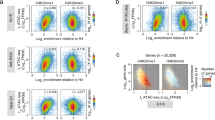
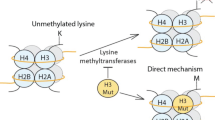
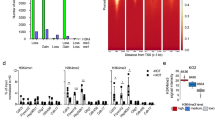
Abstract
Long-range chromatin interactions between enhancers and promoters are essential for transcription of many developmentally controlled genes in mammals and other metazoans. Currently, the exact mechanisms that connect distal enhancers to their specific target promoters remain to be fully elucidated. Here, we show that the enhancer-specific histone H3 lysine 4 monomethylation (H3K4me1) and the histone methyltransferases MLL3 and MLL4 (MLL3/4) play an active role in this process. We demonstrate that in differentiating mouse embryonic stem cells, MLL3/4-dependent deposition of H3K4me1 at enhancers correlates with increased levels of chromatin interactions, whereas loss of this histone modification leads to reduced levels of chromatin interactions and defects in gene activation during differentiation. H3K4me1 facilitates recruitment of the Cohesin complex, a known regulator of chromatin organization, to chromatin in vitro and in vivo, providing a potential mechanism for MLL3/4 to promote chromatin interactions between enhancers and promoters. Taken together, our results support a role for MLL3/4-dependent H3K4me1 in orchestrating long-range chromatin interactions at enhancers in mammalian cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Lee TI, Young RA . Transcriptional regulation and its misregulation in disease. Cell 2013; 152:1237–1251.
Levine M . Transcriptional enhancers in animal development and evolution. Curr Biol 2010; 20:R754–763.
Levine M, Cattoglio C, Tjian R . Looping back to leap forward: transcription enters a new era. Cell 2014; 157:13–25.
Makova KD, Hardison RC . The effects of chromatin organization on variation in mutation rates in the genome. Nat Rev Genet 2015; 16:213–223.
Ong CT, Corces VG . Enhancer function: new insights into the regulation of tissue-specific gene expression. Nat Rev Genet 2011; 12:283–293.
Lee DY, Hayes JJ, Pruss D, Wolffe AP . A positive role for histone acetylation in transcription factor access to nucleosomal DNA. Cell 1993; 72:73–84.
Dekker J, Marti-Renom MA, Mirny LA . Exploring the three-dimensional organization of genomes: interpreting chromatin interaction data. Nat Rev Genet 2013; 14:390–403.
Gorkin DU, Leung D, Ren B . The 3D genome in transcriptional regulation and pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell 2014; 14:762–775.
Nora EP, Lajoie BR, Schulz EG, et al. Spatial partitioning of the regulatory landscape of the X-inactivation centre. Nature 2012; 485:381–385.
Ong CT, Corces VG . CTCF: an architectural protein bridging genome topology and function. Nat Rev Genet 2014; 15:234–246.
Aday AW, Zhu LJ, Lakshmanan A, Wang J, Lawson ND . Identification of cis regulatory features in the embryonic zebrafish genome through large-scale profiling of H3K4me1 and H3K4me3 binding sites. Dev Biol 2011; 357:450–462.
Buecker C, Wysocka J . Enhancers as information integration hubs in development: lessons from genomics. Trends Genet 2012; 28:276–284.
Hardison RC, Taylor J . Genomic approaches towards finding cis-regulatory modules in animals. Nat Rev Genet 2012; 13:469–483.
Heintzman ND, Hon GC, Hawkins RD, et al. Histone modifications at human enhancers reflect global cell-type-specific gene expression. Nature 2009; 459:108–112.
Heintzman ND, Stuart RK, Hon G, et al. Distinct and predictive chromatin signatures of transcriptional promoters and enhancers in the human genome. Nat Genet 2007; 39:311–318.
Rajagopal N, Xie W, Li Y, et al. RFECS: a random-forest based algorithm for enhancer identification from chromatin state. PLoS Comput Biol 2013; 9:e1002968.
Roy S, Ernst J, Kharchenko PV, et al. Identification of functional elements and regulatory circuits by Drosophila modENCODE. Science 2010; 330:1787–1797.
ENCODE Project Consortium. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012; 489:57–74.
Kundaje A, Meuleman W, Ernst J, et al. Integrative analysis of 111 reference human epigenomes. Nature 2015; 518:317–330.
Ernst J, Kheradpour P, Mikkelsen TS, et al. Mapping and analysis of chromatin state dynamics in nine human cell types. Nature 2011; 473:43–49.
Rada-Iglesias A, Wysocka J . Epigenomics of human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells: insights into pluripotency and implications for disease. Genome Med 2011; 3:36.
Wang A, Yue F, Li Y, et al. Epigenetic priming of enhancers predicts developmental competence of hESC-derived endodermal lineage intermediates. Cell Stem Cell 2015; 16:386–399.
Hu D, Gao X, Morgan MA, Herz HM, Smith ER, Shilatifard A . The MLL3/MLL4 branches of the COMPASS family function as major histone H3K4 monomethylases at enhancers. Mol Cell Biol 2013; 33:4745–4754.
Lee JE, Wang C, Xu S, et al. H3K4 mono- and di-methyltransferase MLL4 is required for enhancer activation during cell differentiation. Elife 2013; 2:e01503.
Wang C, Lee JE, Lai B, et al. Enhancer priming by H3K4 methyltransferase MLL4 controls cell fate transition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2016; 113:11871–11876.
Lai B, Lee JE, Jang Y, Wang L, Peng W, Ge K . MLL3/MLL4 are required for CBP/p300 binding on enhancers and super-enhancer formation in brown adipogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res 2017; 45:6388–6403.
Dorighi KM, Swigut T, Henriques T, et al. Mll3 and Mll4 facilitate enhancer RNA synthesis and transcription from promoters independently of H3K4 monomethylation. Mol Cell 2017; 66:568–576 e564.
Rickels R, Herz HM, Sze CC, et al. Histone H3K4 monomethylation catalyzed by Trr and mammalian COMPASS-like proteins at enhancers is dispensable for development and viability. Nat Genet 2017; 49:1647–1653.
Deng W, Lee J, Wang H, et al. Controlling long-range genomic interactions at a native locus by targeted tethering of a looping factor. Cell 2012; 149:1233–1244.
Kagey MH, Newman JJ, Bilodeau S, et al. Mediator and cohesin connect gene expression and chromatin architecture. Nature 2010; 467:430–435.
Sofueva S, Yaffe E, Chan WC, et al. Cohesin-mediated interactions organize chromosomal domain architecture. EMBO J 2013; 32:3119–3129.
Zuin J, Dixon JR, van der Reijden MI, et al. Cohesin and CTCF differentially affect chromatin architecture and gene expression in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111:996–1001.
Rao SSP, Huang SC, Glenn St Hilaire B, et al. Cohesin loss eliminates all loop domains. Cell 2017; 171:305–320 e324.
Dixon JR, Jung I, Selvaraj S, et al. Chromatin architecture reorganization during stem cell differentiation. Nature 2015; 518:331–336.
Li Y, Rivera CM, Ishii H, et al. CRISPR reveals a distal super-enhancer required for Sox2 expression in mouse embryonic stem cells. PLoS One 2014; 9:e114485.
Zhou HY, Katsman Y, Dhaliwal NK, et al. A Sox2 distal enhancer cluster regulates embryonic stem cell differentiation potential. Genes Dev 2014; 28:2699–2711.
Phillips-Cremins JE, Sauria ME, Sanyal A, et al. Architectural protein subclasses shape 3D organization of genomes during lineage commitment. Cell 2013; 153:1281–1295.
van de Werken HJ, de Vree PJ, Splinter E, et al. 4C technology: protocols and data analysis. Methods Enzymol 2012; 513:89–112.
Hnisz D, Abraham BJ, Lee TI, et al. Super-enhancers in the control of cell identity and disease. Cell 2013; 155:934–947.
Rao SS, Huntley MH, Durand NC, et al. A 3D map of the human genome at kilobase resolution reveals principles of chromatin looping. Cell 2014; 159:1665–1680.
Dixon JR, Selvaraj S, Yue F, et al. Topological domains in mammalian genomes identified by analysis of chromatin interactions. Nature 2012; 485:376–380.
Schmitt AD, Hu M, Jung I, et al. A compendium of chromatin contact maps reveals spatially active regions in the human genome. Cell Rep 2016; 17:2042–2059.
Hadjur S, Williams LM, Ryan NK, et al. Cohesins form chromosomal cis-interactions at the developmentally regulated IFNG locus. Nature 2009; 460:410–413.
Ing-Simmons E, Seitan VC, Faure AJ, et al. Spatial enhancer clustering and regulation of enhancer-proximal genes by cohesin. Genome Res 2015; 25:504–513.
Mizuguchi T, Fudenberg G, Mehta S, et al. Cohesin-dependent globules and heterochromatin shape 3D genome architecture in S. pombe. Nature 2014; 516:432–435.
Wendt KS, Yoshida K, Itoh T, et al. Cohesin mediates transcriptional insulation by CCCTC-binding factor. Nature 2008; 451:796–801.
Yan J, Enge M, Whitington T, et al. Transcription factor binding in human cells occurs in dense clusters formed around cohesin anchor sites. Cell 2013; 154:801–813.
Orphanides G, Wu WH, Lane WS, Hampsey M, Reinberg D . The chromatin-specific transcription elongation factor FACT comprises human SPT16 and SSRP1 proteins. Nature 1999; 400:284–288.
Takahata S, Yu Y, Stillman DJ . FACT and Asf1 regulate nucleosome dynamics and coactivator binding at the HO promoter. Mol Cell 2009; 34:405–415.
Eissenberg JC, Shilatifard A . Histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methylation in development and differentiation. Dev Biol 2010; 339:240–249.
Gu B, Lee MG . Histone H3 lysine 4 methyltransferases and demethylases in self-renewal and differentiation of stem cells. Cell Biosci 2013; 3:39.
Dowen JM, Fan ZP, Hnisz D, et al. Control of cell identity genes occurs in insulated neighborhoods in mammalian chromosomes. Cell 2014; 159:374–387.
Loven J, Hoke HA, Lin CY, et al. Selective inhibition of tumor oncogenes by disruption of super-enhancers. Cell 2013; 153:320–334.
Whyte WA, Orlando DA, Hnisz D, et al. Master transcription factors and mediator establish super-enhancers at key cell identity genes. Cell 2013; 153:307–319.
Jin F, Li Y, Dixon JR, et al. A high-resolution map of the three-dimensional chromatin interactome in human cells. Nature 2013; 503:290–294.
Sanyal A, Lajoie BR, Jain G, Dekker J . The long-range interaction landscape of gene promoters. Nature 2012; 489:109–113.
Sexton T, Yaffe E, Kenigsberg E, et al. Three-dimensional folding and functional organization principles of the Drosophila genome. Cell 2012; 148:458–472.
Fang F, Xu Y, Chew KK, Chen X, Ng HH, Matsudaira P . Coactivators p300 and CBP maintain the identity of mouse embryonic stem cells by mediating long-range chromatin structure. Stem Cells 2014; 32:1805–1816.
Hu M, Deng K, Selvaraj S, Qin Z, Ren B, Liu JS . HiCNorm: removing biases in Hi-C data via Poisson regression. Bioinformatics 2012; 28:3131–3133.
Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL . TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 2009; 25:1105–1111.
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, et al. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 2012; 7:562–578.
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA . Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 2009; 4:44–57.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Ren Lab members Drs David Gorkin, Tingting Du, Miao Yu, Jason Guoqiang Li, as well as Drs Shicai Fan (UCSD) and Xi Wang (DKFZ, Germany) for comments during manuscript preparation. We are also very grateful to Samantha Kuan and Dr Bin Li for technical assistance. We thank UCSD Neuroscience Microscopy Shared Facility (NS047101) for FISH imaging and the Murre Lab (UCSD) for sharing protocols and discussions for FISH assay. This work was supported by the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research (BR), NIH (P50 GM085764-04 to BR, U54DK107977 to BR and MH, and R01 GM112720 to JW), an International Postdoc fellowship from the Swedish Vetenskapsrådet (537-2014-6796 to JY) and HHMI (JW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
( Supplementary information is linked to the online version of the paper on the Cell Research website.)
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, Figure S1
Mll3/4 Deficient mESCs Reveal Lost Interaction between Sox2 Gene Body and SE, Related to Figure 1 (PDF 248 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S2
Mll3/4 Are Required for Genome-wide Deposition of H3K4me1 at promoter-distal Enhancers, Related to Figure 1 (PDF 403 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S3
H3K4me1 does not Affect Global Contact Frequency but is Required for FIREs, Related to Figure 2 (PDF 381 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S4
H3K4me1 is Required for FIREs, Related to Figure 2 (PDF 1868 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S6
Change of H3K4me1 is Associated with Change of Cohesin Binding, Related to Figure 5 (PDF 458 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S7
Super-enhancer Call Using H3K27ac ChIP-seq Data, Related to Figure 6 (PDF 329 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S1
H3K4me1 peaks (XLSX 4492 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S2
FIRE score (XLSX 894 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S3
H3K27ac peaks in different group I-IV (XLSX 379 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S4
Super-enhancer (XLSX 157 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S5
Primers used in 4C-seq and shRNA knockdown and qPCR (XLSX 13 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S6
Antibodies (XLSX 11 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S7
Overview statictics of single cell RNA-seq (XLSX 13 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S8
Gene expression values (log2 transformed RPKM) in Wild type and DKO mESC during NPC differentiation, as shown in Figure 5C. (XLSX 3049 kb)
Supplementary information, Data S1
EXTENDED EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (PDF 352 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, J., Chen, SA., Local, A. et al. Histone H3 lysine 4 monomethylation modulates long-range chromatin interactions at enhancers. Cell Res 28, 204–220 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2018.1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2018.1
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Origin, fate and function of extraembryonic tissues during mammalian development
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2025)
-
p300/CBP is an essential driver of pathogenic enhancer activity and gene expression in Ewing sarcoma
EMBO Reports (2025)
-
Genetic coupling of enhancer activity and connectivity in gene expression control
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Liquid condensates: a new barrier to loop extrusion?
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2025)
-
Elucidating the risk factors and oncogene drivers of acute myeloid leukemia
Human Cell (2025)