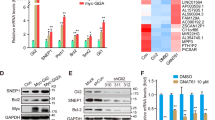
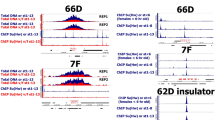
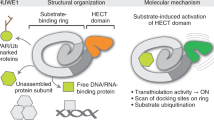
Abstract
Hedgehog (Hh) signaling plays vital roles in animal development and tissue homeostasis, and its misregulation causes congenital diseases and several types of cancer. Suppressor of Fused (Su(fu)) is a conserved inhibitory component of the Hh signaling pathway, but how it is regulated remains poorly understood. Here we demonstrate that in Drosophila Hh signaling promotes downregulation of Su(fu) through its target protein HIB (Hh-induced BTB protein). Interestingly, although HIB-mediated downregulation of Su(fu) depends on the E3 ubiquitin ligase Cul3, HIB does not directly regulate Su(fu) protein stability. Through an RNAi-based candidate gene screen, we identify the spliceosome factor Crooked neck (Crn) as a regulator of Su(fu) level. Epistasis analysis indicates that HIB downregulates Su(fu) through Crn. Furthermore, we provide evidence that HIB retains Crn in the nucleus, leading to reduced Su(fu) protein level. Finally, we show that SPOP, the mammalian homologue of HIB, can substitute HIB to downregulate Su(fu) level in Drosophila. Our study suggests that Hh regulates both Ci and Su(fu) levels through its target HIB, thus uncovering a novel feedback mechanism that regulates Hh signal transduction. The dual function of HIB may provide a buffering mechanism to fine-tune Hh pathway activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ingham PW, McMahon AP . Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev 2001; 15:3059–3087.
Lum L, Beachy PA . The Hedgehog response network: sensors, switches, and routers. Science 2004; 304:1755–1759.
Jia J, Jiang J . Decoding the Hedgehog signal in animal development. Cell Mol Life Sci: CMLS 2006; 63:1249–1265.
Jiang J, Hui CC . Hedgehog signaling in development and cancer. Dev Cell 2008; 15:801–812.
Taipale J, Beachy PA . The Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature 2001; 411:349–354.
Pasca di Magliano M, Hebrok M . Hedgehog signalling in cancer formation and maintenance. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3:903–911.
Ingham PW, Nakano Y, Seger C . Mechanisms and functions of Hedgehog signalling across the metazoa. Nat Rev Genet 2011; 12:393–406.
Hooper JE, Scott MP . The Drosophila patched gene encodes a putative membrane protein required for segmental patterning. Cell 1989; 59:751–765.
Casali A, Struhl G . Reading the Hedgehog morphogen gradient by measuring the ratio of bound to unbound Patched protein. Nature 2004; 431:76–80.
Marigo V, Davey RA, Zuo Y, Cunningham JM, Tabin CJ . Biochemical evidence that patched is the Hedgehog receptor. Nature 1996; 384:176–179.
Stone DM, Hynes M, Armanini M, et al. The tumour-suppressor gene patched encodes a candidate receptor for Sonic hedgehog. Nature 1996; 384:129–134.
Zhao Y, Tong C, Jiang J . Hedgehog regulates smoothened activity by inducing a conformational switch. Nature 2007; 450:252–258.
Corbit KC, Aanstad P, Singla V, Norman AR, Stainier DY, Reiter JF . Vertebrate Smoothened functions at the primary cilium. Nature 2005; 437:1018–1021.
Rohatgi R, Milenkovic L, Scott MP . Patched1 regulates hedgehog signaling at the primary cilium. Science 2007; 317:372–376.
van den Heuvel M, Ingham PW . smoothened encodes a receptor-like serpentine protein required for hedgehog signalling. Nature 1996; 382:547–551.
Denef N, Neubuser D, Perez L, Cohen SM . Hedgehog induces opposite changes in turnover and subcellular localization of patched and smoothened. Cell 2000; 102:521–531.
Alcedo J, Ayzenzon M, Von Ohlen T, Noll M, Hooper JE . The Drosophila smoothened gene encodes a seven-pass membrane protein, a putative receptor for the hedgehog signal. Cell 1996; 86:221–232.
Lum L, Zhang C, Oh S, et al. Hedgehog signal transduction via Smoothened association with a cytoplasmic complex scaffolded by the atypical kinesin, Costal-2. Mol Cell 2003; 12:1261–1274.
Jia J, Tong C, Jiang J . Smoothened transduces Hedgehog signal by physically interacting with Costal2/Fused complex through its C-terminal tail. Genes Dev 2003; 17:2709–2720.
Zhang Y, Mao F, Lu Y, Wu W, Zhang L, Zhao Y . Transduction of the Hedgehog signal through the dimerization of Fused and the nuclear translocation of Cubitus interruptus. Cell Res 2011; 21:1436–1451.
Zhou Q, Kalderon D . Hedgehog activates fused through phosphorylation to elicit a full spectrum of pathway responses. Dev Cell 2011; 20:802–814.
Shi Q, Li S, Jia J, Jiang J . The Hedgehog-induced Smoothened conformational switch assembles a signaling complex that activates Fused by promoting its dimerization and phosphorylation. Development 2011; 138:4219–4231.
Ruel L, Rodriguez R, Gallet A, Lavenant-Staccini L, Therond PP . Stability and association of Smoothened, Costal2 and Fused with Cubitus interruptus are regulated by Hedgehog. Nat Cell Biol 2003; 5:907–913.
Ohlmeyer JT, Kalderon D . Hedgehog stimulates maturation of Cubitus interruptus into a labile transcriptional activator. Nature 1998; 396:749–753.
Pan D, Rubin GM . cAMP-dependent protein kinase and hedgehog act antagonistically in regulating decapentaplegic transcription in Drosophila imaginal discs. Cell 1995; 80:543–552.
Methot N, Basler K . An absolute requirement for Cubitus interruptus in Hedgehog signaling. Development 2001; 128:733–742.
Tabata T, Kornberg TB . Hedgehog is a signaling protein with a key role in patterning Drosophila imaginal discs. Cell 1994; 76:89–102.
Basler K, Struhl G . Compartment boundaries and the control of Drosophila limb pattern by hedgehog protein. Nature 1994; 368:208–214.
Strigini M, Cohen SM . A Hedgehog activity gradient contributes to AP axial patterning of the Drosophila wing. Development 1997; 124:4697–4705.
Tanimoto H, Itoh S, ten Dijke P, Tabata T . Hedgehog creates a gradient of DPP activity in Drosophila wing imaginal discs. Mol Cell 2000; 5:59–71.
Jiang J, Struhl G . Regulation of the Hedgehog and Wingless signalling pathways by the F-box/WD40-repeat protein Slimb. Nature 1998; 391:493–496.
Aza-Blanc P, Ramirez-Weber FA, Laget MP, Schwartz C, Kornberg TB . Proteolysis that is inhibited by hedgehog targets Cubitus interruptus protein to the nucleus and converts it to a repressor. Cell 1997; 89:1043–1053.
Methot N, Basler K . Hedgehog controls limb development by regulating the activities of distinct transcriptional activator and repressor forms of Cubitus interruptus. Cell 1999; 96:819–831.
Jia J, Amanai K, Wang G, Tang J, Wang B, Jiang J . Shaggy/GSK3 antagonizes Hedgehog signalling by regulating Cubitus interruptus. Nature 2002; 416:548–552.
Jia J, Zhang L, Zhang Q, et al. Phosphorylation by double-time/CKIepsilon and CKIalpha targets cubitus interruptus for Slimb/beta-TRCP-mediated proteolytic processing. Dev Cell 2005; 9:819–830.
Smelkinson MG, Kalderon D . Processing of the Drosophila hedgehog signaling effector Ci-155 to the repressor Ci-75 is mediated by direct binding to the SCF component Slimb. Curr Biol: CB 2006; 16:110–116.
Smelkinson MG, Zhou Q, Kalderon D . Regulation of Ci-SCFSlimb binding, Ci proteolysis, and hedgehog pathway activity by Ci phosphorylation. Dev Cell 2007; 13:481–495.
Kent D, Bush EW, Hooper JE . Roadkill attenuates Hedgehog responses through degradation of Cubitus interruptus. Development 2006; 133:2001–2010.
Zhang Q, Zhang L, Wang B, Ou CY, Chien CT, Jiang J . A hedgehog-induced BTB protein modulates hedgehog signaling by degrading Ci/Gli transcription factor. Dev Cell 2006; 10:719–729.
Jiang J . Regulation of Hh/Gli signaling by dual ubiquitin pathways. Cell Cycle 2006; 5:2457–2463.
Ou CY, Wang CH, Jiang J, Chien CT . Suppression of Hedgehog signaling by Cul3 ligases in proliferation control of retinal precursors. Dev Biol 2007; 308:106–119.
Ou CY, Lin YF, Chen YJ, Chien CT . Distinct protein degradation mechanisms mediated by Cul1 and Cul3 controlling Ci stability in Drosophila eye development. Genes Dev 2002; 16:2403–2414.
Zhang Q, Shi Q, Chen Y, et al. Multiple Ser/Thr-rich degrons mediate the degradation of Ci/Gli by the Cul3-HIB/SPOP E3 ubiquitin ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106:21191–21196.
Dunaeva M, Michelson P, Kogerman P, Toftgard R . Characterization of the physical interaction of Gli proteins with SUFU proteins. J Biol Chem 2003; 278:5116–5122.
Sisson BE, Ziegenhorn SL, Holmgren RA . Regulation of Ci and Su(fu) nuclear import in Drosophila. Dev Biol 2006; 294:258–270.
Barnfield PC, Zhang X, Thanabalasingham V, Yoshida M, Hui CC . Negative regulation of Gli1 and Gli2 activator function by Suppressor of fused through multiple mechanisms. Differentiation 2005; 73:397–405.
Chen MH, Wilson CW, Li YJ, et al. Cilium-independent regulation of Gli protein function by Sufu in Hedgehog signaling is evolutionarily conserved. Genes Dev 2009; 23:1910–1928.
Ishii S . Costal-2: a scaffold for kinases mediates Hedgehog signaling. Dev Cell 2005; 8:140–141.
Monnier V, Dussillol F, Alves G, Lamour-Isnard C, Plessis A . Suppressor of fused links fused and Cubitus interruptus on the hedgehog signalling pathway. Curr Biol 1998; 8:583–586.
Preat T, Therond P, Limbourg-Bouchon B, et al. Segmental polarity in Drosophila melanogaster: genetic dissection of fused in a Suppressor of fused background reveals interaction with costal-2. Genetics 1993; 135:1047–1062.
Sisson JC, Ho KS, Suyama K, Scott MP . Costal2, a novel kinesin-related protein in the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Cell 1997; 90:235–245.
Robbins DJ, Nybakken KE, Kobayashi R, Sisson JC, Bishop JM, Therond PP . Hedgehog elicits signal transduction by means of a large complex containing the kinesin-related protein costal2. Cell 1997; 90:225–234.
Chen CH, von Kessler DP, Park W, Wang B, Ma Y, Beachy PA . Nuclear trafficking of Cubitus interruptus in the transcriptional regulation of Hedgehog target gene expression. Cell 1999; 98:305–316.
Stegman MA, Vallance JE, Elangovan G, Sosinski J, Cheng Y, Robbins DJ . Identification of a tetrameric hedgehog signaling complex. J Biol Chem 2000; 275:21809–21812.
Wang G, Amanai K, Wang B, Jiang J . Interactions with Costal2 and suppressor of fused regulate nuclear translocation and activity of cubitus interruptus. Genes Dev 2000; 14:2893–2905.
Monnier V, Ho KS, Sanial M, Scott MP, Plessis A . Hedgehog signal transduction proteins: contacts of the Fused kinase and Ci transcription factor with the kinesin-related protein Costal2. BMC Dev Biol 2002; 2:4.
Cheng SY, Bishop JM . Suppressor of Fused represses Gli-mediated transcription by recruiting the SAP18-mSin3 corepressor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99:5442–5447.
Kogerman P, Grimm T, Kogerman L, et al. Mammalian suppressor-of-fused modulates nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of Gli-1. Nat Cell Biol 1999; 1:312–319.
Svard J, Heby-Henricson K, Persson-Lek M, et al. Genetic elimination of Suppressor of fused reveals an essential repressor function in the mammalian Hedgehog signaling pathway. Dev Cell 2006; 10:187–197.
Cooper AF, Yu KP, Brueckner M, et al. Cardiac and CNS defects in a mouse with targeted disruption of suppressor of fused. Development 2005; 132:4407–4417.
Taylor MD, Liu L, Raffel C, et al. Mutations in SUFU predispose to medulloblastoma. Nat Genet 2002; 31:306–310.
Yue S, Chen Y, Cheng SY . Hedgehog signaling promotes the degradation of tumor suppressor Sufu through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Oncogene 2009; 28:492–499.
Methot N, Basler K . Suppressor of fused opposes hedgehog signal transduction by impeding nuclear accumulation of the activator form of Cubitus interruptus. Development 2000; 127:4001–4010.
Pintard L, Willems A, Peter M . Cullin-based ubiquitin ligases: Cul3-BTB complexes join the family. EMBO J 2004; 23:1681–1687.
Wu JT, Lin HC, Hu YC, Chien CT . Neddylation and deneddylation regulate Cul1 and Cul3 protein accumulation. Nat Cell Biol 2005; 7:1014–1020.
Zhuang M, Calabrese MF, Liu J, et al. Structures of SPOP-substrate complexes: insights into molecular architectures of BTB-Cul3 ubiquitin ligases. Mol Cell 2009; 36:39–50.
Wang C, Pan Y, Wang B . Suppressor of fused and Spop regulate the stability, processing and function of Gli2 and Gli3 full-length activators but not their repressors. Development 2010; 137:2001–2009.
Nybakken K, Vokes SA, Lin TY, McMahon AP, Perrimon N . A genome-wide RNA interference screen in Drosophila melanogaster cells for new components of the Hh signaling pathway. Nat Genet 2005; 37:1323–1332.
Aza-Blanc P, Lin HY, Ruiz i Altaba A, Kornberg TB . Expression of the vertebrate Gli proteins in Drosophila reveals a distribution of activator and repressor activities. Development 2000; 127:4293–4301.
Wang G, Wang B, Jiang J . Protein kinase A antagonizes Hedgehog signaling by regulating both the activator and repressor forms of Cubitus interruptus. Genes Dev 1999; 13:2828–2837.
Jiang J, Struhl G . Protein kinase A and hedgehog signaling in Drosophila limb development. Cell 1995; 80:563–572.
Zhang W, Zhao Y, Tong C, et al. Hedgehog-regulated Costal2-kinase complexes control phosphorylation and proteolytic processing of Cubitus interruptus. Dev Cell 2005; 8:267–278.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Yun Zhao (Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China), Fly Stocks of National Institute of Genetics of Japan (NIG-Fly), Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center (VDRC), the Bloomington Stock Center and Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank at the University of Iowa for providing fly stocks and reagents. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30971679, 31071264 and 31271531) and the National Key Scientific Program of China (2011CB943902, 2010CB945102) to Qing Zhang. Jin Jiang is supported by grants from NIH (GM061269 and GM06745), Welch foundation (I-1603) and NSFC (31328017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
( Supplementary information is linked to the online version of the paper on the Cell Research website.)
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, Figure S1
HIB neither binds Su(fu) nor affects the stability of Su(fu) protein in S2 cells. (PDF 717 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S2
HIB doesn't bind Crn in S2 cells. HA-Crn and Myc-HIB were cotransfected in S2 cells. (PDF 263 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S3
SPOP downregulates endogenous Su(fu) in wing discs but does not change the stabililty of exogenous HA-Su(fu) in S2 cells. (PDF 618 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S4
Hh doesn't affect su(fu) mRNA level or the stability of Su(fu) in the S2 cells. (PDF 344 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S5
Hh affects Su(fu) level in S2 cells. (PDF 369 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S6
HIB-Crn affects Su(fu) level in the S2 cells. (PDF 572 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S7
Loss of Su(fu) alters Hh signaling in a genetic sensitized background. (PDF 327 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S8
HIB doesn't affect su(fu) mRNA nuclear export. (PDF 194 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S9
HIB may affect su(fu) translation. (PDF 369 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S10
Endogenous crn is ubiquitously expressed in wing (A, B) and eye (C, D) discs detected by in situ hybridization. (PDF 275 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S1
The expression of Su(fu) affected by knockdown of the candidate genes in wing discs. (PDF 63 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Zhou, Z., Yao, X. et al. Hedgehog signaling downregulates Suppressor of Fused through the HIB/SPOP-Crn axis in Drosophila. Cell Res 24, 595–609 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2014.29
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2014.29
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
SPOP–PTEN–SUFU axis promotes progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via activating SHH and WNT pathway
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
Positive feedback of SuFu negating protein 1 on Hedgehog signaling promotes colorectal tumor growth
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Functional and transcriptomic analyses of the NF-Y family provide insights into the defense mechanisms of honeybees under adverse circumstances
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2020)
-
Hedgehog signalling in the tumourigenesis and metastasis of osteosarcoma, and its potential value in the clinical therapy of osteosarcoma
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
Capping Enzyme mRNA-cap/RNGTT Regulates Hedgehog Pathway Activity by Antagonizing Protein Kinase A
Scientific Reports (2017)