- RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT
Putting immune cells into ‘night mode’ reduces heart-attack damage

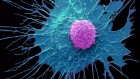
Lower neutrophil activity means that night-time heart attacks tend to be less severe. Credit: Doncaster and Bassetlaw Hospitals/SPL
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 649, 531 (2026)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-026-00008-x
References
Aroca-Crevillén, A. et al. J. Exp. Med. 223, e20250240 (2026).