JK . An autophosphorylation site of the protein kinase SOS2 is important for salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 2009; 2:183–190.
Mahajan S, Sopory SK, Tuteja N . Cloning and characterization of CBL-CIPK signalling components from a legume (Pisum sativum). FEBS J 2006; 273:907–925.
Tripathi V, Parasuraman B, Laxmi A, Chattopadhyay D . CIPK6, a CBL-interacting protein kinase is required for development and salt tolerance in plants. Plant J 2009; 58:778–790.
Mikosch M, Homann U . How do ER export motifs work on ion channel trafficking? Curr Opin Plant Biol 2009; 12:685–689.
An WF, Bowlby MR, Betty M, et al. Modulation of A-type potassium channels by a family of calcium sensors. Nature 2000; 403 (6769):553–556.
Shibata R, Misonou H, Campomanes CR, et al. A fundamental role for KChIPs in determining the molecular properties and trafficking of Kv4.2 potassium channels. J Biol Chem 2003; 278:36445–36454.
Bahring R, Dannenberg J, Peters HC, et al. Conserved Kv4 N-terminal domain critical for effects of Kv channel-interacting protein 2.2 on channel expression and gating. J Biol Chem 2001; 276:23888–23894.
Shi J, Kim KN, Ritz O, et al. Novel protein kinases associated with calcineurin B-like calcium sensors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 1999; 11:2393–2405.
Walter M, Chaban C, Schutze K, et al. Visualization of protein interactions in living plant cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Plant J 2004; 40:428–438.
Waadt R, Schmidt LK, Lohse M, et al. Multicolor bimolecular fluorescence complementation reveals simultaneous formation of alternative CBL/CIPK complexes in planta. Plant J 2008; 56:505–516.
Liman ER, Tytgat J, Hess P . Subunit stoichiometry of a mammalian K+ channel determined by construction of multimeric cDNAs. Neuron 1992; 9:861–871.
Clough SJ, Bent AF . Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 1998; 16:735–743.
Kolukisaoglu Ü, Weinl S, Blazevic D, Batistič O, Kudla J . Calcium sensors and their interacting protein kinases: genomics of the Arabidopsis and rice CBL-CIPK signaling networks. Plant Physiol 2004; 134:43–58.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Leonie Steinhorst for providing the cbl4 mutant line, to Whitney Robertson for providing the akt2-1 mutant line, to Dr Oliver Batistič for providing CBL4G2A and CBL4C3S constructs. We also thank Dr Dietmar Geiger for providing the pGEMKN plasmid. FP and CC-F were supported by grants from CNRS and ANR Genoplante, respectively. This work was supported by grants from the DFG to ID (Heisenberg-fellowship and DFG DR 430/5-1 and 5-2) and to JK (SFB 629/B9 and AFGN Ku931/7-1), from the HFSP to JK (RGP033/2006-C) and from the ANR Genoplante to CC-F, BL and J-BT (ANR-06-GPLA-012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
( Supplementary information is linked to the online version of the paper on the Cell Research website.)
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, Figure S1
Co-localization of AKT2-CIPK6 BiFC complexes with the ER-marker OFP-HDEL. (PDF 138 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S2
AKT2 channel voltage gating is not changed by CIPK6+CBL4. (PDF 158 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S3
The shared developmental phenotype of akt2-1, cbl4 and cipk6 mutant plants in short day conditions can be complemented. (PDF 251 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S4
Localization of the fluorescence markers CBL1nGFP (PM) and OFP-HDEL (ER). (PDF 420 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S5
No interaction of the CIPK6 kinase domain alone with AKT2 was observed in BiFC experiments. (PDF 281 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S6
CIPK6N which lacks C-terminal regulatory domain showed autophosphorylation activity in vitro similar as the full-length kinase protein. (PDF 142 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S1
PCR primers used for this study. (PDF 8 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Held, K., Pascaud, F., Eckert, C. et al. Calcium-dependent modulation and plasma membrane targeting of the AKT2 potassium channel by the CBL4/CIPK6 calcium sensor/protein kinase complex. Cell Res 21, 1116–1130 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2011.50
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2011.50
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The role of CBL–CIPK signaling in plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses
Plant Molecular Biology (2024)
-
Evolution, gene expression, and protein‒protein interaction analyses identify candidate CBL-CIPK signalling networks implicated in stress responses to cold and bacterial infection in citrus
BMC Plant Biology (2022)
-
Overdominant expression of related genes of ion homeostasis improves K+ content advantage in hybrid tobacco leaves
BMC Plant Biology (2022)
-
Evolution of the CBL and CIPK gene families in Medicago: genome-wide characterization, pervasive duplication, and expression pattern under salt and drought stress
BMC Plant Biology (2022)
-
Identification and characteristics of SnRK genes and cold stress-induced expression profiles in Liriodendron chinense
BMC Genomics (2022)